By going through these Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 7 Business Environment students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 11th Notes Chapter 7 Business Environment
Business Environment-
Definition:
Boyard O Wheeler
The total of all things external to firm and industries which affect their organization and operations is called as Business Environment”.
Barry M. Richman and Melvyan Copan
“Environment factors of constraints are largely if not totally external and beyond the control of individual enterprises and their arrangement”.
William F. Glueck
“Business Environment is the process by which strategists monitor the economic, governmental, market, supplier, technological, geographic and social settings to determine opportunities and threat to the firms.
![]()
Importance of Business Environment
- Flexible and Dynamic
- Opportunities and Threats
- Competition
- Utilization of Resources
- Strength and Weakness
- Knowledge
- Image Building
- Adaptability to Socio – Economic – Changes.
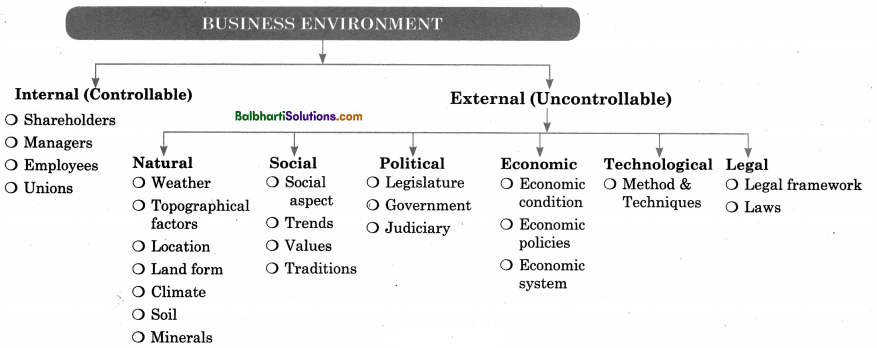
Dimention of Business Environment-
Business Environment:
- Internal (Controllable)
- External (Uncontrollable)
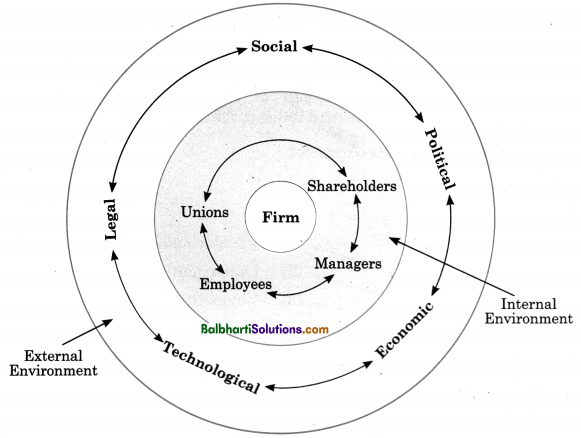
1. Internal (Controllable):
- Shareholders
- Managers
- Employees
- Unions
2. External (Uncontrollable)
Natural:
- Weather
- Topographical factors
- Location
- Land form
- Climate
- Soil
- Minerals
Social:
- Social aspect
- Trends
- Values
- Traditions
Political:
- Legislature
- Government
- Judiciary
Economic:
- Economic condition
- Economic policies
- Economic system
Technological:
Method & Techniques
Legal:
- Legal framework
- Laws
![]()
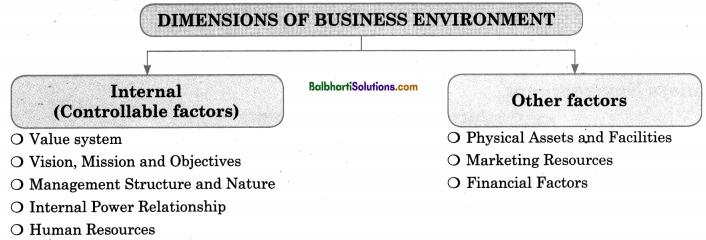
Dimension of Business Environment-
- Internal (Controllable)
- Other factors
Internal (Controllable):
- Value system
- Vision, Mission and Objectives
- Management Structure and Nature
- Internal Power Relationship
- Human Resources
Other factors:
- Physical Assets and Facilities
- Marketing Resources
- Financial Factors
Financial Factors-
![]()
Dimension in Business Environment
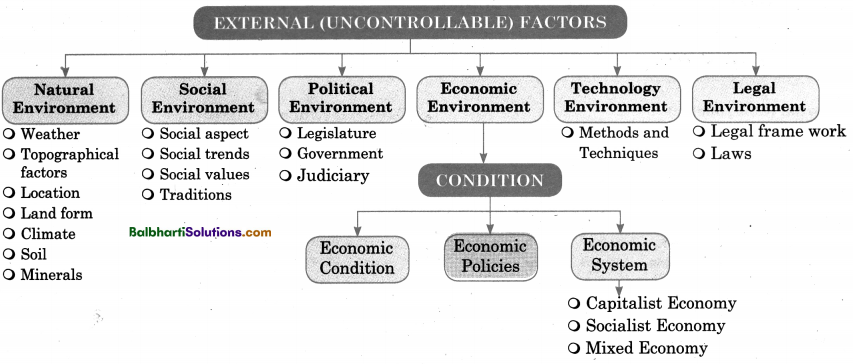
External (Uncontrollable) Factors:
Natural Environment:
- Weather
- Topographical factors
- Location
- Land form
- Climate
- Soil
- Minerals
Social Environment:
- Social aspect
- Social trends
- Social values
- Traditions
Political Environment:
- Legislature
- Government
- Judiciary
Economic Environment:
Condition:
1. Economic Condition
2. Economic Policies
3. Economic System:
- Capitalist Economy
- Socialist Economy
- Mixed Economy
Technology Environment:
Methods and Techniques
Legal Environment
- Legal frame work
- Laws
![]()
New Economic Policy and Business
- New Economic Policy And Business (24TH JULY, 1991)
- Known as (LPG Policy)
- Introduced on 24th July, 1991
- Liberalization
- Privatization
- Globalization
Liberalization-
Meaning: The process of eliminating unnecessary controls and restrictions for smooth functioning of business.
Indian Economic Liberalization Includes:
- Abolishing Industrial Licensing System
- Reduction in physical restrictions on import and import duties
- Reformation of financial system
- Reduction in taxation
- Reduction in control of foreign exchange
- Changing approach towards industrial sickness
- Freedom to decide the scale of business activities
- Attracting foreign investment
- Freedom in fixing prices of goods and services
- Opening of telecommunication sectors
Privatization-
Meaning : To reduce the involvement of state or public sectors by involving of private sector in economic activities.
Need for Privatization :
- More efficiency
- Less Political interference
- Reduction in labour problem
- Ensuring accountability
- Capital Market discipline
Privatization Includes-
- Reduction in number of industries reserved for public sector.
- In order to raise resource disinvestment of shares of selected public sector.
- Improvement in Performance through MOU system.

![]()
Globalisation-
Meaning : Integration of national economy and societies through cross country flows of information, ideas, technologies, goods securities, capital, finance and people.
Includes-
- Removing anti export biasness
- Minimization of high import tariffs
- Lesser reliance on quantitative restrictions on imports
Features of globalization-
- Buying and selling from/to any country
- Freedom to set business anywhere in the world
- Lesser distance between local and international market
- Exchange of new ideas and technology around the world
- Direct foreign participation
Impact of Globalisation-
- Global agreement in trade
- Spreading the economic policies
- Physical and geographical% boundaries are reduced and world is as “global village”.
- Customers are only concerned about the product – quality, price, design, value and appeal.
- Created an economically interdependent international environment
- Increased in privatization of manufacturing and service sector
Impact of New Economic policy on Business-
- Budgetary Support
- Increase in Competition
- New Trade Policy
- Demanding Customers
- New For Development
- Change in Technological Environment
- Change in the Concept of Marketing
Word Meaning:
isolated – unreachable; relevant – appropriate / related; negotiates – work out; thrives – prosper / grow; survive – to stay on; disturbances – distraction / trouble; spell – amount to; threats – dangers; appraise – to judge; orientations – direction of something; demographic – related to structure of population; trends
– movement; strategies – planning; constraints – restrictions; beyond – extreme; overcoming – deal with; sensitivity – reactivity; analyze – to examine; formulate – to prepare; frontiers – limits; intimacy – relationship; controllable – influence; domain – area / sector; structure – formation; logistic – activity of transporting; preservation – to protect; non-replenishable – cannot be renewed; to cope with – to deal with; reciprocal – give and take; ethics – principles; expectancy – hope; heritage – tradition; mobility – ability to move; ideology
– ideas; survival – to exist/to live; monetary – in terms of money; dramatic – considerable; alert – aware; persist – to continue; amendments – changes; eliminating – to remove; accountability – responsibility; disinvestment – reduction in investment; interdependent – depend on each other; implication – indications; reliance – to be dependent; diminishing – reducing; tremendous – huge; discontinuation – not to continue; varying – differ; nurtured – to raise; restructuring – to rearrange; fundamentally – basics; reliable – to good; integration – combination.