By going through these Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 12th Notes Chapter 8 Marketing students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Organisation of Commerce and Management 12th Notes Chapter 8 Marketing
→ Marketing: An action or business of promoting and selling products including market research and advertising.
→ Consumer: Consumer is a person or group of persons that are final user of goods or services, i.e., end-user.
![]()
→ Customer: An individual or organisation who acquires goods or services from a business organisation for a price.
→ Standard of living: Level of economic welfare or level of material well-being of an individual or household. It is usually determined by quantities of the goods and services consumed. It is also referred to a level of wealth, comfort, material goods and necessities available to people to satisfy their wants.
→ Market research: The study of the consumers’ needs and preferences. It is branch of research for business management studying markets and economic opportunities or promotion and distribution of sales.
→ Consideration: Anything given or promised by one party in exchange for the promise or undertaking of another.
→ Misrepresentation: False or incorrect statement made by one party to other with the intention to deceive the other or to make unlawful gain.
→ Image: The character or reputation of a person or thing as generally received.
→ Brand: A name or symbol, number, letter or combination of these given to a product by which the product and its manufacturer are identified.
→ Advertising: An impersonal sales efforts aimed at inducing people to buy the product. It gives information about the products with a view to creating and maintaining demand for the same.
→ Promotion: In marketing, the term ‘promotion’ implies the process of giving information and thereby inducing or persuading prospective customers to buy products or services.
→ Finance (Financing): In marketing ‘financing’ implies, the provision and management of money and credit required to get goods from producer to the consumer or industrial user. It also involves supplying money and credit necessary to meet the expenses of getting goods or products in the hands of consumers.
→ Media: Media is a channel which connects government, business and other organisations with the people at large in society. Radio, television, newspapers, etc. are the examples of media.
→ Environment: The factors which affect surroundings of anything including human beings as well as organisations.
→ Strategies: A plan or method for achieving a business goal, a general method or policy for achieving specific objectives of the business.
→ Production: The total series of stages by which material is changed from one form into another by utilisation of labour, tools and machinery according to plan.
→ Substitutes: Two or more goods or services are said to be substitutes if a rise in the price of one causes an increase in demand for the other, e.g., tea would be a substitute for coffee.
![]()
→ Merger: The amalgamation or combination of two or more businesses.
→ After sales service: A continuing service of maintenance, repair, supply of information on possible uses, etc. provided to the buyers of a product by the seller or manufacturer.
→ Industrialisation: Increasing the number of different types of industries in an economy; to develop industry on an extensive scale in a country, region, etc.
→ Layout: The arrangement of written material, photography or other artwork in an advertisement or page in a book, newspaper, etc.
→ Research and development: TWo closely related activities in modern industry by which new products and processes are being continually developed especially by engineers and designers.
Introduction-
The important objective of all business organisations is to fulfil the needs and wants of the society. This is possible only through marketing of goods and services. Marketing is therefore considered as centre point of all business activities. Production of goods and services become meaningless if business organisations are not able to market their goods and services effectively. Thus, nowadays marketing is indispensable feature of the business. Marketing now becomes part and parcel of modern days of life. Individual as well as social needs are satisfied only through marketing.
Marketing helps to improve standard of living and to gain loyal customers by providing wide variety of goods and services. It also helps to generate and increase employment opportunities. Marketing is pervasive in nature and it influences our daily life. Marketing is a science and an art competitive, growing and cut throat competition inspires organisations to know marketing as a discipline of management.
Meaning and Definition of Marketing-
Marketing is considered as a main function of modern management. Marketing is a social process: through which need (desire) is created, offered and exchange via products and services. Marketing is a wider concept which includes selling and other functions. Marketing and selling though interchangeably used and seem to be similar concept, ‘Marketing’ involves a process of satisfying consumer needs. It includes all those activities which effect transfer of ownership and possession of goods and services for physical distribution, Satisfaction of consumer is the centre point of marketing concept. It is consumer oriented. In brief, marketing is the activity, set of institutions and processes for creating, communicating, handing over and exchanging offerings that have value for the consumers, clients, partners and society at large, it is an indirect activity and integrated process of identification, assessment and satisfaction of human wants.
American Marketing Association, defines Marketing as “the activity, set of institutions, and processesfor creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.”
Concept of Market-
The word ‘Market’ has originated from the Latin word ‘mercatus’. It means ‘to trade’, to trade merchandise’ or ‘a place where business is being carried out’. In brief, market is a place where two or more parties called buyer, seller and intermediary are involved in the buying and selling of goods and services, with the exchange of money called price. In the modern days, buyers and sellers can conduct trade by telephone, internet, mail, social media platforms, etc.
![]()
The different concepts associated with the term market are explained briefly as follows:
1) Place concept of market: In the place concept of market emphasis is given on the place where transaction of trading (i.e buying and selling) of goods and services is done in the exchange of money or money’s worth. In ancient days, place played a significant role in defining the term market. But due to development of information technology the meaning of the term market has widened to great extent.
2) Commodity concept of market: In this concept of market, buying and selling of goods and services are given more importance. In this process, commodity/parties to the transaction, viz. buyer and seller play an important role.
3) Exchange concept of market: This concept of market gives more stress on the exchange of goods or services between buyer and seller. It further states that there should be free or voluntary consent and mutual trust. During the exchange neither any fraud nor misrepresentation should be committed by either party. Similarly coercion or undue influence should not be applied during the exchange.
4) Area concept of market: This concept ot market gives stress on free association between buyer and seller to determine (fix) the price of goods for its trading. According to this concept, buyer and seller can fix the price by taking help of modern communication means and exchange goods or service without meeting each other personally.
5) Demand or Customer concept of market: This concept of market states that customer is the king of the market and market should be studied from the angle of demand or customer. It is further stated that the aggregate (total) demand of potential buyers for the products is considered as market.
6) Space or Digital concept of market: On account of advent of information technology, new concept of market, i.e. space or digital concept comes into existence. Now sophisticated e-commerce portals and mobile applications, internet, computer, etc. have made trading of goods and services easy and convenient for buyers and sellers.
The use of information technology has made it easier for customers to make direct contact with sellers, know about the features, v price, quality, terms and conditions, etc. of any product or service across the globe. Accordingly, the market that uses information technology for trading of the products or services is called digital market. It facilitates communication of quality, features, price and terms of exchange among them.
Types of Market-
The chart showing different types of market is as follow:
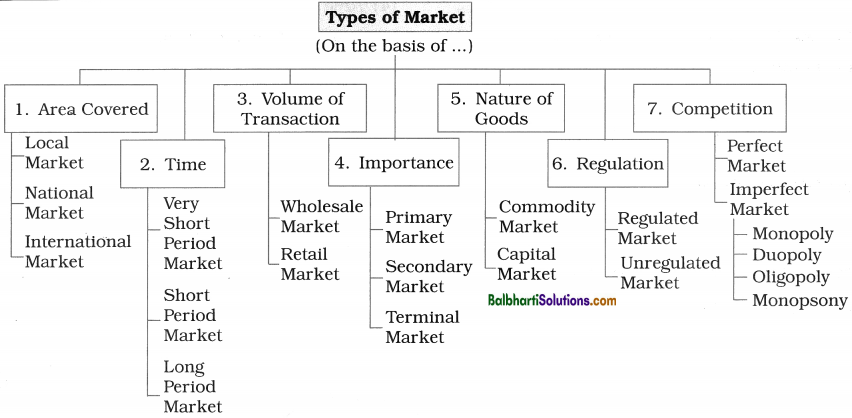
The different types of markets are explained as follows:
1) On the basis of Area Covered:
- Local Market: Market which is established in the local geographical area of a region within which goods and services are bought and sold is called local market, e.g. purchase of goods from nearest shop.
- National Market: Market which is established within a country with which goods and services are bought and sold is called national market, e.g. purchase of clothes from Ahmedabad by a customer residing in Kochi.
- International Market: The market where the goods and services produced in one country are sold in many other countries is called international market, e.g. import of advanced technology from U.S.A. by India.
![]()
2) On the basis of time:
- Very Short Period Market: The market which has its existence for very short period of time is called very short period market. This market has existence for few hours, e.g. market for perishable goods such as fish, vegetables, fruits, etc.
- Short Period Market: The market which is organised and continued for short period is called short period market, e.g. a weekly market, market during festival, fairs, etc. They deal in semi- durable and perishable goods.
- Long Period Market: The market which is organised and continued for long period of time is called long period market, e.g. market for durable commodities.
3) On the basis of Volume of Transaction:
- Wholesale Market: The market in which goods and services are bought and sold in large quantities at cheaper rates is called wholesale market. In this market, goods are sold to retailers in moderate quantities who then sell them to ultimate consumers in very small quantities, e.g. wholesale market for yarn.
- Retail Market: The market in which goods are directly sold by retailers to ultimate consumers in very small quantity is called retail market, e.g. grocery shop located in residential area.
4) On the basis of Importance:
- Primary market: The market where primary products are bought and sold is called primary market, e.g. grain market, fruit market, etc.
- Secondary market: The market where semi-processed and semi-manufactured goods are traded is called secondary market, e.g. iron-ore market.
- Terminal market: The market where finished goods are traded to ultimate consumers is called terminal market, e.g. industrial goods market.
5) On the basis of Nature of Goods:
- Commodity Market: The market where goods, materials or produce, viz. consumer goods and industrial goods are sold is called commodity market, e.g. consumer goods market.
- Capital Market: The market where long term funds are borrowed and given is called capital market, e.g. new issue market.
6) On the basis of Regulation:
- Regulated Market: The market which is governed, regulated and controlled by the statutory or legal provisions of the country is called regulated market, e.g. Stock Exchanges, Foreign Exchanges, etc.
- Unregulated or Free Market: The market which is not regulated or controlled by any specific act of parliament but is operated as per forces of demand and supply is called unregulated or free market, e.g. market for different products or services.
(7) On the basis of Competition:
- Perfect Market: The market where large number of buyers and large number of sellers buy and sell homogeneous product at a prevailing single price is called perfect market. Neither single buyer nor single seller can influence the price. They have perfect knowledge of market condition.
- Imperfect competition : A market which has certain features of imperfection such as single seller, imperfect knowledge of market conditions on the part of buyers and sellers, failure to make adjustment in demand and supply, etc. is called imperfect market, e.g. monopoly market.
Imperfect market is further classified as:
- Monopoly : A market structure which is characterised by a single seller selling unique product which has no close substitute is called monopoly market. Monopoly controls the entire supply in the market. He the price maker.
- Duopoly : A market situation in which two sellers who either sell a homogeneous product or differentiated product is called duopoly market. Sellers enjoy a monopoly in the product produced and sold by them.
- Oligopoly : A market situation in which there are limited (few) number of sellers or producers selling either a homogeneous product or differentiated product is called oligopoly.
- Monopsony : A market situation in which there is only one buyer and purchaser of goods and services offered by many producers or sellers is called monopsony, e.g. labour market, a firm is the sole buyer of certain kind of labour.
Importance of marketing-
The importance of marketing is shown in the following diagram:

Importance of marketing is explained as follows:
(A) Importance of Marketing to the Society:
1) Increase in standard of living: Marketing helps to find out the needs of consumers and accordingly make efforts to supply quality products at cheaper rates to fulfil their needs. This in turn raises and maintains standard of living of the consumers. In recent years, the large scale production of goods and services has considerably reduced the prices which helps to enhance standard of living of the poor and middle class people.
![]()
2) Provides employment: Modern marketing undertakes almost all functions of organisations ; such as buying, selling, financing, transport, warehousing, risk bearing, research and development, etc. which require more human power. This generates more job opportunities in different capacities and helps to solve the problem of unemployment.
3) Decreases distribution costs: Effective and proper utilisation of channel of distribution reduces overall cost of production of products and services. Thus, marketing makes goods and services available at cheaper prices.
4) Consumer awareness: Marketing helps the society by educating the consumers providing them information of availability of goods and services in the market. Marketing also helps in making right purchases.
5) Increases in National Income: Well organised and effective marketing of products and i services facilitates industrialisation, increase job opportunities and develops the economy rapidly. This makes the economy more stronger and stable I which in turn increases national income.
6) Managing consumer expectations: Marketing research enables the business organisations to understand the requirements of the consumers which arc useful in development of products. By studying and considering customers’ review, business organisations make major changes in the products. Government regulations stop marketers to make false and misleading claims.
(B) Importance of Marketing to the Firm:
1) Increases awareness: Marketing provides detailed information and creates awareness among the consumers about the existing products, new arrivals and the company selling specific products in the market.
2) Increases sales: After providing information about the products or services among the customers, marketing attracts them to buy the products or services. Successful marketing campaign enables the business organisations to enhance the sales of the organisation. Expansion in sales increases profit which can be reinvested in the business to earn more profits in the future.
3) Creates trust: The consumers usually prefer to buy goods and services from those business organisations which have trustworthy reputation in the market. Trustworthiness creates customer loyalty and earns loyal customers.
4) Basis for making decisions ; The business organisations are required to take several decisions before delivering the products to the ultimate consumers. The business organisations are required to have several decisions before delivering the products to ultimate consumers. They are required to face many problems in relation to production of goods and services. When business expands, decision making process becomes more complex. Effective marketing facilitates organi¬sations to take right decisions at the right time.
5) Source of new ideas: Marketing facilitates business organisations to know the needs of the consumers. Feedbacks received from the consumers are useful to make improvement in the existing products. Due to marketing, organisations, understand the changing tastes and preferences of the consumers. By considering these changes and new demand pattern, research and development department develops new products in which 4 Ps of marketing mix play major role.
6) Tackling the competition: Due to increasing competition it is now difficult to create monopoly. Marketing creates brand loyalty in the minds of potential buyers. Marketing conveys salient features, advantages, uses, etc. of the goods ! and services to the consumers and induces them to buy the same. The business organisations can make use of modern technology for effective marketing.
(C) Importance of Marketing to the Consumers:
1) Promotes product awareness: The business enterprises undertake marketing activities to promote various marketing activities ; to promote their products. Marketing creates awareness among the customers about different products and brands available in the market. It facilitates consumers to take right decisions on the purchases. The consumers can compare product features, their availability, price, etc. and select right products. Marketing also improves the: quality of life of the consumers.
2) Provides quality products: Due to increasing competition in the market, consumers get information about the products and services available in the market. Marketing also creates moral pressure on the organisations to sell quality products and services to the consumers. If business organisations supply defective products, it will create negative image of the organisations which in turn affects customers’ loyalty adversely.
3) Provides variety of products: Marketing: provides information about the products to the consumers and thereby induces them to purchase them. The business organisations are required to ! launch product by considering market segments. They are required to make available variety of goods to fulfil the requirements of different market segments of the consumers.
4) Helps in selection: In the competitive markets, different variety of products with different brands are available. Marketing enables the consumers to select the best products and services from different options available.
![]()
5) Customer satisfaction: The main aim of marketing policy is to give assurance of good quality products to the consumers. When the needs of the consumers are fulfilled, the consumers get satisfied. Marketing efforts result into customers’ satisfaction by way of honest advertising, assurance of quality products and accessibility of innovative products. In this way marketing makes efforts to give satisfaction to the consumers.
6) Regular supply of goods: Regular supply of goods to the consumers is practicable through effective and efficient distribution channel of marketing. Marketing also helps to stabilise the prices of products in the market.
Functions of Marketing-
1) Marketing research: The marketing research assists the organisations to assess the need in the market, identify the requirement of consumers, time of purchases, quantity of their purchases and prices at which products and services are traded, etc. Marketing helps the business organisations to take decisions on the marketing of products and services.
2) Buying and assembling: This function is related to purchase of raw materials from various places and to bring them at one place for further processing and production. This function is more important because quality and price of raw materials fix the cost and quality of final products.
3) Market planning: This function is concerned with preparing outline of market plan and strategies to accomplish the objectives of the organisation. Market planning means defining, determining and organising the marketing aims and objectives of the business and preparing strategies to achieve those aims and objectives.
4) Product development: Every business organisation is required to develop its products to suit the needs of the consumers. Most of the customers prefer to buy better and attractively designed products. Good and attractive design of the products also increase its turnover and profit. Product development is ongoing (continuous) process due to changing needs and preferences of the customers.
5) Standardisation and grading: Standisation means setting up certain norms in relation to design, quality, size, process, weight, colour, etc. of the products. It ensures uniformity of products and helps to gain customers’ loyalty towards products. Grading means physical sorting and classifying the products according to standard set up. Usually, grading is done in case of agricultural commodities.
6) Packaging and labelling: Designing the package for the products in an attractive manner is called packaging. It protects the products from breakage, leakage, damage and destruction. A slip providing information of product and its producer pasted or affixed on the product container is called ] label and its processing is called labelling, Packaging and labelling give protection to the product and serve an effective tool of marketing.
7) Branding: Giving a distinct name to product to identify it, is called branding. A brand which is registered is called Trademark. It gives separate identity and recognition among the consumers which helps to expand business and increase brand awareness.
8) Customers support service: The business organisations, must take every possible step to ; render support services to the customers. It increases customers’ loyalty towards the business, The customers support services include pre-sales services, after sales services, customer helpline, i technical assistance, product demonstration, etc.
It facilitates organisation to get, increase and retain the customers.
9) Pricing of products: Fixing the prices of the products is an important and challenging function of marketing. While determining the price the business organisation is required to consider several factors such as cost, desired profit, price of the competitors’ product, etc. The price fixed should neither be too high which may lose customers nor too low which compel the organisation to incur loss.
10) Promotional channels: The process of convening the consumers’ information of the products, their features, prices, uses, etc. and inducing them to buy the products is called promotion. Personal selling advertisement, publicity and sales promotion are the important tools of promotion. Promotional activities increase brand awareness in the market.
11) Distribution: The activities which are related to movement of finished products from the place of business to the doorsteps of consumers are called distribution. It comprises of transportation, order processing, material handling, warehousing, inventory control, market forecasting, etc. The importance of distribution mostly depends on the type of product and level of customer satisfaction.
12) Transportation: The physical movement of products, raw materials, etc. from place of origin to the place of production or to the place of consumers is called transportation. It creates place utility. The modes of transport include road, air, water, railways, pipeline transport, etc.
13) Warehousing: Warehousing refers to storing of goods, in a godown to hold them in stock from the time of production or purchase till the time of their sale. Warehousing maintains balance between supply and demand of products and helps to stabilise the prices in the market. Warehousing creates time utility.
Marketing Mix-
Marketing mix refers to the mixture or combination of various marketing variables that business enterprises intermix and control to get expected results from the target market. In other words, it means placing the right product at right price, at right place and at right time. Every business organisation must develop appropriate marketing mix to expand turnover and achieve its objective.
The 4 Ps of marketing mix viz. Product, Price, Place and Promotion were introduced by E. Jerome McCarthy in 1960. Then in 1981, it was further extended by Booms & Bitner by adding of 3 new elements, viz. People, Process and Physical Environment. The first 4 Ps are called product marketing mix and last 3 Ps are called services marketing mix. 7 Ps of marketing mix are shown in the following diagram.
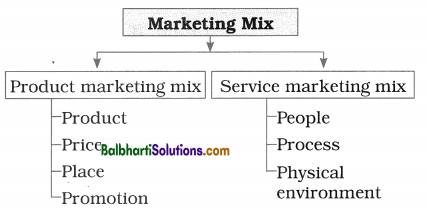
1) Product: An article, goods, commodity, or service that is offered to the customers for sale is called ‘product’. It has capacity to satisfy the needs of customers. The product may be either tangible or intangible. It may be in the form of goods or services. Through market research the business organisations decide the right type of products to be produced and sold. Products sold create impact on the mind of customers on which success or failure of business depends.
2) Price: The amount of money given or required to buy a product is called ‘price’. The factors such as cost of product, willingness of the customers to pay for the product, value, utility, etc. are required to be considered while determing the price of a product. Price of the product should not be too high which affects the demand adversely. Similarly it should not be too low which reduces the profitability.
3) Place: Place is the element of marketing mix that ensures that right product is distributed and made available to the potential buyers at right location and at right time too. The organisations need to distribute the products at a place easily approachable to the potential consumers.
![]()
4) Promotion: Promotion refers to any type of marketing communication used to inform and
persuade potential buyers or consumers to buy the products. Promotion mix comprises of different tools such as advertising, sales promotion, direct marketing, personal selling, etc. Promotional strategies to be used depend on the budget, target market and the message to be communicated.
5) People: The people inside and outside the business create impact or influence on the business. People include all individuals, that play key role in offering the products or services to the customers. Right people appointed to work at right place add value to the business. Organisations must recruit right people, train them and retain them for their success.
6) Process: The steps taken by the business organization to carry the products from the place of business to the place of consumers are called process. Process are significant to provide quality service. Good process saves time and cost and ensures same standard of service by enhancing efficiency.
7) Physical Environment: The marketing environment in which the interactions between the customers and firm takes place is called the physical environment. While offering services, the service providers always try to incorporate certain tangible elements into their offering to increase customer experience. In the service market, physical evidence is necessary to ensure that service is provided successfully. The physical evidence creates an impact on the customers’ satisfaction. Physical evidence comprises location, layout, packaging, branding, interior design, the dress of the employees, their action, waiting area, etc.