Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 5 Environmental Studies Solutions Chapter 11 Our Home and Environment Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 5 EVS Solutions Part 1 Chapter 11 Our Home and Environment
5th Std EVS 1 Digest Chapter 11 Our Home and Environment Textbook Questions and Answers
Use your brain power?
Question 1.
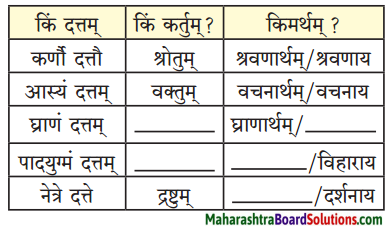
For what purpose do birds use their nest.
Answer:
Birds use their nest to lay their eggs and bring up their young ones.
![]()
what’s the solution?
Question 1.
What can we do to build houses without harming the environment?
Answer:
To build houses without harming the environment we can build permanent eco-friendly houses where we have good ventilation and use non exhaustible sources of energy.
1. Which of the following houses would be suitable in a mountainous region.
Question 1(a).
Which of the following houses would be suitable in a mountainous region. Put a ✓ in the appropriate box. Give reasons for selecting that house.
Answer:
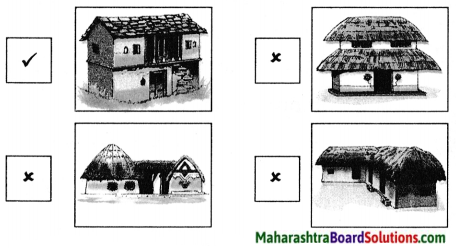
This house is made of natural material available in the mountainous region, that is stone, it is strong to withstand mountainous winds.
Question 1(b).
What materials will you mainly use for building a multi-storeyed house?
(a) Mortar / Coal / Cement / Bricks
(b) Cement / Bricks / Cotton / Iron
(c) Iron / Cement / Mortar / Bricks
Answer:
Iron / Cement / Mortar / Bricks
![]()
2. Arrange the following considerations from the most to least important factor in house building:
Question 1.
Arrange the following considerations from the most to least important factor in house building:
(a) Luxury
(b) Structure
(c) Climate
Answer:
(a) Climate
(b) Structure
(c) Luxury
3. Write the following:
Question (a)
List the eco-friendly things in your house.
Answer:
Things made of mud like a earthen water pot. (Personal response)
Question (b)
Which of the gadgets in the house can be run on solar energy?
Answer:
Solar calculator, solar cooker. Add more to the list.
4. What are the types of pollution that can be observed at a construction site?
Question 1.
What are the types of pollution that can be observed at a construction site?
Answer:
The types of pollution that are seen at a construction site are air, water, soil and noise.
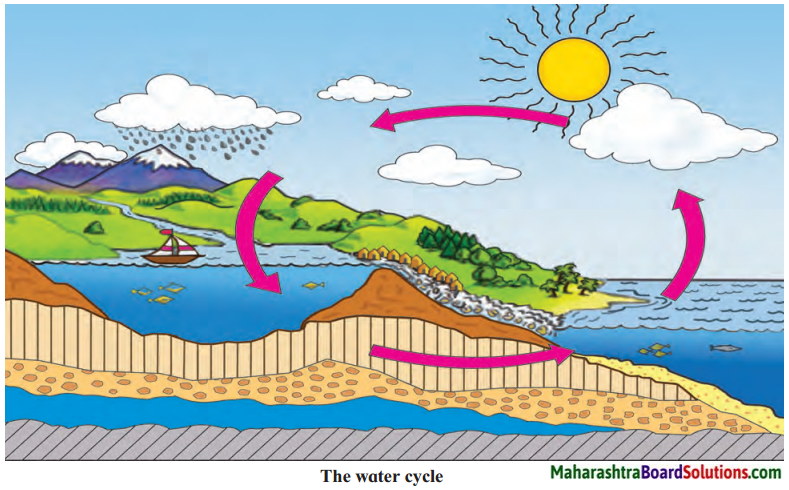
Make friends with maps!
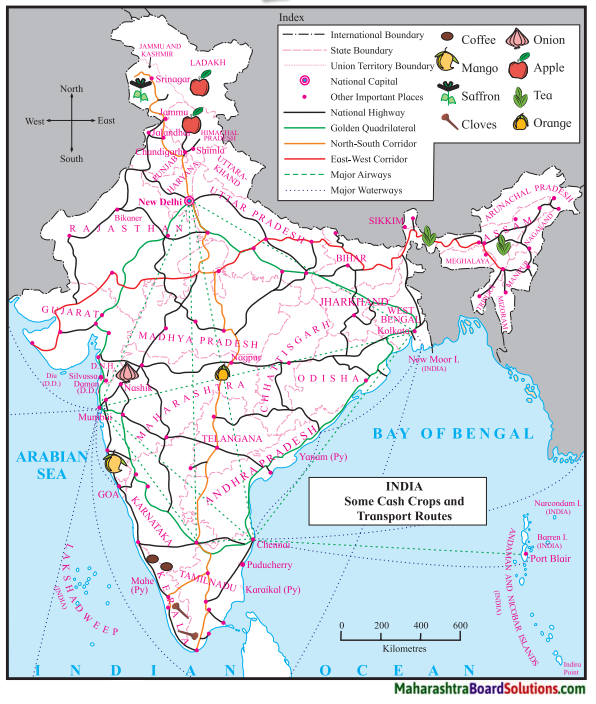
Question 1.
Observe the map and the pictures and complete the following chart.
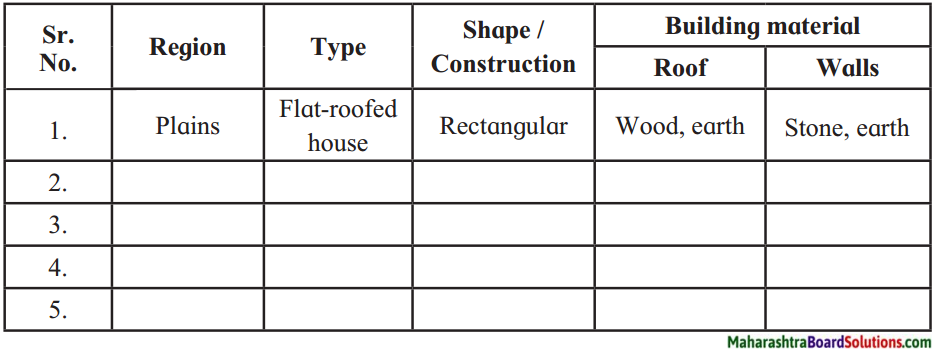
Answer:
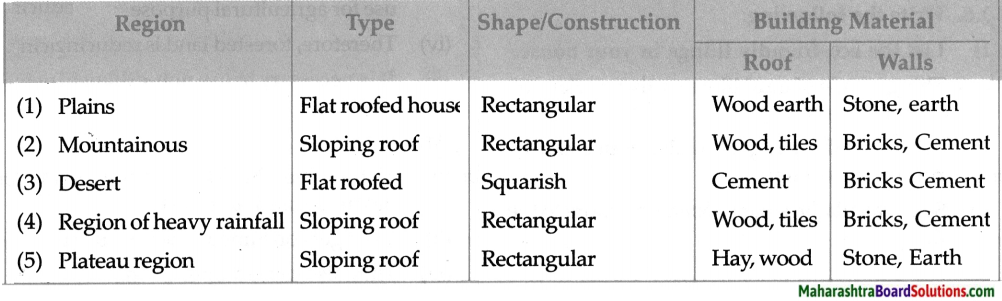
![]()
Try this.
Question 1.
Complete the table given below regarding the original source.
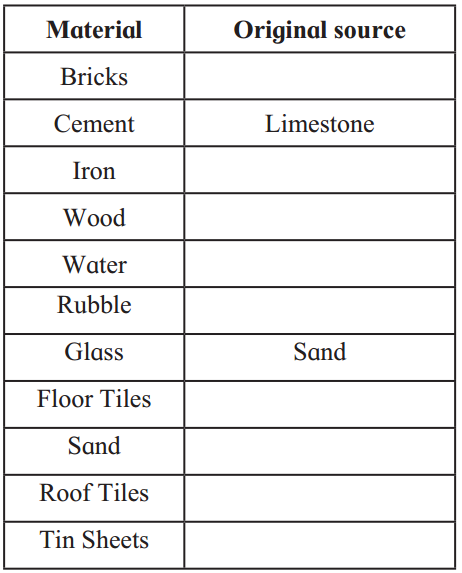
Answer:
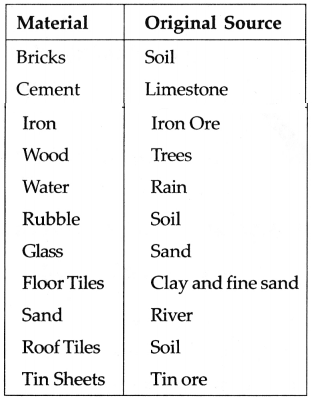
Environmental Studies Part 1 Standard 5th Solutions Chapter 11 Our Home and Environment Additional Important Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the blanks with the correct answers from the options given below:
Question 1.
A section of our society becomes homeless this is a ………………. problem.
(a) political
(b) social
(c) economic
Answer:
(b) social
Question 2.
Houses are built in large numbers due to increasing …………………. .
(a) population
(b) natural resources
(c) land
Answer:
(a) population
![]()
Question 3.
Glass is made from ……………… .
(a) soil
(b) limestone
(c) sand
Answer:
(c) sand
Question 4.
The city of Mumbai comprises of ………………….. islands.
(a) 6
(b) 7
(c) 8
Answer:
(b) 7
Question 5.
Land obtained by filling water bodies is called ………………….. .
(a) coastal lands
(b) reclaimed land
(c) marshy lands
Answer:
(b) reclaimed land
Question 6.
People build houses to suit the ………………… of their region.
(a) climate
(b) population
(c) situation
Answer:
(a) climate
Question 7.
Water, food, clothing and shelter are the basic …………………. of every human being.
(a) height
(b) weight
(c) needs
Answer:
(c) needs
![]()
Question 8.
The ……………….. of the world is increasing all the time.
(a) time
(b) population
(c) water
Answer:
(b) population
Question 9.
Shortage of …………………. land, leads to forest land being used for agriculture.
(a) agricultural
(b) geographical
(c) water
Answer:
(a) agricultural
Question 10.
Trees are …………………. in great numbers and forests are reduced.
(a) watered
(b) fellect
(c) grown
Answer:
(b) fellect
Question 11.
……………… is needed to produce construction material.
(a) Energy
(b) Humans
(c) Forest
Answer:
(a) Energy
Question 12.
Energy is produced using natural …………………. like coal, natural gas or mineral oil.
(a) trees
(b) fuels
(c) minerals
Answer:
(b) fuels
Question 13.
Burning of natural fuels leads to ……………… pollution.
(a) air
(b) water
(c) land
Answer:
(a) air
Question 14.
……………….. or ……………… energy are non-exhaustible sources of energy.
(a) air
(b) wind
(c) solar
Answer:
(b) wind & (c) solar
![]()
Name the following:
Question 1.
Government provides shelter for homeless in cities.
Answer:
Night shelters
Question 2.
Source from which cement is made.
Answer:
Limestone
Question 3.
Natural fuels
Answer:
Coal, natural gas, mineral oil.
Question 4.
Pollution caused by burning fuel.
Answer:
Air
Question 5.
Non exhaustible sources of energy.
Answer:
Solar energy, Wind energy and Biogas.
Question 6.
Two continents having water tourism
Answer:
Europe and North America.
Question 3.
Complete the co-relation:
Answer:
1. Mountainous region: Sloping roof:: Plain: Flat roof.
2. Cement: Limestone :: Bricks : Soil.
3. Coal: Exhaustible energy:: Solar energy: Non exhaustible energy.
Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
What are the different things from which a house gives us protection?
Answer:
A house protects us from sun, wind, cold, rain and wild animals.
Question 2.
Where do homeless people live?
Answer:
Homeless people seek shelter at the roadside, on footpaths, under bridges, in tumble down buildings, in railway or bus stations and open grounds.
Question 3.
What is water tourism?
Answer:
In the coastal region, where under water shelters are built for tourist to view the sea bed and marine life is called water tourism.
Question 4.
Why are many people forced to be ‘homeless’?
Answer:
Many people are forced to be ‘homeless’ because they have insufficient or no means of livelihood.
Question 5.
What are the basic needs of every human being?
Answer:
Water, food, clothing and shelter are the basic needs of every human being.
![]()
Question 6.
Why are houses being built in large numbers?
Answer:
The population of the world is increasing all the time. That is why, houses are being built in large numbers.
Question 7.
What are the ill-effects of urbanization on land?
Answer:
Due to growing urbanization, land which was used for agriculture is now being used to build roads or to raise settlements. This leads to shortage of agricultural land.
Question 8.
Why are trees felled?
Answer:
Shortage of agricultural land leads man to cut down forests and use the land for agriculture.
Question 9.
From where do we get energy?
Answer:
We get energy by using natural fuels like coal, natural gas or mineral oil.
Question 10.
What ill-effects do we face when we use natural fuels?
Answer:
Using natural fuels not only leads to its exhaustion but also to air pollution.
Question 11.
Which are non-exhaustible sources of energy?
Answer:
Solar energy and wind energy are non- exhaustible sources of energy.
Give reasons:
Question 1.
Differences occur in the construction of houses according to the regions.
Answer:
There are differences in the construction of houses according to the region because :
1. People build houses to suit the climate of the region.
2. Using the natural resources that are available.
Question 2.
Many people are forced to be ‘homeless’.
Answer:
Many people are forced to be homeless because they have insufficient or no means of livelihood.
Question 3.
Houses are being built in large numbers.
Answer:
Houses are being built in large numbers because the population of the world is increasing all the time.
Question 4.
Forested land is reducing.
Answer:
- Growing urbanization uses agricultural land to build roads and to raise settlements.
- This leads to shortage of agricultural land.
- So trees are felled in a great number to make use for agricultural purpose.
- Therefore, forested land is reducing.
Question 5.
It is necessary to use non-exhaustible sources of energy.
Answer:
- Natural fuels like coal, natural gas or mineral oil can be used only once.
- They get consumed when we use them.
- They also cause air pollution.
- It takes lakhs of years for these resources to be formed in nature.
- Therefore it is necessary to use non exhaustible sources of energy.
![]()
Answer briefly:
Question 1.
How are natural resources obtained to build a house?
Answer:
Natural resources are obtained to build a house are as follows:
- Digging up hills for quarryingf.
- Extracting sand from seashores and riverbeds.
- Extracting stone and earth from the ground.
- Drawing out excessive amount of ground water.
- Felling trees to clear land.
- Filling up ponds, lakes, streams, rivers, creeks and low lying areas to reclaimed land.
Question 2.
Why do people become homeless?
Answer:
People become homeless because
- Lack of affordable housing.
- Poverty and unemployment.
- Inadequate’ income.
- Natural disasters.
- Physical and mental disorders.
Question 3.
What are the main uses of a house?
Answer:
The main uses of a house are as follows:
- A shelter.
- A resting place.
- Protection against the sun, wind, cold and rains.
- Protection from wild animals and from anti-social elements.
Question 4.
What is the government doing towards the ‘homeless’?
Answer:
1. A section of society being ‘homeless’ is a social problem.
2. That is why the government implements many schemes to provide homes to the homeless.
In some of the cities, the government makes ‘night shelters’ available to the homeless.
Write short notes on:
Question 1.
Characteristics of eco-friendly houses
Answer:
The characteristics of eco-friendly houses are as follows:
- Minimum consumption of natural resources.
- Use of non exhaustible sources of energy such as biogas, wind energy and solar energy.
- Recycling of water.
- Recycling of garbage.
- Avoiding artificial materials and artificial colours.
- Provision for natural light and ventilation in the house.
![]()
Question 2.
Uses of a house
Answer:
Uses of a house are as follows:
1. A shelter.
2. A resting place.
3. Protection against the sun, the wind, the cold and the rains.
4. Protection from wild animals.
5. Keeping ourselves safe from anti-sodal elements.
What’s the solution?
Question 1.
Construction work is going on opposite Ajit’s house. That means constant loud noise and a lot of dust in the air. Ajit and his family have to suffer this all the time. What can Ajit do to find a way out of this problem?
Answer:
Ajit and his family will have to keep their windows closed to avoid the dust and noise. They should use ear plugs when the noise is intense.
![]()
Glossary:
- forested – covered with forests
- urbanization – population shift from rural to urban areas
- reclaimed – recovered.
- shortage – a state in which something cannot be obtained in sufficient amount
- felled – cut down.
- luxury – state of great comfort.
- quarrying – cut into and obtain stone
- inadequate – lacking the quantity required
- consumption – action of using up a resource
- artificial – made by human beings, not natural.