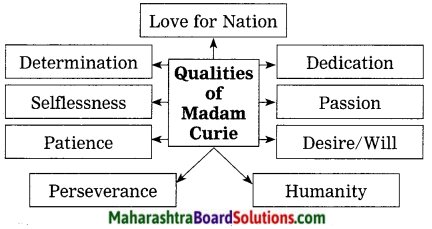
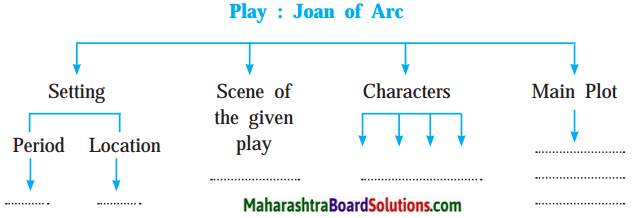
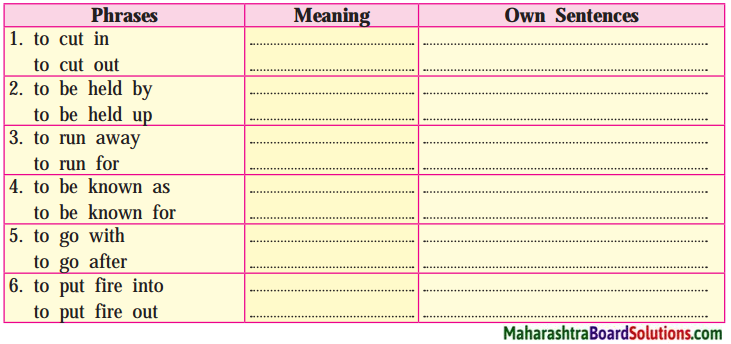
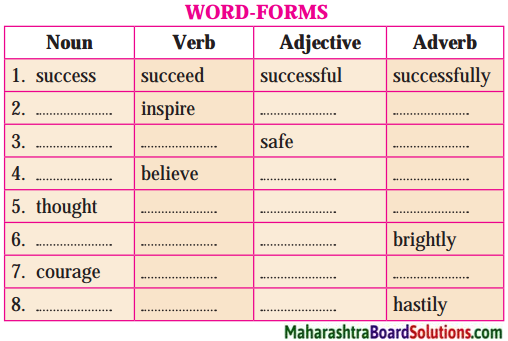
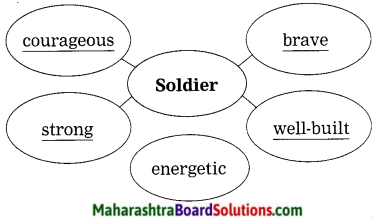
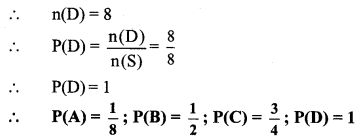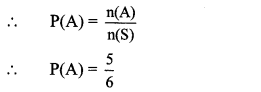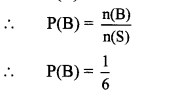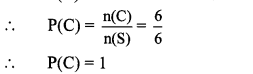10th Standard Maths 1 Practice Set 6.2 Chapter 6 Statistics Textbook Answers Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 6.2 Algebra 10th Class Maths Part 1 Answers Solutions Chapter 6 Statistics.
Class 10 Maths Part 1 Practice Set 6.2 Chapter 6 Statistics Questions With Answers Maharashtra Board
Statistics Practice Set 6.2 Question 1.
The following table shows classification of number of workers and the number of hours they work in a software company. Find the median of the number of hours they work.

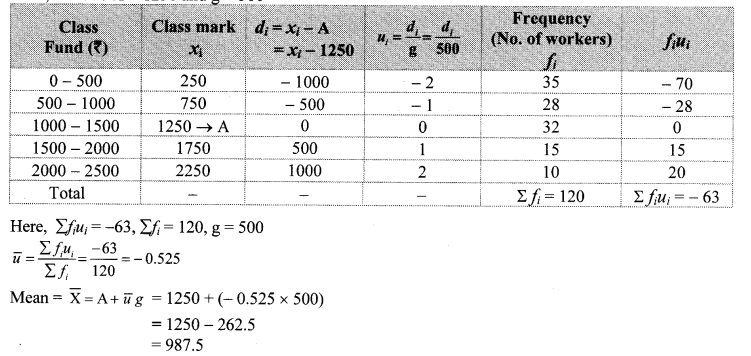
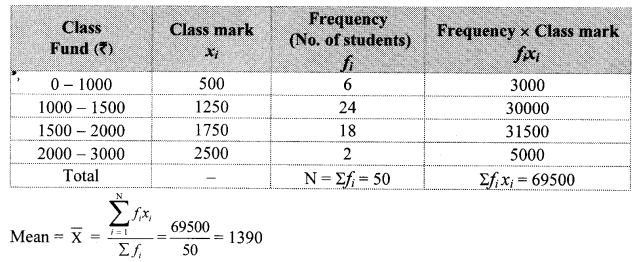
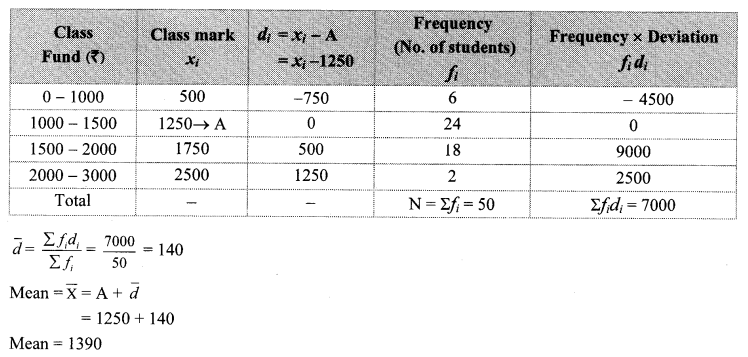
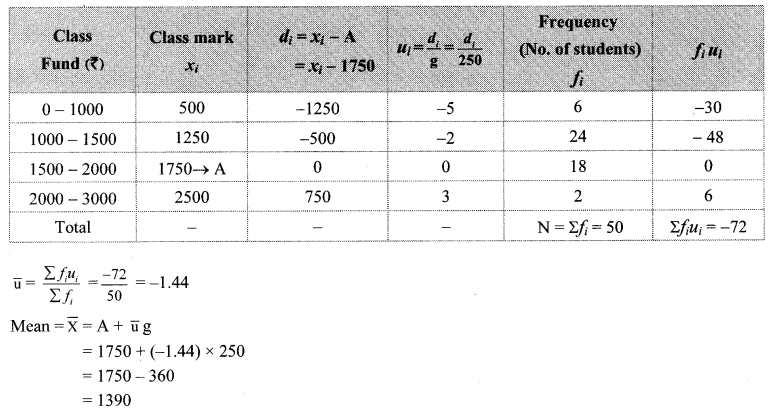
Solution:
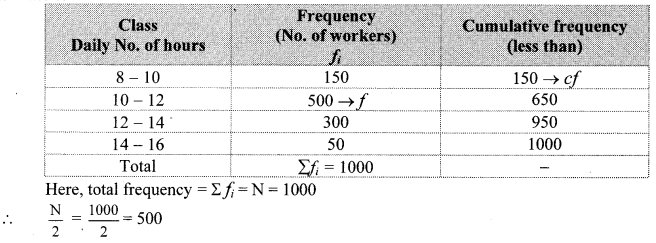
Cumulative frequency which is just greater than (or equal) to 500 is 650.
∴ The median class is 10 – 12.
Now, L = 10, f = 500, cf = 150, h = 2
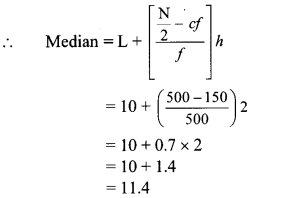
∴ The median of the number of hours the workers work is 11.4 hours.
10th Class Algebra Practice Set 6.2 Question 2.
The frequency distribution table shows the number of mango trees in a grove and their yield of mangoes. Find the median of data.

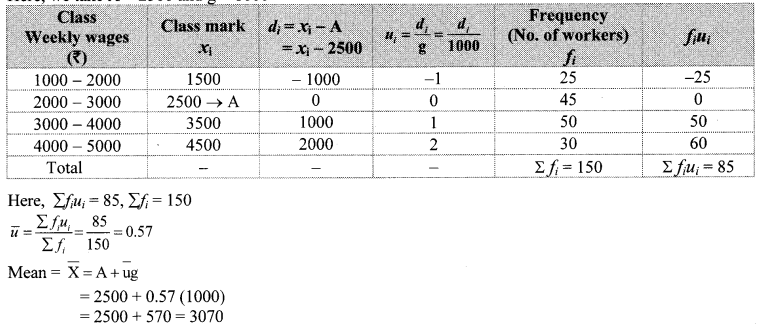
Solution:
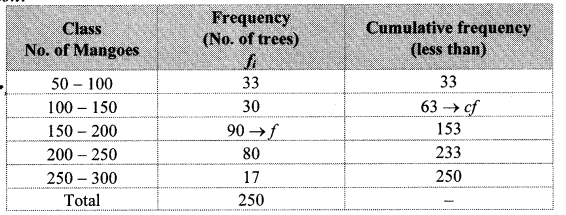
Here, total frequency = ∑fi = N = 250
∴ \(\frac { N }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { 250 }{ 2 } \) = 125
Cumulative frequency which is just greater than (or equal) to 125 is 153.
∴ The median class is 150 – 200.
Now, L = 150, f = 90, cf = 63, h = 50
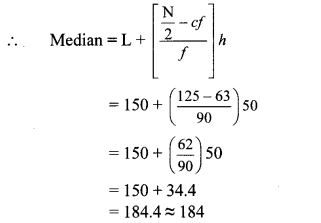
∴ The median of the given data is 184 mangoes (approx).
Statistics Class 10 Practice Set 6.2 Question 3.
The following table shows the classification of number of vehicles and their speeds on Mumbai-Pune express way. Find the median of the data.

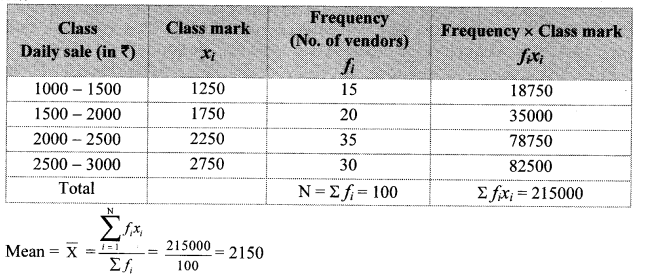
Solution:
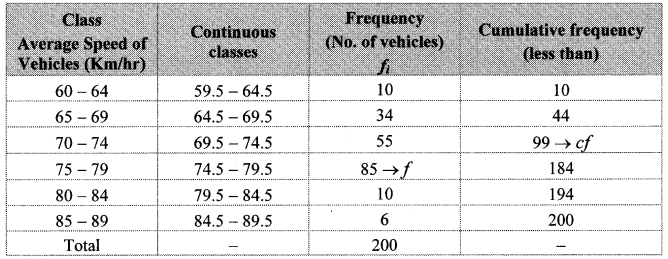
Here, total frequency = ∑fi = N = 200
∴ \(\frac { N }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { 200 }{ 2 } \) = 100
Cumulative frequency which is just greater than (or equal) to 100 is 184.
∴ The median class is 74.5 – 79.5.
Now, L = 74.5, f = 85, cf = 99, h = 5
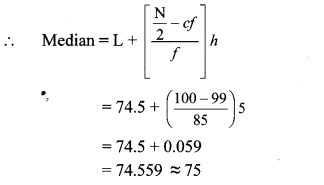
∴ The median of the given data is 75 km/hr (approx.).
Practice Set 6.2 Geometry Class 10 Question 4.
The production of electric bulbs in different factories is shown in the following table. Find the median of the productions.
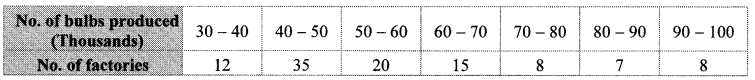
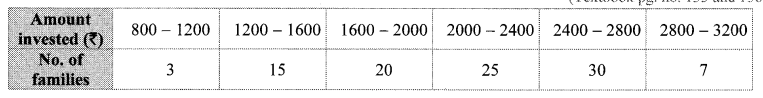
Solution:
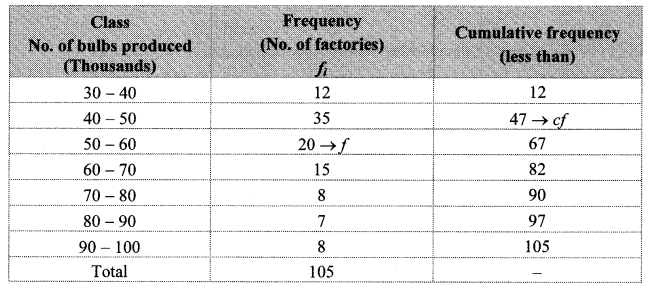
Cumulative frequency which is just greater than (or equal) to 52.5 is 67.
∴ The median class is 50 – 60.
Now, L = 50, f = 20, cf = 47, h = 10
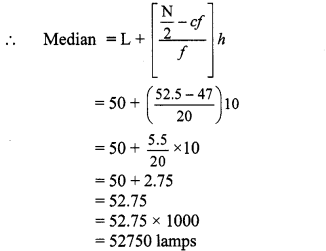
∴ The median of the productions is 52750 bulbs (approx.).
Practice Set 6.2 Question 1.
If the number of scores is odd, then the (\(\frac { n+1 }{ 2 } \))th score is the median of the data. That is, the number of scores below as well as above \({ K }_{ \frac { n+1 }{ 2 } }\) is \(\frac { n-1 }{ 2 } \) Verify the fact by taking n = 2m + I. (Textbk pg. no. 139)
Solution:

The sequence of the terms of scores is 1,2, 3, …….., m, m + 1, m + 2, …, 2m + 1
Thus, we have to prove that m + 1 is the middle term if the number of scores is 2m + 1
i.e. to prove
number of terms from 1 to m = number of terms from m + 2 to 2m + 1 …(i)
Consider the L.H.S. of equation (i)
The sequence is an A.P. with a = 1,d = 1, tn1 = m
tn1 = a + (n1 – 1) d
∴ m = 1 + (n1 – 1)1
∴ m = 1 + n1 – 1
∴ m = n1
Consider the R.H.S. of equation (ii)
The sequence is an A.P. with a = m + 2, d = 1, tn2 = 2m + 1
tn2 = a + (n2 – 1)d
∴ 2m + 1 = m + 2 + (n2 – 1)1
∴ 2m + 1 = m + n2 + 1
∴ m = n2
∴ number of terms from 1 to m = number of terms from m + 2 to 2m + 1 = m = \(\frac { n-1 }{ 2 } \)
∴ m + 1 is the middle term if the number of scores is 2m + 1.
Question 2.
If the number of the scores is even, then the mean of the middle two terms is the median. This is because the number of terms below \({ K }_{ \frac { n }{ 2 } }\) and above \({ K }_{ \frac { n+2 }{ 2 } }\) is equal, which is \(\frac { n-2 }{ 2 } \). Verify this by taking n = 2m. (Textbook pg. no. 139)
Solution:

The sequence of the terms of scores is 1, 2, 3 … m – 1, m, m + 1, m + 2,…., 2m
Thus, we have to prove that m and m + 1 are the middlemost terms if the number of scores is 2m.
i.e. to prove
number of terms from 1 to m – 1 = number of terms from m + 2 to 2m …(i)
Consider the L.H.S. of equation (i)
The sequence is an A.P. with a = 1, d = 1, tn1 = m – 1
tn1 = a + (n1 – 1)d
∴ m – 1 = 1 + (n1 – 1)1
∴m – 1 = 1 + n1 – 1
∴ n1 = m – 1
Consider the R.H.S. of equation (i)
The sequence is an A.P. with a = m + 2, d = 1, tn2= 2m
tn2= a + (n2 – 1) d
∴ 2m = m + 2 + (n2 – 1)1
∴ 2m = m + 2 + n2 – 1
∴ n2 = m – 1
∴ number of terms from 1 to m – 1 = number of terms from m + 2 to 2m = m – 1 = \(\frac { n-2 }{ 2 } \)
∴ m and m + 1 are the middlemost terms if the number of scores is 2m.
- Probability Practice Set 5.1 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Probability Practice Set 5.2 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Probability Practice Set 5.3 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Probability Practice Set 5.4 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Probability Problem Set 5 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Statistics Practice Set 6.1 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Statistics Practice Set 6.2 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Statistics Practice Set 6.3 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Statistics Practice Set 6.4 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Statistics Practice Set 6.5 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Statistics Practice Set 6.6 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Statistics Problem Set 6 Class 10 Maths Solutions