Class 10th Marathi Kumarbharti Chapter 17 सोनाली Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Marathi Solutions Kumarbharti Chapter 17 सोनाली Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions, and Answers.
Std 10 Marathi Chapter 17 Question Answer
Marathi Kumarbharti Std 10 Digest Chapter 17 सोनाली Textbook Questions and Answers
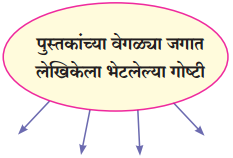
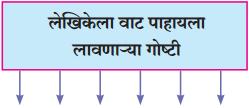
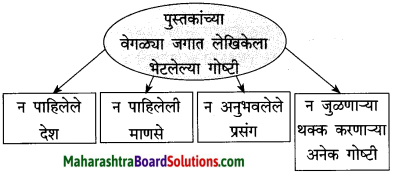
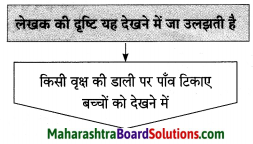
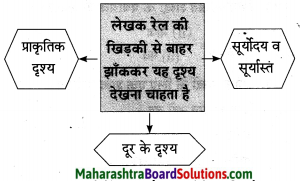
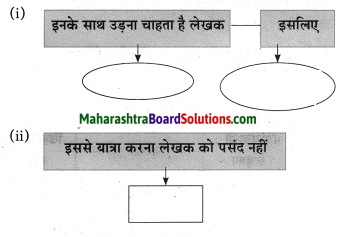
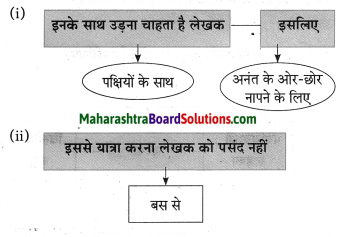
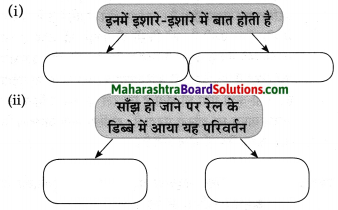
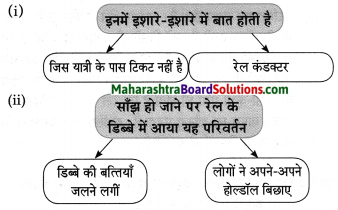
प्रश्न 1.
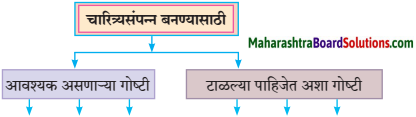
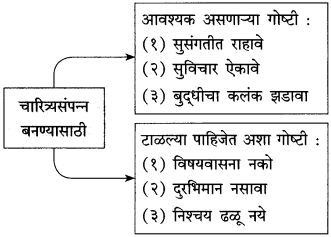
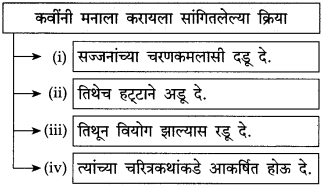
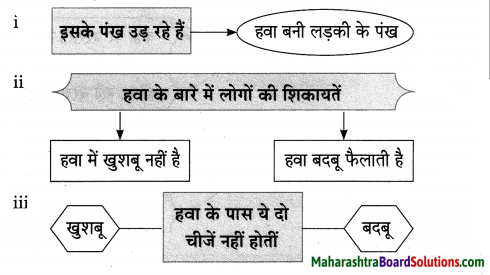
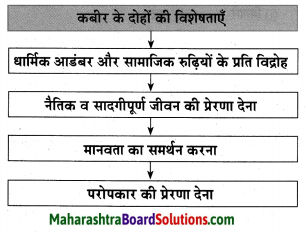
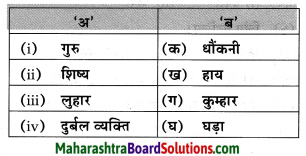
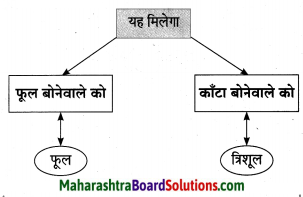
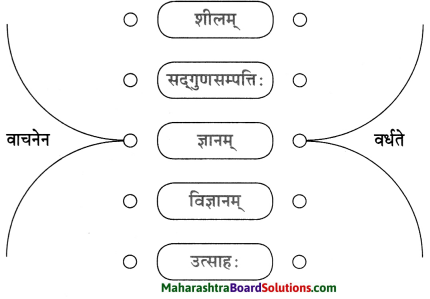
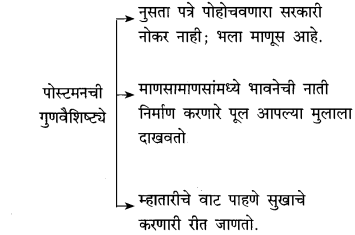
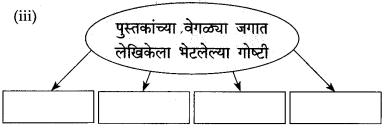
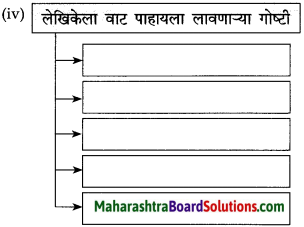
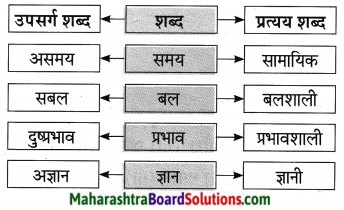
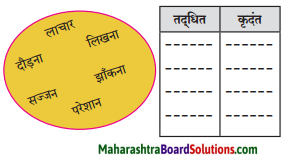
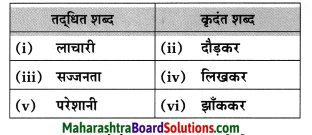
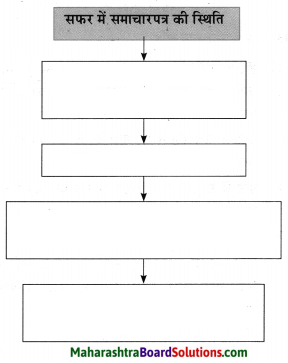
आकृत्या पूर्ण करा.

उत्तर:
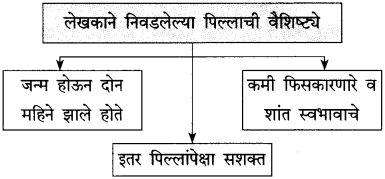
प्रश्न 2.
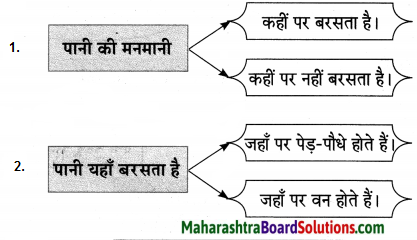
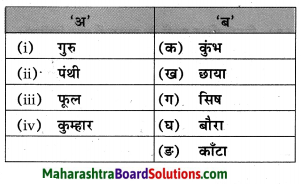
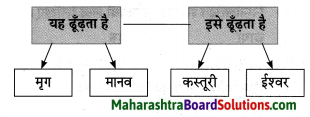
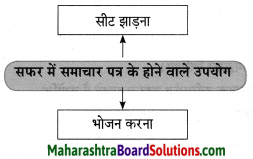
तुलना करा.
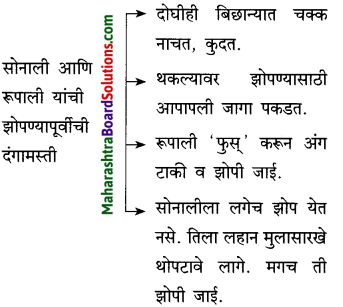
उत्तर:
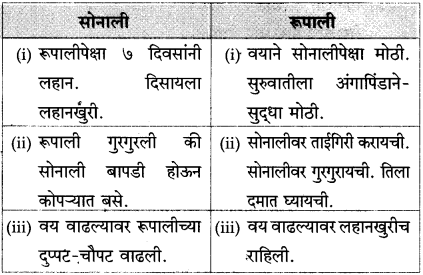
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
खालील वाक्यांतून दिसणारे सोनालीच्या स्वभावाचे पैलू लिहा.
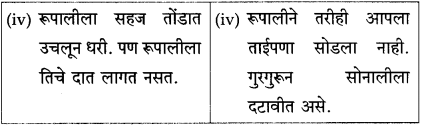
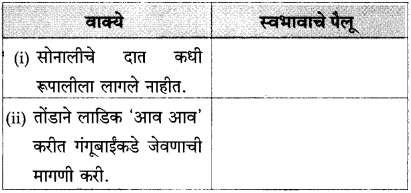
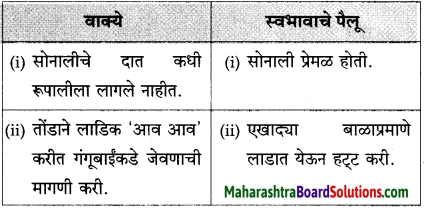
(अ) सोनालीचे दात कधी रूपालीला लागले नाहीत
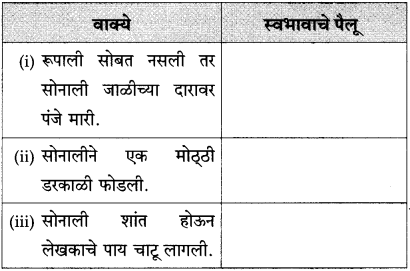
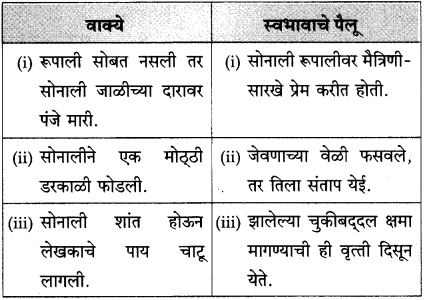
(आ) रूपाली सोबत नसली तर सोनाली जाळीच्या दारावर पंजे मारी
(इ) सोनालीने एक मोठ्ठी डरकाळी फोडली
(ई) सोनाली शांत होऊन लेखकाचे पाय चाटू लागली
(उ) मोठ्याने फिस्कारून सोनाली गृहस्थाच्या अंगावर आली
(ऊ) सोनाली आळीपाळीने आमच्याकडे पाहत होती
प्रश्न 4.
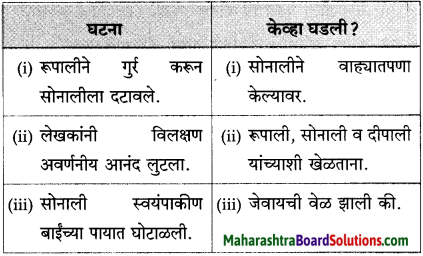
पुढील घटना केव्हा घडल्या ते लिहा. घटना घटना केव्हा घडली
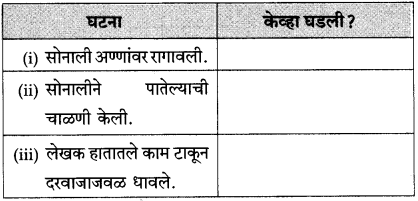
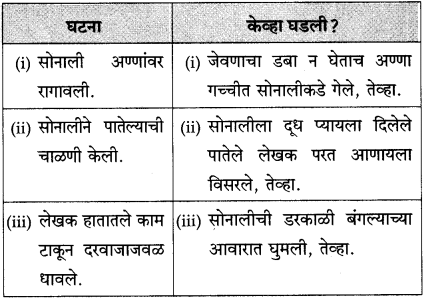
(अ) सोनाली अण्णांवर रागावली.
(आ) सोनालीने पातेल्याची चाळणी केली.
(इ) सोनाली गृहस्थाच्या अंगावर धावली.
(ई) सोनाली बिथरली, गरागरा फिरू लागली.
प्रश्न 5.
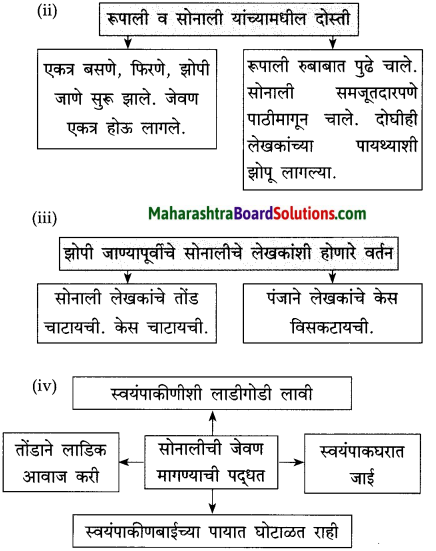
सोनाली आणि रूपाली यांच्यातील मैत्री दर्शवणाऱ्या त्यांच्या दोन सवयी लिहा.
उत्तर:
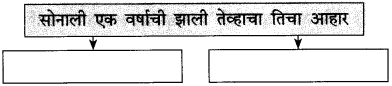
(i) सोनाली व रूपाली एकत्र फिरत, एकत्र झोपत.
(ii) एकत्र जेवण घेत.
प्रश्न 6.
खालील वाक्प्रचारांचे अर्थ सांगून वाक्यांत उपयोग करा.
(अ) डोळे विस्फारून बघणे
(आ) लळा लागणे
(इ) तुटून पडणे
(ई) तावडीत सापडणे
उत्तर:
(अ) डोळे विस्फारून बघणे – डोळे मोठे करून आश्चर्याने बघणे, वाक्य: भर उन्हात पावसाची सर आली, तेव्हा रमेश त्या दृश्याकडे डोळे विस्फारून बघू लागला.
(आ) लळा लावणे – प्रेम वाटणे, माया लावणे. वाक्य: सखू मावशीने त्या अनाथ मुलाला भारी लळा लावला.
(इ) तुटून पडणे – त्वेषाने हल्ला करणे. वाक्य: त्या अनोळखी कुत्र्यावर गल्लीतील कुत्री तुटून पडली.
(ई) तावडीत सापडणे – कचाट्यात पडणे. वाक्य: दूध चोरून पिणारा बोका एकदा आईच्या तावडीत सापडला.
प्रश्न 7.
स्वमत.
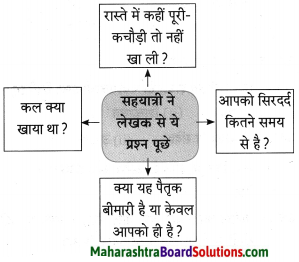
(अ) सोनाली व दीपाली यांच्यातील जिव्हाळा व्यक्त करणारा प्रसंग तुमच्या शब्दांत लिहा.
उत्तर:
एकदा दीपाली सोनालीबरोबर खेळत बसली होती. तेवढ्यात एक पेशन्ट तिथे आला. त्याला ते दृश्य पाहून धक्काच बसला. दीपाली चुकून सिंहिणीकडे गेली असावी, या कल्पनेचे तो धावला आणि त्याने दीपालीला चटकन उचलून घेतले. एक परका माणूस प्रिय व्यक्तीला उचलून घेतो याचा सोनालीला संताप आला. ती त्याच्यावर फिसकारली आणि चवताळून त्याच्यावर धावली. तिचा तो अवतार पाहून त्याने दीपालीला तशीच टाकली. तेवढ्यात अण्णा बाहेर आले. त्यांना घडलेली हकिकत समजली. तो प्रसंग प्रत्यक्ष पाहण्यासाठी अण्णांनी त्या गृहस्थाला दीपालीला उचलायला सांगितले. त्या गृहस्थाने दीपालीला हात लावला, मात्र सोनाली चवताळून त्याच्या अंगावर धावली. लेखकांचे घर हे आता तिला स्वतःचे घर वाटत होते. घरातली माणसे ही आता तिची माणसे झाली होती. परक्या माणसांनी घरातल्या माणसांना हातसुद्धा लावणे तिला मंजूर नव्हते. सोनालीच्या मनातली प्रेमाची ही उत्कट भावना या प्रसंगातून व्यक्त होते.
![]()
(आ) ‘पशुंना कोणी फसवलं, तर त्यांना राग येतो’, यासंबंधी तुम्ही अनुभवलेली एखादी घटना तुमच्या शब्दांत सांगा.
उत्तर:
आम्ही एकदा पारंब्यांना लोंबकळत खेळत होतो. निरंजनने बिस्किटे आणली होती. ती आम्ही वरच्या वर एकमेकांकडे फेकत आणि झेलत होतो. झोके घेता घेता झेल घेणे खूप कौशल्याचे होते. आम्ही बिस्किटे खात होतो. एखादे खाली पडत होते. आमच्या सोबतचा कुत्रा ते पडलेले बिस्कीट खाई. ते पाहून निरंजनला लहर आली. तो खाली उतरला. त्याने एक बिस्कीट दूर फेकले. दूरवर जाऊन त्या कुत्र्याने ते खाल्ले. नंतर नंतर निरंजन बिस्किटे फेकण्याची बतावणी करू लागला. बिचारा कुत्रा धावत जाई पण त्याला काही मिळत नसे. तो रागाने गुरगुर करीत होता. निरंजनने पातळसा दगड घेऊन बिस्कीट म्हणून फेकला. कुत्रा मोठ्या आशेने तिकडे धावला. पण बिस्कीट नाही, हे कळताच तो चवताळला. संतापाने निरंजनकडे घावला. निरंजन घाबरून पारंबीवर चढला. सरसर वर चढू लागला. चवताळलेला कुत्रा तिथे आलाच. त्याने झेप घेतली आणि निरंजनला पकडले. पण निरंजनची पॅन्ट फक्त त्याच्या तोंडात आली. पॅन्ट टरैरै करून फाटली. आम्ही सगळे स्तब्ध होऊन बघतच राहिलो.
भाषाभ्यास
द्वंद्व समास
खालील वाक्ये वाचा आणि त्यातील सामासिक शब्द ओळखा.
(अ) ती दोघे बहीणभाऊ आहेत.
(आ) खरेखोटे समजल्याशिवाय अभिप्राय देऊ नये.
(इ) कष्टाची मीठभाकर आयत्या पक्वानापेक्षा गोड लागते.
ज्या समासातील दोन्ही पदे अर्थदृष्ट्या प्रधान असतात, त्याला ‘वंद्व समास’ असे म्हणतात.
उत्तर:
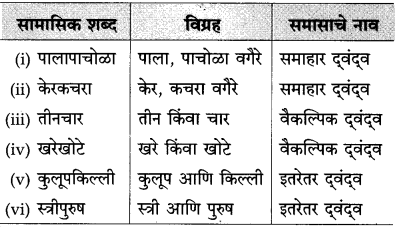
(i) बहीणभाऊ
(ii) खरेखोटे
(ii) मीठभाकर
दुवंद्व समासाचे एकूण तीन प्रकार आहेत.
(१) इतरेतर द्वंद्व समास
(२) वैकल्पिक द्वंद्व समास
(३) समाहार वंद्व समास
प्रश्न 1.
इतरेतर द्वंद्व समास
खालील सामासिक शब्दांचा विग्रह करा.
उदा., आईवडील-आई आणि वडील.
(अ) नाकडोळे
(आ) सुंठसाखर
(इ) कृष्णार्जुन
(ई) विटीदांडू
ज्या समासाचा विग्रह करताना आणि’, ‘व’ या समुच्चयबोधक उभयान्वयी अव्ययांचा उपयोग करावा लागतो, त्या समासाला इतरेतर द्वंद्व समास म्हणतात.
उत्तर:
(i) नाकडोळे → नाक आणि डोळे
(ii) सुंठसाखर → सुंठ आणि साखर
(iii) कृष्णार्जुन → कृष्ण आणि अर्जुन
(iv) विटीदांडू → विटी आणि दांडू
![]()
इतरेतर द्वंद्व समासाची वैशिष्ट्ये
(अ) अर्थासाठी दोन्ही पदांची अपेक्षा असते.
(आ) या समासाचा विग्रह करताना ‘आणि’, ‘व’ ही समुच्चयबोधक अव्यये वापरावी लागतात.
प्रश्न 2.
वैकल्पिक द्वंद्व समास
खालील वाक्ये वाचा आणि त्यातील सामासिक शब्द ओळखा.
उदा., बरेवाईट प्रसंग सगळ्यांच्याच जीवनात येतात. बरेवाईट – बरे किंवा वाईट
(अ) कुठलीही गोष्ट स्वीकारण्यापूर्वी सत्यासत्याचा विचार करावा.
(आ) सभेला चारपाच माणसेच उपस्थित होती.
उत्तर:
(i) सत्यासत्य
(ii) चारपाच.
ज्या समासाचा विग्रह करताना किंवा’, ‘अथवा’, ‘वा’ या विकल्पबोधक उभयान्वयी अव्ययाचा उपयोग करावा लागतो, त्यास ‘वैकल्पिक दवदव समास’ असे म्हणतात.
वैकल्पिक समासाची वैशिष्ट्ये
(अ) दोन्ही प्रधान पदांपैकी एकाचीच अपेक्षा असते.
(आ) समासाचा विग्रह करताना किंवा’, ‘अथवा’, ‘वा’ यांपैकी एखादे विकल्पबोधक उभयान्वयी अव्यय वापरावे लागते.
प्रश्न 3.
समाहार वंद्व समास
उदा., सहलीला जाताना पुरेसे अंथरुण-पांघरुण सोबत घ्यावे.
अंथरुण-पांघरुण- अंथरण्यासाठी व पांघरण्यासाठी लागणाऱ्या वस्तू व इतर कपडे. खालील वाक्ये वाचा व त्यांतील सामासिक शब्द ओळखा.
(अ) कोपऱ्यावरच्या मंडईत भाजीपाला चांगला मिळतो.
(आ) गरिबास कपडालत्ता दयावा, अन्नपाणी दयावे.
उत्तर:
(i) [भाजीपाला]
(ii) [कपडालत्ता] अन्नपाणी
ज्या समासातील पदांचा विग्रह करताना त्यातील पदांच्या अर्थाशिवाय त्याच जातीच्या इतर पदार्थांचाही त्यात समावेश केलेला असतो, त्यास ‘समाहार वंद्व समास’ असे म्हणतात. समाहार वंद्व समासाची वैशिष्ट्ये
(अ) समासातील पदांचा विग्रह करताना त्यातील पदांच्या अर्थाशिवाय त्याच जातीच्या इतर पदार्थांचाही समावेश केलेला असतो.
(आ) समासात आलेल्या आणि त्या जातीच्या इतर वस्तूंच्या समुदायाला महत्त्व असते, म्हणून हा समास एकवचनी असतो.
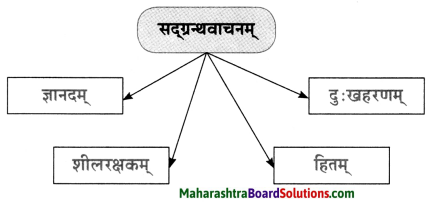
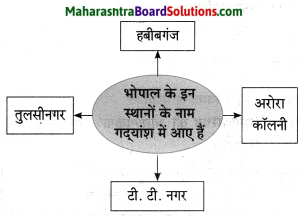
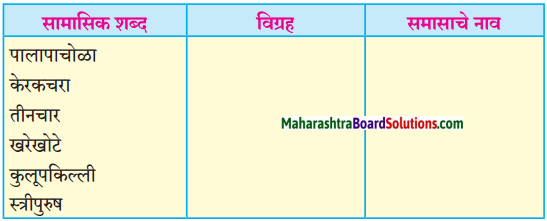
तक्ता पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
![]()
Marathi Kumarbharti Class 10 Textbook Solutions Chapter 17 सोनाली Additional Important Questions and Answers
कृति
कृतिपत्रिकेतील प्रश्न १ (अ) आणि (आ) यांसाठी…
उतारा क्र. १
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार कृती करा:
कृती १: (आकलन)
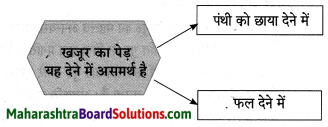
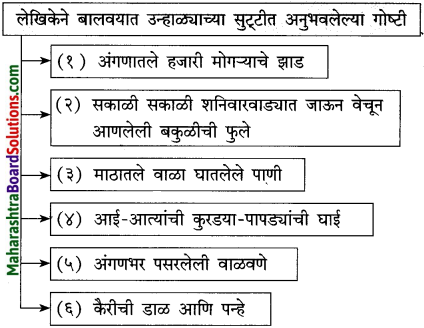
प्रश्न 1.
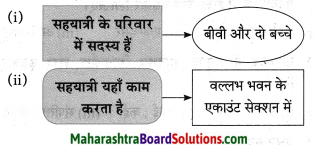
आकृत्या पूर्ण करा:
(i) 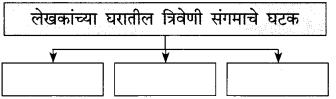
(ii) 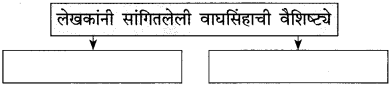
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 2.
माहिती लिहा:
(i) लेखकांनी पाळलेल्या सिंहिणीच्या पिल्लाचे नाव – ………………………………….
(ii) सिंहिणीचे पिल्लू लेखकांकडे आले तो दिवस – ………………………………….
(iii) सिंहिणीच्या पिल्लाचे कायमचे राहण्याचे ठिकाण – ………………………………….
(iv) सिंहिणीच्या पिल्लाचा लेखकांकडील शेवटचा दिवस – ………………………………….
उत्तर:
(i) लेखकांनी पाळलेल्या सिंहिणीच्या पिल्लाचे नाव – सोनाली.
(i) सिंहिणीचे पिल्लू लेखकांकडे आले तो दिवस – २९ ऑगस्ट १९७३.
(iii) सिंहिणीच्या पिल्लाचे कायमचे राहण्याचे ठिकाण – पुण्यातले पेशवे उदयान.
(iv) सिंहिणीच्या पिल्लाचा लेखकांकडील शेवटचा दिवस – ३१ मार्च १९७४.
कृती २: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
माहिती लिहा:
(i) रूपाली:
(ii) दीपाली:
(iii) सोनाली:
उत्तर:
(i) रूपाली: तिचे केस कापसासारखे शुभ्र होते.
(ii) दीपाली: डॉ. सुभाष यांची मुलगी, म्हणजेच लेखकांची नात.
(iii) सोनाली: तिचे केस सोन्यासारखे होते.
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
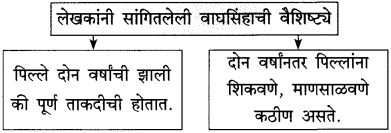
छाव्याला पाळण्याबाबतचा लेखकांचा दृष्टिकोन लिहा:
(i) …………………………
(ii) …………………………
उत्तर:
(i) सर्कशीतल्या वन्य पशुंना शिकवतात तसे सोनालीला शिकवायचे नाही.
(ii) त्या जंगली जनावरावर पोटच्या मुलाप्रमाणे प्रेम करायचे.
प्रश्न 3.
सिंहिणीच्या पिल्लाशी वागण्याचे लेखकांनी ठरवलेले नियम स्पष्ट करा:
(i) …………………………
(ii) …………………………
उत्तर:
(i) सिंहिणीचे पिल्लू जेवल्याशिवाय स्वतः जेवायचे नाही.
(ii) त्या पिल्लाला जवळ घेतल्याशिवाय झोपी जायचे नाही.
प्रश्न 4.
लेखक व त्यांचे पूर्वज यांचा एक परस्परविरोधी गुण लिहा:
(i) लेखकांचे पूर्वज:
(ii) लेखक
उत्तर:
(i) लेखकांचे पूर्वज: यांनी वन्य प्राण्यांची शिकार केली.
(ii) लेखक: यांना वन्य प्राण्यांमधल्या पशुत्वाची शिकार करायची होती.
प्रश्न 5.
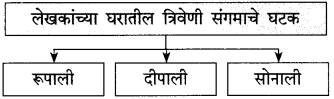
पुढील नावे निश्चित करण्यामागील कारणमीमांसा लिहा:
(i) रूपाली:
(ii) दीपाली:
(iii) सोनाली:
उत्तर:
(i) रूपाली: हिचे केस रुपेरी होते, म्हणून रूपाली.
(ii) दीपाली: लेखकांच्या नातीचा जन्म झाला, म्हणजे घरात दीप आला म्हणून दीपाली.
(iii) सोनाली: हिचे केस सोन्यासारखे होते, म्हणून सोनाली.
![]()
कृती ३: (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
पुढील शब्दांचा वाक्यांत उपयोग करा:
(i) सुतकी
(ii) माणसाळणे.
उत्तर:
(i) सुतकी: दहावीमध्ये कमी गुण मिळाले म्हणून काही मुलांचे आईवडील सुतकी चेहरा करून बसले होते.
(ii) माणसाळणे: वन्य पशू आता खूप माणसाळले आहेत, पण खूप माणसे अजून माणसाळली नाहीत.
प्रश्न 2.
सहसंबंध लक्षात घेऊन उत्तर: लिहा:
(i) माणूस – माणसाळणे. यासारखी अन्य चार उदाहरणे लिहा.
उत्तर:
(१) लाथ – लाथाडणे.
(२) हात – हाताळणे.
(३) उजेड – उजाडणे.
(४) नांगर – नांगरणे,
(ii) सिंह – बछडा, यासारखी अन्य चार उदाहरणे लिहा.
उत्तर:
(१) गाय – वासरू.
(२) बकरी – कोकरू,
(३) वाघ – बछडा.
(४) घोडा – शिंगरू.
कृती ४: (स्वमत / अभिव्यक्ती)
प्रश्न.
या उताऱ्यातून जाणवणारे लेखकांचे स्वभावगुण, त्यांची वृत्ती स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तर:
लेखक त्यांच्या पूर्वजांपेक्षा अधिक उदात्त पातळीवरून विचार करतात. त्यांच्या पूर्वजांनी वन्य प्राण्यांची शिकार केली. त्यांना मारले. लेखकांना मात्र वन्य प्राण्यांना ठार मारणे ही कल्पनाच पसंत नाही. वन्य प्राण्यांशी प्रेमाने वागावे, त्यांना माणसाळावे अशी लेखकांची मनोमन इच्छा होती. म्हणून ते सिंहिणीचे पिल्लू पाळायला आणतात. सिंहिणीला आपण माणसाळावू शकू, तिला प्रेमाने जिंकू अशी जणू काही लेखकांना मनोमन खात्री होती.
लेखक स्वतः प्राण्यांशी आत्मीयतेने वागले, पण त्यांनी घरातल्या सगळ्यांना त्या प्राण्यांशी स्वतःप्रमाणेच वागायला शिकवले. आपल्या चिमुकल्या नातीलासुद्धा निर्धास्तपणे खेळू दिले. रूपाली, सोनाली व दीपाली ही नावे पाहा. तीन बहिणींची नावे असावीत, असे त्यांच्या उच्चारांवरून वाटते. ती दोन्ही पिल्ले त्यांना स्वतःच्या नातीइतकीच प्रिय आहेत. या सर्व बाबींवरून लेखकांची प्राण्यांकडे पाहण्याची निर्मळ वृत्ती दिसून येते.
![]()
उतारा क्र. २
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार कृती करा:
कृती १: (आकलन)
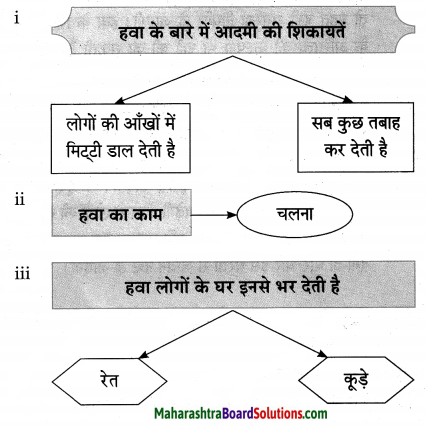
प्रश्न 1.
आकृत्या पूर्ण करा:
उत्तर:

![]()
कृती २: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
पुढील घटना केव्हा घडल्या ते लिहा:
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 2.
कारणे लिहा:
(i) सोनाली व रूपाली यांच्यासाठी लेखकांनी साखळ्या आणल्या; कारण –
(ii) रूपाली गुरगुरल्यावर सोनाली बापडी होऊन कोपऱ्यात जाऊन निमूट बसे; कारण –
उत्तर:
(i) सोनाली व रूपाली यांच्यासाठी लेखकांनी साखळ्या आणल्या; कारण लहानपणापासून साखळीची सवय लावली नाही, तर ही जनावरे मोठेपणी साखळी घालू देत नाहीत.
(ii) रूपाली गुरगुरल्यावर सोनाली बापडी होऊन कोपऱ्यात जाऊन निमूट बसे; कारण रूपाली ही सोनालीपेक्षा ज्येष्ठ होती आणि सोनालीने रूपालीचा ज्येष्ठपणा मान्य केला होता.
प्रश्न 3.
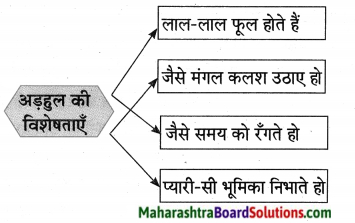
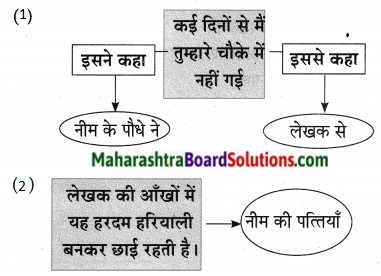
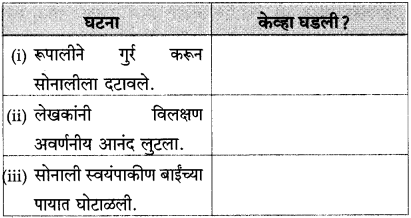
पुढील वाक्यातून दिसणारे सोनालीच्या स्वभावाचे पैलू लिहा:
उत्तर:
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
उत्तर: लिहा: (मार्च १९).
(i) सोनालीचे जागतिक दर्जाचे वेगळेपण दर्शवणारी गोष्ट ……………………
(ii) ‘सोनाली’ हे उत्तर येईल असा प्रश्न तयार करा.
उत्तर:
(i) दूधपोळी नी दूधभात खाणारी जगातली ती एकमेव सिंहीण असावी.
(ii) सिंहकन्येचे नाव काय होते?
कृती ३: (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
अधोरेखित शब्दांच्या जागी कंसांत दिलेल्या जातीचा अन्य योग्य शब्द योजा आणि वाक्य पुन्हा लिहा:
(i) पण दोघी वाढू लागल्या आणि सारं दृश्यच बदललं. (उभयान्वयी अव्यय)
(ii) सोनालीला घेऊन मी कोर्टावर गेलो. (शब्दयोगी अव्यय)
(iii) झोपेत बाईसाहेब लोळतही भरपूर. (क्रियाविशेषण)
उत्तर:
(i) पण दोघी वाढू लागल्या व सारं दृश्यच बदललं.
(ii) सोनालीला घेऊन मी कोर्टामध्ये गेलो.
(iii) झोपेत बाईसाहेब लोळतही खूप.
प्रश्न 2.
सहसंबंध ओळखून चौकटी भरा:
२: [दुप्पट] म्हणून,
(i) ३: [ ]
(ii) ४: [ ]
(iii) ५: [ ]
(iv) निम्मे: [ ]
उत्तर:
(i) ३: [तिप्पट]
(ii) ४: [चौपट]
(ii) ५: [पाचपट]
(iv) निम्मे: [निमपट]
प्रश्न 3.
ताई + गिरी = ताईगिरी याप्रमाणे अन्य चार शब्द लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) दादागिरी
(ii) भाईगिरी
(iii) शिपाईगिरी
(iv) भोंदूगिरी,
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
पुढील वाक्यातील अधोरेखित शब्दाचे वचन बदलून वाक्य पुन्हा लिहा: (मार्च १९)
सोनाली जिभेनं ताटली चाटूनपुसून साफ करी.
उत्तर:
सोनाली जिभेनं ताटल्या चाटूनपुसून साफ करी.
प्रश्न 5.
पुढील वाक्यातील अव्यये ओळखा: (मार्च ‘१९)
सोनाली जेवणाची मागणी करी; पण तिचं जेवण ताटलीत टाकलं, की ती गुरगुरायला लागे. अव्यये –
उत्तर:
अव्यये – [पण] [की]
कृती ४: (स्वमत / अभिव्यक्ती)
प्रश्न .
रूपाली व सोनाली यांच्यात निर्माण झालेल्या दोस्तीचे स्वरूप लिहा. किंवा ‘प्राण्यांनाही भावना असतात’, या विधानाशी तुम्ही सहमत आहात का? सोदाहरण स्पष्ट करा. (मार्च ‘१९)
उत्तर:
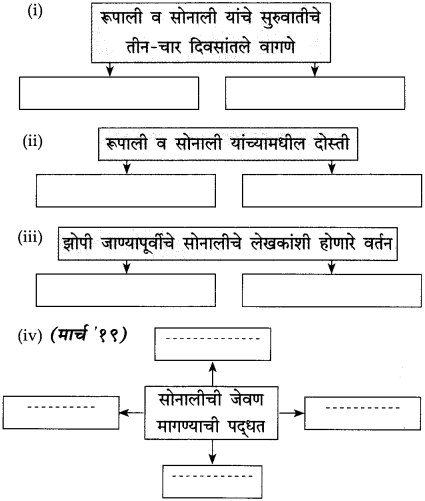
अगदी सुरुवातीच्या काळात रूपाली व सोनाली यांचे एकमेकींशी पटत नसे. त्या एकमेकींशी प्रेमाने वागतच नसत. रूपाली सोनालीवर भुंकायची, तर सोनाली रागाने फिसकारायची, रूपालीवर धावून जायची, पण हे फक्त तीन-चार दिवसच टिकले. मग दोघीही एकमेकींच्या दोस्त बनल्या.
एकदा दोस्त झाल्यावर मात्र त्यांचे सर्व व्यवहार प्रेमाने होऊ लागले. एकत्र बसणे, एकत्र हिंडणे, झोपणे सुरू झाले. त्या एकत्र जेवूसुद्धा लागल्या. रूपाली लेखकांच्या पायथ्याशी झोपत असे. तशी आता सोनालीसुद्धा झोपू लागली. रूपाली या घरात आधी आली होती. म्हणून ती जणू काही ज्येष्ठ होती. रूपाली ज्येष्ठत्वाचा हक्क गाजवीत असे. दोघी सोबत चालू लागल्या की रूपाली रुबाबात पुढे चालत असे. तिचा हा मान सोनाली निमूटपणे मान्य करी आणि रूपालीच्या मागे समजूतदारपणे चालू लागे. थोडक्यात काय, तर त्यांच्यातले पशुत्व हळूहळू लोप पावत होते. त्या दोघींमध्ये माणसासारखे मैत्रीचे नाते रुजत होते.
उतारा क्र. ३
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार कृती करा:
कृती १: (आकलन)
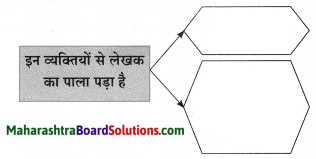
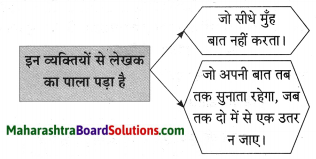
प्रश्न 1.
पुढील वाक्यांतून दिसणारे सोनालीच्या स्वभावाचे पैलू लिहा:
उत्तर:
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
कारणे लिहा:
(i) आम्ही तिला न्यायच्या ऐवजी तीच आम्हांला ओढू लागली होती; कारण –
(ii) लेखकांच्या अनुपस्थितीत सोनालीच्या जेवणाची व्यवस्था अण्णांकडे किंवा गड्याकडे सोपवली होती; कारण –
(iii) सोनालीने उडी मारून लेखकांच्या हातातला डबा पंजाने फटकारा मारून दूर उडवला; कारण –
उत्तर:
(i) आम्ही तिला न्यायच्या ऐवजी तीच आम्हांला ओढू लागली होती; कारण ती आता मोठी झाली होती, तिची उंची वाढली होती आणि तिच्या अंगात ताकद आली होती.
(ii) लेखकांच्या अनुपस्थितीत सोनालीच्या जेवणाची व्यवस्था अण्णांकडे किंवा गड्याकडे सोपवली होती; कारण लेखक डॉक्टर असल्यामुळे त्यांना दवाखान्याच्या कामानिमित्त दूर-दूर जावे लागे.
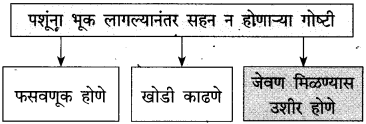
(iii) सोनालीने उडी मारून लेखकांच्या हातातला डबा पंजाने फटकारा मारून दूर उडवला; कारण तिला भूक लागली होती ‘आणि तिला जेवण मिळायला खूप उशीर झाला होता.
प्रश्न 3.
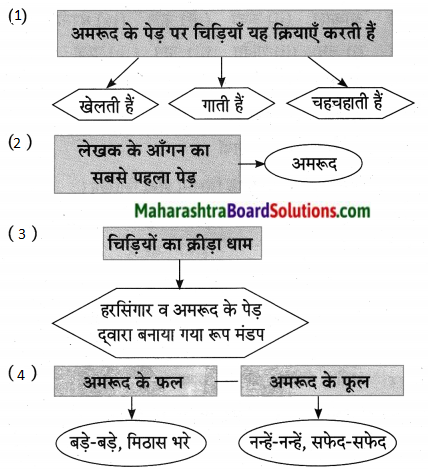
पुढील घटना केव्हा घडल्या ते लिहा:
उत्तर:
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
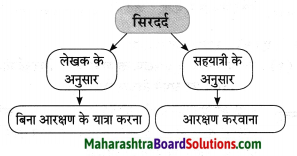
आकृती पूर्ण करा:
उत्तर:

कृती २: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
सोनालीला जेवण देण्याच्या अण्णांच्या पद्धतीतील कृती लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) गच्चीत न जाता जाळीच्या दरवाजाच्या आत बसून तिला चिमट्याने खाऊ घालीत.
(ii) कधी कधी ते गच्चीच्या कठड्याच्या जाळीतून खाऊ घालीत.
प्रश्न 2.
सिंहीण पिसाळण्याला कारणीभूत ठरलेल्या, अण्णांच्या दोन कृती लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) डबा सोबत न घेता तो अण्णांनी हॉलमध्ये ठेवला.
(ii) दार उघडून गच्चीत गेले आणि दरवाजा पुन्हा लावून घेतला.
प्रश्न 3.
अण्णांनी डबा आणलेला नाही, हे कळताच सिंहिणीकडून आलेली पहिली प्रतिक्रिया लिहा.
उत्तर:
अण्णांनी डबा आणलेला नाही, हे लक्षात येताच सोनाली दरवाजाकडे धावली आणि अण्णांच्या अंगावर गुरगुरू लागली.
प्रश्न 4.
अण्णांनी सोनालीला केलेली विनंती आणि सोनालीने त्या विनंतीला दिलेला प्रतिसाद लिहा.
उत्तर:
“सोनाली थांब. मी डबा आणतो. बाजूला हो” अशी विनंती करीत अण्णा दरवाजाकडे सरकू लागले. त्या क्षणी सोनालीने मोठी डरकाळी फोडली. त्या वेळी अण्णा “शांताराम घाव,” अशा हाका मारू लागले.
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
सोनालीची डरकाळी ऐकून लेखकांनी केलेली कृती आणि त्या कृतीला सोनालीकडून झालेली प्रतिक्रिया लिहा.
उत्तर:
सोनालीची डरकाळी ऐकून लेखक गच्चीकडे धावले. लोखंडी पट्टीने त्यांनी जाळीचा दरवाजा उघडला. डबा घेऊन सोनालीजवळ गेले. सोनालीने संतापाने तो डबा पंजाने उडवून दिला. इतस्तत: उडालेले मटण मग तिने चाटून पुसून खाल्ले.
प्रश्न 6.
सोनालीच्या दातांमधील ताकदीचा प्रत्यय देणारी घटना लिहा.
उत्तर:
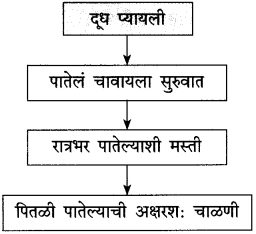
लेखकांनी नेहमीप्रमाणे सोनालीला पातेल्यातून दूध दिले; पण लेखक ते पातेले परत न्यायला विसरले. दूध पिऊन झाल्यावर सोनाली ते पातेले रात्रभर चावत बसली. त्यामुळे पातेल्याची अक्षरश: चाळण झाली होती. यावरून असे दिसते की, पातेल्याला सहज भोके पाडण्याइतकी सोनालीच्या दातांत ताकद होती.
प्रश्न 7.
आकृतिबंध पूर्ण करा: (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-१)
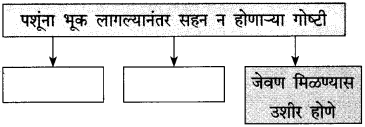
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 8.
अचूक विधान शोधून लिहा: (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-१)
(अ) लेखकाने दिलेले जेवण सोनालीने व्यवस्थित खाल्ले.
(आ) सोनालीने डब्याला फटकारा मारून दूर फेकून दिला.
(इ) सोनालीने लेखकाच्या हातात असलेल्या डब्यातील मटण इतस्तत: विखरून खाल्ले.
(ई) सोनाली अण्णांकडे गुरगुर करीत पाहत राहिली.
उत्तर:
सोनालीने डब्याला फटकारा मारून दूर फेकून दिला.
![]()
प्रश्न 9.
वैशिष्ट्ये लिहा: (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-१) वन्यपशूचे दात-
उत्तर:
वन्यपणूंचे दात-
(i) मजबूत
(ii) चिवट.
प्रश्न 10.
तळी पातेल्याची चाळणी केल्याच्या घटनेचा ओघतक्ता तयार करा: (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-१)
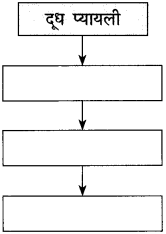
उत्तर:
कृती ३: (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
‘सिंहीण: डरकाळी’ हा सहसंबंध लक्षात घ्या आणि पुढील चौकटी पूर्ण करा:
(i) साप:
(ii) गाय:
(iii) घोडा:
(iv) चिमणी:
उत्तर:
(i) साप: फूत्कार
(ii) गाय: हंबरडा
(ii) घोडा: खिंकाळी
(iv) चिमणी: चिवचिव
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
पुढील नामांना योग्य असे विशेषण लिहा:
(i) डरकाळी:
(ii) अर्थ:
(iii) गच्ची:
(iv) जेवण:
उत्तर:
(i) डरकाळी: भयंकर
(ii) अर्थ: अचूक
(iii) गच्ची: मोठी
(iv) जेवण: स्वादिष्ट
प्रश्न 3.
‘रुंद: रुंदी’ यातील सहसंबंध लक्षात घेऊन पुढील चौकटी पूर्ण करा:
(i) भयंकर:
(ii) ऐटदार:
(iii) उंच:
(iv) चिवट:
उत्तर:
(i) भयंकर: भय
(ii) ऐटदार: ऐट
(iii) उंच: उंची
(iv) चिवट: चिवटपणा
प्रश्न 4.
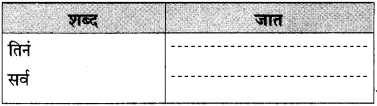
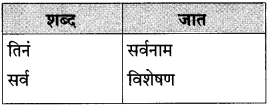
पुढील वाक्यांतील अधोरेखित शब्दांची जात ओळखून लिहा: पंधरा-वीस मिनिटांत तिनं सर्व फस्त केलं. (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-१)
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 5.
सहसंबंध लिहा: (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-१)
(i) खोडी: खोडकरपणा : : ………………………………….. : चिवटपणा.
(ii) पाय: ………………………………….. : : विलंब : उशीर.
उत्तर:
(i) खोडी: खोडकरपणा: चिवट: चिवटपणा.
(ii) पाय: पाद/चरण/पद: विलंब: उशीर.
(ii) मध्ये ‘पाद, चरण व पद’ यांपैकी कोणतेही एक उत्तर लिहावे.]
कृती ४: (स्वमत / अभिव्यक्ती)
प्रश्न 1.
तुम्हाला कोणत्याही पाळीव प्राण्याबाबत आलेला अनुभव तुमच्या शब्दांत लिहा. (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-१)
उत्तर:
मी त्या वेळी सहावीत होतो. माझ्या काकांनी घरात एक ससा पाळायला आणला. त्याचे ते लाललाल डोळे आणि सतत हलणारे ओठ लक्ष वेधून घेत. त्याचे गोरे गोरे, मऊमऊ गुबगुबीत अंग पाहून तर त्याला चटकन उचलून घ्यावेसे वाटे. मांजर, कुत्रा जसे एकेक पाऊल टाकत चालतात, तसा तो चालत नसे. तो टुणटुण उड्या मारीतच चालायचा. कसलाही बारीकसा जरी आवाज झाला, तरी त्याचे कान क्षणार्धात ताठ, उंच होत असत आणि तो पटकन सुरक्षित जागी आसरा घेई. जवळजवळ दिवसभर तो घरात मोकळा फिरत राही. आम्ही त्याला रात्री पिंजऱ्यात ठेवत असू.
सशाच्या ‘शी-शू’ला एक उग्र वास यायचा. सुरुवाती-सुरुवातीला आम्हाला त्याचा त्रास व्हायचा. पण थोड्याच दिवसात त्याला कशी कोण जाणे एक आश्चर्यकारक सवय लागली. तो सकाळी साडेचारपाच वाजता पिंजऱ्याचा दरवाजा खरवडून खरवडून व पिंजऱ्यातल्या पिंजऱ्यात उड्या मारून गोंधळ उडवून दयायचा. मग काका येऊन दरवाजा उघडत. दरवाजा उघडताच तो न्हाणीघराकडे धाव घेई. तिथून स्वच्छतागृहाकडे. तिथे तो शी-शू करी, काका त्याला मग घुवायचे आणि पिंजऱ्यात आणून सोडायचे.
घरात प्राणी पाळण्याची गोष्ट गप्पात आली, की मला हमखास तो ससा आठवतो.
![]()
उतारा क्र. ४
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार कृती करा:
कृती १: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
कारणे लिहा:
(i) त्यासरशी सोनाली मोठ्याने फिसकारली व त्या गृहस्थाच्या अंगावर धावली; कारण –
(ii) शेकडो पुणेकरांनी कॅफे गुडलकच्या चौकात गर्दी केली होती; कारण
(iii) सोनाली बिथरली, गरगरा फिरू लागली; कारण
उत्तर:
(i) त्यासरशी सोनाली मोठ्याने फिसकारली व त्या गृहस्थाच्या अंगावर धावली; कारण दीपालीला त्या गृहस्थांनी उचलून घेतले होते, हे सोनालीला बिलकूल आवडले नव्हते.
(ii) शेकडो पुणेकरांनी कॅफे गुडलकच्या चौकात गर्दी केली होती; कारण उघड्या मोटारीतून येणाऱ्या सिंहिणीला पाहण्याची सर्वांना इच्छा होती.
(iii) सोनाली बिथरली, गरगरा फिरू लागली; कारण आपल्या प्रियजनांपासून आपण दूर जाणार याचे तिला दुःख झाले होते..
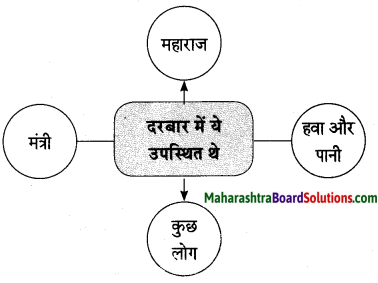
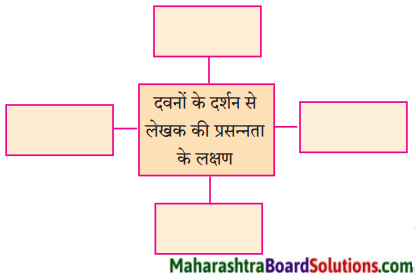
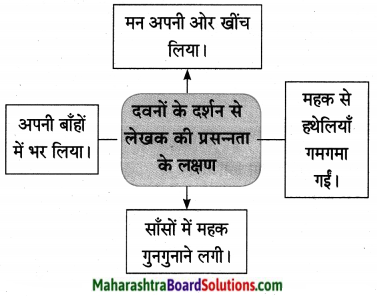
कृती २: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
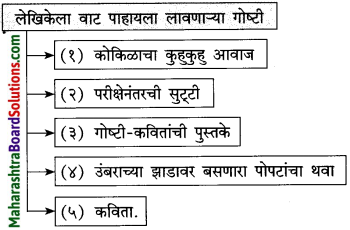
सोनालीला झालेले वियोगाचे दुःख व्यक्त करणारी वाक्ये उताऱ्यातून शोधून लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) सोनाली आतल्या पिंजऱ्यात जायला तयार नव्हती.
(ii) मी आत गेलो की ती आतल्या पिंजऱ्यात येई.
(iii) मी बाहेर आलो की ती बाहेर यायची.
(iv) सोनाली आळीपाळीने आमच्याकडे पाहत होती.
(v) सोनाली बिथरली. गरागरा फिरू लागली.
(vi) मोठ्याने ओरडू लागली. पिंजऱ्याबाहेर येण्यासाठी धडपडू लागली.
प्रश्न 2.
लेखकांना झालेले सोनालीच्या वियोगाचे दुःख व्यक्त करणारी वाक्ये उताऱ्यातून शोधून लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) माझी सोनालीवरची प्रेमाची मालकी संपली.
(ii) दुःखाचा एकेक कढ मी आवंढ्याबरोबर गिळत होतो.
(ii) काय बोलावं तेच मला समजेना.
(iv) जड अंत:करणाने मी पिंजऱ्याकडे पाठ फिरवली आणि मुकाट्याने गाडीत जाऊन बसलो. टीप: वरील उत्तरांमध्ये दोनपेक्षा जास्त घटक आहेत. परीक्षेत दोन किंवा चार घटक लिहिण्यास सांगितले जाण्याची शक्यता आहे. तरीही येथे विदयार्थ्यांच्या माहितीसाठी जास्त घटक देण्यात आलेले आहेत.
![]()
कृती ३: (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
कंसांतील सूचनांनुसार कृती करा:
(i) सोनाली आता एकटीच पिंजऱ्यात राहिली. (भावे प्रयोग करा.)
(ii) महापौरांनी सोनालीचा औपचारिक स्वीकार केला. (कर्तरी प्रयोग करा.)
(iii) अण्णा चटकन दरवाजा लावतात. (कर्मणी प्रयोग करा.)
उत्तर:
(i) सोनालीने आता एकटीनेच पिंजऱ्यात राहावे.
(ii) महापौर सोनालीचा औपचारिक स्वीकार करतात.
(iii) अण्णांनी चटकन दरवाजा लावला.
प्रश्न 2.
उताऱ्यातून पुढील प्रकारातील शब्द शोधून लिहा: (प्रत्येकी चार शब्द)
(i) विशेष नामे
(ii) सामान्य नामे
(iii) भाववाचक नामे
(iv) विशेषण
(v) उभयान्वयी अव्यये
(vi) क्रियाविशेषणे.
उत्तर:
(i) विशेष नामे: सोनाली, रूपाली, दीपाली, अण्णा.
(ii) सामान्य नामे: घर, पेशन्ट, सिंहीण, गृहस्थ.
(iii) भाववाचक नामे: कडकडाट, उत्साह, दुःख, मालकी.
(iv) विशेषण: बोबडा, खूप, जड, सर्व,
(v) उभयान्वयी अव्यये: जसा-तसा, व, आणि, पण.
(vi) क्रियाविशेषणे: आता, आत, तिथे, बाहेर.
व्याकरण व भाषाभ्यास
कृतिपत्रिकेतील प्रश्न ४ (अ) आणि (आ) यांसाठी… अव्याकरण घटकांवर आधारित कृती:
२. अलंकार:
पुढील ओळींतील अलंकार ओळखा वं स्पष्टीकरण लिहा:..
‘ऊस डोंगा परी, रस नोहे डोंगा। काय भुललासी वरलिया रंगा।।’
– संत चोखामेळा
उत्तर:
हा दृष्टान्त अलंकार आहे.
स्पष्टीकरण: माणसाच्या बाह्य वर्तनावर जाऊ नये. अंतरंग ओळखावे. हे तत्व बिंबवताना संत चोखामेळा यांनी उसाचे समर्पक उदाहरण (दृष्टान्त) दिले आहे. ऊस वाकतो पण रस वाकत नाही. त्याप्रमाणे शरीर वाकून उपयोगी नाही. मन नम्र असावे लागते. अशा प्रकारे उसाचा दृष्टान्त दिल्यामुळे हा दृष्टान्त अलंकार आहे.
![]()
३. वृत्त
पुढील ओळींचा लगक्रम लावून गण पाडा व वृत्त ओळखा:
नदीच्या किनारी नदीला म्हणावे
तुझे पूर माझ्या नसांतून यावे.
उत्तर:

वृत्त: हे भुजंगप्रयात वृत्त आहे.
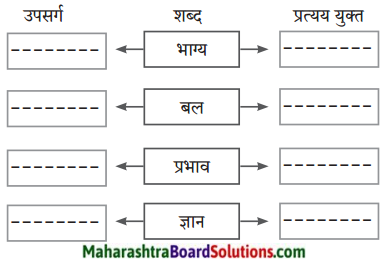
४. शब्दसिद्धी:
(१) ‘भर’ हा प्रत्यय असलेले चार शब्द लिहा:
जसे → रात्र + भर = रात्रभर
उत्तर:
(i) दिवसभर
(ii) ओंजळभर
(ii) हातभर।
(iv) बोटभर।
(२) ‘अप’ हा उपसर्ग असलेले चार शब्द लिहा:
जसे → अप + शकुन = अपशकुन
उत्तर:
(i) अपमान
(ii) अपयश।
(iii) अपशब्द
(iv) अपराध
(३) ‘कडकडाट’सारखे चार अभ्यस्त शब्द लिहा:
उत्तर:
(i) गडगडाट
(ii) फडफडाट
(ii) धडधडाट
(iv) खणखणाट
५. सामान्यरूप:
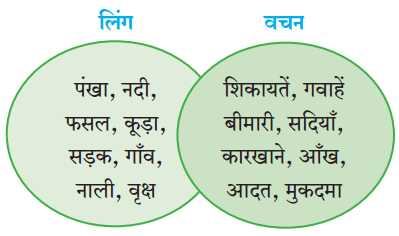
तक्ता पूर्ण करा:
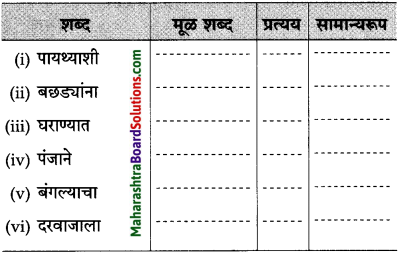
उत्तर:
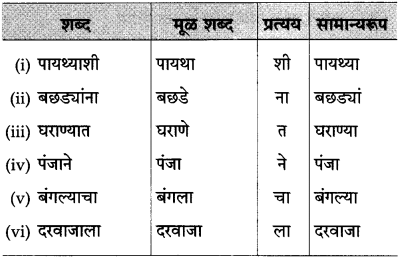
![]()
(२) तक्ता पूर्ण करा: (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-३)
उत्तर:
भाषिक घटकांवर आधारित
कृती: ३१. शब्दसंपत्ती:
(१) गटात न बसणारा शब्द लिहा:
(i) वाघीण, सिंहीण, घोडी, लांडोर, सांडणी.
(ii) पशू, पक्षी, श्वापद, जनावर, प्राणी.
(iii) चंदेरी, रुपेरी, सोनेरी, माधुरी, पांढरी.
(iv) पहिला, दुसरा, तिसरा, चौथा, सहावा.
उत्तर:
(i) लांडोर
(ii) पक्षी
(iii) माधुरी
(iv) सहावा.
(२) पुढील शब्दांतील अक्षरांपासून चार अर्थपूर्ण शब्द लिहा:
(i) सोनालीवरची→ सोनाली नाव। वरची
(ii) दरवाजा → दर रवा रजा वाद
(३) पुढील शब्दसमूहाबद्दल एक शब्द लिहा:
(सराव कृतिपत्रिका-३)
(6) दिशा दाखवणारा –
(ii) वाहन चालवणारा।
उत्तर:
(i) दिशादर्शक
(ii) चालक
(४) विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिहा:
(i) उठलो x ………………………………
(ii) भूतकाळ x ………………………………
(iii) वर्णनीय x ………………………………
(iv) रात्री x ………………………………
उत्तर:
(i) उठलो x बसलो
(ii) भूतकाळ x वर्तमानकाळ
(iii) वर्णनीय x अवर्णनीय
(iv) रात्री x दिवसा.
![]()
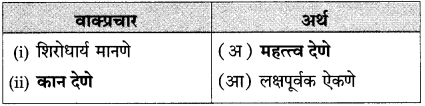
(५) सहसंबध ओळखा: (मार्च ‘१९)
(i) गुण x दोष: जहाल x
(ii) प्रत्यक्ष x: आदर x अनादर.
उत्तर:
(i) गुण x दोष: जहाल x मवाळ
(ii) प्रत्यक्ष x अप्रत्यक्ष: आदर x अनादर.
२. लेखननियम:
(१) अचूक शब्द निवडून लिहा:
(i) हुबेहुब / हूबेहूब / हुबेहूब / हूबेहुब,
(ii) समिक्षा/समीक्षा/सममीक्षा / समिक्शा.
(iii) निर्मिती / नीर्मिती / निमिर्ती / निर्मीती.
(iv) स्तीमित /स्तिमीत /स्तीमीत /स्तिमित.
(v) पारंपारिक / पारंपारीक / पारंपरिक / पारंपरीक,
उत्तर:
(i) हुबेहूब
(ii) समीक्षा
(iii) निर्मिती
(iv) स्तिमित
(v) पारंपरिक
(२) पुढील वाक्ये लेखननियमांनुसार लिहा:
(i) एकदा त्यांना वीचित्र अनूभव आला.
(ii) असं करुन त्यांचा वीश्वास वाढला.
(iii) याच गच्चिवर दोघि पहील्या पावसाल्यात नाचल्या.
(iv) नूसतं सकशिसारखं वन्य पशुनां ट्रेनिंग देणे हा हेतु नव्हता.
(v) आणी त्याच क्षणी नवे विचार, नव्या कल्पना माझ्या मनात कारंज्याच्या तूषाराप्रमाणे उडू लागतात. (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-३)
उत्तर:
(i) एकदा त्यांना विचित्र अनुभव आला.
(ii) असं करून त्यांचा विश्वास वाढला.
(iii) याच गच्चीवर दोधी पहिल्या पावसाळ्यात नाचल्या.
(iv) नुसतं सर्कशीसारखं वन्य पशुंना ट्रेनिंग देणं हा हेतू नव्हता.
(v) आणि त्याच क्षणी नवे विचार नव्या कल्पना माझ्या मनात कारंज्याच्या तुषाराप्रमाणे उडू लागतात.
३. विरामचिन्हे:
पुढील वाक्यांतील चुकीची विरामचिन्हे ओळखून योग्य विरामचिन्हे घाला व वाक्ये पुन्हा लिहा:
(i) दोन वर्षांचे झाले. की वाघ; सिंह पूर्ण ताकदीचे होतात!
(ii) ते म्हणाले; सोना. थांब मी डबा आणतो?
उत्तर:
(i) दोन वर्षांचे झाले, की वाघ-सिंह पूर्ण ताकदीचे होतात.
(ii) ते म्हणाले, “सोना, थांब मी डबा आणतो.”
![]()
४. पारिभाषिक शब्द:
पुढील पारिभाषिक शब्दांना मराठी प्रतिशब्द दया:
(i) Agent – ………………………………
(ii) Calligraphy – ………………………………
(iii) Comedy – ………………………………
(iv) Census – ………………………………
(v) Orientation – ………………………………
*(vi) Fellowship – ………………………………
* (vii) Goodwill – ………………………………
(viii) Index – ……………………………… (मार्च ‘१९)
(ix) Valuation – ………………………………
(x) Threapy – ……………………………… (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-२)
उत्तर:
(i) Agent – प्रतिनिधी
(ii) Calligraphy – सुलेखन
(iii) Comedy – सुखात्मिका
(iv) Census – जनगणना
(v) Orientation – उद्बोधन / निदेशन
(vi) Fellowship – अभिछात्रवृत्ती
(vii) Goodwill – सदिच्छा
(viii) Index – अनुक्रमणिका.
(ix) Valuation – मूल्यमापन
(x) Therapy – उपचारपद्धती.
५. अकारविल्हे/भाषिक खेळ:
(१) पुढील शब्द अकारविल्हेनुसार लावा:
(i) मांजर → पिल्लू → कुत्रा → छावा.
(ii) हात → पाय → नाक → डोळे.
उत्तर:
(i) कुत्रा → छावा → पिल्लू → मांजर.
(ii) डोळे → नाक → पाय → हात.
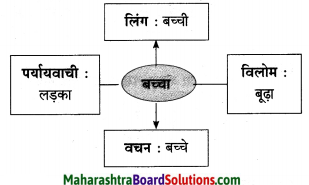
(२) कृती करा:
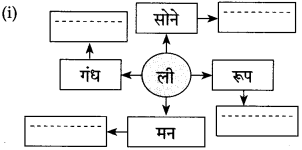
उत्तर:
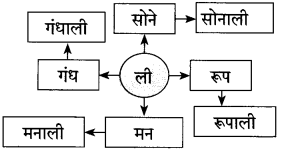
![]()
(ii) जसे: वाघाची – डरकाळी; तसे –
(१) सिंहाची – ………………………………
(२) कुत्र्याचे – ………………………………
(३) गाईचे – ………………………………
(४) हत्तीचा – ………………………………
उत्तर:
(१) सिंहाची – गर्जना
(२) कुत्र्यांचे – भुंकणे
(३) गाईचे – हंबरणे
(४) हत्तीचा – चीत्कार.
Marathi Kumarbharti Std 10 Guide
- आकाशी झेप घे रे Class 10 Marathi Textbook Solutions
- सोनाली Class 10 Marathi Textbook Solutions
- निर्णय Class 10 Marathi Textbook Solutions
- तू झालास मूक समाजाचा नायक Class 10 Marathi Textbook Solutions
- सर्व विश्वचि व्हावे सुखी Class 10 Marathi Textbook Solutions
- व्युत्पत्ती कोश Class 10 Marathi Textbook Solutions