Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Maths Solutions covers the Std 6 Maths Chapter 17 Geometrical Constructions Class 6 Practice Set 39 Answers Solutions.
6th Standard Maths Practice Set 39 Answers Chapter 17 Geometrical Constructions
Question 1.
Draw line l. Take any point P on the line. Using a set square, draw a line perpendicular to line l at the point P.
Solution:
Step 1:

Step 2:
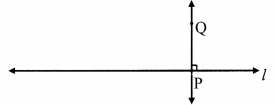
line PQ ⊥ line l
Question 2.
Draw a line AB. Using a compass, draw a line perpendicular to AB at point B.
Solution:
Step 1:
![]()
Step 2:
![]()
Step 3:
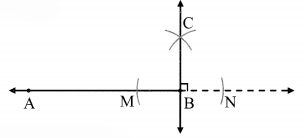
line BC ⊥ line AB.
Question 3.
Draw line CD. Take any point M on the line. Using a protractor, draw a line perpendicular to line CD at the point M.
Solution:
Step 1:
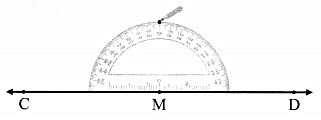
Step 2:
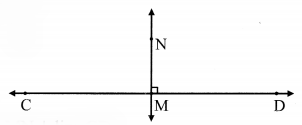
line MN ⊥ line CD
Maharashtra Board Class 6 Maths Chapter 17 Geometrical Constructions Practice Set 39 Questions and Activities
Question 1.
When constructing a building, what is the method used to make sure that a wall is exactly upright? What does the mason in the picture have in his hand? What do you think is his purpose for using it? (Textbook pg. no. 87)
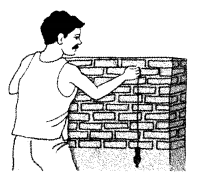
Solution:
When constructing a building, a weight (usually with a pointed tip at the bottom) suspended from a string called as plummet or plump bob is aligned from the top of the wall to make sure that the wall is built exactly upright.
The mason in the picture is holding a plumb bob.
The string of the plumb bob is suspended from the top of the wall, such that plumb bob hangs freely. By observing whether the vertical wall is parallel to the string we can check if the constructed wall is vertical.
Question 2.
Have you looked at lamp posts on the roadside? How do they stand? (Textbook pg. no. 87)
Solution:
The lamp posts on the road side are standing erect or vertical.
Question 3.
For the above explained construction, why must we take a distance greater than half of the length of AB? What will happen if we take a smaller distance? (Textbook pg. no. 88)
Solution:
For the above construction, in step-3 we take distance greater than half of the length of AB, so that the arcs drawn by keeping the compass on points A and B intersect each other at point Q.
If the distance in compass is less than half of the length of AB, then the arcs drawn by keeping the compass at A and B will not intersect each other.