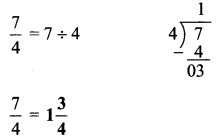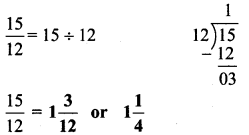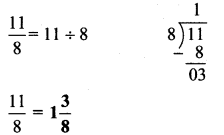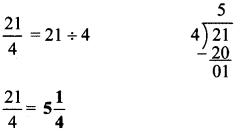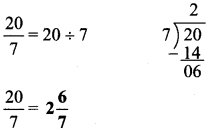Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 5 (अ) आओ, आयु बताना सीखो, (ब) महाराष्ट्र की बेटी Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Hindi Solutions Chapter 5 (अ) आओ, आयु बताना सीखो, (ब) महाराष्ट्र की बेटी
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 6 Solutions Chapter 5 (अ) आओ, आयु बताना सीखो, (ब) महाराष्ट्र की बेटी Textbook Questions and Answers
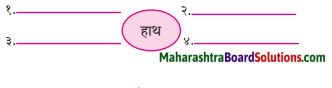
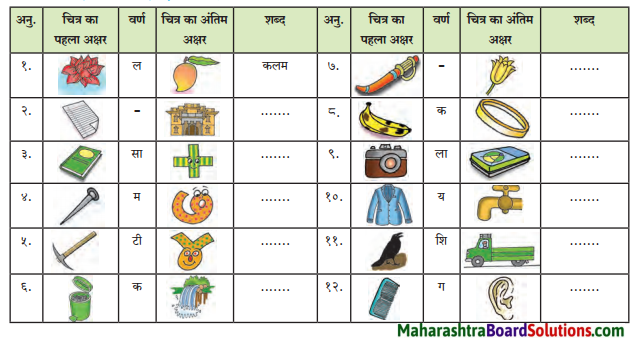
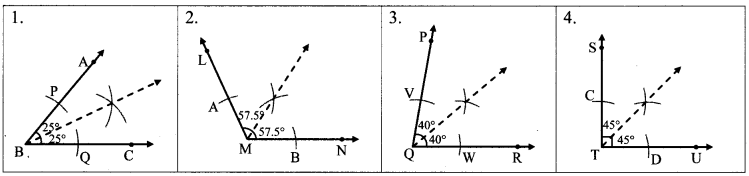
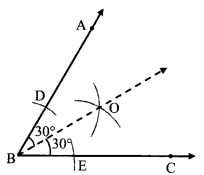
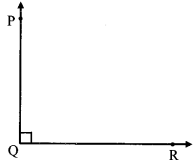
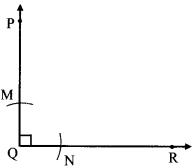
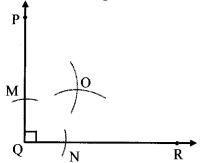
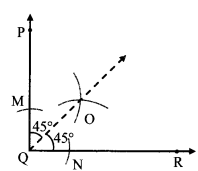
अंतर बताओ:
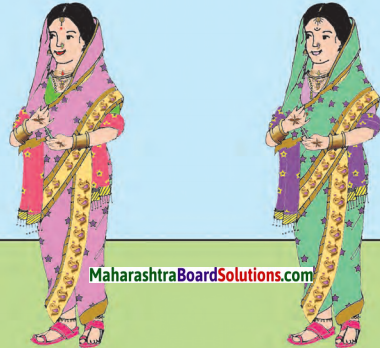
![]()
Answer:
१. माँगटीके की बनावट अलग है।
२. शॉल का रंग अलग है।
३. बिंदिया का आकार अलग है।
४. हार के लोलक का रंग अलग है।
५. हाथ पर लगी मेंहदी की बनावट अलग है।
६. साड़ी के किनारे पर से चित्र गायब है।
७. चोली का रंग अलग है।
८. होंठ लाल है।
९. साड़ी का रंग अलग है।
१०. ठुड्डी पर तिल है।