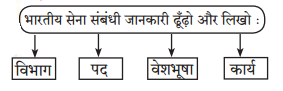
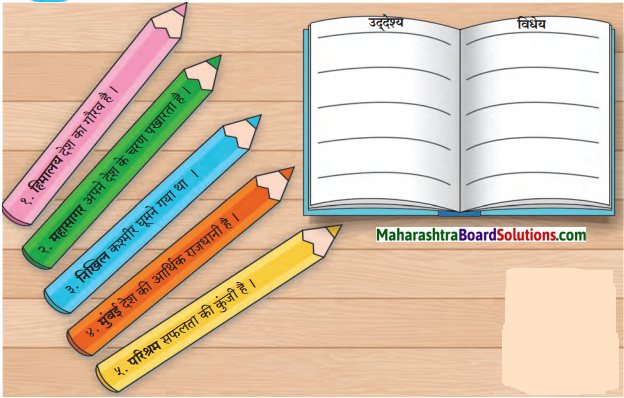
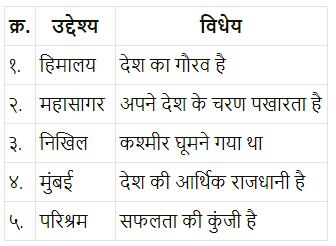
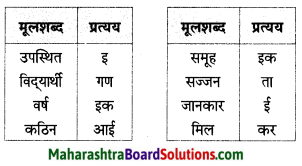
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 5 बसंत गीत Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Hindi Solutions Chapter 5 बसंत गीत
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions Chapter 5 बसंत गीत Additional Important Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक शब्द में लिखिए।
Question 1.
कौन सजकर आया है?
Answer:
वसंत ऋतु
Question 2.
मकरंद किसने चुराया?
Answer:
मधुप ने
Question 3.
कलि-कलि पर कलोल कौन कर रहा है?
Answer:
कुसुम
Question 4.
कोयल क्या गाती है?
Answer:
गीत
Question 5.
बौर किस पर लगा है?
Answer:
आम पर
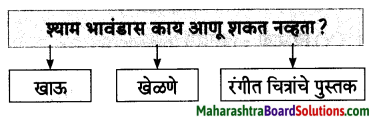
![]()
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक वाक्य में लिखिए।
Question 1.
वसंत ऋतु में मोर क्या कर रहा है?
Answer:
वसंत ऋतु में मोर ठुमक-ठुमककर नाच रहा है।
Question 2.
सरसों कैसी फूली हैं?
Answer:
सरसों पीली-पीली फूली हैं।
Question 3.
बिछौने के ऊपर अमित रंग कौन बरसाती है?
Answer:
बिछौने के ऊपर अमित रंग हरी-हरी मटर बरसाती है।
Question 4.
वसंत ऋतु में सुगंध कहाँ-कहाँ फैल रही है?
Answer:
वसंत ऋतु में वन-बाग और बगीचों में सुगंध फैल रही है।
![]()
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से सही शब्द चुनकर रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए।
(कोयलिया, ऋतु, कलि-कलि, मधुप गन, अमवा)
Question 1.
अजी गाओ रे ………. बसंत सजि आयो।
Answer:
ऋतु
Question 2.
……………’ करत कलोल कुसुम मन।
Answer:
कलि-कलि
Question 3.
गुन-गुन-गुन गुन गूंजे ………
Answer:
मधुप गन
Question 4.
गीत ………… गायो।
Answer:
कोयलिया
Question 5.
अरु बौर ……… पे छायो।
Answer:
अमवा
![]()
व्याकरण और भाषाभ्यास
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के तीन पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए।
- कुसुम
- मधुप
- सुगंध
- वन
- वसंत ऋतु
Answer:
- फूल, पुष्प, सुमन
- भ्रमर, भौंरा, मधुकर
- खुशबू, महक, सुवास
- कानन, अरण्य, जंगल
- ऋतुराज, मधुमास, मधुऋतु
उचित विशेषण-विशेष्य की जोड़ियाँ मिलाइए।

Answer:
१ – ख
२ – ग
३ – घ
४ – क
![]()
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के समान तुकवाले (लयात्मक) शब्द कविता के आधार पर लिखिए।
- मुस्कायो
- उड़ायो
- छायो
- आयो
Answer:
- चुरायो
- गायो
- बरसायो
- आयो
लेखन विभाग
वसंत ऋतु में प्रकृति में क्या-क्या परिवर्तन होते हैं? कविता के आधार पर लिखिए।
Answer:
वसंत ऋतु के आने पर प्रकृति पूरी तरह से सज गई है। कवि सबसे इस सौंदर्य का गान गाने के लिए कह रहे हैं। प्रत्येक कलि कल्लोल कर रही है और उन्हें देख फूल मुस्कुराने लगे हैं। भौरों का समूह गुन-गुन का गुंजार कर रहे हैं और फूलों से मधुर मकरंद चुरा रहे हैं। वन, बाग और बगीचे में चारों तरफ खुशबू फैल रही है। मोर ठुमकठुमककर नाच रहे हैं और कोयल गीत गा रही है। पीलीपीली सरसों में फूल खिल चुके हैं और आमों पर बौर छा गए हैं। हरी-हरी मटर असीमित रंग बरसा रही हैं। वसंत में प्रकृति सज गई है सभी मिलकर वसंत गीत गा रहे हैं।
![]()
आकारिक मूल्यमापन
- मौसम के अनुसार होनेवाले परिवर्तन पर चर्चा कीजिए।
- बसंत ऋतु से संबंधित अन्य कोई कविता सुनिए।
वर्षा ऋतु
शीत ऋतु
ग्रीष्म ऋतु - तीनों ऋतु में हम कौन-से कपड़े पहनते हैं? चार्ट बनाओ।