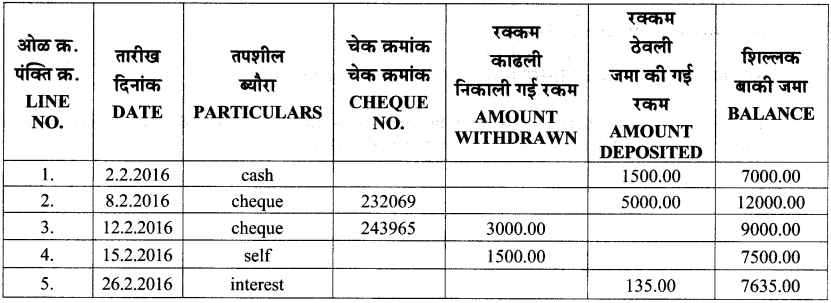
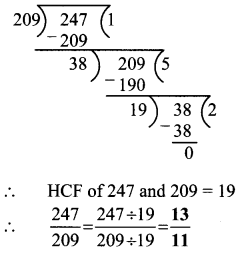
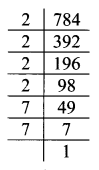
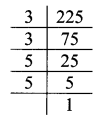
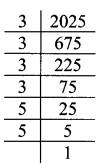
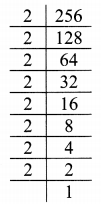
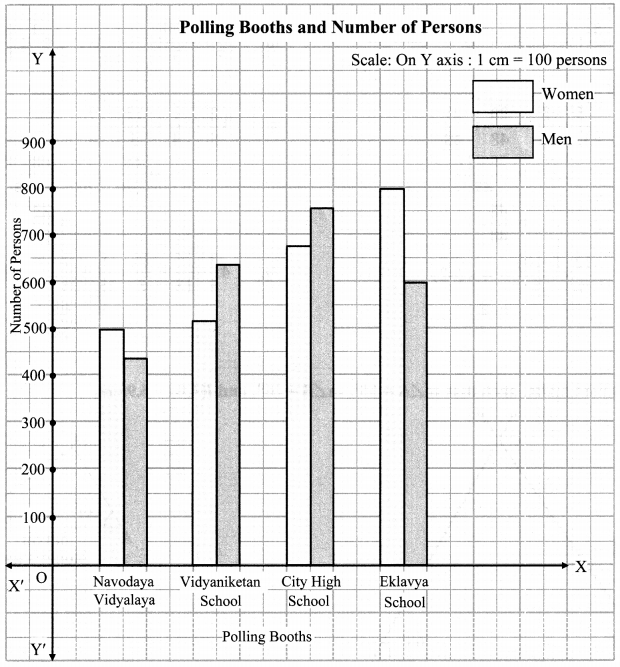
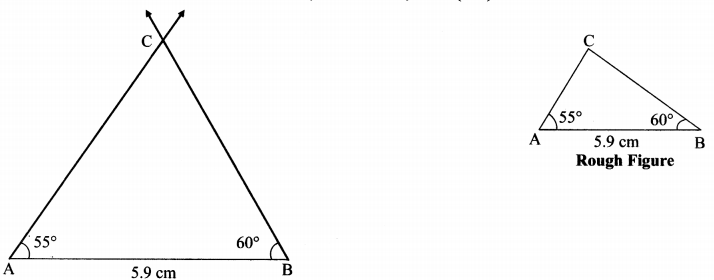
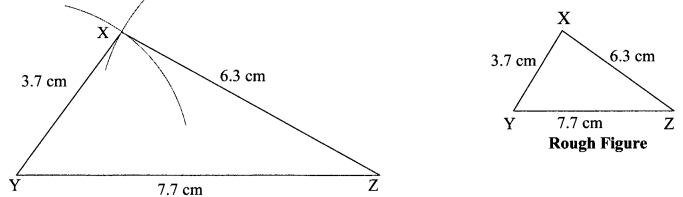
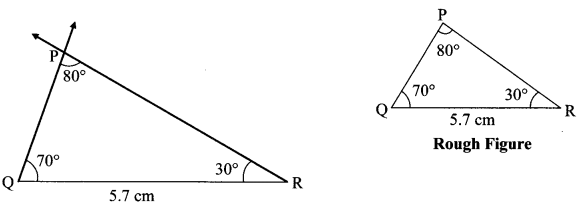
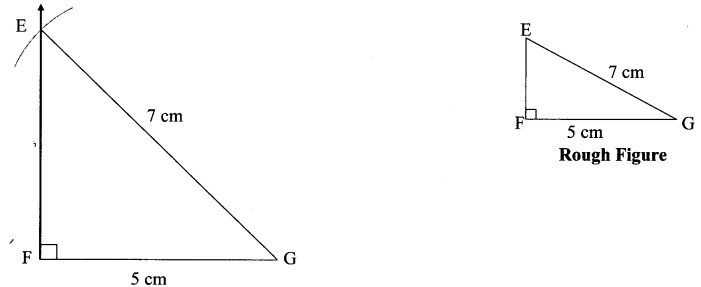
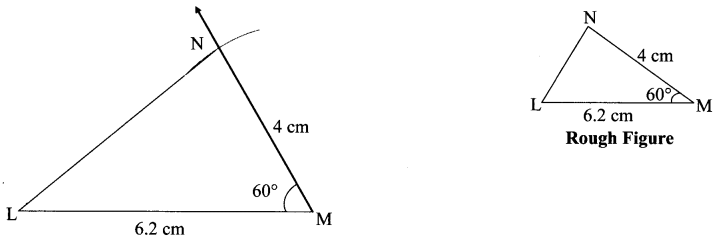
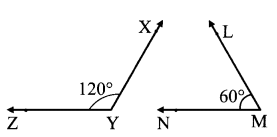
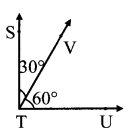
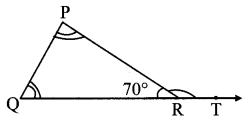
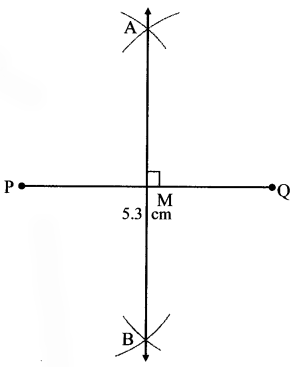
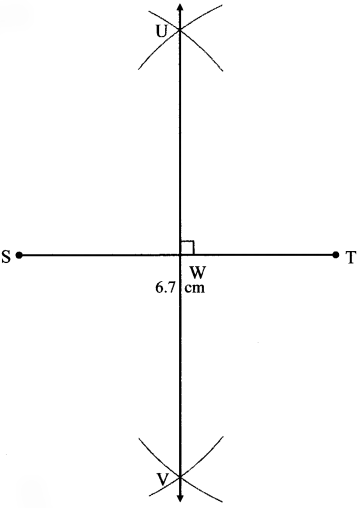
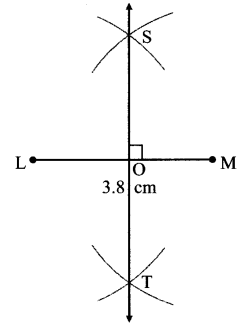
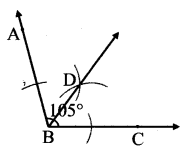
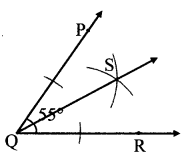
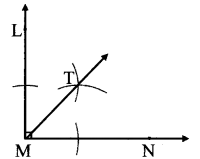
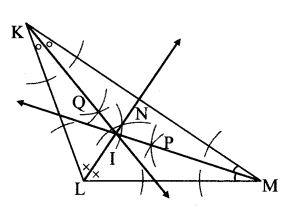
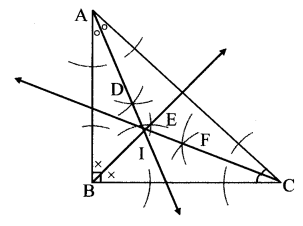
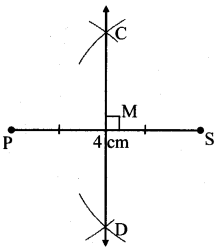
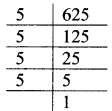
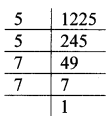
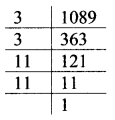
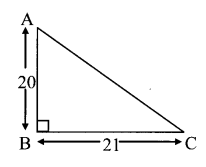
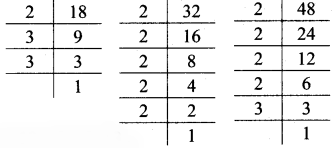
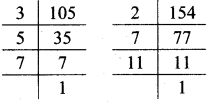
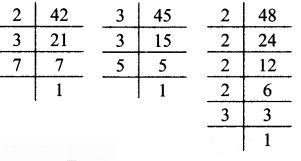
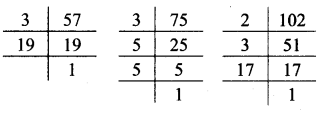
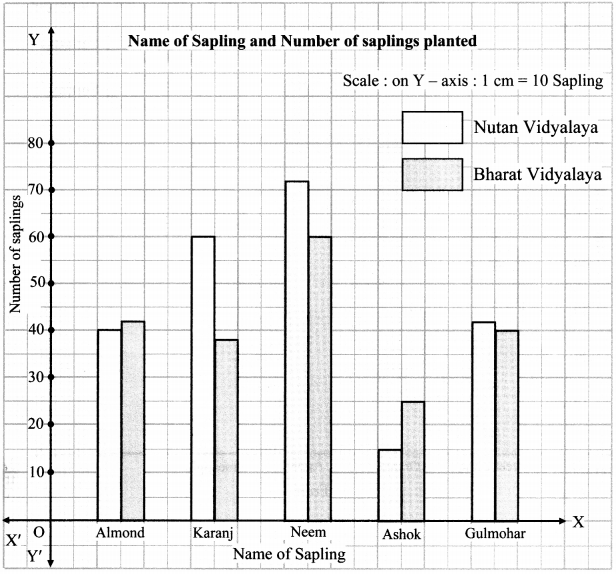
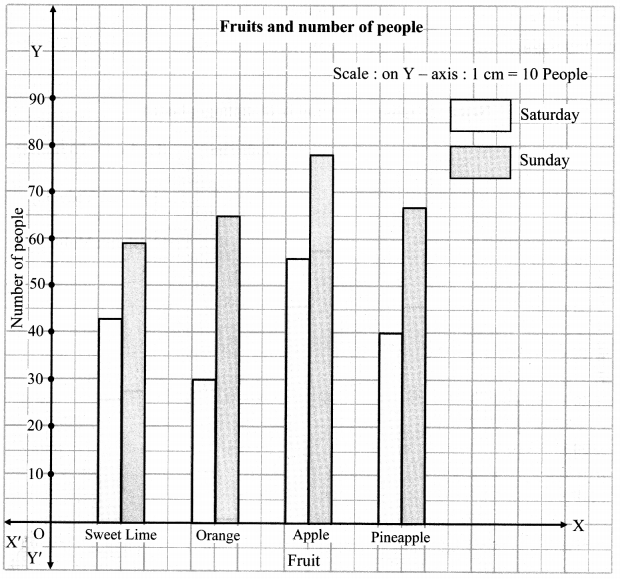
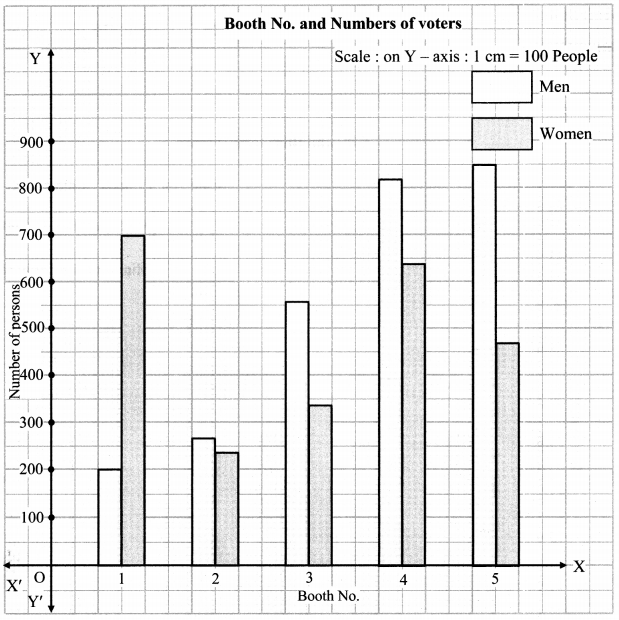
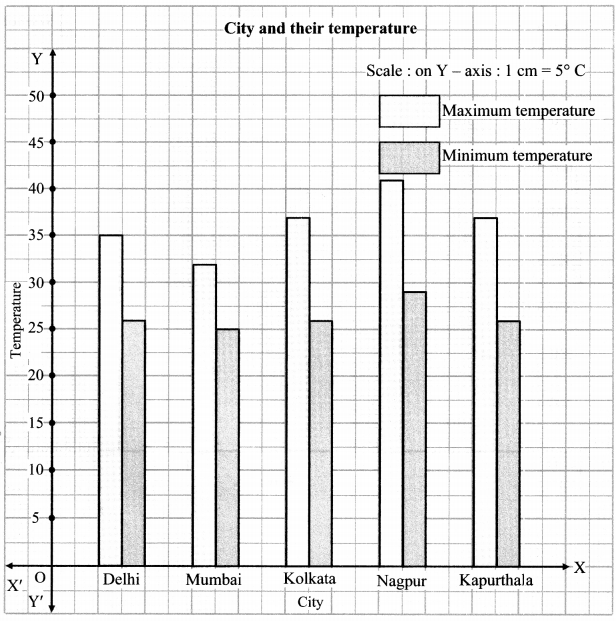
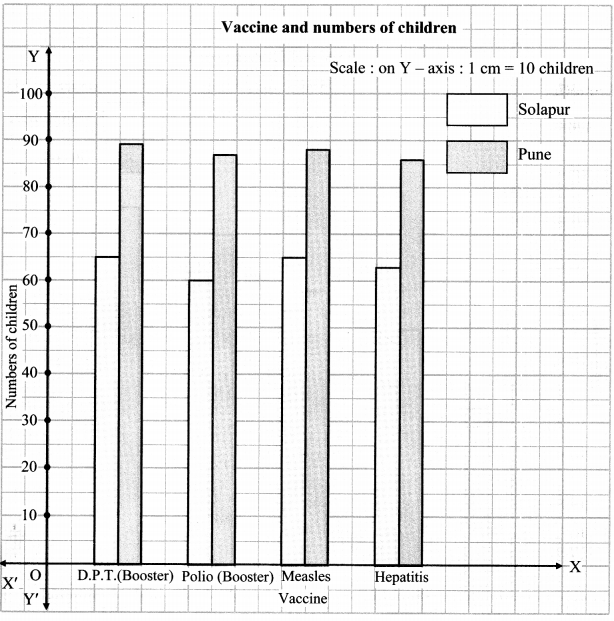
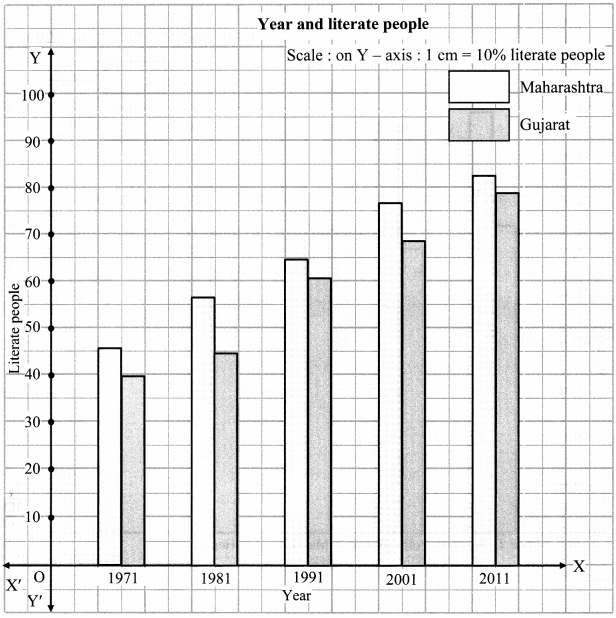
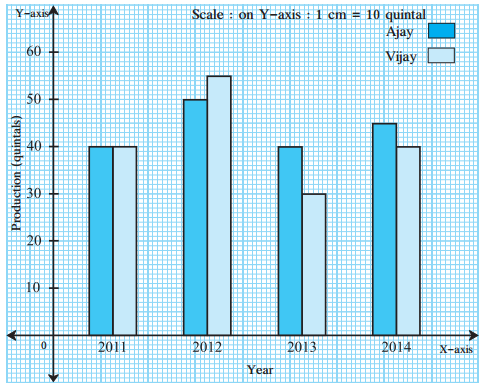
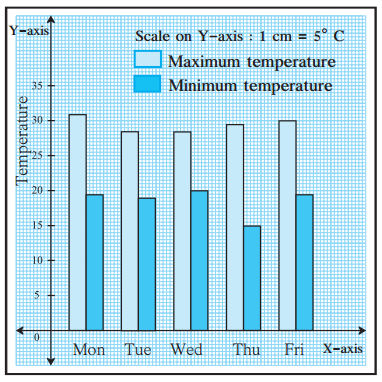
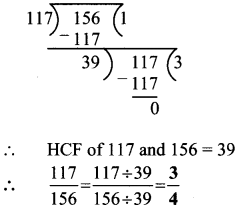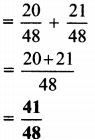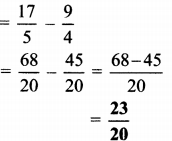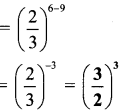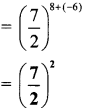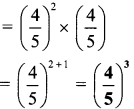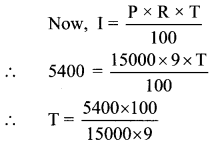Balbharati Maharashtra State Board 7th Std Textbook Solutions Answers Digest
- Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions
- Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Science Solutions
- Maharashtra State Board Class 7 History Solutions
- Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Civics Solutions
- Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Geography Solutions
- Maharashtra State Board Class 7 English Solutions
- Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Hindi Solutions
- Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Marathi Solutions