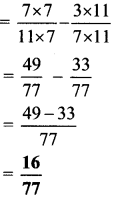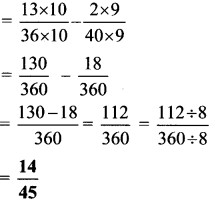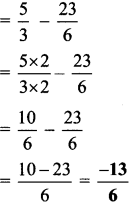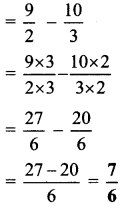Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions covers the 7th Std Maths Practice Set 18 Answers Solutions Chapter 4 Angles and Pairs of Angles.
Angles and Pairs of Angles Class 7 Practice Set 18 Answers Solutions Chapter 4
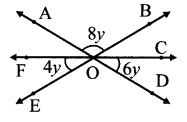
Question 1.
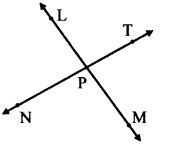
Name the pairs of opposite rays in the figure alongside.
Solution:
- Ray PL and ray PM
- Ray PN and ray PT
Question 2.
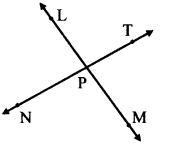
Are the ray PM and PT opposite rays? Give reasons for your answer.
Solution:
No.
Ray PM and Ray PT do not form a straight line and hence are not opposite rays.
Maharashtra Board Class 7 Maths Chapter 4 Angles and Pairs of Angles Practice Set 18 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
Observe the adjacent figure and answer the following questions. (Textbook pg. no. 28)
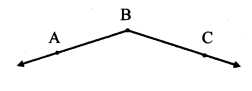
- Name the rays in the figure alongside.
- Name the origin of the rays
- Name the angle in the given figure
Solution:
- Ray BA and ray BC
- Point B
- ∠ABC or ∠CBA
Question 2.
Observe the adjacent figure and answer the following questions. (Textbook pg. no. 28)
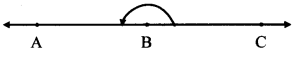
- Name the angle in the figure alongside.
- Name the rays whose origin is point B
Solution:
- ∠ABC or ∠CBA
- Ray BA and ray BC
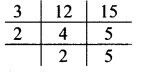
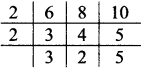


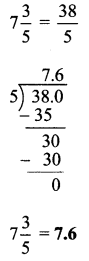

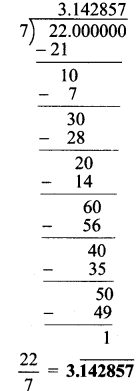

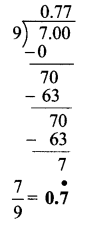
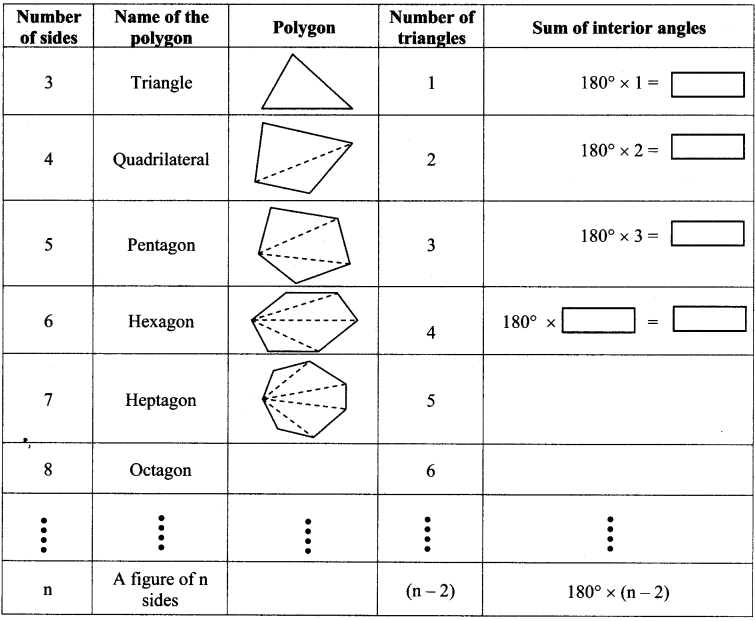
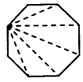 , 180° x 6 = 1080°
, 180° x 6 = 1080°