Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Geography Solutions Chapter 11 Contour Maps and Landforms Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Geography Solutions Chapter 11 Contour Maps and Landforms
Class 7 Geography Chapter 11 Contour Maps and Landforms Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
How can the distribution of the height and landform in a region be shown?
Answer:
(i) While studying different landforms on the surface of the earth, one has to consider various facets of landforms like altitude, relief, slope, direction of slope and the drainage.
(ii) For this maps prepared using mathematical survey methods are used.
(iii) These maps help us to understand the above characteristics of the landforms.
Question 2.
To whom are contour maps useful?
Answer:
(i) Contour maps are useful to mountaineers, trekkers, soldiers, defence officers.
(ii) The nature of the ground and its shape can be estimated .
(iii) Defence officers use contour maps for strategic planning.
(iv) It is possible to identify suitable site for any project from the contour map of the region.
Question 3.
What do you understand by observing contour lines?
Answer:
(i) Contour lines are isolines of height.
(ii) These are drawn by joining the places of equal altitude.
(iii) These help in identification of land forms and their altitude from sea level.
(iv) These lines also help us to understand the nature and direction of the slope.
![]()
Question 4.
How will a contour map be useful to a fanner?
Answer:
(i) It is helpful selecting the type of farming to be practiced plantation farming in hilly regions, intensive farming in low lying region.
(ii) In order to reduce the erosion of soil, trenches are dug out in the direction perpendicular to the slope of the land.
(iii) Trees are planted along such trenches. When the farmer digs out such trenches, he will be careful in maintaining the level.
2. Fill the blanks with appropriate words:
Question 1.
If the contour lines are closer to each other, the slope is ______.
Answer:
steep
Question 2.
The contour lines on the map represent ______.
Answer:
places of same altitude
Question 3.
The slope can be understood from the distance between the ______.
Answer:
contour lines
![]()
Question 4.
If the distance between two contour lines is more then the ______ is gentle.
Answer:
slope
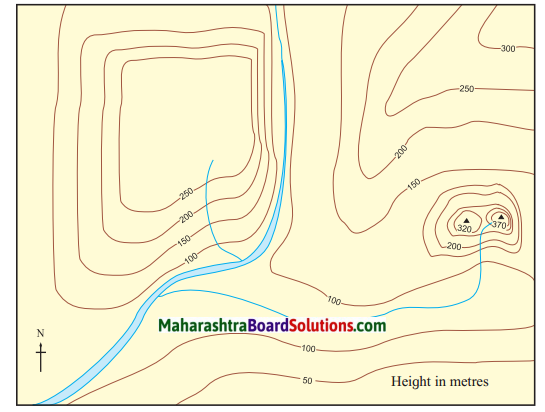
3. Identify the landforms in the following map:
Class 7 Geography Chapter 11 Contour Maps and Landforms InText Questions and Answers
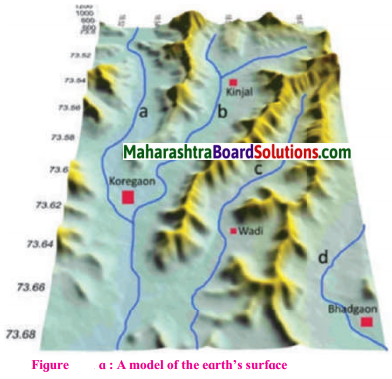
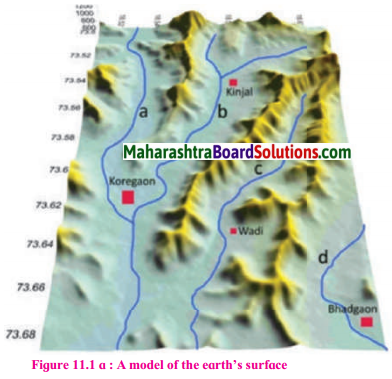
A model of the relief in an area is shown in fig. Observe it carefully and answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Which landforms do you seen in the model?
Answer:
Mountains & river valleys are seen in the model.
![]()
Question 2.
Which colours have been used on them?
Answer:
Yellow & blue colours have been used in the model.
Model of the Earth’s surface:
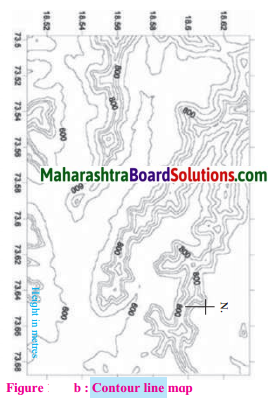
Question 1.
What all you seen in the map?
Answer:
We can see many contour lines on the map showing a hilly region. We can see the altitude of the hill ranges as well as its slope.
Question 2.
What is the general direction of the ranges shown in the map?
Answer:
The general direction of the ranges shown in the map is east-west
Question 3.
Towards which direction is the flat land located in the map?
Answer:
The flat land is located towards the east.
Question 4.
What are the maximum and minimum values of the lines in the map?
Answer:
The maximum value of the lines in the map is 800 & minimum value is 600.
Question 5.
What do these values indicate?
Answer:
These lines indicate the altitude of the region from the sea level.
Question 6.
Do you find any similarities in the map and the model in fig. (a)? What are those?
Answer:
The model in figure (a) & the contour line map in figure (b) are of the same region. The values of latitudes & longitudes are same on both the maps.
![]()
Question 7.
Which figure give us more information and what is that information?
Answer:
Fig. (b) Contour line map gives more information. It gives us information about the altitude of the landforms slope of the land forms with latitudes & longitudes
Question 8.
Is there any similarity between this map and the sketch map of the potato hill?
Answer:
Yes, similar to the sketch map of the potato hill,
the contour line map too is a 3D figure (Model of earth’s surface) which has been converted into a 2D map. The Contour line map is depicting contour line intervals.
Consider you have gone for mountaineering. You have to conquer a peak on the hill “A”. A map of this hill is given below. Studying the contour lines in the map, find the side from which you will reach the peak safely and easily. Mark your path on the map with a pencil.
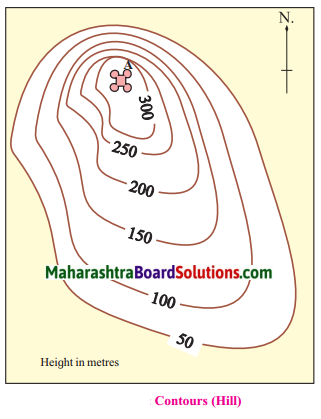
Answer:
I will climb from eastwards to reach the peak safely as the slope eastwards is gentle and not steep. Lesser distance between the contour lines, indicates steep slope. The distance between the lines is greater eastwards, which shows the slope is more gentle on that side.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 11 Contour Maps and Landforms Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Contour lines join places with the same on a map.
Answer:
altitude
Question 2.
Generally, contour lines do not _______ each other.
Answer:
cross.
![]()
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
How are contour maps helpful to us?
Answer:
(i) Contour maps help us to understand various facets of landforms, like altitude, relief, slope, direction of slope and the drainage.
(ii) These maps are of immense use to mountaineers, trekkers, soldiers, defence officers, etc.
(iii) These maps prove to be of great use in planning of a region.
Question 2.
Contour lines generally do not cross each other. Give reason.
Answer:
(i) Contour lines join places with the same altitude on a map.
(ii) Therefore they generally do not cross each other.
Observe the model and the map given below and answer the following questions:
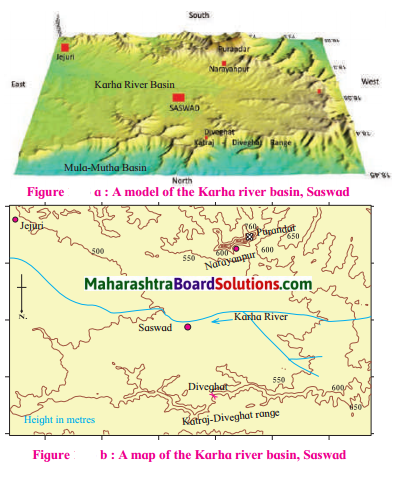
A 3D model is given in fig. (a) The northern part of the model shows the basin of the rivers Mula-Mutha. To its south is the Katraj. Diveghat range extending from the west to the east. Beyond that some portion of Karha basin is seen.
Question 1.
In which direction does fort Purandar lie?
Answer:
Fort Purandar lies in the south direction.
Question 2.
What is the direction of flow of the river Karha?
Answer:
River Karha flows from west to east.
![]()
Question 3.
In which parts are the hill ranges not observed?
Answer:
The hill ranges are not observed in the eastern parts.
Question 4.
Which part of the model is not seen in the map? Why?
Answer:
The Karha river & the direction of its flow, the contour height and the slope of the land are part of map & not seen in the model.
Question 5.
In which direction does the altitude of Katraj- Diveghat range decrease?
Answer:
The altitude of katraj-Diveghat range decreases from west to east.
Question 6.
In which direction are higher hill ranges located?
Answer:
Higher hill ranges are located in the southern direction.
Use your brain!
When one sees a landform on a contour map, what is the observer’s position with respect to landform? For example, a hill is shown with the help of contours on a map. From where do you think you are looking at it?
Answer:
Aerial view. From somewhere above, may be from an aeroplane or helicopter.
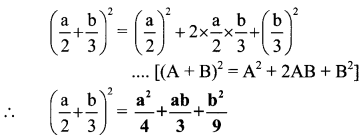
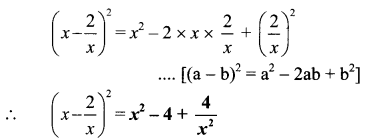
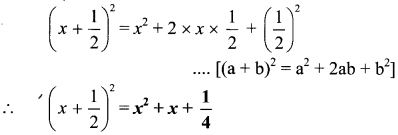
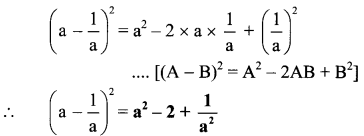


 Answer:
Answer: