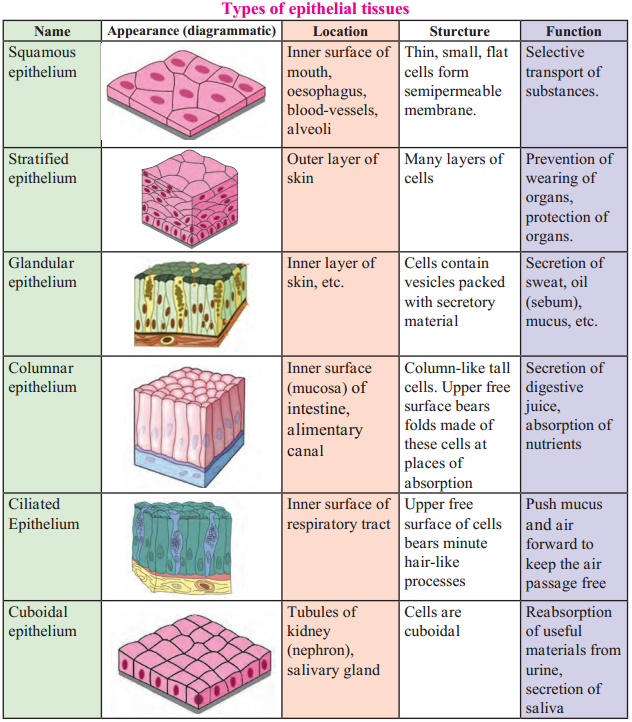
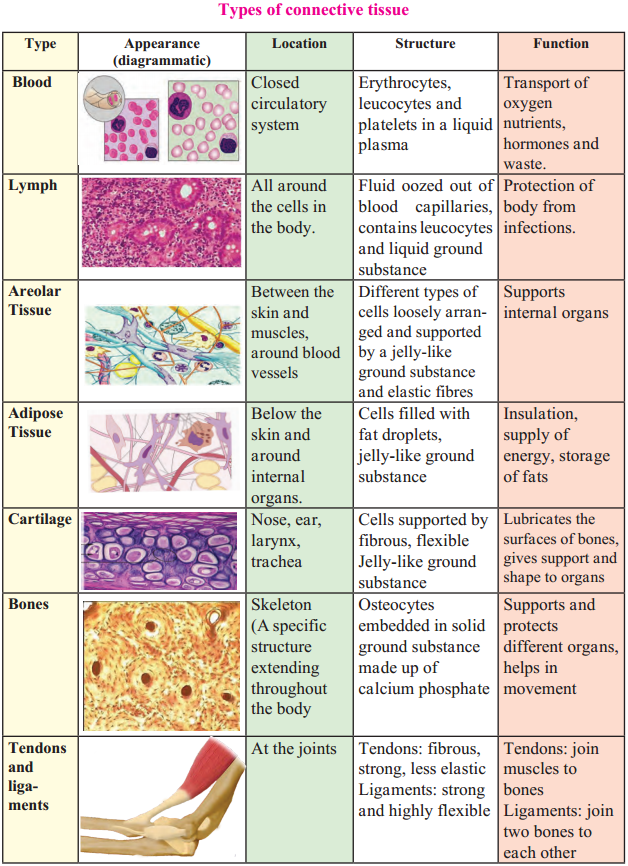
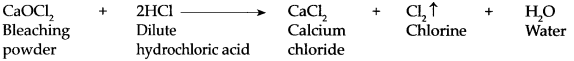
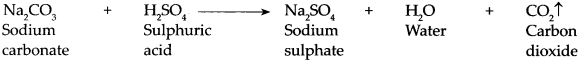
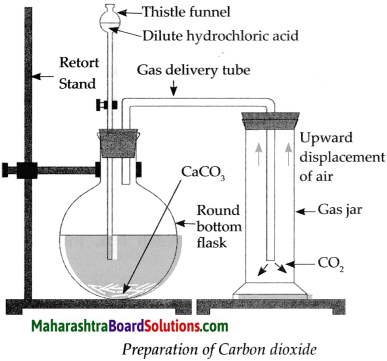
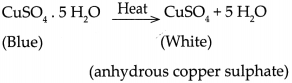
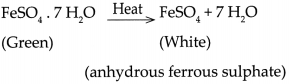
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Properties of Sea Water Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Properties of Sea Water
Class 9 Geography Chapter 6 Properties of Sea Water Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Tick the correct box according to the salinity of the ocean water ✓

Answer:
(a) Low
(b) Low
(c) High
(d) High
(e) Low
(f) High.
![]()
2. Give reasons.
(a) Salinity is low in the land-locked Baltic Sea.
Answer:
- The Baltic Sea lies in the temperate region.
- In temperate regions, the sunrays are slanting and therefore, the temperatures are lower.
- The supply of fresh water is also more, as numerous rivers empty their waters into the Baltic sea.
- Therefore, in spite of being landlocked, due to low rate of evaporation and ample supply of fresh water, the salinity of the Baltic Sea is low.
(b) There is higher salinity in the northern Red Sea while lower in the southern.
Answer:
- The Red Sea is one of the saltiest bodies of water in the world, owing to high evaporation.
- The salinity is 36%o in the southern part because of the effect of the Gulf of Aden.
- It reaches 41 %o in the northern part, owing mainly to the Gulf of Suez and the high evaporation as well as very little precipitation.
- Hence, there is more salinity in the northern Red Sea while lesser in the south.
(c) Oceans located at the same latitude do not have same salinity.
Answer:
- The salinity of the oceans depends on factors like rate of evaporation and supply of fresh water.
- In Oceans where rate of evaporation is more than the supply of fresh water, the salinity is higher.
- In Oceans where supply of freshwater exceeds the rate of evaporation, salinity is low.
- Salinity is not affected much in areas where supply of freshwater and the evaporation of water is low.
- Thus, oceans located on the same latitude do not have the same salinity.
(d) With increasing depth, the temperature of sea water decreases to a certain limit.
Answer:
With increasing depth, the temperature of sea water decreases to a certain limit because –
- While most of the sunrays radiate back from the surface of the sea, some of them penetrate to certain depths in the water.
- As a result, the intensity of sunrays decreases with the increasing depth.
- The temperature decreases up to 2000m depth.
- After 2000m, the temperature of the seawater is uniform everywhere.
![]()
(e) There are more salt-pans on the Western coast of India than its eastern coast.
Answer:
- The Arabian Sea lies lying to the west and Bay of Bengal lies to the east of India.
- Many large peninsular rivers drain their waters in the Bay of Bengal and on the contrary, only small seasonal coastal rivers drain in the Arabian Sea.
- Hence, the salinity of the eastern coast is 34%, while it is 35% in the Arabian Sea.
- Thus, there are more salt-pans on the Western coast of India than its Eastern coast.
(f) Salinity increases in the mid-latitudinal zones.
Answer:
- Mid-latitudinal zones lies between 25° to 35° north and south of the equator.
- In this zone, the rainfall is less and the supply of fresh water from rivers is also low.
- This region experiences high-temperature conditions which are marked by the presence of hot deserts of the world. These high-temperature conditions lead to a high rate of evaporation.
- Thus, the salinity of the seas is found to be higher in mid-latitudinal zones.
3. Answer the following questions.
(a) What are the factors affecting the salinity of the sea water?
Answer:
- The uneven distribution of temperature on earth and uneven supply of freshwater affects the salinity of seawater.
- In the tropical zone, temperature is higher. Rate of evaporation is also higher and therefore, the salinity is higher.
- Around 5° N and S of the equator, in the equatorial calm belt, the sky is cloudy for a long period of time and convectional rainfall occurs every day.
- Large rivers like Congo and Amazon in the equatorial regions meet the sea. Therefore, supply of freshwater is abundant, too. But because of higher temperatures, rate of evaporation is more and therefore, the seas in these areas are more saline.
- In mid-latitudinal zones (25° to 35° N and S), rainfall is lesser and the supply of freshwater from rivers is also low. This zone has the hot deserts of the world. Thus, the salinity of the seas is found to be higher here.
- In temperate regions, the sunrays are slanting and therefore, the temperatures are lower. Because of the melting of the snow, the supply of water is also more, and therefore, in this zone, salinity decreases with increasing latitudes.
- In the polar areas, temperatures are very low. Evaporation is also very less in polar areas. So, salinity is low.
- Landlocked seas have higher salinity than open seas as the rate of evaporation is more. There is a lack of supply of fresh water from large rivers. Thus, there is a difference in the salinities of open and closed seas.
![]()
(b) Explain the distribution of salinity around the Tropic of Cancer and tropic of Capricorn.
Answer:
- The uneven distribution of temperature on earth, and uneven supply of freshwater affects the salinity of sea water.
- Region, between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn is called as the Tropical zone.
- In the tropical zone, temperature is higher.
- Hence, the rate of evaporation is also higher, and therefore, salinity is higher.
(c) What are the factors affecting the temperature of the sea water?
Answer:
- Temperature is a major property of the sea water.
- Sea water upto the depth of 500m is called as surface water. The surface temperature of the sea water is not uniform everywhere. This is dependent on different factors. .
- Latitudinally, the surface temperature of the seawater decreases from the equatorial areas towards the poles.
- The average temperature in equatorial areas is around 25° C, while it is about 2° C near the poles.
- Besides this, cyclones, rainfall, sea waves, ocean currents, salinity, pollution, convectional currents, and seasons also affect the surface temperature.
- Regions where cold ocean currents flow, the surface temperature of ocean water is less, while the regions where the warm currents move, the temperature increase.
(d) Explain the changes occurring in the temperature of sea water according to the depth.
Answer:
- While most of the sunrays radiate back from the surface of the sea, some of them penetrate to certain depths in the water.
- As a result, the intensity of sunrays decreases with the increasing depth.
- The temperature decreases up to 2000m depth.
- After 2000m, the temperature of the seawater is uniform everywhere.
- It is around 4°C everywhere from the equatorial regions to the polar areas.
- Temperature reduces only up to 4° C according to depth, and therefore, the water at greater depths does not freeze.
- The temperature of the seawater changes rapidly with depth at the equatorial areas. The difference in temperature is lesser in polar areas.
- There is also a difference in open seas and landlocked seas. In low latitudes, because the salinity of the landlocked seas is more, the temperature of the landlocked seas is higher than the open seas.
![]()
(e) Name the factors affecting salinity.
Answer:
Due to the sun’s heat, evaporation happens at a faster rate. Evaporated water turns into water vapour and reduces in quantity. But amount of salt remains the same in the remaining water and therefore the salinity of water increases.
- In seas where the rate of evaporation is high than the supply of fresh water, salinity is high.
- In seas where the supply of freshwater exceeds the rate of evaporation, salinity is low.
- Salinity is not affected much in seas where both the supply of freshwater and evaporation of water is low.
4. Explain how temperature affects the following.
(a) the density of sea water
Answer:
- If temperature reduces, density of water increases.
- Hence, cold water is denser than hot water.
(b) the salinity of sea water
Answer:
- If the salinity of water is high, the density of water increases.
Activity:
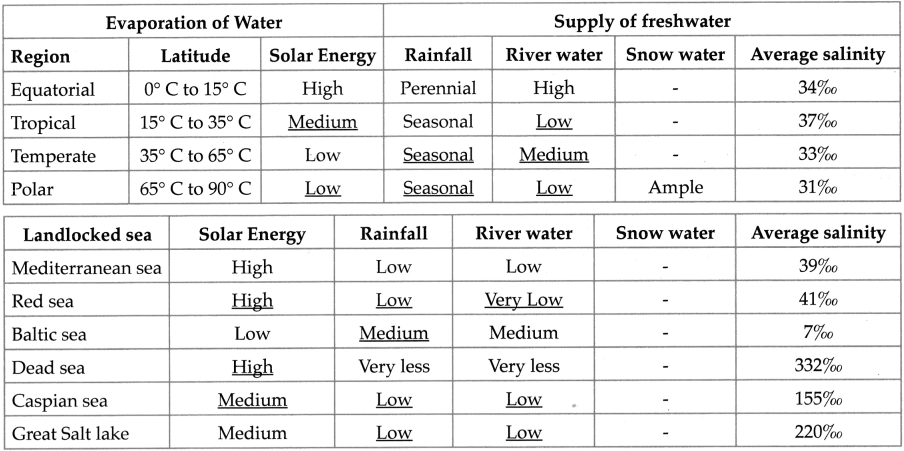
Complete the table showing the salinity of open and land-locked seas.
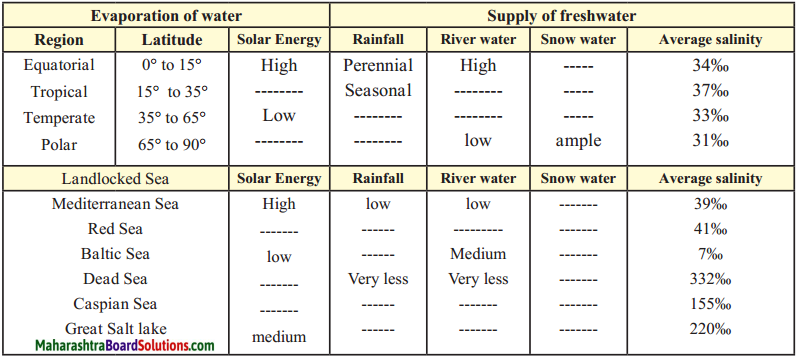
Answer:
Class 9 Geography Chapter 6 Properties of Sea Water Intext Questions and Answers
Observe the following Map and answer the questions:
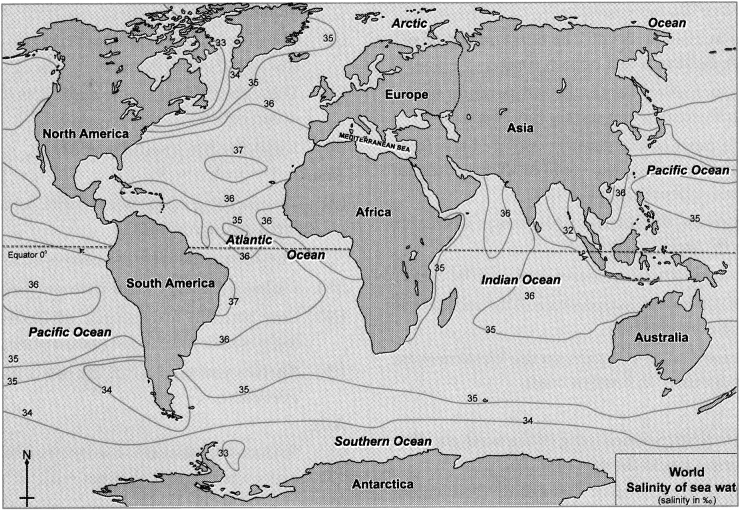
Question 1.
What is the salinity around the tropics?
Answer:
The salinity around the tropics is 36%o.
![]()
Question 2.
Which region has the least salinity?
Answer:
The Bay of Bengal has the least salinity of 32%o.
Question 3.
Which ocean has salinity more than 37%o?
Answer:
Atlantic ocean has salinity of more than 37%o.
Question 4.
What are the reasons of differences in salinity on a global level?
Answer:
The uneven distribution of temperature on earth, and uneven supply of freshwater, etc. are the reasons for differences in salinity on a global level.
Observe the Graph and answer the questions:
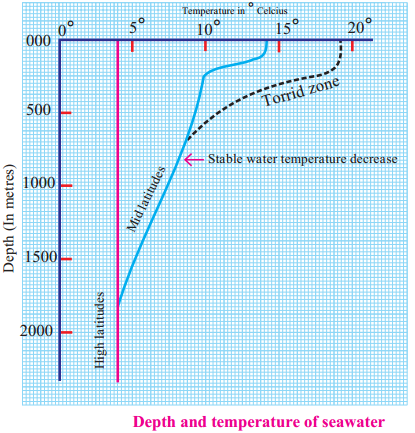
Question 1.
What is the maximum temperature of seawater in equatorial areas? How much is this temperature at a depth of 500 m?
Answer:
The maximum temperature of sea water in equatorial areas is 18° C. The temperature at the depth of 500 m is 11° C.
Question 2.
What is the temperature of seawater at the sea level in the mid-latitudes?
Answer:
The temperature of seawater at the sea level in the mid-latitudes is 14° C approximately.
Question 3.
How much has this temperature changed at 1500 m depth?
Answer:
The temperature is about 5° C at the depth of 1500 m. Thus the temperature of sea water at mid-latitudes has changed from 14°C at the sea level to about 5°C at the depth of 1500 m i.e. temperature has changed (reduced) by 9°C.
![]()
Question 4.
What does the thermal graph for the high latitude say? What is its temperature at 500, 1000 and 1500 m depths?
Answer:
In high latitudes the temperature of sea water at all depths remains constant at 4° C.
Question 5.
After what depth does the seawater temperature remain stable everywhere?
Answer:
After 2000 m, the temperature of the sea water is uniform everywhere.
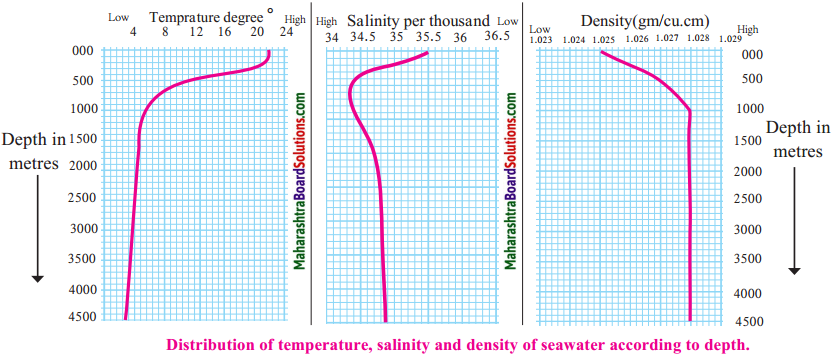
Question 6.
With increasing depth, what decreases: temperature, salinity or density?
Answer:
Temperature and salinity decreases with increasing depth.
Question 7.
After what depth does the change in these factor become almost zero?
Answer:
After the depth of 1000 m there is no change in all these factors.
Question 8.
Till what depth is the change in these factors higher?
Answer:
The higher change can be seen up to a depth of about 500m.
Question 9.
Explain the correlation between all the three factors.
Answer:
If the temperature is less, density is more. If the salinity is less, then density is also less. However temperature affects the density more as compared to the salinity. If the temperature is less, then the density is more despite less salinity.
Let’s Recall.
Question 1.
Which is the largest water storage of the world?
Answer:
Oceans are the largest water storage of the world.
![]()
Question 2.
Why is the seawater salty?
Answer:
- Salt in the ocean comes from rocks on land.
- Rivers carry dissolved salts to the ocean.
- Water evaporates from the oceans to fall again as rain and to feed the rivers, but the salts remain in the ocean.
Question 3.
What are the reasons for high salinity in the oceans?
Answer:
High rate of evaporation and low supply of fresh water leads to high salinity in the oceans:
Question 4.
How can we obtain the salts from the ocean water?
Answer:
- Sea water contains a large amount of common salt and the salts of other metals dissolved in it.
- Near the sea-shore, the sea water is collected in shallow pits (salt pans) and allowed to evaporate in the sunshine.
- In a few days, the water evaporates, leaving behind salt.
- The salt so obtained is collected and transported to factories, where it is purified and packed for consumption.
Question 5.
What is the use of the salts in the oceans to us?
Answer:
- The salts is used in the food we eat.
- It is used for making various chemicals and medicines.
- Salt is also used to preserve things for longer periods. It is also used in ice factories.
Can You Tell?
Question 1.
What is the difference in the temperatures of the land and the sea?
Answer:
During the daytime land is hotter than the sea whereas, during the night time land is cooler than the sea.
Question 2.
What would be the difference in the temperature of the seawater from the equatorial region to the polar areas?
Answer:
Latitudinally, the surface temperature of the seawater decreases from the equatorial areas towards the poles. The average temperature in equatorial areas is around 25° C while it is about 2° C near the poles.
Think about it.
Question 1.
If you think about India there is the Arabian sea to the west and the Bay of Bengal to the east. The salinity of the eastern coast is 34%o while it is 35%o in the Arabian sea. What could be the reason of higher salinity in the western coastal region?
Answer:
Many large peninsular rivers drain their waters in the Bay of Bengal and on the contrary only small seasonal coastal rivers drain in the Arabian sea. Hence the salinity of Arabian sea is more than the Bay of Bengal.
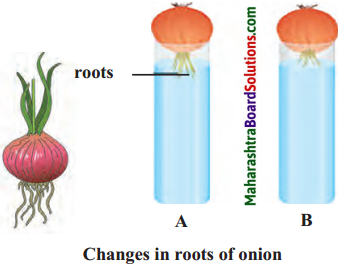
Try this.
Question 1.
In which container has the water increased or decreased?
Answer:
- The water has increased in the container which is in the classroom in which freshwater was added.
- The water has decreased in the container which was kept in the sun outside.
![]()
Question 2.
What could be the reasons behind the decrease or increase?
Answer:
- Since freshwater was added to one of the containers in the classroom the water level increased.
- The water has decreased in the container which was kept outside in the sun due to evaporation.
Question 3.
What could be the reason behind the low and high salinity of the water in the container?
Answer:
- In the container which as kept outside in the sun, due to high rate of evaporation, the salinity is high.
- As we kept on adding fresh water to the container kept in the classroom the salinity is low.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 6 Properties of Sea Water Additional Important Questions and Answers
Select the correct option:
Question 1.
The average temperature in equatorial areas is
(a) 25° C
(b) 35° C
(c) 15° C
(d) 5° C
Answer:
(a) 25°C
Question 2.
The average temperature in mid-latitudes is
(a) 25° C
(b) 10° C
(c) 16° C
(d) 5° C
Answer:
(c) 16°C
Question 3.
The average temperature near poles is about
(a) 10° C
(b) 20° C
(c) 15° C
(d) 2° C
Answer:
(d) 2°C
![]()
Question 4.
With the increasing depth of sea, the intensity of sunrays
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remains constant
(d) is uneven
Answer:
(b) decreases
Question 5.
Seawater upto the depth of 500m is called
(a) ground water
(b) surface water
(c) deep water
(d) saline water
Answer:
(b) surface water
Question 6.
ocean is the most saline ocean in the world.
(a) Pacific
(b) Arctic
(c) Indian
(d) Atlantic
Answer:
(d) Atlantic
Question 7.
The sea lying on the border of Israel and Jordan has a salinity of %o.
(a) 37
(b) 50
(c) 256
(d) 332
Answer:
(d) 332
Question 8.
The buoyancy of the sea water increases because of its
(a) evaporation
(b) salinity
(c) density
(d) high temperature
Answer:
(b) salinity
![]()
Question 9.
has an altitude of – 400m.
(a) Baltic Sea
(b) Arabian Sea
(c) Dead Sea
(d) the Mediterranean Sea
Answer:
(c) Dead sea
Question 10.
act as temperature controllers at a global level.
(a) Ocean currents
(b) Sea breeze
(c) Land breeze
(d) Trade winds
Answer:
(a) Ocean currents
Question 11.
is a major porperty of the sea water.
(a) Temperature
(b) Uniform salinity
(c) Buoyancy
(d) Equal Density
Answer:
(a) Temperature
Question 12.
have higher salinity than open seas.
(a) Equatorial seas
(b) Landlocked seas
(c) Freshwater lakes
(d) Seas in polar regions
Answer:
(b) landlocked seas
Question 13.
Temperature decreases upto depth.
(a) 500 m
(b) 1000 m
(c) 1500 m
(d) 2000 m
Answer:
(d) 2000m
![]()
Question 14.
In regions where cold currents flow, the surface temperature of ocean water is
(a) high
(b) less
(c) uniform
(d) uneven
Answer:
(b) less
Question 15.
Temperature of seawater changes rapidly with depth in areas.
(a) equatorial
(b) mid latitudinal
(c) temperate
(d) polar
Answer:
(a) equatorial
Question 16.
In seas where the rate of evaporation is than the supply of fresh water, salinity is high.
(a) less
(b) high
(c) same
(d) low
Answer:
(b) high
Question 17.
The salinity of Bay of Bengal is than that of Arabian sea.
(a) less
(b) more
(c) same
(d) equal
Answer:
(a) less
Question 18.
In areas the salinity of sea water is low.
(a) equatorial
(b) mid-latitudinal
(c) temperate
(d) polar
Answer:
(d) polar
![]()
Question 19.
The salinity of Battic sea is %.
(a) 332
(b) 32
(c) 37
(d) 7
Answer:
(d) 7
Match the Column:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Equatorial areas (2) Mid-latitudinal areas (3) Temperate regions |
(a) Salinity of 332%o (b) Slanting sunrays, melting of snow (c) Cloudy sky and convectional rainfall (d) Hot deserts |
Answer:
(1-c),
(2- d),
(3 – b)
Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
What is the major property of seawater?
Answer:
Temperature is a major property of seawater.
Question 2.
What is the average surface temperature of seawater in equatorial areas, mid-latitudes & poles?
Answer:
The average surface temperature of seawater is equatorial areas is around 25°C in mid-latitude it is around 16°C & 2°C near the poles.
Question 3.
After what depth is the seawater temperature uniform everywhere?
Answer:
After 2000m, the temperature of seawater is uniform everywhere
![]()
Question 4.
Name the instruments used to measure salinity?
Answer:
Hydrometer, Refractometer and salinometer are used to measure salinity.
Question 5.
Which is the most saline ocean?
Answer:
The Atlantic ocean is the most saline ocean.
Give geographical reasons:
Question 1.
The climate of the earth gets affected by ocean currents.
Answer:
- The ocean currents are generated because of the difference in the properties of seawater.
- They act as temperature controllers at the global level.
- The distribution of temperature gets controlled due to the ocean currents.
- Thus, the climate of the earth gets affected by ocean currents.
Question 2.
Dead Sea has a salinity of 332%0.
Answer:
- The sea lying on the border of Israel and Jordan has a salinity of 332%0.
- The average salinity of ocean is 35%o.
- Jordan is the only large river meeting this sea.
- Low rainfall, low supply of freshwater and high evaporation is the reason of high salinity.
Question 3.
The surface temperature of the sea is not uniform everywhere.
Answer:
- The surface temperature of sea water is not uniform everywhere and it changes with latitudes.
- The surface temperature of the seawater decreases from the equatorial areas towards the poles.
- The average temperature in equatorial areas is around 25° C, it is 16° C in mid-latitudes while it is about 2° C near the poles.
- Besides this, cyclones, rainfall, sea waves, ocean currents, salinity, pollution, convergence flow, seasons, etc. also affect the surface temperature.
- Thus the surface temperature of the sea is not uniform everywhere.
![]()
Question 4.
The seas in equatorial calm belt are more saline.
Answer:
- Around 5° N and S of the equator, in the equatorial calm belt, the sky is cloudy for a long period of time and convectional rainfall occurs every day.
- Large rivers like Congo and Amazon in the equatorial regions meet the sea.
- Therefore, supply of freshwater abundant too.
- But because of higher temperatures, rate of evaporation is more and therefore, the seas in these areas are more saline.
Explain
Question 1.
Factors affecting surface water temperature
Answer:
- Temperature is a major property of the seawater. The surface temperature of the seawater is not uniform everywhere. This is dependent on different factors.
- Latitudinally, the surface temperature of the seawater decreases from the equatorial areas towards the poles.
- Besides this, cyclones, rainfall, sea waves, ocean currents, salinity, pollution, convergence flow and seasons also affect the surface temperature.
- Regions where cold ocean currents flow, the surface temperature of ocean water is less. The regions where the warm currents move, the temperature increase.
Question 2.
Density of sea water
Answer:
- Temperature and salinity are the two properties of sea water that control the density of the sea water.
- If temperature reduces, density of water increases.
- Cold water is denser, and so is saline water.
- As compared to salinity, temperature affects the density more. Hence, sometimes, more saline water has lower temperature at the surface.
- Sea water having higher temperature and low salinity, can have lower density.
Question 3.
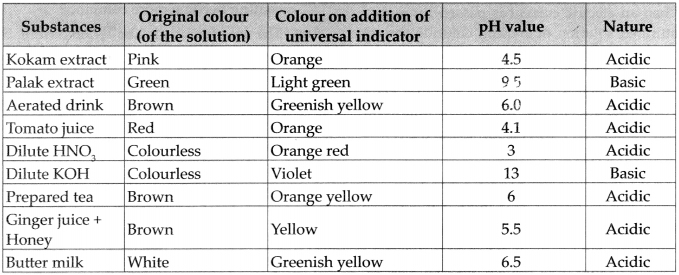
Measurement of salinity of sea water.
Answer:
- The weight of all dissolved salts in water in ratio of parts per thousand of water is called the salinity of seawater.
- For example, if the weight of dissolved salts in 1000g (1 kg) of seawater is 40g, then the salinity is 40%o i.e. 40 per thousand parts.
- Hydrometer, refractometer and salinometer are also used to measure salinity.
![]()
Question 4.
Factors affecting salinity of sea water.
Answer:
| Latitudes | Temperature / Rate of evaporation | Supply of fresh water | Salinity |
| Tropical Zone 5°N – 5°Sof equator | High | Abundant from (River Congo / Amazon) | High |
| Midlatitudes (25° – 35° N and S) | High (hot desert are found here) | low | High |
| Temperate regions | Temperature is lower due to slanting sunrays | The supply of water is more due to melting snow | low |
| Polar regions | Very low | low | low |