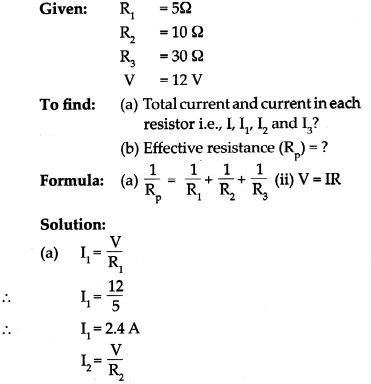
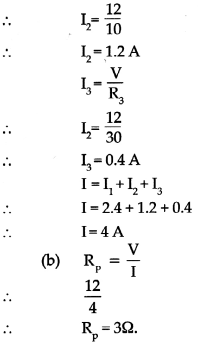Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 History Solutions Chapter 5 Education Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 9 History Solutions Chapter 5 Education
Class 9 History Chapter 5 Education Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Choose the right option and rewrite the sentence:
Question 1.
The Scientist who developed the Param – 8000 supercomputer _________.
(a) Dr Vijay Bhatkar
(b) Dr R. H. Dave
(c) P. Parthasarathy
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Dr. Vijay Bhatkar
![]()
Question 2.
The magazine Jeevan Shikshan is published by _______.
(a) Balbharati
(b) University Education Commission
(c) MSCERT
(d) NCERT
Answer:
(c) MSCERT
Question 3.
The educational institution called IIT is famous for educational in the area of _______.
(a) Agriculture
(b) Medicine
(c) Skilled managers
(d) Engineering
Answer:
(d) Engineering
2. Do as directed.
Question 1.
Complete the table below with details about individuals in the education field and their work.
| Individual | Work |
| First education minister of India | Maulana Abul Kalam Azad. |
| —————– | Chairman of the University Education Commission |
| Prof Sayyad Rauf | ………….. |
| …………………….. | Kosbad Project |
Answer:
| Individual | Work |
| First education minister of India | Maulana Abul Kalam Azad. |
| Dr. Sarvapalli Radhakrishna | Chairman of the University Education Commission |
| Prof Sayyad Rauf | Preparation of common state-wide curriculum for Std. I to VII for Maharashtra. |
| Anutai Wagh | Kosbad Project |
![]()
Question 2.
Obtain information about the National Council of Educational Research and Training, from the internet, and present it in the form of a timeline.
Answer:
| 1st September 1961 | The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) was established in Delhi. |
| 27th January 1967 | The Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research (Balbharati) was established in Pune. |
| 1986 | The National Policy on Education was adopted. |
| 1988 | The ‘Primary Education Curriculum was prepared. |
| 1995 | The Competency-based primary education curriculum. |
| 1975 | India met with success in its attempt to use a satellite for the purpose of education. |
| 1970 | The United Nations declared the year 1970 as the International Education Year. A seminar was organised in New Delhi and led to the establishment of an open university. |
| 1974 | The government appointed a committee under the chairmanship of P. Parthasarathy |
3. Explain the following statements giving reasons for your answer:
Question 1.
The District Primary Education Programme was undertaken.
Answer:
(i) In 1994, the District Primary Education Programme (DPEP) was started with the objective of universalisation of primary education. It was implemented in seven States including Maharashtra.
(ii) The plan envisaged 100% attendance in primary schools, arresting student drop-out, education for girls and for the physically handicapped.
(iii) It included programmes such as research on and evaluation of primary education, alternative education, creating societal awareness, etc.
Question 2.
The NCERT was established.
Answer:
(i) National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) was established in Delhi on the 1st of September 1961.
(ii) Its main objective is to help the Central Government in matters of school education in the context of a comprehensive policy and in implementing educational schemes. The NCERT was given the responsibility of educational research and development, training, extension, educational programmes, restructuring of school curriculum and textbooks.
(iii) It has played a central role in designing school curricula and textbooks with the cooperation of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE).
(iv) It provides guidance and cooperation in the area of primary and secondary education to the state governments.
(v) It has been involved in designing workbooks and handbooks for teachers, in teacher training, in developing teaching-learning techniques and conducting talent search examinations at the national level.
Question 3.
The farmers were benefited by the Indian Agricultural Research Institute.
Answer:
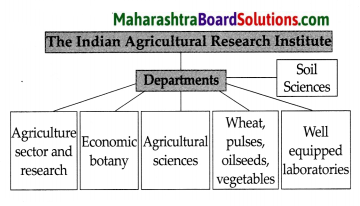
(i) The Indian Agricultural Research Institute was given the status of a University in 1958 and work began in departments such as the development of the agriculture sector, research, well-equipped laboratories, soil science, agricultural sciences, economic botany and other departments.
(ii) Research also began on wheat, pulses, oilseeds, vegetables and many other problems.
(iii) Its most significant achievement is the fundamental research it has conducted on the methods of taking multiple crops in a year, which has been of great benefit to farmers.
4. Write notes:
Question 1.
Indira Gandhi National Open University
Answer:
(i) Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU) was established with the objective that the stream of education should make
its way into every average household of the country.
(ii) The United Nations had declared 1970 as the International Education Year. In the same year, a seminar was organised in New Delhi on the subject of Open University by the Government of India Departments of Education and Social Welfare, Information and Broadcasting, University Grants Commission along with UNESCO. The idea of establishing an open university evolved in this seminar.
(iii) In 1974, the government appointed a committee under the chairmanship of P. Parthasarathy and the Open University took shape on 20 September, 1985 in accordance with its recommendations and suggestions. It was named after Prime Minister Indira Gandhi. Those who are unable to get a college education in the formal way are given concessions in eligibility criteria, age and other conditions for admission to this university.
(iv) In 1990, the IGNOU started an audio-visual distance education programme through Akashvani and Doordarshan. It conducted more than one thousand curricula of various branches.
It provides facilities for education through 58 training centres in the country and 41 centres in foreign countries.
![]()
Question 2.
Kothari Commission
Answer:
(i)In 1964 a Commission was appointed under the Chairmanship of Dr D. S. Kothari. Dr J. P. Naik made valuable contributions to the work of this Commission.
(ii)The Commission also recommended the 10+2+3 pattern for secondary, higher secondary and university education. This system was implemented from 1972.
(iii)The Commission also suggested a uniform national system of education, the inclusion of the mother tongue, Hindi and English in education, as well as continuing education, adult education, education by correspondence and open universities to make education trickle down to the lowest rungs of society.
(iv)It also recommended increased provision in the government’s budget for expenditure on education of neglected sections like the scheduled castes and tribes. Maharashtra government adopted the 10+2+3 pattern in 1972 and conducted the first Std X Board exam in 1975.
Question 3.
Bhabha Atomic Research Centre
Answer:
(i) Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) has conducted valuable research in the fields of nuclear physics, solid state physics, spectroscopy, chemical and life sciences.
(ii) It also started a school to train scientists for setting up nuclear reactors.
Question 4.
Balbharati
Answer:
(i) The Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research (Balbharati) was established in Pune on 27 January 1967.
(ii) Balbharati prepares textbooks for school children. Textbooks are made in eight languages, namely, Marathi, Hindi, English, Urdu, Kannad, Sindhi, Gujarati and Telugu. ‘Kishor’, a monthly magazine for children, is also published by Balbharati.
5. Answer the following questions in detail:
Question 1.
Which programmes were included in the Operation Blackboard scheme?
Answer:
(i) The government made funds available to help improve the standard of the schools and to fulfil minimum educational needs such as at least two proper classrooms, toilets, one of the two teachers to be female, a blackboard, maps, laboratory apparatus, a small library, a playground, sports equipment, etc. This scheme helped the primary education system to gain some momentum.
(ii) In 1994, this scheme was expanded and provision was made for one additional classroom and for appointing one more teacher in schools with an enrolment of more than 100 students, with priority given to girls’ schools, schools with a majority of scheduled caste and tribe students and schools in rural areas.
(iii) It was also made binding upon the State government to appoint female teachers to fifty per cent of the posts in schools.
Question 2.
What role do agriculture schools/colleges play in the development of agriculture?
Answer:
(i) The Indian Agricultural Research Institute was given the status of a University in 1958 and work began in departments such as the development of the agriculture sector, research, well-equipped laboratories, soil science, agricultural sciences, economic botany and other departments. Research also began on wheat, pulses, oilseeds, vegetables and many other problems.
(ii) Its most significant achievement is the fundamental research it has conducted on the methods of taking multiple crops in a year, which has been of great benefit to farmers.
Question 3.
Describe with examples of the progress that India has made in the field of medicine.
Answer:
(i) The Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR) was established for conducting research in the medical field. It was given the responsibility of cooperating with universities, medical colleges, government and non-government research institutes and giving them guidance and financial support for research activities.
(ii) Twenty-six centres were started in different parts of the country for research on various diseases. Their research has made it possible to control tuberculosis and leprosy.
(iii) The All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) was established to give further impetus to advanced education and research in medicine.
(iv) It was given the responsibility of undergraduate and postgraduate courses in medicine. Colleges for undergraduate and postgraduate education in most branches of medicine, good research facilities and well- equipped hospitals are the significant features of this institute.
(v) The institute also provides medical treatment to the common people at nominal rates. It has established special colleges for training in nursing, and super-speciality centres for treatment of disorders of the heart, brain and eyes.
(vi) For further development of the medical field, the Medical Council of India was restructured in 1958 and was entrusted with the task of determining criteria for quality of medical education, its supervision and inspection.
(vii) These institutes have the responsibility of conducting research on various diseases, developing tests and standardisation of medicines.
![]()
Question 4.
Write a note on the curricular and co-curricular activities conducted in your school.
Answer:
(i) Languages – Our school motivates us to participate in theatres or plays organised on works of Shakespeare and Munshi Premchand. We also take part in elocution and poetry recitation competitions to enhance public speaking. Our school makes every child read the newspaper headlines from Marathi and English dailies in the auditorium turn wise.
(ii) Maths and Science – Scientific experiments mentioned in our textbook are practically performed by each of us under the supervision of our teachers. On Sundays, our Math teachers take special classes on Vedic Maths. Our school has also organised trips to Nehru Planetarium and ‘Jantar Mantar’ to give us an understanding of the astronomical aspects of science. Every year our school conducts Homi Bhabha scholarship exam. A display of the best 25 science projects is done in the school hall.
(iii) Social Studies – Field studies are taken up to explain to us the topography of Indian landscapes. The school library holds a large number of book and documentaries over world history trips to museums and historical places.
Class 9 History Chapter 5 Education Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct option from the given options and rewrite the statements:
Question 1.
In 1995, the _____ scheme was started to provide proper nourishment for the students.
(a) free ration
(b) foodgrain subsidy
(c) mid-day meal
(d) medical-check up
Answer:
(c) mid-day meal
Question 2.
_______was the first education minister of Independent India.
(a) Vallabhbhai Patel
(b) Maulana Abdul Kalam Azad
(c) Sachchidanand Sinha
(d) J.B.Kriplani
Answer:
(b) Maulana Abdul Kalam Azad
Question 3.
_____ recommended increased provision in government’s budget for expenditure on education of neglected sections like the SC/ST.
(a) University Education Commission
(b) Mudaliar Commission
(c) National Council of Educational Research and Training
(d) Kothari Commission
Answer:
(d) Kothari Commission
Question 4.
_______, a scientist with ISRO played an important role in providing satellite education.
(a) K. Kasturirangan
(b) Eknath Chitnis
(c) A. S. Kirankumar
(d) G. Madhavan Nair
Answer:
(b) Eknath Chitnis
Question 5.
In 1990 _____ started an audio-visual distance education programme through Akashwani and Doordarshan.
(a) ISRO
(b) NCERT
(c) IGNOU
(d) CSIR
Answer:
(c) IGNOU
Question 6.
The National Institute for Research in Mathematical and Physical Sciences’ in ______ was established in 1962.
(a) Chandigarh
(b) Kerala
(c) Karnataka
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer:
(d) Tamil Nadu
![]()
Question 7.
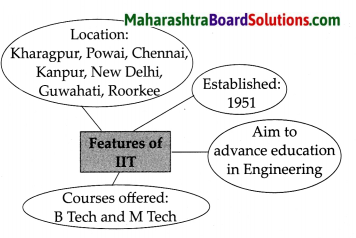
India’s first IIT was setup at _______ at West Bengal in 1951.
(a) Kharagpur
(b) Midnapore
(c) Hooghly
(d) Howrah
Answer:
(a) Kharagpur
Identify and write the wrong pair in the following sets:
Question 1.
(1) TCS – obtained an American contract for software production.
(2) FTII – Systematic training in all aspects of film-making.
(3) C-DAC – developed Param – 8000
(4) IIM – imparting training in industrial design.
Answer:
Wrong Pair : IIM – imparting training in industrial design.
Question 2.
(1) The Advanced Centre for Treatment Research and Education in Cancer – Branch of Tata Memorial Centre
(2) AIIMS – advanced education and research in medicine.
(3) DPEP – Charts showing learning competencies upto Std.V
(4) National Policy on Education 1986 – Common core curriculum was framed for all states.
Answer:
Wrong Pair : DPEP – Charts showing learning competencies upto Std.
Question 3.
(1) National Institute of Design – Ahmedabad
(2) Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education – Pune
(3) The National Institute for Research in the Mathematical and Physical Science – Delhi
(4) Indian Institute of Technology – West Bengal
Answer:
Wrong Pair: The National Institute for Research in the Mathematical and Physical Science – Delhi
Question 4.
(1) J.P. Naik – Kothari Commission
(2) P. Parthasarthy – Committee on Open University
(3) Sayyad Rauf – Drafted common state wide curriculum
(4) Dr. Sarvapalli Radhakrishnan – Director of NCERT.
Answer:
Wrong Pair : Dr. Sarvapalli Radhakrishnan Director of NCERT.
Question 5.
(1) Dave Committee – minimum levels of learning.
(2) The Art Department – designing workbooks and hand books.
(3) Kosbad project – Education of Adivasis
(4) Council of Scientific and Industrial Research – Promote scientific research.
Answer:
Wrong Pair : The Art Department – designing workbooks and hand books.
Question 6.
(1) MSCERT – Jeevan Shikshan
(2) Balbharati – Kishor
(3) The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education – Countrywide classroom.
(4) SITE – Satellite Education.
Answer:
Wrong Pair : The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education – Countrywide classroom
Question 7.
(1) Tarabai Modak – Kuranshalas
(2) Anutai Wagh – Kosbad Projects
(3) Eknath Chitnis – Education Minister
(4) R. H. Dave – Competency based Primary Education Curriculum.
Answer:
Wrong Pair: Eknath Chitnis – Education Minister
Complete the concept maps:
Question 1.
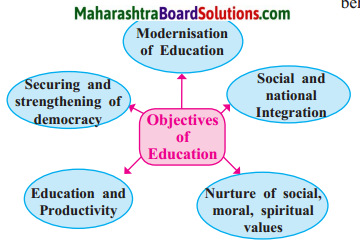
Objectives of Education:
Answer:
![]()
Question 2.
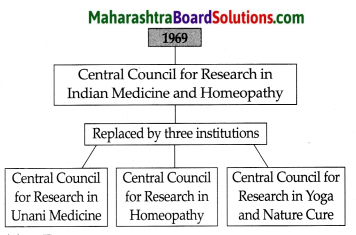
Central Council for Research in Indian Medicine and Homeopathy:
Answer:
Question 3.
Departments of the Indian Agricultural Research Institute:
Answer:
Question 4.
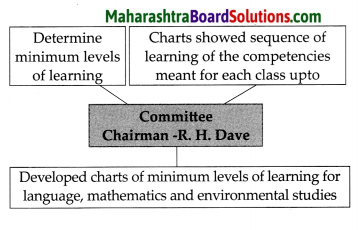
Role of Dave Committee:
Answer:
Question 5.
Features of the IIT
Answer:
Question 6.
IIMs in India
Answer:
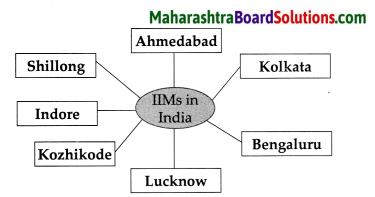
Question 7.
Concept map of basic responsibilities of NCERT
Answer:
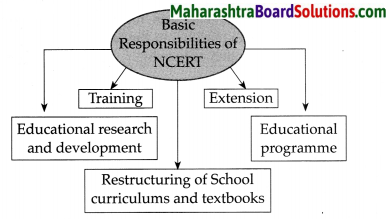
![]()
Write short notes:
Question 1.
AIIMS
Answer:
(i) The All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) was established to give further impetus to advanced education and research in medicine.
(ii) It was given the responsibility of undergraduate and post-graduate courses in medicine.
(iii) Colleges for undergraduate and postgraduate education in most branches of medicine, good research facilities and well-equipped hospitals are the significant features of this institute.
(iv) The institute also provides medical treatment to the common people at nominal rates.
(v) It has established special colleges for training in nursing, and super-speciality centres for treatment of disorders of the heart, brain and eyes.
(vi) For further development of the medical field, the Medical Council of India was restructured in 1958 and was entrusted with the task of determining criteria for quality of medical education, its supervision and inspection.
Question 2.
Achievements of CSIR
Answer:
(i) In the post-independence period in 1950, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) was established with the objective to promote scientific research in the country and to take the benefits of the research to all the people.
(ii) The achievements of the CSIR include making the ink used for marking voters’ fingers during elections, medicines for malaria, elephantiasis and tuberculosis, water purification technology, reduction in the time required for bamboo production.
(iii) It also used DNA fingerprinting for the first time in India, conducted a genetic study of the Adivasis of the Andamans and proved that those tribes are 60,000 years old and developed the earthquake early warning system.
(iv) It has also played an important role in the use of neem as a pesticide, use of turmeric for healing wounds and in the case of the patents for varieties of rice.
(v) The CSIR has prepared a digital encyclopedia of Indian traditional knowledge and made it available in eight international languages.
Question 3.
NCERT
Answer:
(i) National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) was established in Delhi on the 1st of September 1961.
(ii) Its main objective is to help the Central Government in matters of school education in the context of a comprehensive policy and in implementing educational schemes. The NCERT was given the responsibility of educational research and development, training, extension, educational programmes, restructuring of school curriculum and textbooks.
(iii) It has played a central role in designing school curricula and textbooks with the cooperation of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). ’
(iv) It provides guidance and cooperation in the area of primary and secondary education to the state governments.
(v) It has been involved in designing workbooks and handbooks for teachers, in teacher training, in developing teaching-learning techniques and conducting talent search examinations at the national level.
![]()
Read the passage and answer the questions and answer the questions based on it.
Passage I
National Council of Educational Research and Training. This body was established in Delhi on the 1st of September 1961. Its main objective is to help the Central Government in matters of school education in the context of a comprehensive policy and in implementing educational schemes. The NCERT was given the responsibility of educational research and development, training, extension, educational programmes, restructuring of school curriculum and textbooks. It has played a central role in designing school curricula and textbooks with the cooperation of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). It provides guidance and cooperation in the area of primary and secondary education to the state governments. It has been involved in designing workbooks and handbooks for teachers, in teacher training, in developing teaching-learning techniques and conducting talent search examinations at the national level.
SCERTs were established in all States on the lines of the NCERT. The Maharashtra State Council of Educational ‘Research and Training was established in Pune, This institute performs various functions such as , improving the standard of primary education, in service training of teachers, training in the areas of syllabii and evaluation, vocational guidance for students after Std X and Std XII exams and other , educational functions This institute is known as the , academic authority. It brings out a periodical called Jeevan Sikshan. ‘
Question 1.
What was the main objective behind establishment of NCERT?
Answer:
The main objective behind establishment of NCERT is to help the central government in matters of school education in the context of a comprehensive policy and in implementing educational schemes.
Question 2.
SCERT was established only in Maharashtra State on the lines of the NCERT. Identify True or False.
Answer:
False.
Question 3.
State 4 research institutes in India.
Answer:
Following are the 4 research institutes in India:
- Council of Scientific & Industrial Research.
- Bhabha Atomic Research Centre.
- Indian Council of Medical Research.
- Indian Agricultural Research Institute.
Passage II
National Policy on Education 1986: According to this policy, certain changes of a fundamental nature were brought about in primary, secondary and higher , secondary education in keeping with the changing needs of society. Under this policy, a common core curriculum was framed for all States. The expectation , is that, by this means, all students in India will get equal educational opportunity. There is scope in the national curriculum for individual States to bring in flexibility in accordance with their cultural, geographical and historical needs.
The ‘Primary Education Curriculum 1988’ was prepared on the basis of the plan of action designed at the national level for the effective implementation of the National Policy on Education 1986. The competency based primary Education curriculum 1995: Even as the Primary Education Curriculum , 1988 was being implemented, a Committee was formed at the national level with Dr. R. H. Dave as its Chairman, to determine minimum levels of learning, The Dave as Committee developed charts of minimum , levels of learning in language, mathematics and environmental studies up to Std V. The charts showed the sequence of learning of the competencies meant for each class.
Use of a satellite: In 1975, India met with success in its attempt to use a satellite for the purpose of education, Eknath Chitnis, a scientist with ISRO, played an , important role in it.
SITE (Satellite Instructional Television Experiment) , was undertaken for educational purposes under the leadership of the Space Applications Centre at Ahmedabad. The concept of satellite education came , out of this experiment. America had helped India in , this programme. The programme helped to make provisionsforagoodstandardofeducationinruralareas.
![]()
Question 1.
What was done to implement the National Policy on Education 1986?
Answer:
For the effective implementation of National Policy on Education 1986, the Primary Education Curriculum 1988 was prepared on the basis of the action plan formulated at the National level.
Question 2.
How did the Dave committee determine the minimum levels of learning?
Answer:
To determine the minimum levels of learning the Dave committee developed charts in language, mathematics and environmental studies upto Std. V. Sequential learning competencies were depicted on these charts to set standards through levels of learning.
Question 3.
Who is your favourite educationist? State his/ her educational ideas which impacted the society.
Answer:
(i) My favourite educationist are Rabindranath Tagore, Dr. Annie Besant and Dr. Sarvapalli Radha Krishnan.
(ii) They all enlightened the society with their educational ideas and deeds. Dr. Annie Besant in particular was iconic.
(iii) Her ideas of education were imbibed with political freedom, women’s liberation and universal brotherhood. Her teachings of ‘Home Rule’ and ‘theosophy’ impacted our society during British Rule. She taught these ideas through political lectures to motivate the youth.
Answer the following questions in detail:
Question 1.
What does the District Primary Education Programme envisage?
Answer:
(i) In 1994, the District Primary Education Programme (DPEP) was started with the objective of universalisation of primary education. It was implemented in seven States including Maharashtra.
(ii) The plan envisaged 100% attendance in primary schools, arresting student drop-out, education for girls and for the physically handicapped.
(iii) It included programmes such as research on and evaluation of primary education, alternative education, creating societal awareness, etc.
Question 2.
State the contribution of Tarabai Modak in educating adivasis.
Answer:
(i) Tarabai Modak began work in the field of education in Bordi and Kosbad.
(ii) She started Anganwadis for Adivasi children.
(iii) She worked hard to bring in the Teaming by doing’ method, to start kuranshalas (meadow schools) and to spread vocational technical education.
Question 3.
What purpose did the Kosbad Project serve?
Answer:
(i) Anutai Wagh established an institution at Kosbad for the progress of Adivasis in Thane district.
(ii) It is known as the Kosbad Project.
(iii) She started creches, nurseries, primary schools, adult education classes, balsevika training schools, etc. for the education of Adivasis.
Question 4.
What was proposed by the Mudaliar Commission?
Answer:
(i) In 1952-53, the Mudaliar Commission was appointed.
(ii) At that time, the pattern of education consisted of 11 + 4 years for the first degree or of 11 + 1 + 3 years.
(iii) The Commission studied secondary education, the nature of the curriculum, medium of instruction, teaching methodology and made certain recommendations.
(iv) This Commission proposed the concept of Higher Secondary Education. However, it was found difficult to implement it all over the country.
![]()
Question 5.
State the recommendation of Kothari Commission.
Answer:
(i) The Kothari Commission recommended the 10+2+3 pattern for secondary, higher secondary and university education. This system was implemented from 1972.
(ii) The Commission also suggested a uniform national system of education, the inclusion of the mother tongue, Hindi and English in education, as well as continuing education, adult education, education by correspondence and open universities to make education trickle down to the lowest rungs of society.
(iii) It also recommended increased provision in the government’s budget for expenditure on education of neglected sections like the scheduled castes and tribes.
Question 6.
What do you know about the Education Board of your state?
Answer:
(i) The Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education was established on the 1st of January 1966 at Pune.
(ii) This Board conducts the school leaving examinations of Std. X and Std. XII.
(iii) It also publishes a periodical called ‘Shikshan Sankraman’.
Question 7.
State the functions of MSCERT.
Answer:
(i) The Maharashtra State Council of Educational Research and Training was established in Pune.
(ii) This institute performs various functions such as improving the standard of primary education,
in-service training of teachers, training in the areas of syllabi and evaluation, vocational guidance for students after Std X and Std XII exams and other educational functions.
Question 8.
How did the concept of satellite education evolve in India?
Answer:
(i) SITE (Satellite Instructional Television Experiment) was undertaken for educational purposes under the leadership of the Space Applications Centre at Ahmedabad.
(ii) The concept of satellite education came out of this experiment. America had helped India in this programme.
(iii) The programme helped to make provisions for a good standard of education in rural areas.
Question 9.
Discuss the responsibilities of Indian Council for Medical Research.
Answer:
(i) Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR) was established for conducting research in the medical field.
(ii) It was given the responsibility of cooperating with universities, medical colleges, government and non-government research institutes and giving them guidance and financial support for research activities.
Question 10.
Which institute works for advanced research in cancer?
Answer:
The Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer is a branch of the Tata Memorial Centre. It functions as the national centre for treatment, research and education in relation to cancer.
Observe the pictures/personality and write relevant information:
Question 1.

Answer:
(i) Kothari Commission recommended the 10+2+3 pattern for secondary, higher secondary and university education.
(ii) The objectives of Education were :
- Modernisation of Education.
- Social and national integration.
- Nurture of social, moral, spiritual values.
- Education and Productivity.
- Securing and strengthening of democracy.
(iii) The following are the other recommendations made by the Kothari commission:
- A uniform national system of education
- inclusion of mother tongue (along with Hindi and English)
- Continuing education
- Adult education
- Education by correspondence
- Open Universities.
![]()
Question 2.

Answer:
(1) The open university was established with the objective that the stream of education should make its way into every average household of the country.
(2) In 1974, the government appointed a committee under the chairmanship of P. Parthasarthy and open university took shape on 20th September 1985 in accordance with its recommendations and suggestions.
It was named after Prime Minister – Indira Gandhi.
(3) In 1990, IGNOU started an audio-visual distance education programme through Akashwani and Doordarshan.
(4) It provides facilities for education through 58 centres in the country and 41 centres in foreign countries.
Question 3.

Answer:
(1) CSIR was established with the objective to promote scientific research in the country and to take the benefits of the research to all the people.
(2) CSIR conducted research in fields like:
- Physics, chemistry, pharmaceuticals, food processing and mining
(3) The achievements of CSIR include:
- Making the ink used for marking voter’s fingers during elections
- Medicines for malaria, elephantiasis and tuberculosis
- water purifying technology
- DNA fingerprinting for the first time in India.
(4) CSIR has prepared a digital encylopoedia of Indian traditional knowledge and made it available in eight international languages.