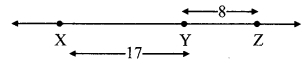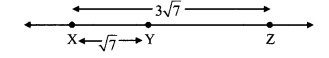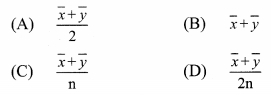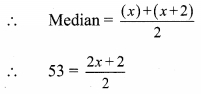9th Standard Maths 2 Practice Set 3.2 Chapter 3 Triangles Textbook Answers Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 3.2 Geometry 9th Class Maths Part 2 Answers Solutions Chapter 3 Triangles.
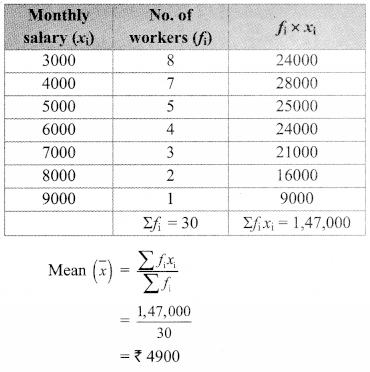
Class 9 Maths Part 2 Practice Set 3.2 Chapter 3 Triangles Questions With Answers Maharashtra Board
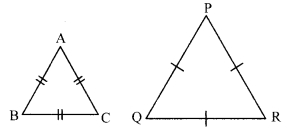
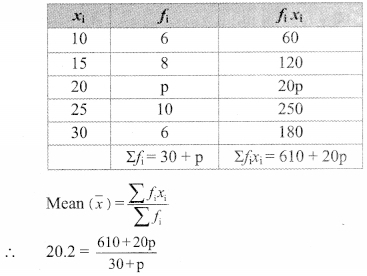
Question 1.
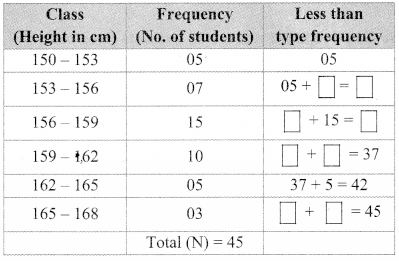
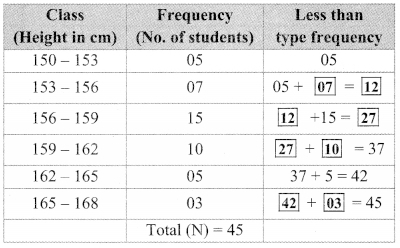
In each of the examples given below, a pair of triangles is shown. Equal parts of triangles in each pair are marked with the same signs. Observe the figures and state the test by which the triangles in each pair are congruent.
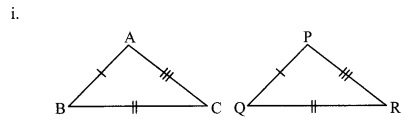
By SSS test
∆ABC ≅ ∆PQR
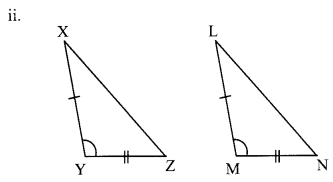
By SAS test
∆ XYZ ≅ ∆LMN
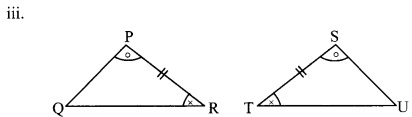
By ASA test
∆PRQ ≅ ∆STU
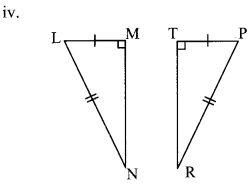
By hypotenuse side test
∆LMN ≅ ∆PTR
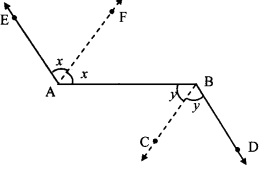
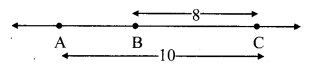
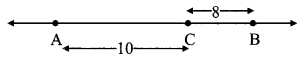
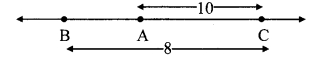
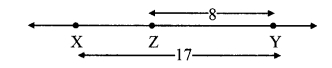
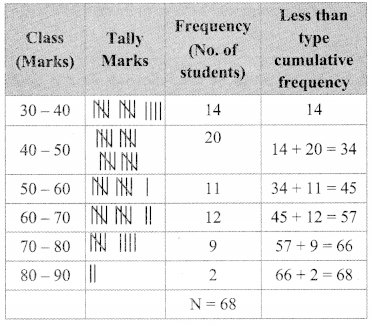
Question 2.
Observe the information shown in pairs of triangles given below. State the test by which the two triangles are congruent. Write the remaining congruent parts of the triangles.
Solution:
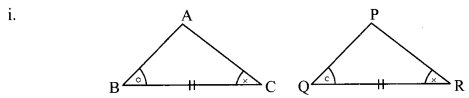
From the information shown in the figure,
In ∆ABC and ∆PQR,
∠ABC ≅ ∠PQR
seg BC ≅ seg QR
∠ACB ≅ ∠PRQ
∴ ∆ABC ≅ ∆PQR [ASA test]
∴ ∠BAC ≅ ∠QPR [Corresponding angles of congruent triangles]
seg AB ≅ segPQ and segAC ≅ seg PR [Corresponding sides of congruent triangles]
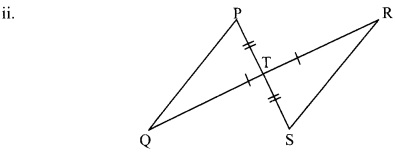
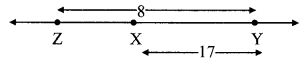
From the information shown in the figure,
In ∆PTQ and ∆STR,
seg PT ≅ seg ST
∠PTQ ≅ ∠STR [Vertically opposite angles]
seg TQ ≅ seg TR
∴ ∆PTQ ≅ ∆STR [SAS test]
∴ ∠TPQ ≅ ∠TSR and ∠TQP ≅ ∠TRS [Corresponding angles of congruent triangles]
seg PQ ≅ seg SR [Corresponding sides of congruent triangles]
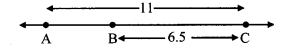
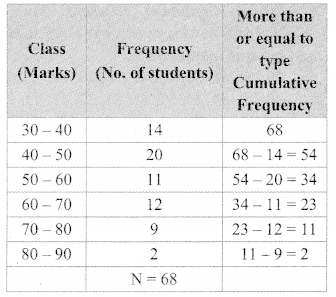
Question 3.
From the information shown in the figure, state the test assuring the congruence of ∆ABC and ∆PQR. Write the remaining congruent parts of the triangles.
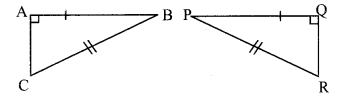
Solution:
In ∆BAC and ∆PQR,
seg BA ≅ seg PQ
seg BC ≅ seg PR
∠BAC ≅ ∠PQR = 90° [Given]
∴ ∆BAC ≅ ∆PQR [Hypotenuse side test]
∴ seg AC ≅ seg QR [c.s.c.t.]
∠ABC ≅ ∠QPR and ∠ACB ≅ ∠QRP [c.a.c.t.]
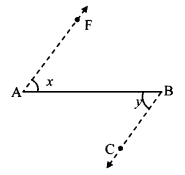
Question 4.
As shown in the adjoining figure, in ∆LMN and ∆PNM, LM = PN, LN = PM. Write the test which assures the congruence of the two triangles. Write their remaining congruent parts.
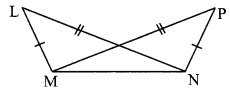
Solution:
In ∆LMN and ∆PNM,
seg LM ≅ seg PN
seg LN ≅ seg PM [Given]
seg MN ≅ seg NM [Common side]
∴ ∆LMN ≅ ∆PNM [SSS test]
∴ ∠LMN ≅ ∠PNM,
∴ ∠MLN ≅ ∠NPM, and ∠LNM ≅ ∠PMN [c.a.c.t.]
Question 5.
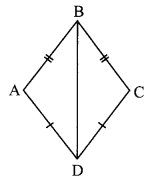
In the adjoining figure, seg AB ≅ seg CB and seg AD ≅ seg CD. Prove that ∆ABD ≅ ∆CBD.
Solution:
proof:
In ∆ABD and ∆CBD,
seg AB ≅ seg CB
seg AD ≅ seg CD [Given]
seg BD ≅ seg BD [Common side]
∴ ∆ABD ≅ ∆CBD [SSS test]
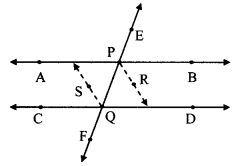
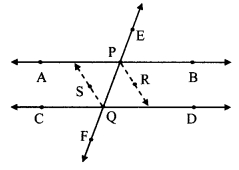
Question 6.
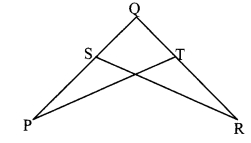
In the adjoining figure, ZP ≅ ZR, seg PQ ≅ seg RQ. Prove that APQT ≅ ARQS.
Proof:
In ∆PQT and ∆RQS,
∠P ≅ ∠R
seg PQ ≅ seg RQ [Given]
∠Q ≅ ∠Q [Common angle]
∴ ∆PQT ≅ ∆RQS [ASA test]
Maharashtra Board Class 9 Maths Solutions