By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 8 Social Change students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 8 Social Change
→ All human societies and their cultures are dynamic and undergo continuous change.
→ Change is an integral part of human society. It may be cyclical.
→ The nature of change and the direction of change varies from one society to another, but change is inevitable.
→ Changes might be slow or rapid; the consequences of change may be constructive/positive or destructive/negative.
![]()
→ Changes proceed from one stage to another in a single direction known as linear change or changes can take place in several directions known as multi-linear change.
→ The view of looking at society from the point of view of structures and functions is called structural functionalism.
→ The term social change refers to changes that take place in the structure and functioning of social Institution.
Characteristics of Social Changes:
- University
- Continuous process.
- Temporal
- Interactional chain reaction
- Neutrality
- Short-term and Long-term change
- Planned or Unplanned change
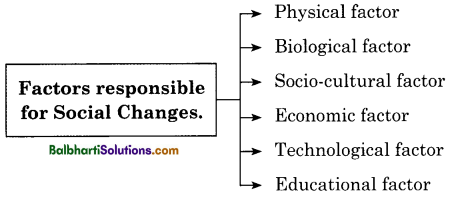
Factors responsible for Social Changes:
- Social change is a result of the interaction of multiple factors.
- No single factor is responsible for the change in society.
![]()
Factors responsible for Social Changes:
- Physical factor
- Biological factor
- Socio-cultural factor
- Economic factor
- Technological factor
- Educational factor