By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 5 Rural Development in India students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 5 Rural Development in India
→ Meaning Of Rural Development:
- Leads to economic growth of a country.
- It is a ‘subset’ of term “development”.
- Relates to overall development and improvement in quality of life
- It should be sustainable, in order to remove poverty from any country.

![]()
→ Definition of Rural Development:
World Bank defines :
“Rural development is a strategy designed to improve the economic and social life of a specific group of people – the rural poor. Rural development involves extending the benefits of development to the poorest among those, who seek livelihood in the rural areas. The group includes small scale farmers, tenants and the landless’’.
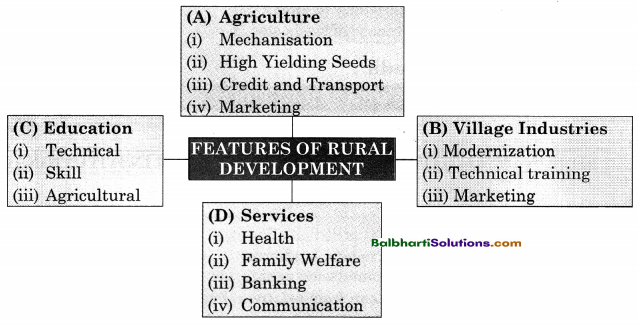
→ Features of Rural Development:
(A) Agriculture:
- Mecha nisation
- High Yielding Seeds
- Credit and Transport
- Marketing
(B) Village Industries:
- Modernization
- Technica’ training
- Marketing
(C) Education
- Technical
- Skill
- Agricultural
(D) Services
- Health
- Family Welfare
- Banking
- Communication
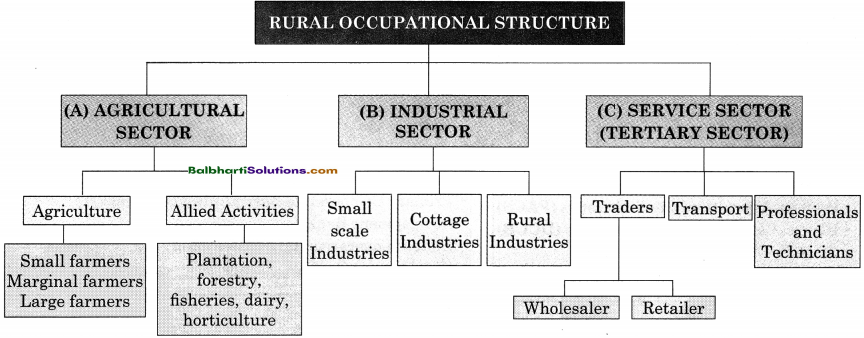
→ Rural Occupational Structure:
(A) Agricultural Sector
(B) Indrustrial Sector
(C) Services Sector (Tertiary Sector)
(A) Agricultural Sector
- Agriculture
- Allied Activities
1. Agriculture
- Small farmers
- Marginal farmers
- Large farmers
Allied Activities:
Plantation, forestry, fisheries, dairy, horticulture
(B) Indrustrial Sector:
- Small scale Industries
- Cottage Industries
- Rural Industries
(C) Services Sector (Tertiary Sector):
- Traders
- Transport
- Proffessional and Technicians
Traders:
- Wholesaler
- Retailer
![]()
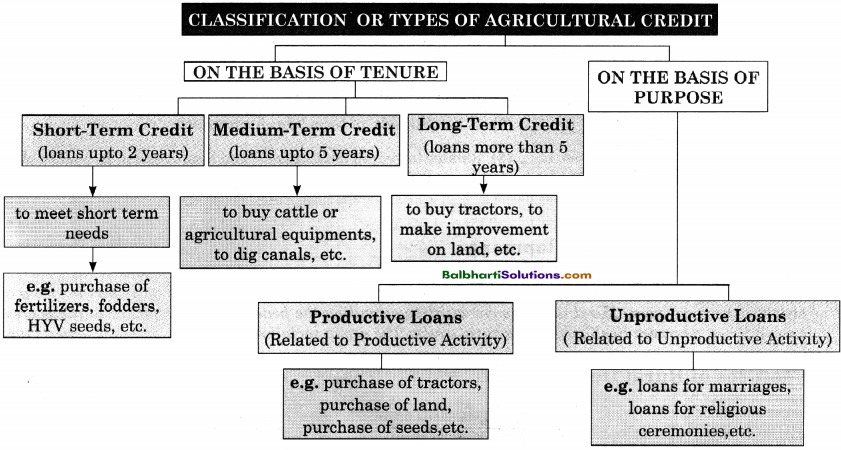
→ Classification or Types of Agricultural Credit:
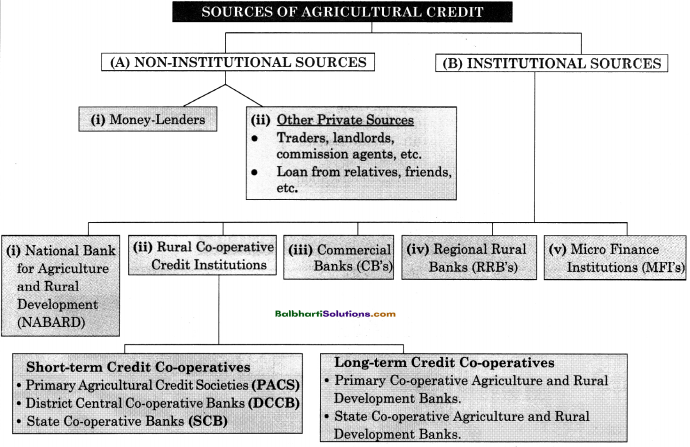
→ Sources of Agricultural Credit:
(A) Non-Institutional Sources
(B) Institutional Sources
(A) NON-INSTITUTIONAL Sources
- Money-Lenders
- Other Private Sources
- Other Private Sources:
- Traders, landlords, commission agents, etc.
- Loan from relatives, friends, etc.
(B) Institutional Sources:
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- Rural Co-operative Credit Institutions
- Commercial Banks (CB’s)
- Regional Rural Banks (RRB’s)
- Micro Finance Institutions (MFI’s)
Rural Co-operative Credit Institutions
- Short-term Credit Co-operatives
- Long-term Credit Co-operatives
Short-term Credit Co-operatives:
- Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)
- District Central Co-operative Banks (ÐCCB)
- State Co-operative Banks (SCB)
Long-term Credit Co-operatives:
- Primary Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks.
- State Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks.
→ Significance or Importance of Rural Development in India :
- Public health and sanitation
- Literacy rate
- Empowerment of women
- Enforcement of law and order
- Land reforms
- Infrastructure development
- Availability of credit
- Eradication of poverty

![]()
Word Meaning:
predominantly – mainly, rural – village area, subset – part of a larger group, connotes – suggest, consensus – general opinion, alleviate – to reduce, strategy – planning, tenants – a person who occupies land or property on rental basis, marginal – very small, cottage – industry carried out in people’s home, witnessed – to see, affordable – reasonable price, instrument – a tool, gender disparity – not having equal rights for male and female, safeguard – protect, enforcement – carrying out, ceiling – limitation, connectivity – to link, eradication – to remove, pre-requisite – requirement, inadequate – not sufficient, tenure – time period, unproductive – not able to use in productive activity, collateral security – asset kept against loan, prevalent – spread, mortgage – to keep asset against the loan, promotion – to support, consequent – as follows, inflexibility – not able to change, legitimate – allowed by law.