By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 6 Population in India students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 6 Population in India
→ Population :
- It refer to the number of people living in an area at a given point of time.
- It is measured once in every 10 years.
- It is measured through census survey.
- India ranks second in the world next to China.
- Population statistics are collected, compiled and published by Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India.
![]()
→ Kautilya wrote ‘Arthashastra’ in 3rd century B. C.
→ Year 1872 is marked as first population Census of India
→ World population crossed 500 crores on 11th July, 1987
→ 11th July is observed as “World Population Day”
→ There was marginal decline in population during the period 1911 – 1921 due to spread of epidemics – influenza, cholera, plague, malaria, etc.
→ The year 1921 is designated as ‘Year of Great Divide”.
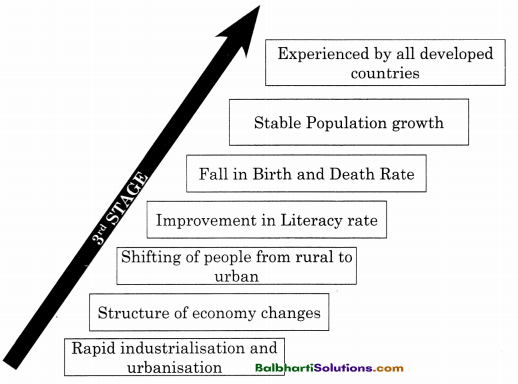
→ Theories Of Population Growth
(a) Malthusian Theory
(b) Theory of Demographic Transition
(a) Malthusian Theory:
- Thomas Robert Malthus
- “An Essay on the Principle of Population” (1798)
- Population increases in Geometric Progression and Food supply increases in Arithmetic Progression (Imbalance between population and food supply)
- Imbalance can be balanced by preventive checks and natural checks
(b) Theory of Demographic Transition:
- A. J. Coale and E. M, Hoover
- “Population growth and Economic Development in low-income countries” (1958).
- This theory explains transition from high to low birth rates and death rates.
- Stage of Demographic transition:
- First stage (Low growth of population)
- Second stage (High growth of population)
- Third stage (Low or Stable population)
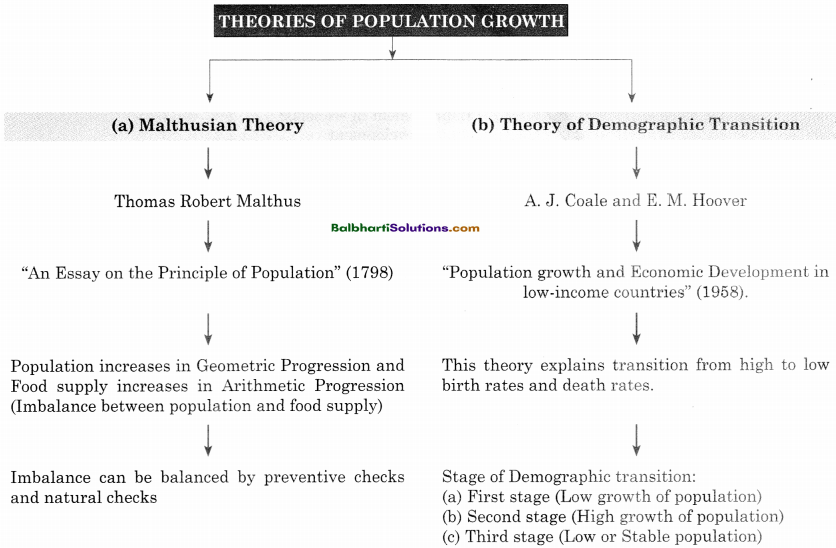
→ Features of 1st Stage of Demographic Transition.
Low growth of population
↑
High birth and High death rate
↑
People ruled by old customs and beliefs
↑
Illiteracy among people, mass poverty, orthodoxy etc.
↑
Agriculture as main occupation (Pre-industrialised and primitive stage)
↑
Low economic development
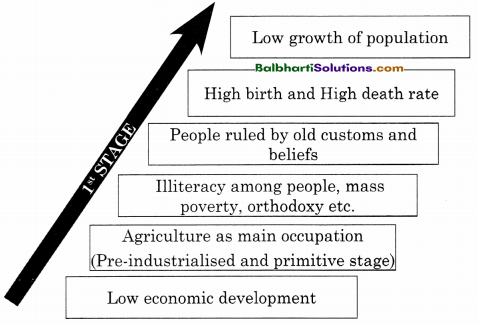
→ Features of 2nd Stage of Demographic Transition.
Experienced by India and other developing countries
↑
Birth rate remained high
↑
Death rate falls rapidly
↑
Improvement in economic development
↑
Introduction of Industrialisation
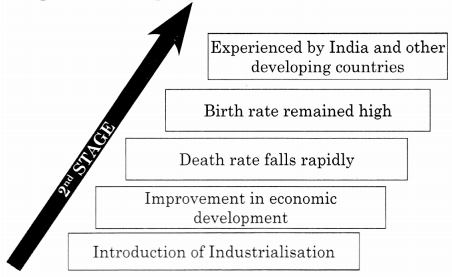
![]()
→ Features of 3rd Stage of Demographic Transition.
Experienced by all developed countries
↑
Stable Population growth
↑
Fall in Birth and Death Rate
↑
Improvement in Literacy rate
↑
Shifting of people from rural to urban
↑
Structure of economy changes
↑
Rapid industrialisation and urbanisation
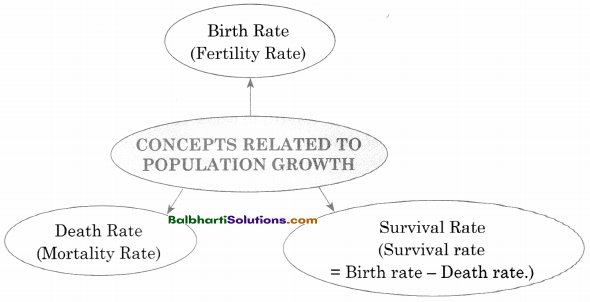
→ Concept related to Population Growth
- Birth rate
(Fertility Rate) - Death Rate
(Mortality Rate) - Survival Rate
(Survival Rate = Birth rate – Death rate)
→ Situation where the growth of population is faster than the growth and development of an economy, it is called as Population explosion.
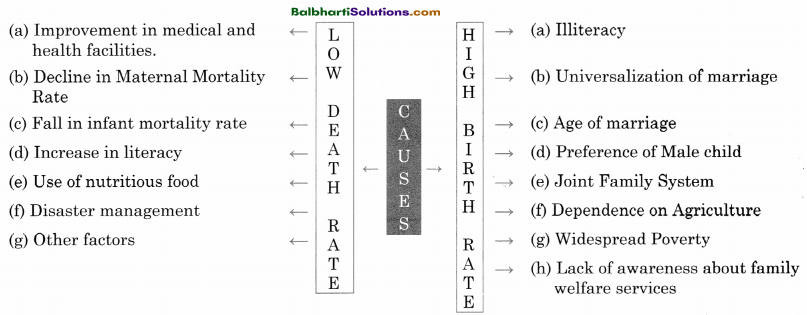
→ Causes:
Low Death Rate:
(a) Improvement in medical and health facilities.
(b) Decline in Maternal Mortality Rate
(c) Fall in infant mortality rate
(d) Increase in literacy
(e) Use of nutritious food
(f) Disaster management
(g) Other factors
High Death Rate:
(a) Illiteracy
(b) Universalization of marriage
(c) Age of marriage
(d) Preference of Male child
(e) Joint Family System
(1) Dependence on Agriculture
(g) Widespread Poverty
(h) Lack of awareness about family welfare services
![]()
→ Effects of Population Explosion:
(a) Increased pressure on land
(b) Increased pressure on agriculture
(c) Pressure on infrastructure and basic amenities
(d) Imbalance between demand for and supply of food
(e) Inflation
(f) Environmental problems
(g) Social problems
(h) Low national income

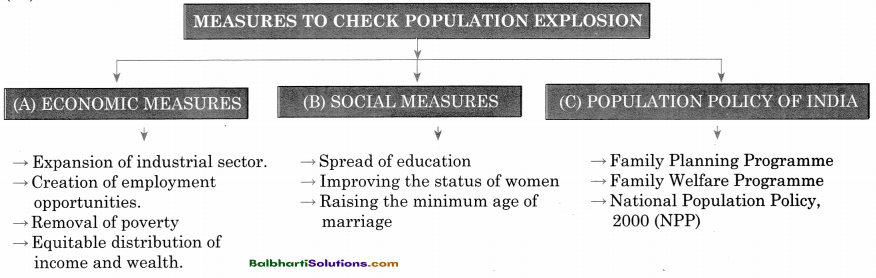
→ Measures To Check Population Explosion:
(A) Economic Measures
(B) Social Measures
(C) Population Policy Of India
(A) Economic Measures
- Expansion of industrial sector.
- Creation of employment opportunities.
- Removal of poverty
- Equitable distribution of income and wealth.
(B) Social Measures
- Spread of education
- Improving the status of women
- Raising the minimum age of marriage
(C) Population Policy Of India
- Family Planning Programme
- Family Welfare Programme
- National Population Policy, 2000 (NPP)
→ Feature Of National Population Policy:
- Free and compulsory education — upto the age of 14 years.
- Reduce infant mortality rate to below 30 per 1000 live births.
- Reduce Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) to below 100 per 1,00,000 live births.
- Universal immunization of children.
- Delayed marriage for girls — preferably from 18 to 20.
- Prevention and control of communicable diseases.
- Achieve a stable population by 2045.
→ Human Resource :
- Population constitutes a nation’s valuable human resource.
- It is not equally distributed all over the world.
- It differs in terms of education, age and sex.
- UNDP — introduced the concept of‘Human Development’ in 1990.
→ Role of human resources in economic development:
- Contributes to reduction in civil disturbances in a society, then increased political stability.
- Contributes to improvement in life expectancy and literacy rate. This improves the quality of life.
- Provision of educational facilities especially among women that contributes to population control.
- Helps to bring about research and development.
- It leads to .increase in human productivity.
- It leads to overall improvement in the society.
Word Meaning:
rapidly – very quickly; epidemics – wide spread of disease at particular time; decadal – a period of 10 years; designated – selected; tremendous – huge; declining – decreasing; propounded – presented; geometric progression – increased in numbers with a constant ratio between each other; arithmetic progression – a sequence of numbers which differs the same from each other; preventive checks – precautionary measures; demographic transition – changes in structure of population; primitive – ancient/old; superstitions – old belief; verge – border; inferences – conclusion; rigid – unable to change; obligations – something one must do as per the law; ignorant – lack of knowledge: optimum – favourable; beliefs – religious feelings or opinion; malnutrition – not having enough food as required; inflation – increase in price; enrichment – improve the quality; mortality – death; life expectancy – expected age of survival; rational – well reasoned; immunization – making a person to immune against infection; orthodoxy – traditional.