Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 2 तूफानों से क्या डरना Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Hindi Solutions Chapter 2 तूफानों से क्या डरना
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 6 Solutions Chapter 2 तूफानों से क्या डरना Textbook Questions and Answers
लेखन विभाग
स्वयं अध्ययन:
दिए गए चित्र को देखकर हाव-भाव की नकल कीजिए:

Answer:
(१) खुशी का भाव
(२) क्रोध का भाव
(३) डर या भय का भाव
(४) हैरानी का भाव
(५) दुख-उदासी का भाव
(६) उपेक्षा का भाव
(७) बेफिक्री का भाव
![]()
खोजबीन:
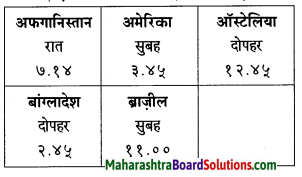
भारतीय स्थानीय समय के अनुसार देश – विदेश के समय की तालिका तैयार कीजिए:
(भारत में रात के ८.१४ बजने पर अन्य देशों का समय)
Answer:
भाषा की ओर:
कविता में आए किन्हीं पाँच शब्दों के विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिखो।
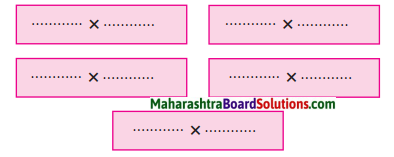
Answer:
(१) अंत x आरंभ
(२) जीवन x मरण
(३) अँधेरा x उजाला
(४) प्यार x नफ़रत
(५) हार x जीत
सुनो तो जराः
छात्र रेडिओ पर एकाग्रता से भजन सुनेंगे और उसे दोहराएंगे।
Answer:
(छात्र स्वयं करेंगे।)
![]()
बताओ तो सही:
साक्षरता अभियान के बारे में जानकारी लिखिए:
Answer:
साक्षरता अभियान भारत सरकार द्वारा शुरू किया गया एक ऐसा उपक्रम है, जिसके माध्यम से देश की अशिक्षित जनता को पढ़ाने-लिखाने एवं साक्षर बनाने का लक्ष्य सामने रखा गया है। इस अभियान के द्वारा समाज का निम्न या गरीब वर्ग जो शिक्षा से या उसके महत्त्व से दूर है, उसे साक्षर करने का भरकस प्रयास भारत सरकार द्वारा किया जा रहा है।
वाचन जगत से:
मीराबाई के पद पढ़िए और उनका सरल अर्थ लिखिए:
(दोहे और पद लेखन)
मतवारे बादल आये रे,
हरी को संदेसो कछु न लाये रे।
दादुर मोर पपीहा बोले,
कोएल सबद सुनावे रे।
काली अंधियारी बिजली चमके,
बिरहिना अती दर्पाये रे।
मन रे परसी हरी के चरण,
लिसतें तो मन रे परसी हरी के चारण।
Answer:
सरल अर्थ: मीराबाई कहती हैं कि बादल गरज – गरज कर आ रहे हैं, किंतु मेरे प्रभु का कोई संदेश नहीं लाये हैं। वर्षा ऋतु में मोर ने अपने पंख फैलाये हैं और कोयल भी मधुर आवाज में गा रही है। काले बादल घिर आए हैं और उनके भीतर बिजली कौंधने से मन अधिक व्याकुल हो रहा है। विरह की आग बढ़ती चली जा रही है। मन केवल प्रभु के दर्शन करने का अभिलाषी है।
![]()
जरा सोचो ….. चर्चा करोः
यदि समय का चक्र रुक जाए तो ….’ विषय पर अपने विचार प्रकट करें। (काल्पनिक लेखन)
Answer:
विद्वानों के कथन के अनुसार ‘समय ही जीवन है। किंतु अगर हम कल्पना करें कि समय अपनी जगह रुक गया तो पूरी सजीव सृष्टि ही रुक जाएगी। सभी पशु-पक्षी, प्राणी, जलचर, प्रकृति की सभी चीजें यहाँ तक कि स्वयं मनुष्य भी अपनी जगह हारकर बैठ जाएगा। समय का पहिया चलता है, इसीलिए तो जीवन निरंतर अबाध गति से चलता रहता है। समय का चक्र रुकने से मनुष्य अपने वर्तमान और भविष्य दोनों से वंचित हो जाएगा। समय के कारण ही मनुष्य अपने जीवन में अग्रसर होते रहता है। समय का चक्र रुकने से पूरे संसार एवं मनुष्य का जीवन थम-सा जाएगा। पूरी दुनिया समय के चक्र के अनुसार ही चलती है।
कविता का सार:
इस कविता का सार लिखिए। (सारांश लेखन)
Answer:
इस कविता का मुख्य सार यह है कि जीवन में मुसीबतें तो आती रहती हैं। उन मुसीबतों का सामना हमें निडर होकर करना चाहिए। हमारे भीतर के घमंड़ रूपी अहंकार को हमें समाप्त कर परस्पर सहयोग से आगे बढ़ना चाहिए। नफ़रत को छोड़कर प्रेम-भाव से सबको गले लगाना चाहिए।
सदैव ध्यान में रखिए:
हमारी सोच सकारात्मक क्यों होनी चाहिए? (अनुच्छेद लेखन)
Answer:
मानव का मन अत्यंत चंचल होता है। उसमें कई विचार आते जाते रहते हैं, किंतु मनुष्य को हमेशा अपनी सोच सकारात्मक रखनी चाहिए। सकारात्मक सोच हमेशा अच्छे विचारों को जन्म देती है। इसके विपरीत नकारात्मक सोच मन में बुरे विचार पैदा कर मनुष्य के विकास में बाधा का निर्माण करती है। कई विद्वानों के अनुसार सकारात्मक सोच सामाजिक विकास के साथ-साथ मनुष्य का मानसिक एवं सर्वागीण विकास भी करती है।
विचार मंथन:
करत – करत अभ्यास के जड़मति होत सुजान। (अनुच्छेद लेखन)
Answer:
प्रस्तुत पंक्ति का अर्थ यह है कि निरंतर प्रयल एवं अभ्यास करने से बुद्धिहीन या मूर्ख व्यक्ति भी चतुर बन सकता है। निरंतर किसी भी कार्य में कार्यरत रहने से मनुष्य अपने लक्ष्य को प्राप्त कर सकता है।
![]()
अध्ययन कौशलः
समाज सेवी महिला की जीवनी पढ़कर प्रेरणादायी अंश को चुनकर लिखिए एवं बताइए। (मदर टेरेसा की जीवनी)
Answer:
मदर टेरेसा के जीवन के प्रेरणादायी अंश निम्नलिखित हैं –
- मदर टेरेसा के द्वारा कोई निर्धन खाली हाथ नहीं गया।
- स्वयं को मिले सारे पुरस्कार गरीबों के नाम स्वीकार किए।
- मदर टेरेसा ने ८ अगस्त, १९४८ को तीन साड़ियाँ और पाँच रुपये का एक नोट लेकर, मानवता की सेवा शुरू की।
- एक भिक्षु की दी हुई भेंट उन्होंने केवल उसकी भावना को ठेस न पहुँचे इसके लिए स्वीकार की।
- टीटागढ़ के कुष्ठ – सेवा केंद्र में कुष्ठरोगियों की नज़दीक से सेवा की।
- समाज में स्थित निम्न, गरीब, पीड़ा से कराहते लोगों की पीड़ा को दूर किया।
- ‘मैं तो प्रभु के हाथ की एक पेंसिल मात्र हूँ। यह उनका ही कार्य है।’ यह कहकर वे जीवन भर समाज के हित में कार्य करती रहीं।
समझो हमें:
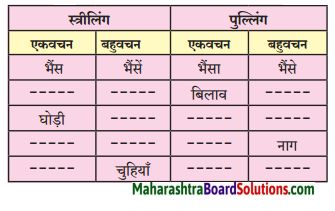
पंचमाक्षर (ङ, अ, ण, न, म) के अनुसार पंतगों में उचित शब्दों की जोड़ियाँ मिलाइए:
Answer:
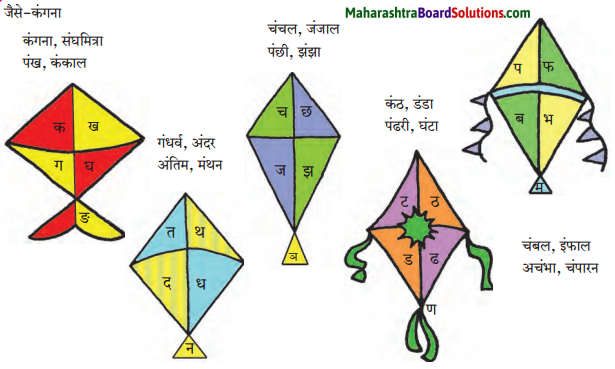
![]()
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 6 Solutions Chapter 2 तूफानों से क्या डरना Additional Important Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित कविता की पंक्तियों को पूर्ण कीजिए:
Question 1.
धूप – छाँव जीवन का हिस्सा, ……….
Answer:
कभी उजाला, कभी अँधेरा
Question 2.
…………………, दूर अँधेरा करना जी।
Answer:
आत्मज्ञान के दीप जलाकर
Question 3.
तूफाँ तो आते रहते हैं, ……………………।
Answer:
इनसे भी क्या डरना जी
Question 4.
…………, जीवन में रंग भरना जी।
Answer:
सत्कर्मों की तूलिका से
Question 5.
नफ़रत करना नहीं किसी से, …..
Answer:
प्यार सभी से करना जी
![]()
निम्नलिखित वाक्य सही हैं या गलत लिखिए:
Question 1.
जीवन में हमेशा सुख-दुख आते रहते हैं।
Answer:
सही
Question 2.
समय हमेशा बदलता रहता है।
Answer:
सही
Question 3.
जीवन में आनेवाली मुसीबतों से हमें डरना चाहिए।
Answer:
गलत
Question 4.
हमें जो मिलता है, उसी में हमें संतोष रखना चाहिए।
Answer:
सही
Question 5.
हमें सभी से नफ़रत करनी चाहिए।
Answer:
गलत
![]()
निम्नलिखित शब्दों का वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए:
Question 1.
हिम्मत
Answer:
कठिन प्रसंग में मनुष्य को अपनी हिम्मत नहीं हारनी चाहिए।
Question 2.
नफ़रत
Answer:
हमें किसी से भी नफ़रत नहीं करनी चाहिए।
Question 3.
सत्कर्म
उत्तरः
मनुष्य को हमेशा सत्कर्म करने चाहिए।
Question 4.
धीरज
Answer:
मुसीबत के समय हमें अपना धीरज नहीं खोना चाहिए।
Question 5.
अभिमान
Answer:
हमें अपने देश पर अभिमान होना चाहिए।
![]()
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक-एक वाक्य में लिखिए:
Question 1.
कवयित्री ने जीवन में किससे न डरने की बात कही है?
Answer:
कवयित्री ने जीवन में तूफान रूपी मुसीबतों से न डरने की बात कही है।
Question 2.
जीवन कौन-सा खेल है?
Answer:
जीवन हार-जीत का खेल है।
Question 3.
मनुष्य को अपना जीवन कैसे व्यतीत करना चाहिए?
Answer:
मनुष्य को अपना जीवन हँसकर व्यतीत करना चाहिए।
Question 4.
रात के बाद क्या आता है?
Answer:
रात के बाद हमेशा सवेरा आता है।
![]()
Question 5.
प्रत्येक मनुष्य की एक-दूसरे के प्रति ज़िम्मेदारी क्या है?
Answer:
एक-दूसरे को सच्ची राह दिखाना प्रत्येक मनुष्य की ज़िम्मेदारी
Question 6.
कवयित्री ने कौन-सा दीप जलाने के लिए कहा है?
Answer:
कवयित्री ने आत्मज्ञान का दीप जलाने के लिए कहा है।
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर दो-तीन वाक्यों में लिखिए:
Question 1.
हम अपने जीवन में किस प्रकार खुशहाली ला सकते
Answer:
हम अपने जीवन में अच्छे कर्म करके तथा दूसरों की मदद करके खुशहाली ला सकते हैं।
Question 2.
मनुष्य को अपने जीवन में धीरज क्यों धरना चाहिए।
Answer:
मनुष्य को अपने जीवन में धीरज इसलिए धरना चाहिए, क्योंकि मनुष्य के जीवन में आने वाला समय हमेशा एक जैसा नहीं रहता। सब्र का फल हमेशा मीठा ही होता है। दुःख के बाद सुख आता है। यही जीवन की रीत है।
![]()
Question 3.
समाज में महामारी क्यों फैली हुई है?
Answer:
समाज मे महामारी मनुष्य के स्वयं के गलत कार्य और अभिमान के कारण फैली हुई है।
व्याकरण और भाषाभ्यास
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए:
- दिन
- खुश
- हिस्सा
- समय
- राह
Answer:
- दिवस
- प्रसन्न
- भाग
- काल
- रास्ता
![]()
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के समान तुक वाले (लयात्मक) शब्द लिखिए:
- हिम्मत
- खेल
- हाथ
- डरना
- सच्ची
Answer:
- कीमत
- भेल
- साथ
- मरना
- कच्ची
![]()
निम्नलिखित वर्णों को सही स्थान पर रखकर अर्थपूर्ण शब्द तैयार कीजिए:
- दमद
- बजीन
- सहकर
- जाउला
- मयस
- महारीमा
Answer:
- मदद
- जीवन
- हँसकर
- उजाला
- समय
- महामारी