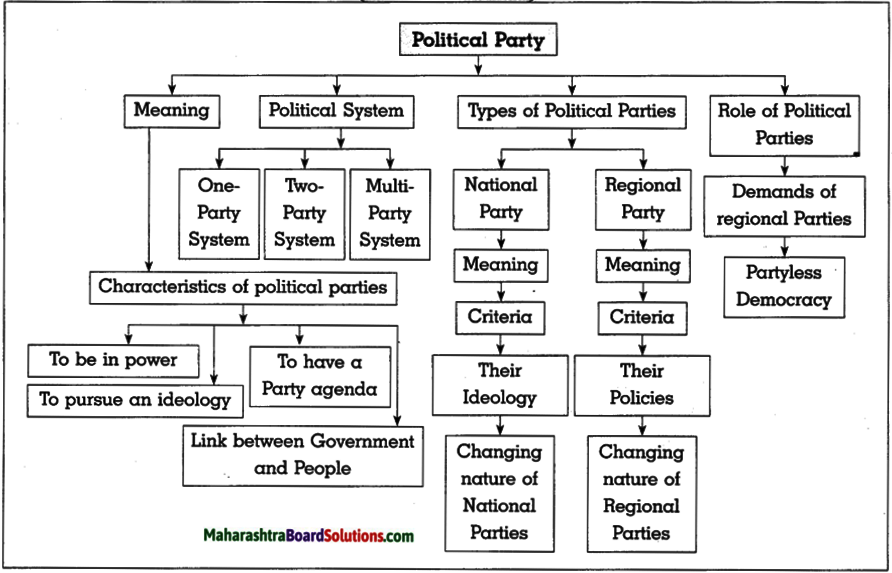
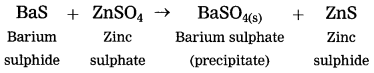
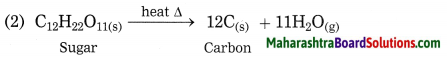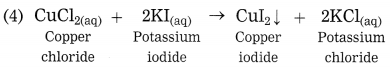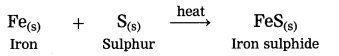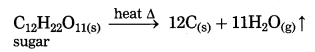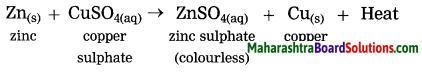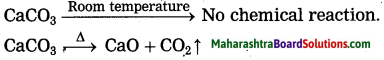Std 10 Geography Chapter 6 Question Answer Population Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Population Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Population Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Geography Class 10 Chapter 6 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
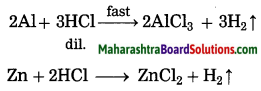
1. Are the following sentences right or wrong? Correct the wrong ones.
Question a.
Literacy rate is higher in Brazil than India.
Answer:
Right.
Question b.
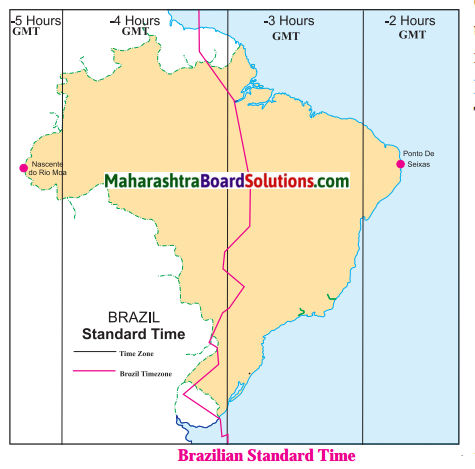
In Brazil, people prefer living in the south east as compared to the north east.
Answer:
Right.
![]()
Question c.
The life expectancy of Indians is decreasing.
Answer:
Wrong.
Question d.
The north-western part of India is densely populated.
Answer:
Wrong.
Question e.
The western part of Brazil is densely populated.
Answer:
Wrong
![]()
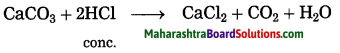
2. Answer the following questions as per the instructions:
Question a.
Arrange the following states of India in descending order of their population. Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
Descending order: Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh.
Question b.
Arrange the states of Brazil in ascending order of their population: Amazonas, Rio de Janeiro,
Alagoas, Sao Paulo, Parana.
Answer:
States of Brazil: Alagoas, Amazonas, Parana, Rio de Janeiro, Sao Paulo.
Question c.
Classify the factors affecting the distribution of population into favourable and unfavourable.
Answer:
| Favourable Factors | Unfavourable Factors |
| (1) Nearness to Sea | Lack of roads |
| (2) Temperate Climate | Lack of Industries |
| (3) New cities and towns | Tropical moist forests |
| (4) Minerals | Semi arid climate |
| (5) Cultivable land |
![]()
3. Answer the following questions:
Question a.
Explain the similarities and differences between the population distribution in Brazil and India.
Answer:
(a) Similarities in population distribution in Brazil and India:
- In Brazil as well as in India, population is very unevenly distributed.
- Inaccessible dense forests and absence of facilities are the barriers to human settlements.
- North, north west and north east of both the countries are the regions of low population.
- Population is concentrated in flat fertile regions which have abundant water resources, transport facilities, mild climate and development of agriculture industries and trade in the plain region.
- Coastal regions are densely populated in Brazil and in India.
(b) Differences between population distribution in Brazil and India.
- The average density of population in India is 382 persons per sq.km, and that of Brazil is about 23 persons per sq.km.
- Though the area of both the countries is occupied by vast river basins, the distribution of population is extremely opposite in both the river basins.
- The Amazon River Basin is sparsely populated while the Ganga River Basin is densely populated.
Question b.
Giving examples, correlated to, climate and population distribution
Answer:
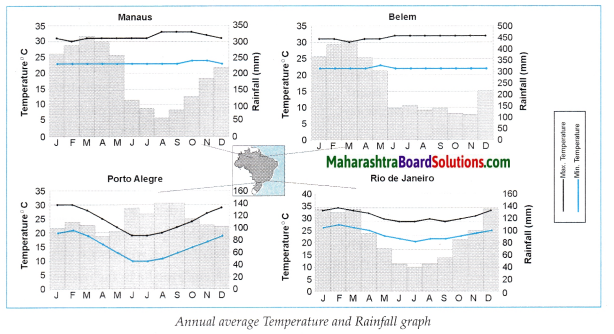
Climate and population distribution are closely interreleted. Temperature and rainfall, the two elements of climate greatly influence the population concentration.
(i) Dense population is found in regions with mild climate and moderate rainfall.
E.g. the coastal plains of Brazil, the northern plain as well as the coastal plains of India
(ii) Places with heavy rainfall, inaccessibility and dense forests have low population.
E.g. the interiors of the Amazon Basin in Brazil, north eastern states in India.
(iii) The snow covered regions due to extremely cold climatic conditions have less population.
E.g. the northernmost part of Jammu & Kashmir.
(iv) In certain regions, due to less rainfall and extreme climatic conditions population is sparse.
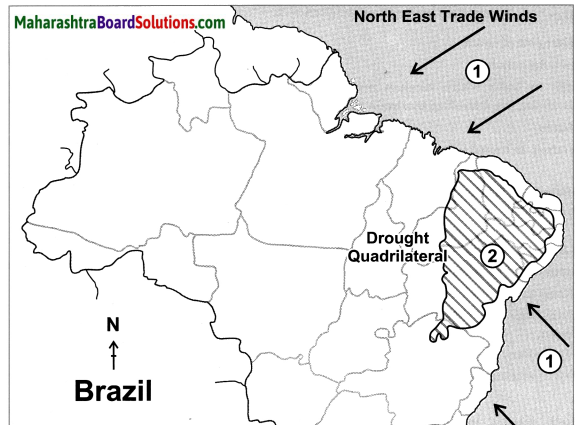
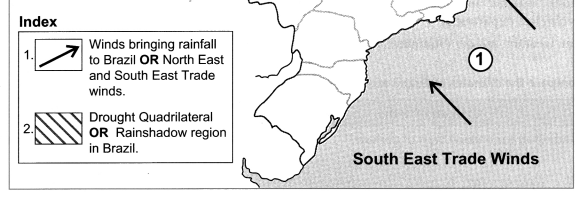
E.g. Thar desert of Rajasthan and the Drought Quadrilateral region of Brazil.
4. Give geographical reasons:
Question a.
Population is an important resource.
Answer:
- The qualitative aspects of a population are important for a nation’s economic and social progress.
- Natural resources of any country gets utilised properly because of the population.
- Economic growth and development will be slow if population resource is not utilised properly.
- Thus an optimum and quality population can bring about a country’s development.
Question b.
Brazil’s population density is very less.
Answer:
- Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world with respect to area and has a population of about 19 crores (Census 2010).
- It occupies 5.6% of world’s total land area and accounts for only 2.78% of the world’s total population.
- Thus Brazil occupies more percent of world’s land and less percent of world’s total population. Therefore,
- the density of population is very less in Brazil, i.e. around 23 persons per sq.km.
Question c.
India’s population density is high.
Answer:
- India is the second most populous country in the world, with a population of about 121 crores (Census 2011).
- India occupies only 2.41% of the land area of the world, but supports 17.5% of the world’s population.
- Thus India has less percent of world’s land and supports high percent of world’s population.
- Hence, India’s average population density is high i.e. 382 persons per sq. km.
Question d.
The density of population is sparse in the Amazon Basin.
Answer:
- The interior part of the Amazon Basin has a very unfavourable hot and humid climate.
- It receives heavy rainfall of nearly 2000 mm and has dense inaccessible forests.
- Transportation, agricultute and industries are not well developed here.
- All these factors are barriers to the development of human settlements.
- So, the density of population is sparse in the Amazon Basin.
Question e.
Population density is high in the Ganga plains.
Answer:
- Ganga plains are fertile low lying plains formed due to the deposition work of River Ganga and its tributaries.
- Mild climate, moderate rainfall and fertile soil have led to the development of agriculture and industries.
- This region also has a dense network of roadways and railways.
- So, the population density is high in the Ganga Plains.
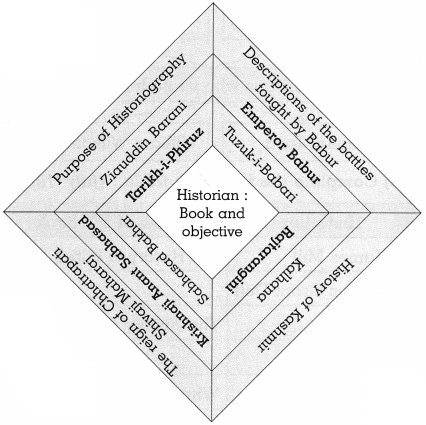
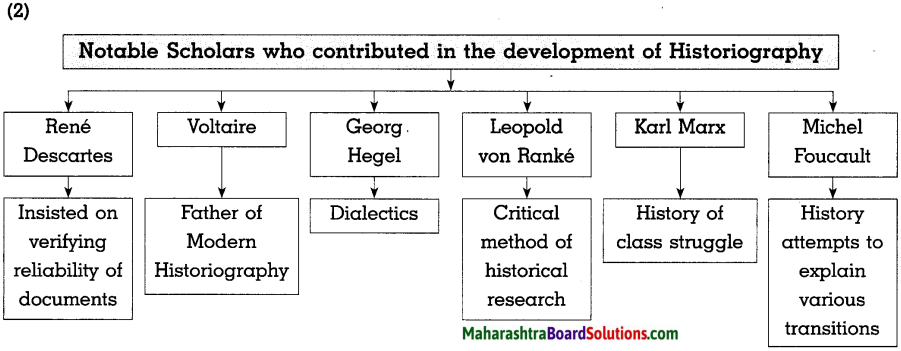
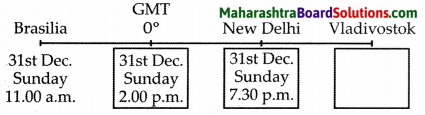
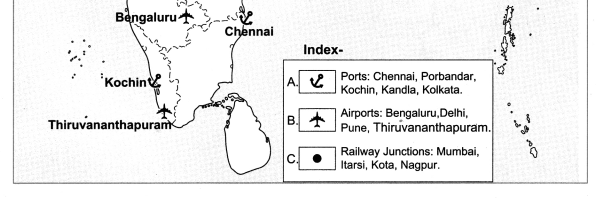
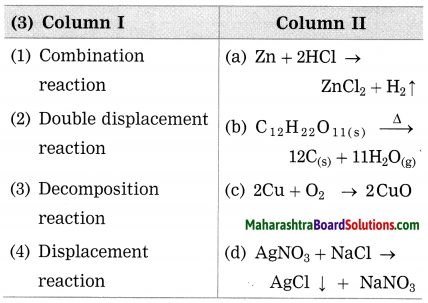
5. Observe the following diagram and answer the following questions:
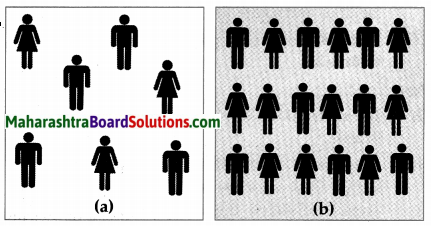
Question 5A.
Compare and classify the population densities shown in the figure ‘a’ and ‘b’ representing 1 sq. km. of area.
Answer:
In the fig. (a) density of population is 7 persons per sq. km. The region is sparsely populated.
In the fig. (b), the density of population is 18 persons per sq. km. The region is densely populated.
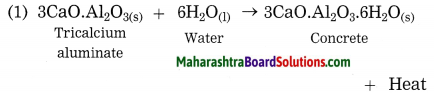
Question 5B.
If in figure B one sign = 100, then what will be the sex ratio?
Answer:
One symbol = 100 persons
There are 10 female symbols.
Number of females = 100 x 10
= 1000
There are 8 male symbols
Number of males = 100 x 8
= 800
| Males | 800 | 1000 |
| Females | 1000 | ? |
Number of females = \(\frac { 1000 X 1000 }{ 800 }\)
= 1250
Sex Ratio is 1250 females per 1000 males.
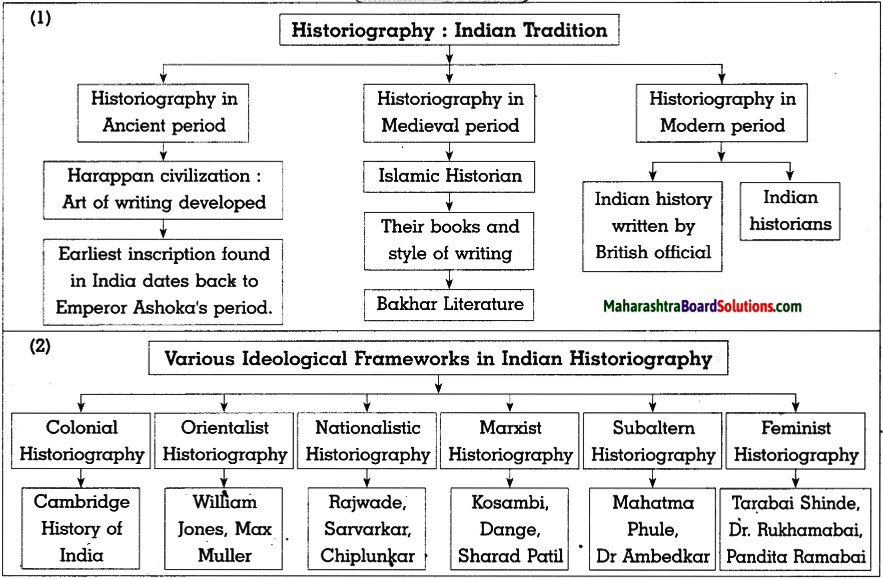
Question 6.
Comment upon the population density of fig (b).
(i) fig (b) shows the population density of India as per 2011.
(ii) The density of population is divided into four categories. They are:
(a) Less than 100 persons per sq.km. .
(b) 101-250 persons per sq.km.
(c) 251-500 persons per sq.km.
(d) more than 500 persons per sq.km.
Answer:
| S.No. | Population Density (per sq.km.) | Name of the States / Union Territories |
| (1) | less than 100 | Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim. |
| (2) | 101 to 250 | Meghalaya, Manipur, Nagaland, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chattisgarh. |
| (3) | 251 to 500 | Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha, Jharkhand, Assam, Tripura. |
| (4) | more than 501 | West Bengal, Bihar, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh,Kerala and Tamil Nadu, Delhi, Chandigarh, Puducherry, Diu, Daman, Dadra Nagar, Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands. |
![]()
Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Population Intext Questions and Answers
Study the maps and answer the following questions
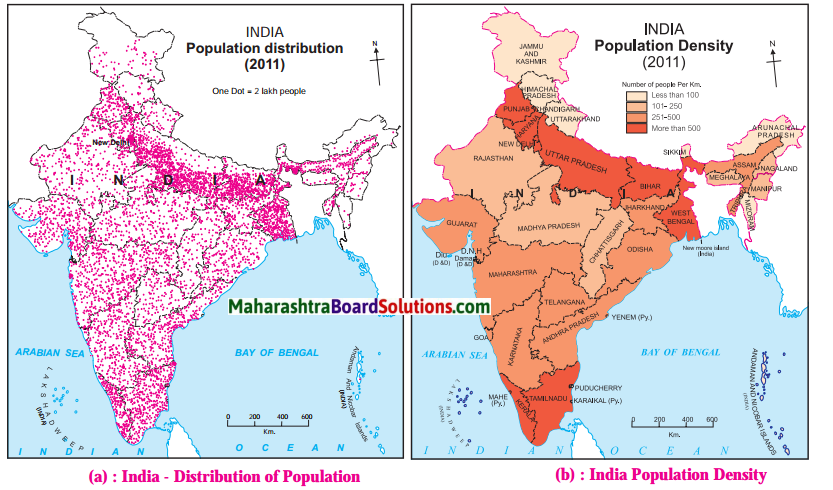
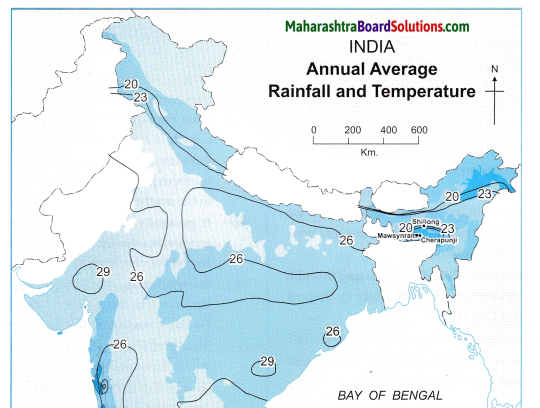
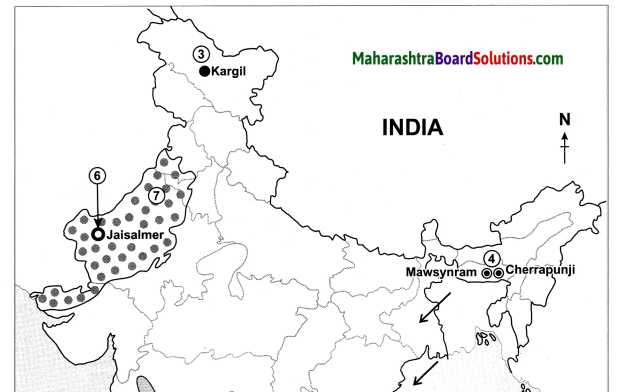
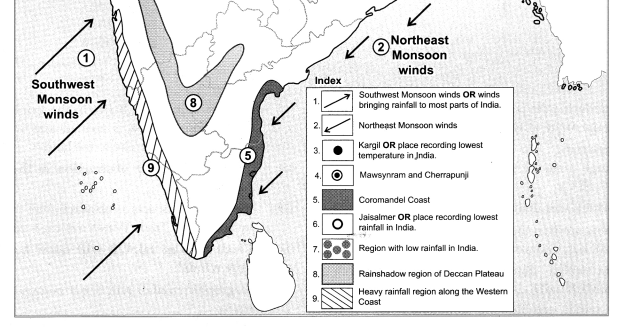
Question 1.
States with the highest population density.
Answer:
West Bengal, Bihar, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
Question 2.
On the basis of maps given above, classify the distribution population in India in the following table.
Answer:
| S.No. | Population Density (per sq.km.) | Name of the States / Union Territories |
| (1) | less than 100 | Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim. |
| (2) | 101 to 250 | Meghalaya, Manipur, Nagaland, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chattisgarh. |
| (3) | 251 to 500 | Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha, Jharkhand, Assam, Tripura. |
| (4) | more than 501 | West Bengal, Bihar, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, Delhi, Chandigarh, Puducherry, Diu, Daman, Dadra Nagar, Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands. |
Question 3.
States with lowest population density.
Answer:
Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Mizoram.
Question 4.
Correlate the climate and physiography of India with its population distribution and write a note on it.
Answer:
(i) Climate and population distribution are closely inter-related.
(ii) Temperature and rainfall are the two elements of climate which greatly influence the population distribution.
(iii) Dense population is found in regions with mild climate and moderate rainfall.
E.g. the northern plain as well as the coastal plains of India
(iv) Places with heavy rainfall, inaccessibility and dense forests have low population.
E.g. northeastern states in India.
(v) The snow-covered regions due to extremely cold climatic conditions have less population.
E.g. the northernmost part of Jammu and Kashmir.
(vi) In certain regions, due to less rainfall and extreme climatic conditions population is sparse.
E.g. Westernmost part of India in the Thar desert, Rajasthan.
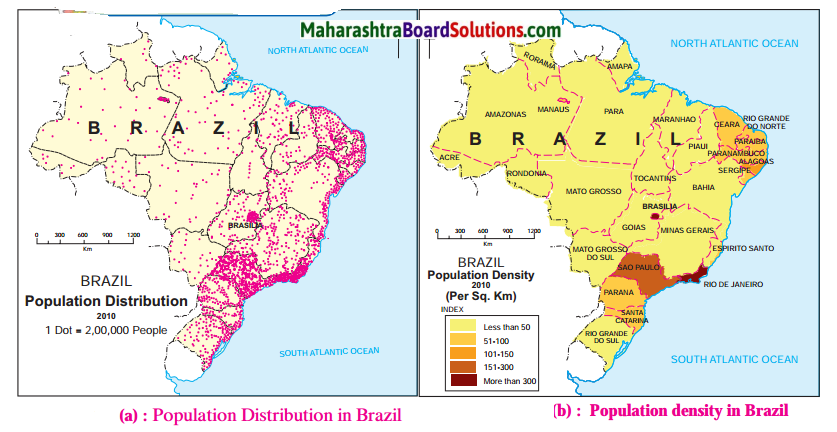
![]()
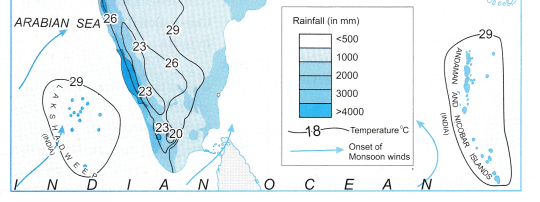
Question 1.
In which area is population greatly concentrated?
Answer:
Population is greatly concentrated in the south eastern part of Brazil.
Question 2.
In which area is the distribution of population sparse?
Answer:
The Amazon Basin in the nothern part and the central and western parts of Brazil have sparse distribution of population.
Question 3.
Prepare a note on factors responsible for the uneven distribution of population based on the study of Brazil you have made so far.
Answer:
The distribution of population in Brazil is uneven:
- There is sparse population in the Amazon Basin due to hot and humid climate, heavy rainfall, dense forests, inaccessibility.
- The population is low in the swampy areas of Pantanal.
- Low population is found in the central and western part of Brazil due to lack of minerals, low rainfall, hot and dry climatic conditions.
- The distribution of population is moderate in Brazilian Highlands.
- High population is found in the coastal regions and the southern part of Brazil. This is due to flat fertile land and abundant availability of minerals due to which agriculture, industries and trade have developed.
Question 4.
Identify the type of map showing distribution fig. (a) of textbook.
Answer:
The type of map showing distribution of population is a dot map.
Question 5.
On the basis of the map (b), classify the distribution of population in Brazil in the following table.:
| S. No. | Population Density | Names of the places |
| (1) | Less than 50 | Acre, Amazonas, Roraima, Rondonia, Para, Amapa, Mata Grasso, Mato Grasso Do Sul, Goias, Tocantins, Maranhao, Piaui, Bahia, Minas Gerais, Rio Gande Do Sul |
| (2) | 51 -100 | Paraiba, Pamambuco, Parana, Santa Catarina, Sergipe, Rio Grande Do Norte, Ceara |
| (3) | 101 -150 | Alagoas |
| (4) | 151 – 300 | Sao Paulo |
| (5) | More than 300 | Rio de Janerio, Brasilia |
USE YOUR BRAIN POWER
Question 1.
Calculate the population density of the area shown in 1 sq.km, of square in ‘a’ and ‘b’ each
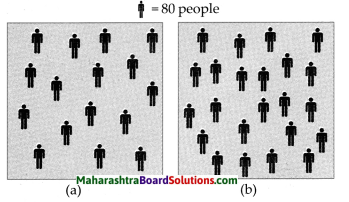
Answer:
(a) In fig. (a) there are 16 ![]()
Each ![]() = 80 people
= 80 people
Total number of people = 16 x 80 = 1280
Fig. (a) has a population density of 1280 people per sq. km.
(b) In fig. (b) there are 23 ![]()
Each ![]() = 80 people
= 80 people
Total number of people = 23 x 80 = 1840
Fig. (b) has a population density of 1840 people per sq. km.
![]()
GIVE IT A TRY
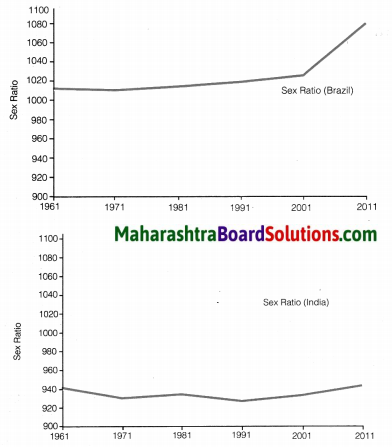
Question 1.
What could be the reasons of lower sex ratio in any region?
Answer:
With reference to both the countries, the characteristics of population are prominently notable.
- The sex ratio of Brazil has been more than 1000 since decades.
- Considering the sex ratio of Brazil, the number of women have considerably increaesed than men since 2001.
- In India men outnumber women.
- In India we see fluctuations in the sex ratio since few decades. There has been a slight increase in the sex ratio after 1991.
Question 2.
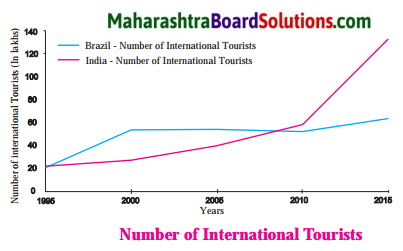
Write a similar conversation using the graph
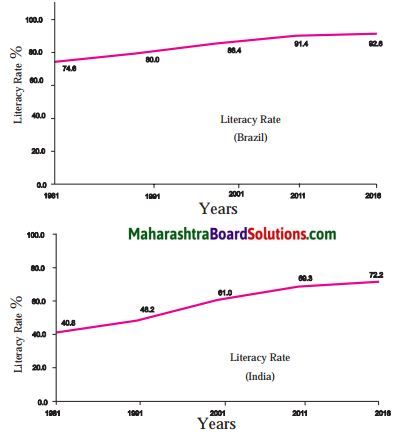
Answer:
A: What do these graphs show?
B: These graphs show the literacy rate of India and Brazil.
A: What do you mean by literacy rate?
B: It means the total percentage of the population of an area at a particular time aged seven years or above ‘ who can read and write with understanding.
A: It means that, as on today’s date, the literacy rate of our country is 72.2%.
B: But, Brazil had an even higher literacy rate decades back in 1981, i.e. 74.6% and it has touched 92.6 as of today (2018), which is quite commendable.
A: Yes, definitely But, we have also seen a steady growth in the literacy rate of the country, especially, during the period between 1991 and 2011.
B: Still, though we are growing, we are way behind Brazil today with 72.2% because they have a much higher literacy percentage of 92.6.
A: What measures can be adopted to increase the literacy rate of our country?
B: We can make people aware of the need and importance of education, help in teaching them, introducing various literacy campaigns by making use of free calls, free sms services, etc.
Question 3.
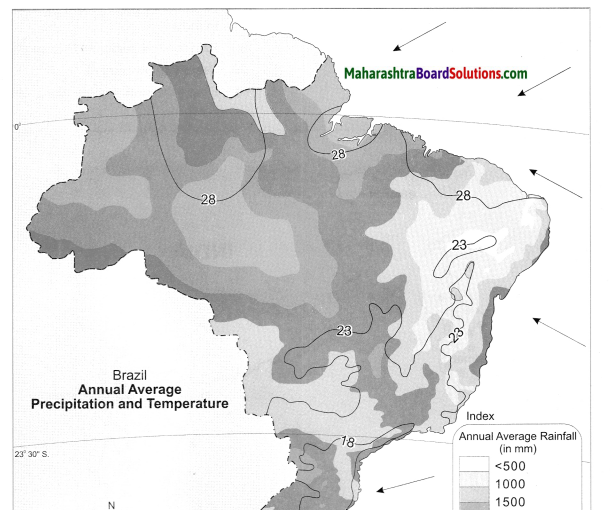
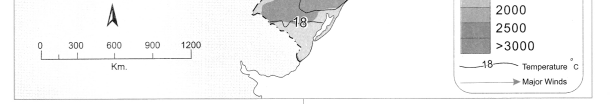
Study the indices of density maps of both the countries. What difference do you find? What conclusions can you draw?

Answer:
(i) India’s density of population is proportionately catered while Brazil’s density of population is concentrated only on the eastern coast.
(ii) After studying the indices of the density maps of both the countries, we can conclude that India’s population density is much higher than that of Brazil.
(iii) The lowest value on the map of India indicates less than 100 whereas on the Brazil map it is less than 50.
(iv) Places in Brazil which are highest in density is grouped in the category of more than 300 people’ per sq. km. whereas in India it is more than 500 persons per sq. km.
![]()
Question 4.
Considering the above discussion, what should be done so that our manpower is utilized properly, sex ratio improves and population growth is controlled? Write two to three sentences on each.
Answer:
(i) Measures to utilise man power properly:
- Good education, health and training facilities are the basic requirements to improve human resources.
- The focus of education should not just be to chum out jobseekers but also to chum out job creators.
- The young population should be encouraged to be entrepreneurs.
(ii) Measures to improve sex ratio:
- Build an environment to save and protect the girl child.
- Ban sex determination test.
(iii) Measures to control population growth:
- Family planning measures to be encouraged through media.
- Spread of education among illiterate masses, especially about the benefits of having a small family.
- Child marriage should be strictly prohibited.
TRY THIS
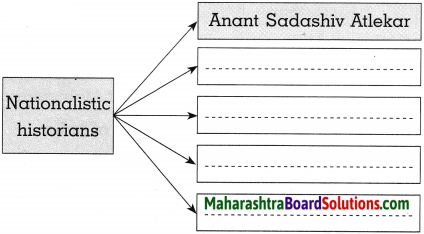
Age and Sex Pyramid:
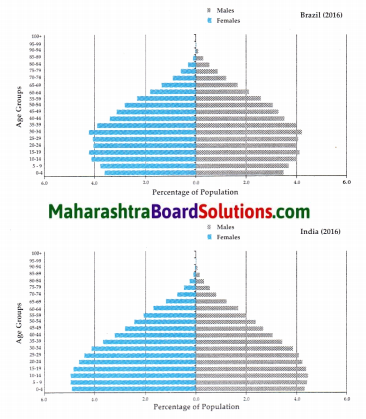
Question 1.
What is this figure called? What is it always known as?
Answer:
The figure is called the Age-Sex Pyramid. It is also known as Population Pyramid.
Question 2.
What does the graph depict?
Answer:
The graph depicts the percentage of male and female population of various age groups in Brazil & India for the year 2016.
Question 3.
In which country is the proportion of adults more?
Answer:
The proportion of adults is comparatively more in India.
Question 4.
‘This country’s population is getting slowly older’. Which country is being referred to? Why?
Answer:
‘This country’s population is getting slowly older – The country being referred to is Brazil. As compared to India, a larger percentage of Brazil’s population falls in the above 60 years age group. So it is said that Brazil’s population is getting slowly older.
Question 5.
In which country are the number of children comparatively more?
Answer:
The proportion of children is comparatively more in India.
Question 6.
While comparing the age-sex pyramids, which pyramid has a broader base?
Answer:
While comparing the age-sex pyramids, India’s pyramid has a broader base.
![]()
USE YOUR BRAIN POWER
Question 1.
Is there a relationship between increase in life expectancy and growth of population ? How?
Answer:
(i) Yes, there is a relationship between increase in life expectancy and growth of population.
(ii) Increased life expectancy means there are more people who live longer, which means healthier and better quality of life.
(iii) This kind of population generally prefers fewer children which leads to decreased birth rates.
Question 2.
If the proportion of dependent age groups increases in the composition of population, how will it affect the economy of a country?
Ans.
(i) If the proportion of dependent age groups increases in the composition of population, it will have an adverse effect on the economy of a country.
(ii) The reason is if the working population is less, the economic activities will reduce and will have a direct impact on the economic growth and development of that nation.
(iii) The production will decrease in comparison to consumption leading to inflation also the per capita income and GDP will decrease.
(iv) Export will reduce and imports will increase.
(v) The proportion of the working population will increase, slowing down the pace of development.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Population Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct option and rewrite the statements:
Question 1.
The ______ aspects of a population are important for a nation’s economic and social progress.
(a) quantitative
(b) qualitative
(c) measurable
(d) calculable
Answer:
(b) qualitative
Question 2.
India is the ________ most populous country in the world.
(a) second
(b) fifth
(c) seventh
(d) sixth
Answer:
(a) second
Question 3.
Due to farming, industries and trade, the proportion of the population got in _____ a few places.
(a) distributed
(b) sparse
(c) concentrated
(d) equal
Answer:
(c) concentrated
Question 4.
In mountainous / hilly regions, dry desert areas and densely forested areas, population density is __________ because of inaccessibility, absence of facilities and tough life.
(a) high
(b) very high
(c) sparse
(d) moderate
Answer:
(c) sparse
![]()
Question 5.
Brazil is the _______ populated country in the continent of South America.
(a) second most
(b) third most
(c) fifth most
(d) most
Answer:
(d) most
Question 6.
With a population of around 19 crores, according to Census 2010, Brazil ranks _______ in the world.
(a) 3rd
(b) 5th
(c) 7th
(d) 9th
Answer:
(b) 5th
Question 7.
With respect to area, Brazil stands _______ in the world.
(a) 3rd
(b) 5th
(c) 7th
(d) 9th
Answer:
(b) 5th
Question 8.
A majority of Brazilians have concentrated within 300 kilometers of the ________.
(a) Guyana highlands
(b) Amazon river,
(c) Eastern coastal areas
(d) Pantanal wetlands
Answer:
(c) Eastern coastal areas
Question 9.
The interior of the Amazon basin is ____ populated.
(a) densely
(b) moderately
(c) highly
(d) very sparsely
Answer:
(d) very sparsely
Question 10.
The central and western parts of Brazil is ______ populated.
(a) densely
(b) sparsely
(c) moderately
(d) less
Answer:
(d) less
Question 11.
The density of population in the _______ of Brazil is moderate.
(a) Amazon Basin
(b) coastal lowlands
(c) highlands
(d) forested areas
Answer:
(c) highlands
Question 12.
In India, there has been a _______ in the sex ratio, after 1991.
(a) decrease
(b) slight increase
(c) consistency
(d) steep increase
Answer:
(b) slight increase
Question 13.
The proportion of _______ in India is more.
(a) middle-aged people
(b) old people
(c) children
(d) youth
Answer:
(d) youth
Question 14.
The rate of population growth is now ______ in India.
(a) increasing
(b) declining
(c) stable
(d) stagnant
Answer:
(b) declining
![]()
Question 15.
It is observed that Brazil’s population may not increase in the next ______ decades.
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
Answer:
(a) two
Question 16.
The eastern coastal areas of Brazil are also called the coastal ________.
(a) lowlands
(b) highlands
(c) ravines
(d) badlands
Answer:
(a) lowlands
Question 17.
In most of the developing countries life expectancy is still less, but with socio economic development it is ________.
(a) decreasing
(b) increasing
(c) gradually declining
(d) steeply increasing
Answer:
(b) increasing
Match the columns:
| S.No | Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) | Coastal lowlands | (a) sparsely populated |
| (2) | Amazon Basin interior | (b) moderately populated |
| (3) | Highlands | (c) densely populated (within 300 kms. of the area) |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – a
3 – b
Answer the following questions in one or two sentence.
Question 1.
According to Census 2011, what is India’s population and how much is its average population density?
Answer:
According to Census 2011 India’s population is around 121 crores, and its average population density is 382 persons per sq. km.
Question 2.
What percentage of the total land area of the world is occupied by India and Brazil?
Answer:
India occupies only 2.41% of the land area of the world, whereas Brazil occupies 5.6% of the world’s total land area.
Question 3.
What is the difference in the percentage of the world population supported by India and Brazil?
Answer:
India supports 17.5% of the world’s population, whereas Brazil supports 2.78% of the world’s total population. The difference is 14.72% (India has a large population than Brazil)
Question 4.
According to Census 2010, what is the total population of Brazil and what is its average population density?
Answer:
According to Census 2010, Brazil’s total population is around 19 crores and its average population density is 23 persons per sq. km.
Question 5.
What is sex ratio?
Answer:
Sex ratio means, the number of females per 1000 males in a region.
Question 6.
What is a population pyramid?
Answer:
A population pyramid, also called age-sex pyramid, is a graphical illustration that shows the age and sek/gender related aspects of various age groups in a population.
![]()
Question 7.
How is the population pyramid useful? OR State the uses of a population pyramid.
Answer:
- The population pyramid is used to study the age and sex related aspects of a region’s population
- We can know the number/percentage of various age groups of males and females in a country.
- It also helps us to know the proportion of children, youth and old people in a country.
Question 8.
What is life expectancy?
Answer:
Life expectancy means the average number of years, a person born in a country is expected to live.
Question 9.
Which factors lead to an increase in average life expectancy?
Answer:
Improvement in medical facilities, progress in the medical field and access to nutritious food lead to an increase in average life expectancy.
Name the following:
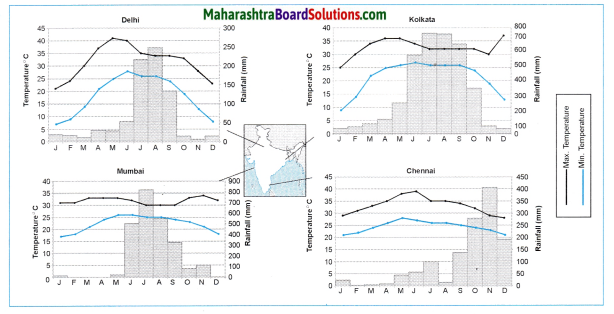
Question 1.
Indian cities that are densely populated.
Answer:
Delhi, Kolkata, Mumbai, Pune, Bengaluru, Chennai.
Question 2.
Factors that play an important role in the distribution of population.
Answer:
Physiography and climate.
Question 3.
Factors due to which human settlements have been established for many centuries.
Answer:
Fertile land, plain land and availability of water.
Question 4.
Factors due to which population got concentrated in a few places, in India.
Answer:
Farming, industries and trade.
Question 5.
Areas which have sparse population density in India.
Answer:
Mountainous / hilly regions, dry desert areas, dense forest areas.
Question 6.
Factors due to which population density is sparse in a few areas.
Answer:
Inaccessibility, absence of facilities and tough life.
Question 7.
The most populated country in South American.
Answer:
Brazil.
Question 8.
Brazil’s rank in the world with regard to population as well as land area.
Answer:
Fifth.
Question 9.
The part of Brazil has the maximum concentration of population
Answer:
Eastern coastal areas or coastal lowlands.
Question 10.
The part of Brazil that is sparsely populated.
Answer:
Amazon River Basin.
Question 11.
The region of Brazil that is moderately populated.
Answer:
The Highlands.
Question 12.
The parts of Brazil that are less populated.
Answer:
Central, western and interior of Amazon basin.
Question 13.
Out of Brazil and India, the country where men outnumber women.
Answer:
India.
Question 14.
Increase in this factor is an indicator of development of that society.
Answer:
Life expectancy, Sex Ratio and Literacy Rate.
Question 15.
The development of this aspect of an economy leads to an increase in average life expectancy.
Answer:
Socio-economic development.
![]()
Are the following sentences right or wrong?
Question 1.
India is the fifth most populous country in the world.
Answer:
Wrong.
Question 2.
India’s average population density is 832 persons per sq. km. as per the 2011 Census.
Answer:
Wrong.
Question 3.
Brazil is the second-most populous country in the World.
Answer:
Wrong.
Question 4.
Brazil ranks fifth in the world with respect to area.
Answer:
Right.
Question 5.
The total population of Brazil is around 91 crores.
Answer:
Wrong.
Question 6.
In Brazil and India, population is evenly distributed.
Answer:
Wrong.
Question 7.
The central and western part of Brazil are less populated.
Answer:
Right.
Question 8.
The sex ratio of Brazil has been less than 1000 since centuries.
Answer:
Wrong.
Question 9.
It is observed that in Brazil, the rate of population growth is increasing.
Answer:
Wrong.
Fill the map with the given information:
Question 1.
On a map of India, show the following.
- Largest state areawise.
- Smallest state areawise.
- State with highest population.
- State with lowest population.
- State having highest density of population.
- State having lowest density of population.
- State having highest sex ratio.
- State having lowest sex ratio.
- State having highest literacy rate.
- State having lowest literacy rate.
Answer:
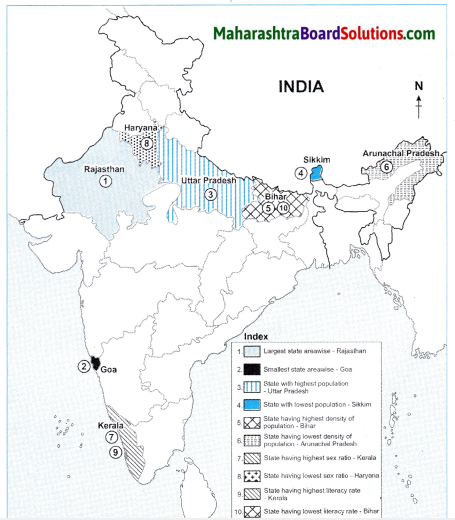
![]()
Question 2.
On a map of Brazil, show the following.
- Largest state areawise.
- Smallest state areawise.
- State with highest population.
- State with lowest population.
- State having highest density of population,
- State having lowest density of population.
Answer:
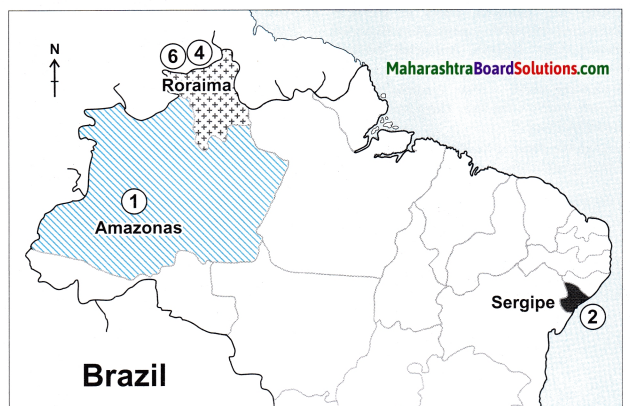
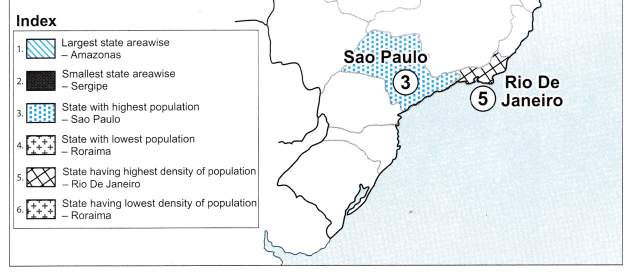
Give geographical reasons:
Question 1.
In India, population is very unevenly distributed.
Answer:
(i) In India, population is very unevenly distributed.
(ii) Physiography and climate play an important role in the distribution of population.
(iii) Due to fertile land, plain land and availability of water, human settlements have been established in some parts for many centuries.
(iv) Due to farming, industries and trade, the . proportion of the population has become concentrated in a few places.
(v) For example, the Northern Plains of the country, Delhi, Kolkata, Mumbai, Pune, Bengaluru, Chennai, etc.
(vi) On the contrary, in mountainous / hilly regions, dry desert areas, dense forest areas, density is sparse because of inaccessibility, absence of facilities and tough life.
![]()
Question 2.
The distribution of population is very uneven in Brazil.
Answer:
(i) The distribution of population is very uneven in Brazil. .
(ii) A majority of the Brazilians are concentrated within 300 kilometers of the eastern coastal areas also called the coastal lowlands because agriculture and industries are well developed here.
(iii) In the interior of the Amazon Basin population is very sparse due to.
(iv) Unfavourable climate, heavy rainfall,
inaccessibility and dense forests which are the barriers to development of human settlements here.
(v) The central and western part of Brazil is less moderate.
Question 3.
The average life expectancy in India is increasing.
Answer:
(i) Earlier the average life expectancy in India was low due to, lack of medical facilities which lead to high incidence of diseases and epidemics like chicken pox, malaria, cholera, etc.
(ii) Today with improvement in access to medical facilities and improvement in technology, diseases and epidemics are controlled.
(iii) Also today people in India have an improved standard of living, they eat nutritious food and there is awareness of good health.
All this has led to increase in average life expectancy in India.
Question 4.
In north-eastern India, sparse distribution of population is found.
Answer:
(i) North East India comprises of dense forests and uneven topography.
(ii) There exist unfavourable climatic conditions in this part.
(iii) There is less development of transport, communication and industries here.
So, in north-eastern India, sparse distribution of population is found.
Question 5.
In India, number of men outnumber women. Is this condition found in all the states of India?
Answer:
In India, men outnumber women, on an average. But in Kerala women outnumber men. Sex Ratio of Kerala is 1084 females per 1000 males (2011 Census).
Question 6.
Explain the reasons of low sex ratio in India.
Answer:
Some of the reasons for lower sex ratio in any region are:
- Illiteracy: Narrow mindedness and lack of education leads to gender bias in the society.
- Preference for a male child : There is preference of a boy child over a girl child. Nutrition to girls is ignored.
- Poverty: Povertystruck families do not prefer a girl child as they consider female child a burden due to practices like dowry prevalent in the society.
- Female foeticide and female infanticide: Female foeticide and female infanticide are on the rise due to the wrong use of modem technology.
- Maternity deaths: Higher maternity deaths have lowered the sex ratio.
Question 7.
Explain – The growth rate of population in India is decreasing but population is increasing.
Answer:
(i) Growth rate of population is calculated on the basis of difference between birth rate and death rate.
(ii) Earlier the difference between birth rate and death rate was high, so the growth rate was high.
(iii) Today the growth rate is decreasing because the difference between birth rate and death rate is not as high as it was earlier.
So it is said that in India the growth rate of population is decreasing, but the population is increasing.
Question 8.
Explain the uneven distribution of population in India.
Answer:
(i) Dense population is found in regions with mild climate and moderate rainfall. E.g. the northern plain as well as the coastal plains of India
(ii) Places with heavy rainfall, inaccessibility and dense forests have low population. E.g. north eastern states in India.
(iii) The snow covered regions due to extremely cold climatic conditions have less population. E.g. the northernmost part of Jammu & Kashmir.
(iv) In certain regions, due to less rainfall and extreme climatic conditions population is sparse. E.g. westernmost part of India in the Thar desert, Rajasthan.
(v) Moderate population is found in the plateau regions of Narmada valley.
![]()
Try this
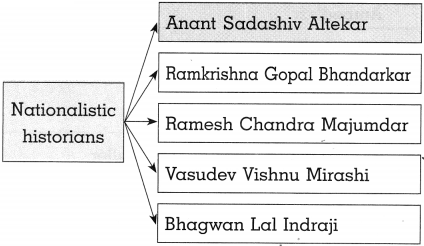
Population growth rate graphs :
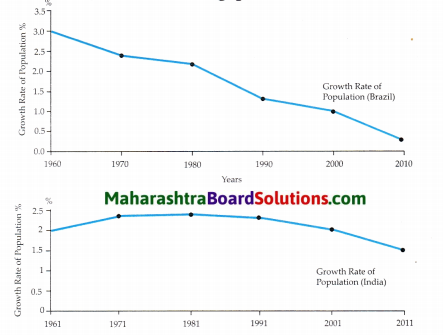
Look at the graphs in Fig. indicating the population growth rate of Brazil and India and answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What is the common feature in both the graphs?
Answer:
Both the graphs are indicating a downward trend in population growth rate of Brazil and India.
Question 2.
What is India’s growth rate of population in 2011?
Answer:
India’s population growth rate in 2011 is 1.5%.
Question 3.
In which two decades has the population growth rate of India remained almost stable?
Answer:
The population growth rate of India has remained almost stable during the two decades 1971 to 1981 and 1981 to 1991.
Question 4.
From which time period has Brazil seen a sharp decline in the population growth rate?
Answer:
From 1980-1990, Brazil has seen a sharp decline in the population growth rate.
Question 5.
What is the main point of difference between the two graphs?
Answer:
(i) In the first decade between 1961-1971 the growth rate in India showed an upward trend whereas Brazil has a downward trend throughout.
(ii) Also the decline in Brazil is more sharp but India’s decline in the growth rate is marginal.
Question 6.
What is the interesting feature of Brazil’s growth rate of population?
Answer:
The interesting feature of Brazil’s population growth rate is that it is about to touch 0.0 and then will begin its negative growth rate i.e. the population will start decreasing.
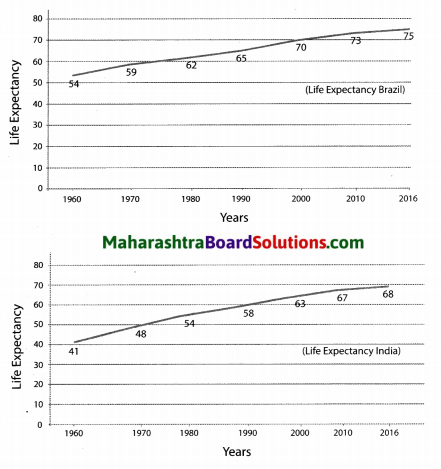
Observe the figure carefully and answer the following questions given below.
Question 1.
What is the class interval of the data?
Answer:
The class interval of the data is 10 years.
Question 2.
In which decade was India’s life expectancy the highest?
Answer:
Highest life expectancy in India was in the decade of 1960-1970.
![]()
Question 3.
In which year has the difference in the life expectancy between Brazil and India been the maximum? By how much?
Answer:
In the year I960, the difference between the life expectancy of Brazil and India has been the maximum by 13 years. (54 – 51)
Question 4.
Has the difference in life expectancy been increasing or decreasing?
Answer:
During the past 36 years, i.e. from 1980 onwards, the difference between the life expectancy of Brazil and India has remained constant. It has been 7 to 8 years.
Question 5.
What is the similarity between both the graphs?
Answer:
Both India and Brazil have experienced an increase in the life expectancy. Both the graphs indicate an upward trend continuously.
Question 6.
Is the increase in life expectancy a positive or a negative indicator of an economy? Why?
Answer:
The increase in life expectancy is a positive indicator for any economy because longer the people’s average age, longer is their contribution towards the growth of an economy.
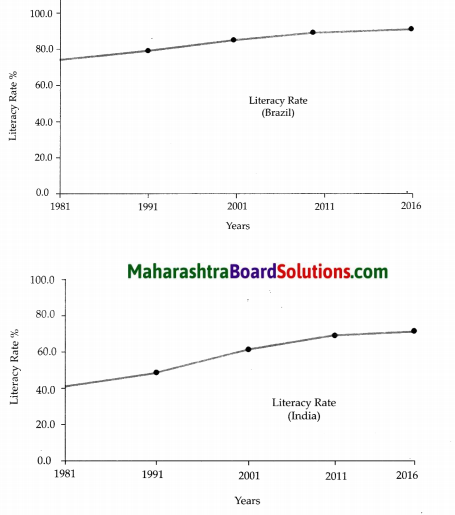
Based on the figure, observe carefully and answer the questions given below.
Question 1.
What do the graphs indicate?
Answer:
The graphs indicate the literacy rate of India and Brazil (in percentage).
![]()
Question 2.
What is this general conclusion that you can come to, after observing both the graphs?
Answer:
On observing both the graphs, we can conclude that Brazil is and has always been way ahead of India with regard to literacy rate.
Question 3.
Which country has higher literacy rate?
Answer:
Brazil has a higher literacy rate.
Question 4.
What was the literacy rate of Brazil in 2011?
Answer:
Brazil had a literacy rate of 91.4% in 2011.
Question 5.
What is the difference in the literacy rate of Brazil and India in 2016?
Answer:
Literacy rate of Brazil and India had a difference of 20.4% (92.6 – 72.2) in 2016.
Question 6.
What is the difference in the literacy rate of India between the years 2001 and 2011?
Answer:
The difference in the literacy rate of India is 8.3% (69.3 – 61) between the years 2001 and 2011.
Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions Answers
- Field Visit Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions
- Location and Extent Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions
- Physiography and Drainage Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions
- Climate Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions
- Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions
- Population Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions
- Human Settlements Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions
- Economy and Occupations Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions
- Tourism, Transport and Communication Class 10 Geography Textbook Solutions