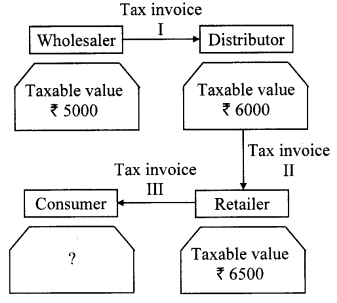
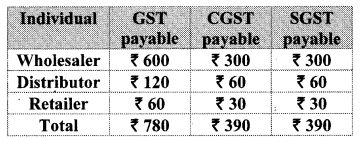
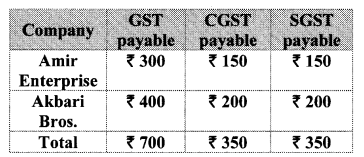
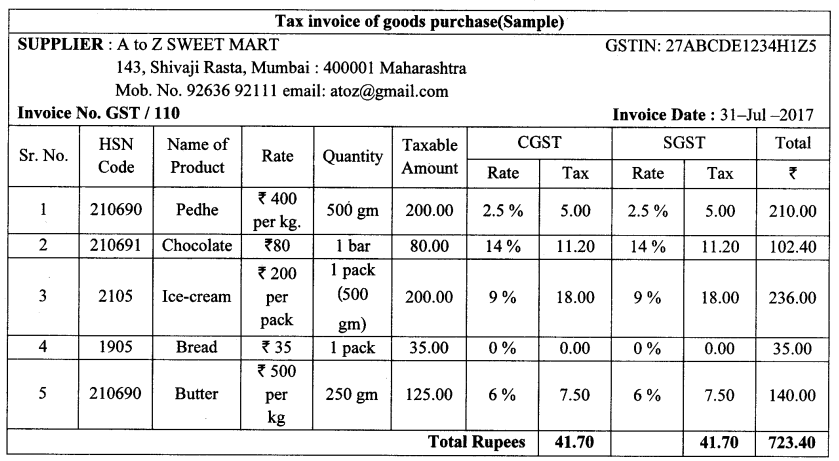
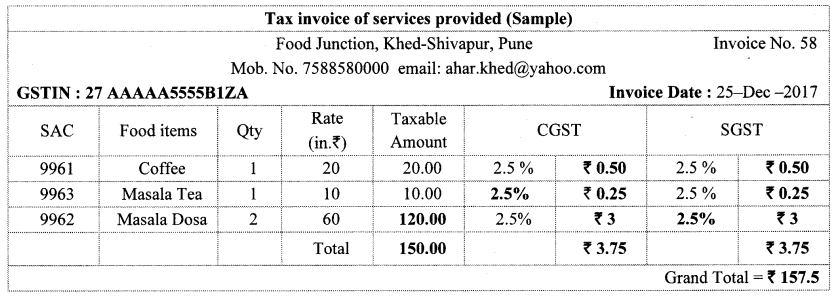
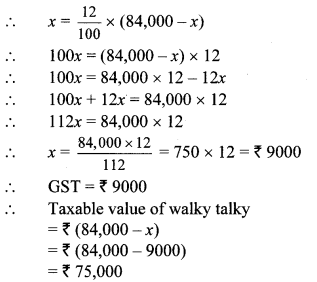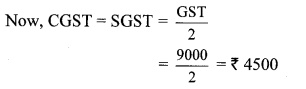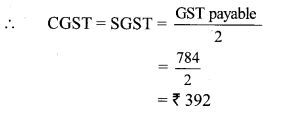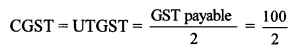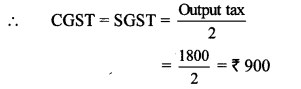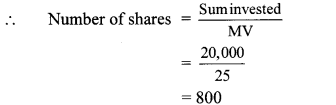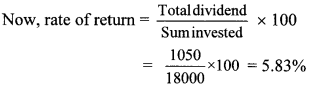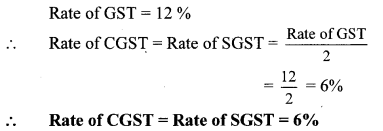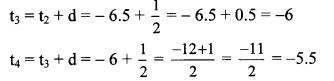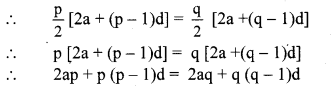10th Standard Maths 1 Problem Set 4B Chapter 4 Financial Planning Textbook Answers Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Maths Solutions covers the Problem Set 4B Algebra 10th Class Maths Part 1 Answers Solutions Chapter 4 Financial Planning.
Class 10 Maths Part 1 Problem Set 4B Chapter 4 Financial Planning Questions With Answers Maharashtra Board
Financial Planning Class 10 Problem Set 4b
Question 1.
Write the correct alternative for the following questions.
i. If the Face Value of a share is ₹ 100 and Market value is ₹ 75, then which of the following statement is correct?
(A) The share is at premium of ₹ 175
(B) The share is at discount of ₹ 25
(C) The share is at premium of ₹ 25
(D) The share is at discount of ₹ 75
Answer:
(B)
ii. What is the amount of dividend received per share of face value ₹ 10 if dividend declared is 50%.
(A) ₹ 50
(B) ₹ 5
(C) ₹ 500
(D) ₹ 100
Answer:
Dividend = 10 × \(\frac { 50 }{ 100 } \) = ₹ 5
(B)
iii. The NAV of a unit in mutual fund scheme is ₹ 10.65, then find the amount required to buy 500 such units.
(A) 5325
(B) 5235
(C) 532500
(D) 53250
Answer:
(A)
iv. Rate of GST on brokerage is _______
(A) 5%
(B) 12%
(C) 18%
(D) 28%
Answer:
(C)
v. To find the cost of one share at the time of buying the amount of Brokerage and GST is to be ______ MV of share.
(A) added to
(B) subtracted from
(C) Multiplied with
(D) divided by
Answer:
(A)
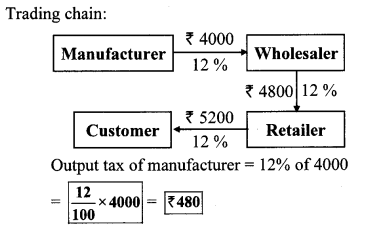
Problem Set 4b Algebra Class 10 Question 2. Find the purchase price of a share of FV ₹ 100 if it is at premium of ₹ 30. The brokerage rate is 0.3%.
Solution:
Here, Face Value of share = ₹ 100,
premium = ₹ 30, brokerage = 0.3%
MV = FV + Premium
= 100 + 30
= ₹ 130
Brokerage = 0.3% of MV
= \(\frac { 0.3 }{ 100 } \) × 130 = ₹ 0.39
Purchase price of a share = MV + Brokerage
= 130 + 0.39
= ₹ 130.39
Purchase price of a share is ₹ 130.39.
Question 3.
Prashant bought 50 shares of FV ₹ 100, having MV ₹ 180. Company gave 40% dividend on the shares. Find the rate of return on investment.
Solution:
Here, Number of shares = 50, FV = ₹ 100,
MV = ₹ 180, rate of dividend = 40%
∴ Sum invested = Number of shares × MV
= 50 × 180
= ₹ 9000
Dividend per share = 40% of FV
= \(\frac { 40 }{ 100 } \) × 100
Dividend = ₹ 40
∴ Total dividend on 50 shares = 50 × 40
= ₹ 2000
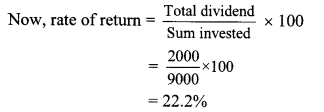
∴ Rate of return on investment is 22.2%.
Question 4.
Find the amount received when 300 shares of FV ₹ 100, were sold at a discount of ₹ 30.
Solution:
Here, FV = ₹ 100, number of shares = 300,
discount = ₹ 30
MV of 1 share = FV – Discount
= 100 – 30 = ₹ 70
∴ MV of 300 shares = 300 × 70
= ₹ 21,000
∴ Amount received is ₹ 21,000.
Question 5.
Find the number of shares received when ₹ 60,000 was invested in the shares of FV ₹ 100 and MV ₹ 120.
Solution:
Here, FV = ₹ 100, MV = ₹ 120,
Sum invested = ₹ 60,000
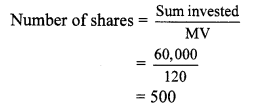
∴ Number of shares received were 500.
Question 6.
Smt. Mita Agrawal invested ₹ 10,200 when MV of the share is ₹ 100. She sold 60 shares when the MV was ₹ 125 and sold remaining shares when the MV was ₹ 90. She paid 0.1% brokerage for each trading. Find whether she made profit or loss? and how much?
Solution:
For purchasing shares:
Here, sum invested = ₹ 10,200, MV = ₹ 100
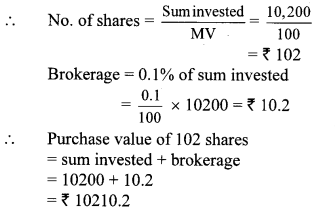
For selling shares:
60 shares sold at MV of ₹ 125.
∴ MV of 60 shares = 125 × 60
= ₹ 7500
Brokerage = \(\frac { 0.1 }{ 100 } \) × 7500 = ₹ 7.5
∴ Sale value of 60 shares = 7500 – 7.5 = ₹ 7492.5
Now, remaining shares = 102 – 60 = 42
But 42 shares sold at MV of ₹ 90.
∴ MV of 42 shares = 42 × 90 = ₹ 3780
∴ Brokerage = \(\frac { 0.1 }{ 100 } \) × 3780 = ₹ 3.78
∴ Sale value of 42 shares = 3780 – 3.78 = ₹ 3776.22
Total sale value = 7492.5 + 3776.22 = ₹ 11268.72
Since, Purchase value < Sale value
∴ Profit is gained.
∴ Profit = Sale value – Purchase value
= 11268.72 – 10210.2
= ₹ 1058.52
∴ Smt. Mita Agrawal gained a profit of ₹ 1058.52.
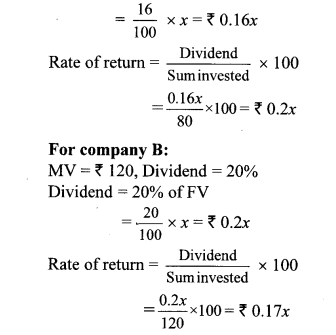
Question 7. Market value of shares and dividend declared by the two companies is given below.
Face value is same and it is 7 100 for both the shares. Investment in which company is more profitable?
i. Company A – ₹ 132,12%
ii Company B – ₹ 144,16%
Solution:
For company A:
FV = ₹ 100, MV = ₹ 132,
Rate of dividend = 12%
Dividend = 12% of FV
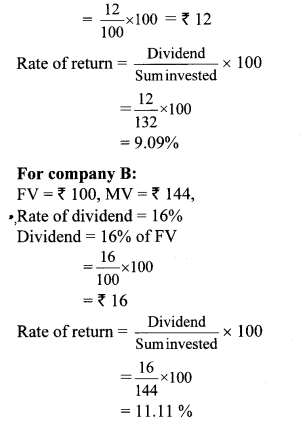
∴ Rate of return of company B is more.
∴ Investment in company B is more profitable.
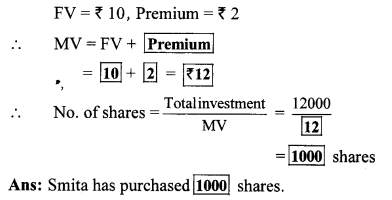
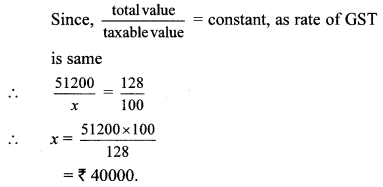
Question 8. Shri. Aditya Sanghavi invested ₹ 50,118 in shares of FV ₹ 100, when the market value is ₹ 50. Rate of brokerage is 0.2% and Rate of GST on brokerage is 18%, then How many shares were purchased for ₹ 50,118?
Solution:
Here, FV = ₹ 100, MV = ₹ 50
Purchase value of shares = ₹ 50118,
Rate of brokerage = 0.2%, Rate of GST = 18%
Brokerage = 0.2% of MV
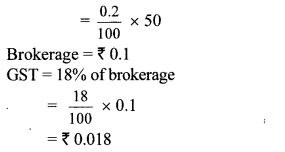
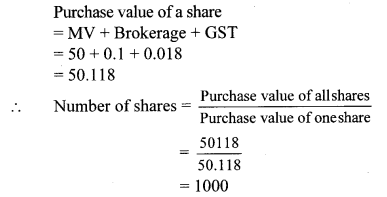
∴ 1000 shares were purchased for ₹ 50,118.
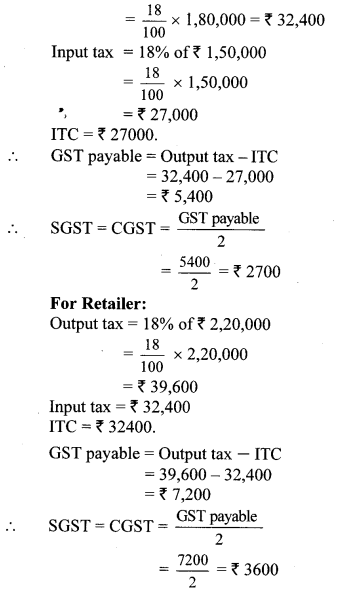
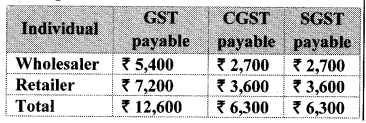
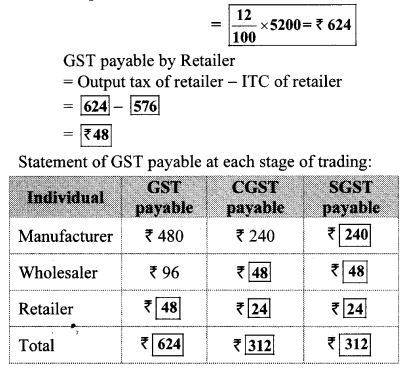
Question 9. Shri. Batliwala sold shares of ₹ 30,350 and purchased shares of ₹ 69,650 in a day. He paid brokerage at the rate of 0.1% on sale and purchase. 18% GST was charged on brokerage. Find his total expenditure on brokerage and tax.
Solution:
Total amount = sale value + Purchase value
= 30350 + 69650
= ₹ 1,00,000
Rate of Brokerage = 0.1 %
Brokerage = 0.1 % of 1,00,000
= \(\frac { 0.1 }{ 100 } \) × 1,00,000
= ₹ 100
Rate of GST = 18%
∴ GST = 18 % of brokerage
= \(\frac { 18 }{ 100 } \) × 100
∴ GST = ₹ 18
Total expenditure on brokerage and tax
= 100 + 18 = ₹ 118
∴ Total expenditure on brokerage and tax is ₹ 118.
Alternate Method:
Brokerage = 0.1 %, GST = 18%
At the time of selling shares:
Total sale amount of shares = ₹ 30,350
Brokerage = 0.1% of 30,350
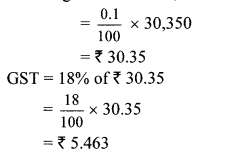
For purchasing shares:
Total purchase amount of shares = ₹ 69,650
Brokerage = 0.1% of 69,650
= \(\frac { 0.1 }{ 100 } \) × 69650
= ₹ 69.65
GST = 18% of 69.65
= \(\frac { 18 }{ 100 } \) × 69.65
= ₹ 12.537
∴ Total expenditure on brokerage and tax = Brokerage and tax on selling + Brokerage and tax on purchasing
= (30.35 + 5.463) + (69.65 + 12.537)
= ₹ 118
∴ Total expenditure on brokerage and tax is ₹ 118.
Question 10. Sint. Aruna Thakkar purchased 100 shares of FV 100 when the MV is ₹ 1200. She paid brokerage at the rate of 0.3% and 18% GST on brokerage. Find the following –
i. Net amount paid for 100 shares.
ii. Brokerage paid on sum invested.
iii. GST paid on brokerage.
iv. Total amount paid for 100 shares.
Solution:
Here, FV = ₹ 100,
Number of shares = 100, MV = ₹ 1200
Brokerage = 0.3%, GST = 18%
i. Sum invested = Number of shares × MV
= 100 × 1200 = ₹ 1,20,000
∴ Net amount paid for 100 shares is ₹ 1,20,000.
ii. Brokerage = 0.3% of sum invested
= \(\frac { 0.3 }{ 100 } \) × 1,20,000 = ₹ 360
∴ Brokerage paid on sum invested is ₹ 360.
iii. GST = 18% of brokerage
= \(\frac { 18 }{ 100 } \) × 360 = ₹ 64.80
∴ GST paid on brokerage is ₹ 64.80.
iv. Total amount paid for 100 shares
= Sum invested + Brokerage + GST
= 1,20,000 + 360 + 64.80
= ₹ 1,20,424.80
∴ Total amount paid for 100 shares is ₹ 1,20,424.80.
Question 11. Smt. Anagha Doshi purchased 22 shares of FV ₹ 100 for Market Value of ₹ 660. Find the sum invested. After taking 20% dividend, she sold all the shares when market value was ₹ 650. She paid 0.1% brokerage for each trading done. Find the percent of profit or loss in the share trading. (Write your answer to the nearest integer)
Solution:
For purchasing shares:
Here, FV = ₹ 100, MV = ₹ 660, Number of shares = 22, rate of brokerage = 0.1%
Sum invested = MV × Number of shares
= 660 × 22
= ₹ 14,520
Brokerage = 0.1 % of sum invested
= \(\frac { 0.1 }{ 100 } \) × 14520 = ₹ 14.52
∴ Amount invested for 22 shares
= Sum invested + Brokerage
= 14520 + 14.52
= ₹ 14534.52
For dividend:
Rate of dividend = 20%
∴ Dividend per share = 20 % of FV
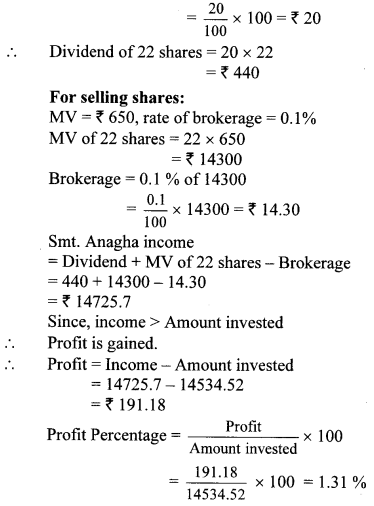
∴ Percentage of profit in the share trading is 1 % (nearest integer).
Alternate Method:
For purchasing share:
Here, FV = ₹ 100, MV = ₹ 660, Number of shares = 22, rate of brokerage = 0.1%
Sum invested = MV × Number of shares
= 660 × 22
= ₹ 14,520
Brokerage = 0.1 % of MV
= \(\frac { 0.1 }{ 100 } \) × 660 = ₹ 0.66
Amount invested for 1 share = 660 + 0.66
= ₹ 660.66
For dividend:
Rate of dividend = 20%
Dividend = 20% of FV = \(\frac { 20 }{ 100 } \) × 100 = ₹ 20
For selling share:
MV = ₹ 650, rate of brokerage = 0.1%
Brokerage = 0.1 % of MV
= \(\frac { 0.1 }{ 100 } \) × 650 = ₹ 0.65 100
Amount received after selling 1 share
= 650 – 0.65 = 649.35
∴ Amount received including divided
= selling price of 1 share + dividend per share
= 649.35 + 20
= ₹ 669.35
Since, income > Amount invested
∴ Profit is gained.
∴ profit = 669.35 – 660.66 = ₹ 8.69
Profit Percentage = \(\frac { 8.69 }{ 660.66 } \) × 100= 1.31%
∴ Percentage of profit in the share trading is 1 % (nearest integer).
Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Maths Solutions Part 1
- Arithmetic Progression Practice Set 3.1 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Arithmetic Progression Practice Set 3.2 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Arithmetic Progression Practice Set 3.3 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Arithmetic Progression Practice Set 3.4 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Arithmetic Progression Problem Set 3 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Financial Planning Practice Set 4.1 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Financial Planning Practice Set 4.2 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Financial Planning Practice Set 4.3 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Financial Planning Practice Set 4.4 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Financial Planning Problem Set 4A Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Financial Planning Problem Set 4B Class 10 Maths Solutions