By going through these Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to Sociology students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Sociology Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to Sociology
→ Initially, sociology as a discipline emerged in Europe, but sociology emerged as an independent and separate discipline in the mid 19th century. Sociology is the science of social relationships and social behaviour. The French philosopher Auguste Comte is considered to be the ‘Father of Sociology’.
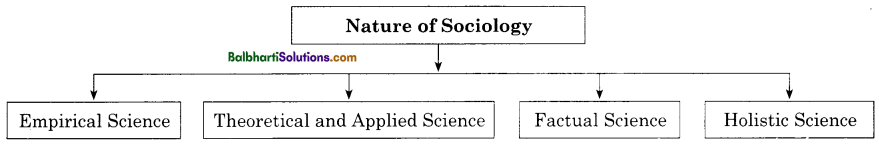
Nature of Sociology:
- Empirical Science
- Theoretical and Applied Science
- Factual Science
- Holistic Science
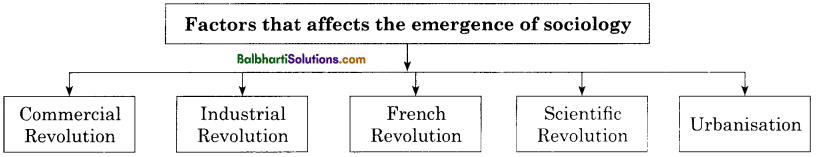
The emergence of Sociology: The roots of the emergence of sociology as a scientific discipline can be traced during the French Revolution and Industrial Revolution of European history which embodied tremendous Social, Political, and Economical changes. This period of change in European Society is known as the ‘Enlightenment period.’
![]()
Factors that affect the emergence of sociology:
- Commercial Revolution
- Industrial Revolution
- French Revolution
- scientific revolution
- Urbanization
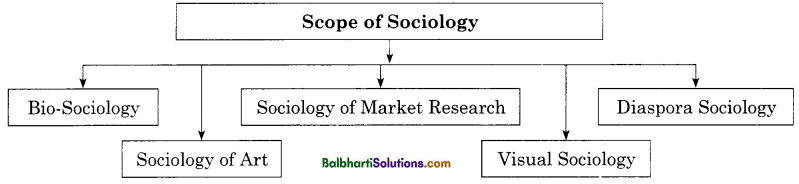
→ The subject matter of Sociology is very wide, because all aspects of social interactions are included in Sociology.
Scope of Sociology:
- Bio-Sociology
- Sociology of Art
- Sociology of Market Research
- Visual Sociology
- Diaspora Sociology
![]()
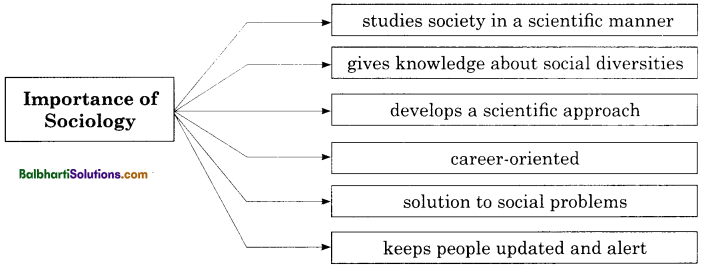
Importance of Sociology:
- studies society in a scientific manner
- gives knowledge about social diversities
- develops a scientific approach
- career-oriented
- solution to social problems
- keeps people updated and alert