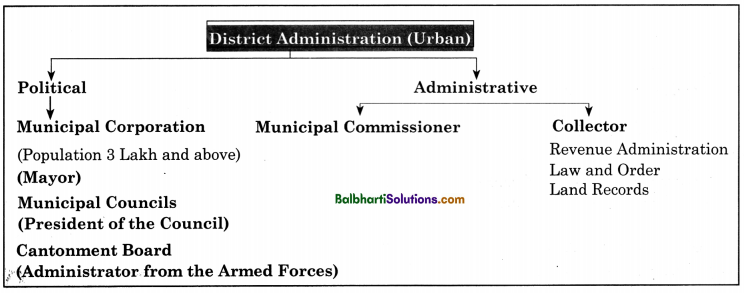
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 5 Environmental Studies Solutions Chapter 3 Life on Earth Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 5 EVS Solutions Part 2 Chapter 3 Life on Earth
5th Std EVS 2 Digest Chapter 3 Life on Earth Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Answer the following question in one sentence.
Question a.
What instrument do we need to see a unicellular organism?
Answer:
We need a microscope to see a unicellular organism.
Question b.
Where did the protozoa appear first?
Answer:
The protozoa appeared first in water.
![]()
2. Answer the following in brief.
Question a.
How were the sun and the planets in our solar system created?
Answer:
- Around 4-5 million years ago, an enormous cloud of very hot gases and dust was spinning at a great speed in space.
- Its circular motion and great speed caused its division into several portions.
- This splitting created the sun and the planets in our solar system.
Question b.
Write any two characteristics of animals.
Answer:
- Animals move to find food and for other purposes.
- Some species of animals lay eggs and their young ones are born out of the egg; whereas animals of some
- other species give birth to their young ones.
![]()
3. Find the names of the planets in the box below.
Question 1.
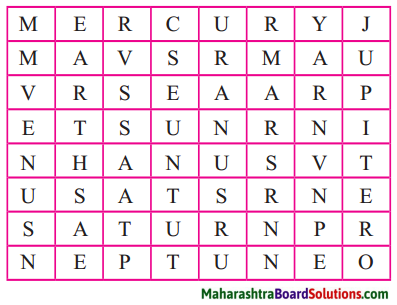
Answer:
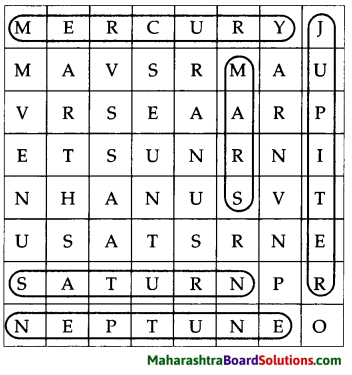
- Mercury
- Jupiter
- Venus
- Mars
- Saturn
- Neptune
- Earth
- Uranus
![]()
4. Arrange the events given below in chronological order.
Question 1.
Arrange the events given below in chronological order.
(a) Water bodies appeared on the earth’s surface.
(b) The sun and the planets revolving around it were created.
(c) Protozoa appeared in water.
(d) An enormous cloud of hot gases and dust was formed in space.
Answer:
(a) An enormous cloud of hot gases and dust formed in space.
(b) The sun and the planets were formed.
(c) Water bodies appeared on the earth’s surface.
(d) Protozoa appeared in water
![]()
Activity :
Question 1.
Make a model of the solar system using balls of different sizes.
Project :
Question 1.
Visit a zoo or make a list of animals which are seen in your neighbourhood and note their characteristics.
Environmental Studies Part 2 Standard 5th Solutions Chapter 3 Life on Earth Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
- An enormous’ cloud of very hot gases and dust spinning at a great speed was formed in ………… .
- The cloud’s circular motion and great speed caused it to divide into several portions, creating the …………………. and ……………..
- ………. and …………….. are planets.
- The ………. is the only planet where life is known to exist
- After the creation of the earth, it took about ………. years for its surface to cool down and for water bodies to be formed on it.
- It is believed that various kinds of unicellular? organisms or living things, first appeared in …………. .
- Unicellular organisms are known as ……….
- Gradually, ……………….. living things developed from these unicellular ones.
- Protozoa can only be seen through a ………..
- The living world on the Earth consists of ………. and ………
- Animals ………………… in order to get food or for other purpose.
- Animals of some species lay eggs. Their young ones are born out of …………………
- Some species, a mother gives ……………… to the young ones.
- The protozoa are so ………….. that they cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- Animals of some ………….. lay eggs.
- Various kinds of .. ………… organisms first appeared in water.
Answer:
- space
- Sun, planets
- Mercury, Venus
- Earth
- 80 crore
- Water
- Protozoa
- Multi cellular
- Microscope
- Plants, animals
- Move
- Eggs
- Birth
- Tiny
- Species
- Unicellular
Answer each question in one sentence :
Question 1.
When did the formation of the earth begin?
Answer:
On the basis of scientific research, it is believed that the formation of earth came into being around 4.5 billion years ago.
![]()
Question 2.
On the onset of creation, what was first formed?
Answer:
An enormous cloud of very hot gases and dust spinning at a great speed was formed in space.
Question 3.
How were the sun and planets formed?
Answer:
The circular motion of the great cloud caused it to divide into several portions thus creating the sun and planets.
Question 4.
Name the planets in our solar system.
Answer:
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are the planets in our solar system.
Question 5.
What forms the solar system?
Answer:
The sun and planets which revolve around the sun forms the solar system.
Question 6.
Which is the only planet where life is known to exist?
Answer:
The Earth is the only planet where life is known to exist
![]()
Question 7.
How many years did it take for the surface of the Earth to get cooled?
Answer:
After the creation of the Earth, it took about 80 crore years for its surface to cool down and for water bodies to be formed on it.
Question 8.
What kind of living organisms appeared first? What are they known as?
Answer:
Various kinds of unicellular organisms or living things first appeared in water, they are known as ‘Protozoa’.
Question 9.
When did the multicellular living organisms appear?
Answer:
After the creation of unicellular organisms in water, gradually, multicellular living organisms developed from the unicellular ones.
Question 10.
State the main characteristics of animals in which young ones are born.
Answer:
Animals of some species lay eggs and their young ones are bom out of an egg. While in some other species, a mother gives birth to their young ones.
![]()
Question 11.
Which planets revolve around the sun?
Answer:
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are the planets that revolve around the sun.
Question 15.
How many years ago was the cloud formed in space?
Answer:
The cloud was formed in space about 4-5 billion years ago
Answer the following questions in brief:
Question 1.
How did life develop on Earth? Or What was the origin of life on earth?
Answer:
- After the creation of the Earth, it took about 80 crore years for its surface to cool down and for water bodies to be formed on it.
- Various kinds of unicellular organisms known as protozoa, first appeared in water.
- Gradually, multicellular living things developed from these unicellular ones.
- Thus, life developed on Earth.
![]()
Glossary :
- enormous : very large
- unicellular : consisting of one cell
- organism : an individual animal, plant or single-called life form





 उत्तर:
उत्तर: