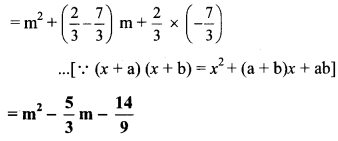Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions Class 8 Maths Chapter 6 Practice Set 6.1 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 6.1 8th Std Maths Answers Solutions Chapter 6 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions.
Std 8 Maths Practice Set 6.1 Chapter 6 Solutions Answers
Question 1.
Factorize:
i. x² + 9x + 18
ii. x² – 10x + 9
iii. y² + 24y + 144
iv. 5y² + 5y – 10
v. p² – 2p – 35
vi. p² – 7p – 44
vii. m² – 23m + 120
viii. m² – 25m + 100
ix. 3x² + 14x + 15
x. 2x² + x – 45
xi. 20x² – 26x + 8
xii. 44x² – x – 3
Solution:
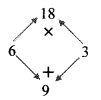
i. x² + 9x + 18
= x² + 6x + 3x + 18
= x (x + 6) + 3(x + 6)
= (x + 6) (x + 3)
ii. x² – 10x + 9
= x² – 9x – x + 9
= x (x – 9) – 1(x – 9)
= (x – 9)(x – 1)
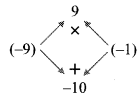
iii. y² + 24y + 144
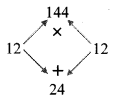
= y² + 12y + 12y + 144
= y(y + 12) + 12(y + 12)
= (y + 12)(y + 12)
iv. 5y² + 5y – 10
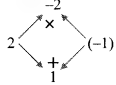
= 5(y² + y – 2)
… [Taking out the common factor 5]
= 5(y² + 2y – y – 2)
= 5[y(y + 2) – 1(y + 2)]
= 5 (p + 2)(y- 1)
v. p² – 2p – 35
= p² – 7p + 5p – 35
= p(p – 7) + 5(p – 7)
= (p – 7)(p + 5)
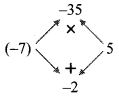
vi. p² – 7p – 44
= p² – 11p + 4p – 44
= p(p – 11) + 4(p – 11)
= (p – 11)(p + 4)
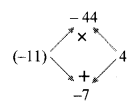
vii. m² – 23m + 120
= m² – 15m – 8m + 120
= m (m – 15) – 8 (m – 15)
= (m – 15) (m – 8)
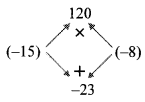
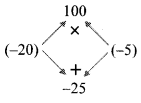
viii. m² – 25m + 100
= m² – 20m – 5m + 100
= m(m – 20) – 5(m – 20)
= (m – 20) (m – 5)
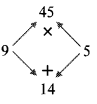
ix. 3x² + 14x + 15 3 × 15 = 45
= 3x² + 9x + 5x + 15
= 3x(x + 3) + 5(x + 3)
= (x + 3) (3x + 5)
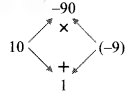
x. 2x² + x – 45 2 × (- 45) = -90
= 2x² + 10x – 9x – 45
= 2x(x + 5) – 9 (x + 5)
= (x + 5) (2x – 9)
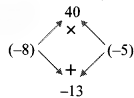
xi. 20x² – 26x + 8
= 2(10x² – 13x + 4) 10 × 4 = 40
… [Taking out the common factor 2]
= 2(10x² – 8x – 5x + 4)
= 2[2x(5x – 4) – 1(5x – 4)]
= 2 (5x – 4) (2x – 1)
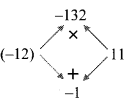
xii. 44x² – x – 3 44 × (-3) = -132
= 44x² – 12x + 11x – 3
= 4x(11x – 3) + 1(11x – 3)
= (11x – 3) (4x + 1)
Maharashtra Board Class 8 Maths Solutions
- Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions Practice Set 6.1 Class 8 Maths Solutions
- Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions Practice Set 6.2 Class 8 Maths Solutions
- Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions Practice Set 6.3 Class 8 Maths Solutions
- Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions Practice Set 6.4 Class 8 Maths Solutions