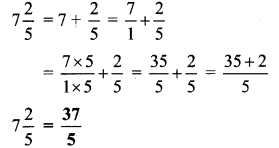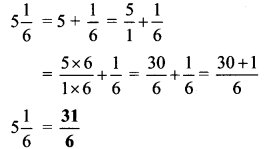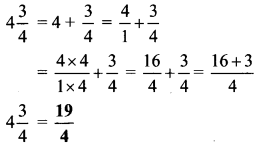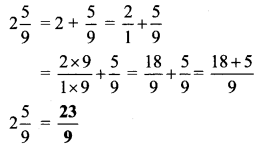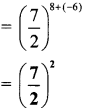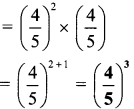Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Geography Solutions Chapter 5 Precipitation Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Geography Solutions Chapter 5 Precipitation
Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 Precipitation Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Identify the precipitation type with the help of the description given:
(a) It is the main source of the water that you use. Sometimes it is torrential and sometimes continuous. Most of the agriculture in India is dependent on it.
(b) It seems as if water droplets are floating in the atmosphere. In London, one cannot see the Sun till the afternoon during winters because of this phenomenon.
(c) It never precipitates like this in equatorial areas. Precipitation in the solid form sometimes causes damage to the crops.
(d) A white cotton-like layer spreads on the earth’s surface. Because of this form of precipitation, the State of Jammu and Kashmir has to change its capital in winters. In Maharashtra, it does not precipitate like this.
Answer:
(a) rainfall
(b) fog
(c) hail
(d) snow
![]()
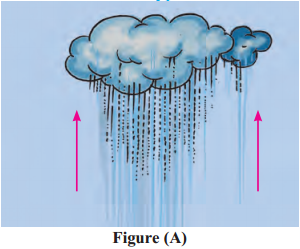
2. Look at the following pictures and identify the correct rainfall type.
Answer:
Convectional rainfall
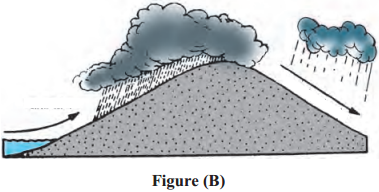
Answer:
Orographic rainfall
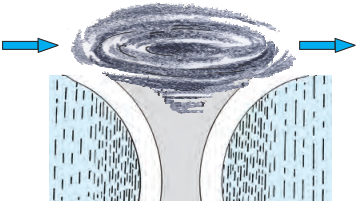
Answer:
Cyclonic rainfall
3. Look at the figures above and answer the following questions:
Question 1.
In fig B, on which side of the mountain is it raining more?
Answer:
The windward side is receiving more rainfall.
Question 2.
Shade the rain shadow region in fig B and name it.
Answer:
Students to show the leeward side in the picture.
Question 3.
What is the difference between A and C?
Answer:
In figure 5.4 i.e. convectional rainfall the hot air rises upwards and then the air cools and begins to condense and due to continuous condensation rainfall occurs. Here rainfall is accompanied by lightning and thunder.
In figure 5.6 , i.e. cyclonic rainfall, air from surrounding regions comes towards the centre of the cyclone and starts moving upwards. As it rises, the temperature of the air reduces, condensation occurs and rainfall takes place.
![]()
Question 4.
Stormy winds and floods are associated with which rainfall type?
Answer:
Stormy winds and floods are associated with Cyclonic rainfall.
Question 5.
What type of rainfall occurs in Singapore?
Answer:
Cyclonic rainfall occurs in Singapore.
4. Identify the odd man out:
Question 1.
Orographic rainfall, acid rain, cyclonic rainfall, convectional rainfall
Answer:
Acid rain
Question 2.
Snowfall, rainfall, hailstones, dew
Answer:
Dew
Question 3.
Thermometer, rain gauge, anemometer, measuring jar
Answer:
Measuring jar
5. Answer in brief:
Question 1.
In what ways does precipitation occur on the earth?
Answer:
Precipitation means water falls in the solid or liquid state from the clouds to the earth surface. Snow, hailstorms, rainfall are the major forms of precipitation.
(i) Snow:
Answer:
- When the temperature in the atmosphere falls below the freezing point the water vapour directly turns into snowflakes. This is called sublimation.
- Hence the vapour in the form of gas transform into solid snow. Precipitation in the form of solid particles is known as snowfall.
- As snow is in the solid form. It does not run like water and layers of the snow get deposited on the top of the others and when the snow melts the region gets fresh water.
![]()
(ii) Hail:
- When there is lot of heat on the earth’s surface, the upward air flow blows at a greater speed. Because of this upward flow, the temperature of air reduces and the condensation of the water vapour takes place, and dark clouds are formed.
- Because of the upward movement of the air, these water droplets go at higher altitude and solidify forming hailstones.
- As the hailstones are heavy, they fall toward the earth’s surface because of gravity. The crops may get destroyed and loss of life and property may occur.
- Hailstones occurs in summer in India, Africa and in some parts of south east Asia.
(iii) Rainfall:
- We get water generally in the form of rainfall. The temperature of the air with water vapour reduces when it goes higher and condensation of the vapour occurs.
- Clouds formed with the condensed water droplets and dust particles accumulate.
- As these water droplets increase in the size, they cannot float in the air anymore because of their weight. They come down as rainfall
- The different types of rainfall are: Convectional rainfall, Orographic rainfall and Cyclonic rainfall.
(iv) Fog, dew and frost:
- When the condensation or solidification of the water vapour in the atmosphere occurs near the earth’s surface, it leads to the formation of fog, dew and frost.
Question 2.
Comment on the rainfall occurring in the rain shadow area.
Answer:
- The winds coming from lakes or seas are moisture-laden and they are obstructed by the high mountain ranges coming in their way
- They start going upwards along the slope of the moutains. The temperature of these winds drop and condensation occurs and rainfall takes place.
- This rainfall takes place because of the obstruction of the mountains which results in the condensation of water vapour.
- The windward side of the mountain gets more rain; the amount of vapour in the air reduces after crossing the mountain and the moisture-holding capacity of the air increases.
- The leeward side of the mountain gets lesser rainfall as compared to windward side.
- Thus, the leeward side area is identified as rain shadow area as it recieves meagre rainfall.
Question 3.
Which type of rainfall occurs in most of the world? Why?
Answer:
- Orographic rainfall occurs in most parts of the world.
- Convectional rainfall is regional in nature.
- There is a certainty in the convectional rainfall occurring in the equatorial areas.
- Comparatively, the orographic and cyclonic rainfall is less certain.
- And therefore, such areas are prone to very heavy rainfall, floods or droughts frequently.
![]()
Question 4.
If condensation occurs closer to the earth’s surface, what types of forms become visible?
Answer:
If condensation and solidification of the water vapour in the atmosphere closer to the earth surface are visible, they are in the form of fog, dew or frost.
(i) Fog:
- The temperature of the layers of the air near the surface of the earth reduces. As the temperature reduces, water vapour condenses.
- In this process the water vapour turns into microscopic water particles and float in the air.
- When the density of these droplets in the air increases it leads to the formation of fog
(ii) Dew:
- When moisture-laden air near the earth surface comes in contact with very cold objects condensation of water vapour takes place.
- They turn into very small water droplets and stick to the surface of cold objects, e.g. eg: leaves and this is called dew.
(iii) Frost:
- When the temperature of the air reaches less then 0 degree Celcius the water droplet stuck to the surface of the cold objects and freezes.
- This frozen water droplet is called as frost.
Question 5.
What precautions should be taken while measuring rainfall?
Answer:
- Rainfall is an important source of water on planet earth and rainfall is formed because of changes in the temperature of the air with water vapour.
- The instrument that is used to measure rainfall is called rain gauge.
- The funnel i.e. used for measuring rain has a specific diameter and the rain falling in this funnel is collected in bottle fitted in the gauge.
- The collected water is then measured with the help of measuring jar. In the areas of heavy rainfall, the reading of the rain with rain gauge should be taken every three hours. The measuring jar reads rain in millimetres
- The gauge has to be kept on open ground on 30cm high flat-mount.
- So that the rain water is collected without any obstruction.
![]()
6. Distinguish between
Question 1.
Dew and frost
Answer:
| Dew | Frost | ||
| (i) | When moisture-laden air near the earth’s surface comes into contact with very cold objects, condensation of vapour takes place into small water droplets called dew. | (i) | If the temperature of the air is less then CPC, the water droplets stuck to the surface of cold objects, freezes forming frost. |
| (ii) | Water vapour condenses and forms droplets of water. | (ii) | Water droplets stuck to cold surface turns to frozen water droplets. |
| (iii) | Dew sticks to the cold object but does not freeze. | (iii) | It sticks to the cold object and freeze. |
Question 2.
Snow and hail
Answer:
| Snow | Hail | ||
| (i) | Precipitation in the form of solid particles of snow is known as snow fall. | (i) | Precipitation in the form of frozen water droplets falling rapidly to the ground is know as hail. |
| (ii) | The fall of temperature in the atmosphere below the freezing point causes snow fall | (ii) | Extreme heat on the surface of the earth initiates the process of hail formation. |
| (iii) | Heavy accumulation of snow can collapse the transportation and communication system of the area. | (iii) | It destroys crops and causes loss of life an |
Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 Precipitation Intext Questions and Answers
Can you tell?
Question 1.
The blade of grass look like this in winter mornings. From where does the water on the blades of grass come?

Answer:
- The blade of grass looks like this in winter mornings because of dew. These are small water droplets.
- The dew is formed in winter because moisture-laden air near the earth surface comes in contact with cold objects due to which condensation of vapour takes place, turning into small water droplets.
Question 2.
Snow is found everywhere in the winters in Kashmir.
Answer:
Snow is found everywhere in winters of Kashmir because Kashmir is located at a higher altitude where the temperature falls below freezing point. Hence water vapour directly turn into snowflakes leading to snowfall.
![]()
Question 3.
Why isn’t snow found in our surroundings?
Answer:
Because we have a moderate temperature and we are closer to the sea, snow is not found in our surroundings.
Question 4.
Generally, it rains between June and September in our region.
Answer:
We get rainfall between June and September, in our region when the moisture-laden south-west monsoon winds are obstructed by the Western Ghats leading to orographic rainfall.
Question 5.
How do the rain droplets form?
Answer:
Clouds form when condensed water droplets and dust particles accumulate forming large rain droplets.
Question 6.
In London, there is a fog like this till the afternoon in the winters.
Answer:
In London there is fog till the afternoon in winters because London is far away from equator and it has temperate oceanic climate and they have cool summers.
Question 7.
We do not have fog until afternoons in summers.
Answer:
We do not have fog until afternoons in summer because we are near to equator and we have tropical climate and hot summers.
Question 8.
Sometimes hailstones destroy the standing crops in the field.
Answer:
Hailstones are solid and heavy in nature and they hit the earth due to gravity and this is the reason they destroy the crops in the field.
![]()
Question 9.
Why don’t we get hailstones frequently?
Answer:
For the formation of hailstones the following 2 conditions are required:
- Intense heating which results in upwards air flow.
- The decrease in air temperature at higher layers of the atmosphere.
- As India is a tropical country, we do not find cooler air at higher levels because of the intense heating of land.
Think about it.
Question 1.
We use a raincoat or umbrella to protect ourselves from rainfall. What will you use to protect yourself from severe hailstorms?
Answer:
If a person is outside without any coverage, he needs to seek shelter immediately, making sure to protect his head from hailstones.
Question 2.
Because of the conventional processes, convectional rainfall occurs in the afternoon in equational areas. But why doesn’t it rain in afternoons in the oceanic areas of the equatorial belt?
Answer:
One of the necessary conditions of convectional rainfall is intense heating of surface which causes air to expand and rise. Since land heats up faster than water, it rains only on the land in the equatorial regions and not in the oceanic areas.
Question 3.
Why are the areas of high rainfall situated in tropical areas?
Answer:
- Tropical areas receive direct rays of the Sun almost throughout the year. Hence the rate of evaporation1 is high here.
- The tropical region receives convectional rainfall throughout the year and also orographic rainfall is experienced here.
- Thus areas of high rainfall are situated in the tropical area.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 Precipitation Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the statements choosing the correct option from the bracket:
Question 1.
……………. part of the earth’s surface is full of water.
(a) 30.7%
(b) 4.09%
(c) 60.5%
(d) 70.8%
Answer:
(d) 70.8%
![]()
Question 2.
When the temperature in the atmosphere falls below the freezing point and the water vapour directly turns into snowflakes, the process is called as ……………..
(a) sublimation2
(b) frostbite3
(c) carbonation
(d) convection
Answer:
(a) sublimation
Question 3.
In areas located at higher altitudes and high latitudes, where the temperatures are below 0°C get precipitation in the form of ………….
(a) dew
(b) rain
(c) snow
(d) hail
Answer:
(c) snow
Question 4.
Because of ………………. crops may get destroyed and loss of life and property may occur.
(a) dew
(b) rain
(c) snow
(d) hail
Answer:
(d) hail
Question 5.
Hails do not occur in ……………… areas.
(a) temperate
(b) equatorial
(c) landlocked
(d) mountainous
Answer:
(b) equatorial
Question 6.
In equatorial areas, …………. type of rainfall occurs almost daily in the afternoons.
(a) frontal
(b) convectional
(c) cyclonic
(d) orographic
Answer:
(b) convectional
![]()
Question 7.
…………… rainfall occurs because of obstruction from high mountain ranges.
(a) Frontal
(b) Convectional
(c) Cyclonic
(d) Orographic
Answer:
(d) orographic
Question 8.
Cyclonic rainfall occurs more in …………… zones.
(a) temperate
(b) equatorial
(c) torrid
(d) polar
Answer:
(a) temperate
Question 9.
…………… rainfall occurs in most of the parts in the world.
(a) Frontal
(b) Convectional
(c) Orographic
(d) Cyclonic
Answer:
(c) orographic
Question 10.
Snowfall can also be measured with the help of ……………
(a) hygrometer
(b) rain gauge
(c) barometer
(d) anemometer
Answer:
(b) rain gauge
Question 11.
A layer of ice is equivalent to 10mm of rainfall.
(a) 10mm
(b) 50mm
(c) 100mm
(c) 120mm
Answer:
(c) 120mm
![]()
Question 12.
When moisture-laden air near the earth’s surface comes in contact of very cold objects and form water droplets which stick to the surface of the cold objects is formed.
(a) dew
(b) frost
(c) hail
(d) fog
Answer:
(a) dew
Question 13.
If the temperature of the air reaches less than 0°C, the water droplets stuck to the surfaces of cold objects freeze and form
(a) dew
(b) frost
(c) hail
(d) fog
Answer:
(b) frost
Question 14.
If precipitation does not take place, then conditions of arise.
(a) floods
(b) hail
(c) snowstorm
(d) drought
Answer:
(d) drought
Question 15.
Visibility reduces because of
(a) floods
(b) drought
(c) fog
(d) dew
Answer:
(c) fog
Match the column:
Question 1.
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Snowflakes | (a) upward air flow |
| (2) Hailstones | (b) sublimation |
| (3) Dew | (c) microscopic water particles floating in the air |
| (4) Fog | (d) condensation4 on cold objects |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – a),
(3 – d),
(4 – c)
![]()
Question 2.
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Orographic rainfall (2) Convectional Rainfall (3) Cyclonic Rainfall |
(a) Daily in equatorial areas (b) More in temperate zones (c) Mountain barrier |
Answer:
(1 – c),
(2 – a),
(3 – b)
Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
What percentage of the earth’s surface is covered with water?
Answer:
70.8% of the earth’s surface is covered with water.
Question 2.
Why do we see different forms of condensation?
Answer:
Different forms of condensation are seen due to changes in atmospheric conditions.
Question 3.
What is precipitation?
Answer:
When water falls in the solid or liquid state from the clouds to the ground, it is called as precipitation.
Question 4.
Name the major forms of precipitation.
Answer:
Snow, hailstones and rainfall are the major forms of precipitation.
Question 5.
Explain the process of sublimation.
Answer:
When the temperature in the atmosphere falls below the freezing point, water vapour directly turns into snowflakes this process is called sublimation.
Question 6.
In India, hails occur in which season?
Answer:
Hails occur in summer reason in India.
![]()
Question 7.
Why don’t hails occur in cold zones?
Answer:
Hails do not occur in cold zones because of lack of upward flow.
Question 8.
Why don’t hails occur in equatorial areas?
Answer:
Hails do not occur in equatorial areas because of the heat in the atmosphere.
Question 9.
Which type of rainfall occurs because of obstruction of mountain?
Answer:
Orographic rainfall occurs because of obstruction of mountains.
Question 10.
Convectional rainfall is mainly experienced in which region?
Answer:
Convectional rainfall is mainly experienced in equatorial region.
Question 11.
What is a Cyclone?
Answer:
Cyclone is a specific air formation when the pressure at an area is less than the surrounding regions.
Question 12.
What is acid rain?
Answer:
Precipitation of water with dissolved acids is called acid rain.
Study the rainfall map of the world given below and answer the following question:
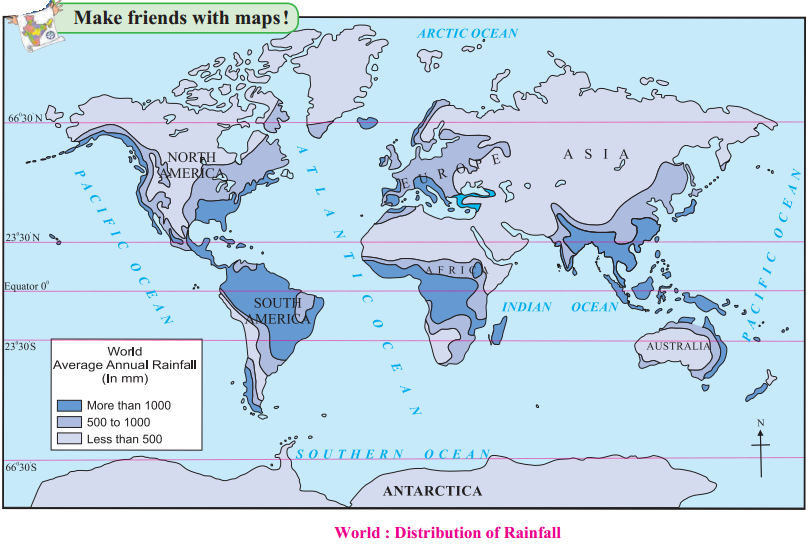
Question 1.
Which region experiences more rainfall?
Answer:
The tropical region experiences more rainfall.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the reason for low rainfall in the Central Peninsular India?
Answer:
The Central Peninsular India falls on the leeward side of the Western Ghats and hence a rain shadow region is formed here.
Question 3.
Why does the eastern part of Central African continent gets less rainfall than the western part despite its location close to the equator?
Answer:
- Eastern part of the African Continent is a rain shadow region of westerly monsoon winds whereas the western part lies on the windward side and gets more rain.
- The eastern part of Africa also comes under the influence of the North east trade winds but still receive less rains as they are dry winds originating from the land.
Question 4.
Why does the amount of high rainfall in the western part of the European continent reduce in the eastern part?
Answer:
There are many mountain ranges in the western part of Europe. These obstruct the rain-bearing clouds coming from the west and therefore the amount of rainfall received is high in the west and it reduces towards the east.
Question 5.
Why is rainfall more only in the eastern coast of Australia?
Answer:
The eastern part of Australia is a mountainous region. The winds blowing from the Pacific Ocean are obstructed by these mountains resulting in orographic rainfall towards the east and the formation of a rain shadow zone towards the west.
Observe the horizontal profile of Maharashtra in the following figure and answer the following questions:
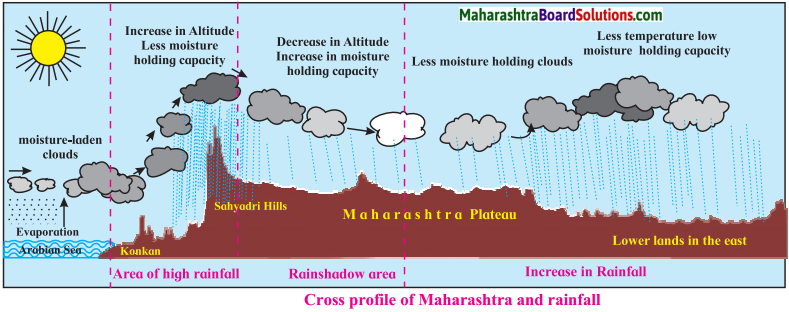
Question 1.
What type of rainfall occurs in Maharashtra?
Answer:
Orographic rainfall occurs in Maharashtra.
Question 2.
Where will the rain shadow area lie in Maharashtra?
Answer:
The rain shadow area lies to the Leeward side of Sahyadri hills (Maharashtra plateau).
![]()
Question 3.
Think about the figure and estimate the rainfall of your district.
Answer:
The answer may vary.
Give reasons:
Question 1.
Crops may get destroyed due to hailstones.
Answer:
- As hailstones are heavy they fall towards the earth’s surface, but because of the frequent upward flow of air, they are repeatedly taken upwards.
- Here, a new layer of snow encapsulates the hail. This happens quite a few times.
- Hence, concentric layers are formed while the hail grows in size.
- These big heavy hailstones fall rapidly to the ground because of gravity. This type of precipitation is called as hail.
- Hence due to hail, crops may get destroyed.
Question 2.
There is a difference between ice and snow.
Answer:
- In areas located at higher altitudes and high- latitudes, where the temperatures are below 0°C get precipitation in the form of snow.
- Snow is friable and opaque. This snow accumulates in the form of layers on top of each other.
- Because of the pressure from the upper layers, the lower layers of the snow become homogeneous, massive and transparent.
- Massive transparent snow formed in such a way is called ice.
Thus, there is a difference between ice and snow.
Question 3.
In equatorial areas, convectional rainfall occurs almost daily in the afternoons.
Answer:
- In equatorial areas, the surface gets heated because of the sun’s heat and the air near it also gets heated.
- As it gets heated, it spreads and becomes lighter and moves upwards. It cools down when it goes upward. The moisture-holding capacity of cold air is less.
- Consequently, condensation of the water vapour occurs and rainfall occurs in equatorial areas.
- Thus in equatorial areas, convectional rainfall occurs almost daily in the afternoons.
Question 4.
A rain shadow area is formed on the leeward side of the Western Ghats.
Answer:
- Winds coming from Arabian sea are moisture-laden. They are obstructed by the Western Ghats coming in their way.
- According to the slope of the Western Ghats, the moisture-laden winds start going upwards.
- The temperature of these winds drop and condensation occurs and rainfall takes place. Thus, because of the obstruction of the Western Ghats, orographic rainfall occurs.
- The windward side of the mountains gets more rain; amount of vapour in the air reduces after crossing the mountain and the water vapour carrying capacity of the air increases.
- The leeward side of the mountain gets lesser rainfall and hence a rain-shadow area is formed here.
![]()
Question 5.
Snowfall is not experienced in Maharashtra.
Answer:
- Solid snow particles are formed in regions where the temperature falls below the freezing point leading to the process of sublimation.
- In the sublimation process, the water vapour directly turns into snowflakes.
- In Maharashtra, during winters the temperature never falls below the freezing point.
- Hence snowflakes are never formed in the atmosphere.
- Thus snowfall is not experienced in Maharashtra.
Question 6.
Hailstones do not occur frequently.
Answer:
- Strong vertical movements of air with very high difference in temperature are an ideal condition for the formation of hailstones.
- Presence of moisture is also necessary in the air.
- Such conditions do not exist frequently.
- Hence hailstones are not experienced frequently.
Question 7.
Dew and frost occur on a large scale in winters.
Answer:
- During winters when moisture-laden air near the earth’s surface comes in contact very cold objects, condensation of the vapour takes place.
- They turn into very small water droplets. These water droplets get stick to the surface of the cold objects. This is called dew.
- If the temperature of the air is less than 0°C, the water droplets stuck to the surfaces of cold objects freeze.
- This frozen water droplet is called frost.
- Thus dew and frost occur on a large scale in winters.
Draw diagram of Rain Gauge:
Answer:
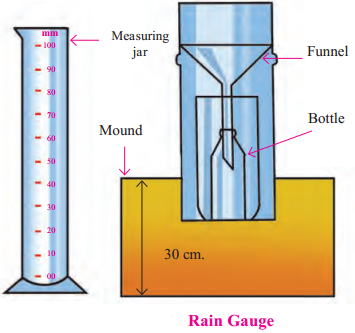
Question 6.
Explain the effects of precipitation.
Answer:
- The main source of potable water available on the earth is precipitation.
- As extreme rainfall is destructive so is the absence of rainfall.
- Floods may occur because of heavy rainfall and causes loss to life and property.
- If precipitation does not take place then conditions of drought arise. It causes a shortage of food and food may have to be imported and farmers’ conditions becomes grave.
- The economy of an agrarian1 country like India is dependent on agriculture. The agriculture in India to a large extent is dependent on monsoons. Hence rainfall in India is important to the whole country.
- A good rainfall at the right time increases crop production while untimely rain can damage the crope.
- Acid rains which is a combination of harmful gases and rainwater is harmful to the living organisms as well as non-living objects.
![]()
Explain:
Question 1.
Snowfall
Answer:
- When the temperature in the atmosphere falls below the freezing point, the water vapour directly turns into snowflakes. This is called sublimation.
- Here, the vapour in the form of gas transforms into solid snow.
- Precipitation in the form of solid particles is known as snowfall.
- In high latitudinal and temperate regions, snowfall occurs at the mean sea level while in tropical areas, snowfall occurs at places located higher than the snowline altitude.
Question 2.
Formation of hailstones.
Answer:
- When there is a lot of heat on the earth’s surface, the upward air flow blows at a great speed.
- Because of this upward flow, the temperature of the air reduces and the condensation of the water vapour takes place.
- Dark clouds are formed. Because of the upward movement of air, these water droplets go at a higher altitude.
- Here, solidification of these droplets occur and hailstones are formed.
Question 3.
Cyclonic rainfall
Answer:
- Cyclone is the specific air formation when the pressure at an area is less than the surrounding regions.
- Air from the surrounding region comes toward the center of the cyclone and starts moving upwards.
- As it rises, the temperature of the air reduces, condensation occurs and rainfall takes place.
- It rains in areas over which the cyclone passes. Cyclonic rainfall occurs more in temperate zones and its area is also quite extensive.
- Comparatively, cyclonic rainfall occurring in tropical regions is limited in extent and is stormy in nature.
Question 4.
Rain Gauge.
Answer:
- The instrument that is used to measure rainfall is called rain gauge.
- The funnel that is used for measuring rain has a specific diameter. The rain falling in this funnel is collected in a bottle fitted in the gauge.
- The collected water is then measured with the help of measuring jar. The measuring jar reads in millimetres.
- In areas of heavy rainfall, the reading of the rain is taken every three hours.
- The gauge is kept on open ground on a 30cm flat-mount. Hence, the rainwater is collected without any obstruction.
Question 5
Fog, dew and frost
Answer:
(i) Fog:
- The temperature of the layers of the air near the surface of the earth reduces. As temperature reduces, water vapour condenses.
- In this process, vapour turns into microscopic water particles and float in the air.
- When the density of these droplets in the air increases, fog occurs.
(ii) Dew:
- When moisture-laden air near the earth’s surface comes in contact with very cold objects, condensation of the vapour takes place. They turn into very small water droplets.
- These water droplets get stick to the surface of the cold objects. This is called dew.
(iii) Frost:
- If the temperature of the air reaches less than 0°C, the water droplets stuck to the surfaces of cold objects and freeze.
- This frozen water droplet is called frost.
![]()
Question 6.
Acid Rain
Answer:
- Because of air pollution in industrial areas, various gases get mixed in the air.
- Different adds are created when the water vapour in the air reacts chemically with these gases. For example, nitric add, sulphuric add, etc.
- Acids dissolved in rainwater fall with the rain j during precipitation. Such a type of rain which has acids dissolved in it is called acid rain.
- Such type of rainfall is harmful to the living organisms and the non-living objects.
Question 7.
Convectional Rainfall
Answer:
- In equatorial areas, the surface gets heated because of the sun’s heat and the air near it also gets heated. As it gets heated, it spreads and becomes lighter and moves upwards.
- It cools down when it goes upward & as the j moisture-holding capacity of cold air is less, condensation and rainfall occurs.
- This type of rainfall is called as Convectional! Rainfall.
- In equatorial areas, such a type of rainfall occurs almost daily in the afternoons. Rainfall is accompanied by lightning and thunder.
- The Congo basin of the Africa and the Amazon basin in the South America experience convectional rainfall.
- Such a rainfall has a very limited area on the earth.
Question 8.
Orographic rainfall
Answer:
- Winds coming from lakes or seas are moisture-laden. They are obstructed by the high mountain ranges coming in their way.
- They start going upwards along the slope of the mountains.
- The temperature of these winds drop and condensation occurs and rainfall takes place. Thus because of the obstruction of the mountains, this type of rainfall occurs.

- The windward side of the mountains gets; more rain; the amount of vapour in the air reduces after crossing the mountain and the moisture-holding capacity of the air increases.
- The leeward side of the mountain gets lesser rainfall and hence this area is identified as rain- shadow area.