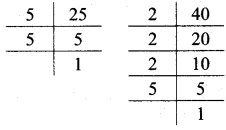
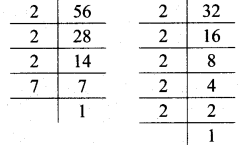
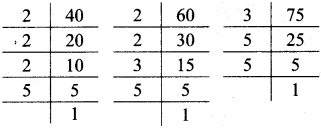
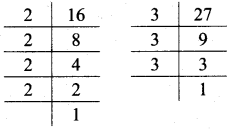
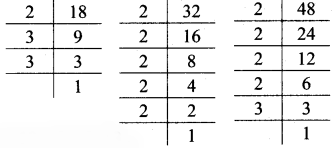
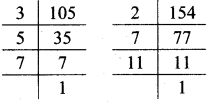
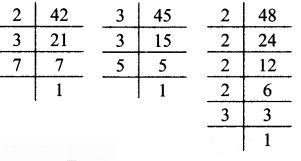
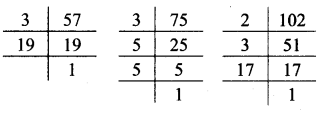
Multiplication and Division of Integers Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Practice Set 8 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions covers the 7th Std Maths Practice Set 8 Answers Solutions Chapter 2 Multiplication and Division of Integers.
Std 7 Maths Practice Set 8 Solutions Answers
Question 1.
Multiply:
- (-5) × (-7)
- (-9) × (6)
- (9) × (-4)
- (8) × (-7)
- (-124) × (-1)
- (-12) × (-7)
- (-63) × (-7)
- (-7) × (15)
Solution:
- 35
- -54
- -36
- -56
- 124
- 84
- 441
- -105
Maharashtra Board Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Multiplication and Division of Integers Practice Set 8 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
In the previous class, we have learnt to add and subtract integers. Using those methods, fill in the blanks below. (Textbook pg. no. 11)
- 5 + 7 = __
- 10 + (-5) = __
- -4 + 3 = __
- (-7) + (-2) = __
- (+8) – (+ 3) = __
- (+8) – (-3) = __
Solution:
- 12
- 5
- -1
- -9
- 5
- 11
Question 2.
Write a number in each bracket to obtain the answer ‘3’ in each operation. (Textbook pg. no. 11)
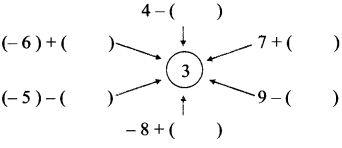
Solution:
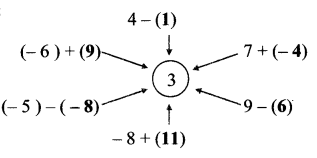
Question 3.
Multiply the given integers and complete the table given below. (Textbook pg. no. 12)

Solution:
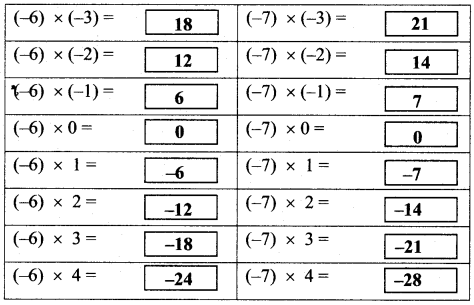
Class 7 Maths Solution Maharashtra Board
- Multiplication and Division of Integers Practice Set 8 Class 7 Maths Solution
- Multiplication and Division of Integers Practice Set 9 Class 7 Maths Solution
- HCF and LCM Practice Set 10 Class 7 Maths Solution
- HCF and LCM Practice Set 11 Class 7 Maths Solution
- HCF and LCM Practice Set 12 Class 7 Maths Solution
- HCF and LCM Practice Set 13 Class 7 Maths Solution
- HCF and LCM Practice Set 14 Class 7 Maths Solution