10th Standard Maths 2 Problem Set 4 Chapter 4 Geometric Constructions Textbook Answers Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Maths Solutions covers the Problem Set 4 Geometry 10th Class Maths Part 2 Answers Solutions Chapter 4 Geometric Constructions.
Class 10 Maths Part 2 Problem Set 4 Chapter 1 Geometric Constructions Questions With Answers Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
Select the correct alternative for each of the following questions.
i. The number of tangents that can be drawn to a circle at a point on the circle is ______
(A) 3
(B) 2
(C) 1
(D) 0
Answer:
(C)
ii. The maximum number of tangents that can be drawn to a circle from a point outside it is ______
(A) 2
(B) 1
(C) one and only one
(D) 0
Answer:
(A)
iii. If ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR and \(\frac { AB }{ PQ } \) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 5 } \), then ______
(A) AABC is bigger.
(B) APQR is bigger.
(C) both triangles will be equal
(D) can not be decided
Answer:
(A)
Question 2.
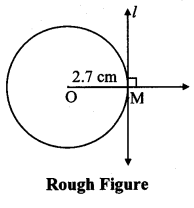
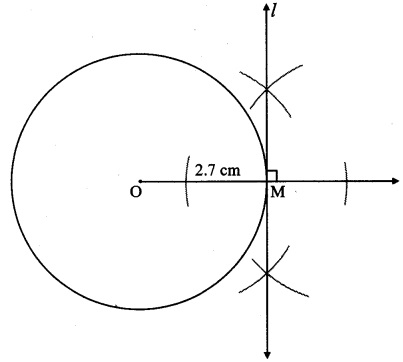
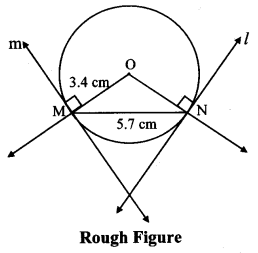
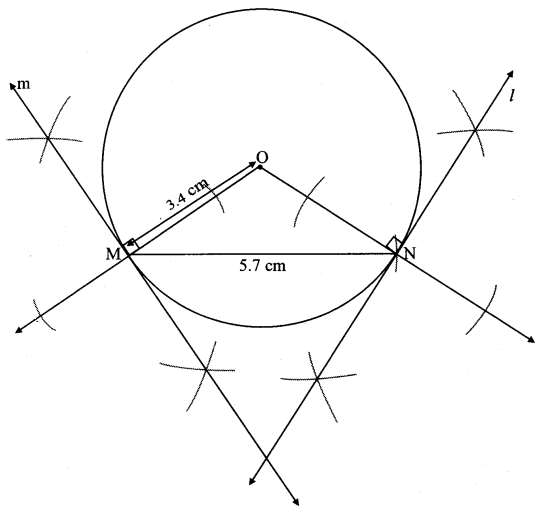
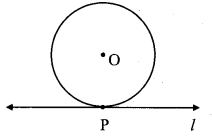
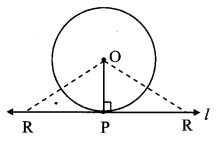
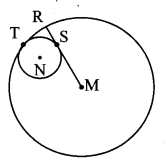
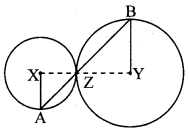
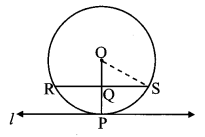
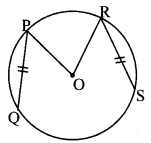
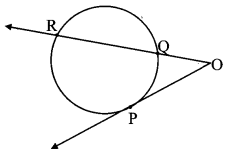
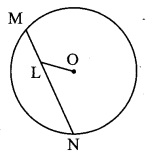
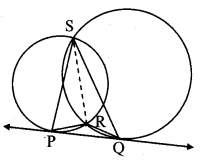
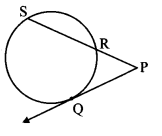
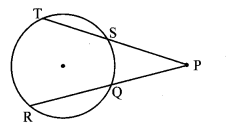
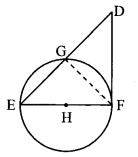
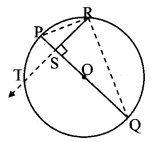
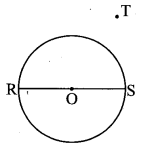
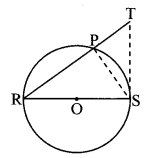
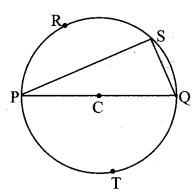
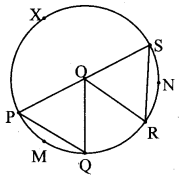
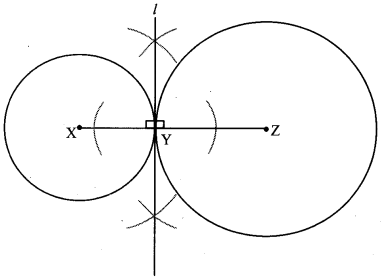
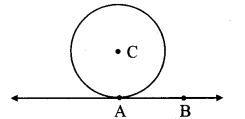
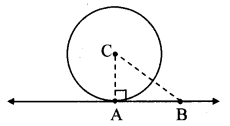
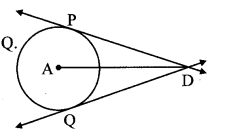
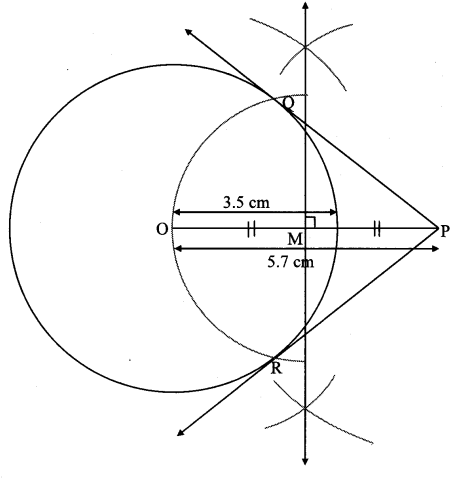
Draw a circle with centre O and radius 3.5 cm. Take point P at a distance 5.7 cm from the centre. Draw tangents to the circle from point P.
Solution:
Analysis:
As shown in the figure, let P be a point in the exterior of circle at a distance of 5.7 cm.
Let PQ and PR be the tangents to the circle at points Q and R respectively.
∴ seg OQ ⊥ tangent PQ …[Tangent is perpendicular to radius]
∴ ∠OQP = 90°
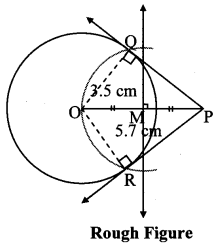
∴ point Q is on the circle having OP as diameter. …[Angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle]
Similarly, point R also lies on the circle having OP as diameter.
∴ Points Q and R lie on the circle with OP as diameter.
On drawing a circle with OP as diameter, the points where it intersects the circle with centre O, will be the positions of points Q and R respectively.
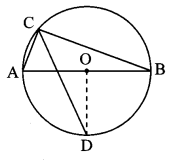
Question 3.
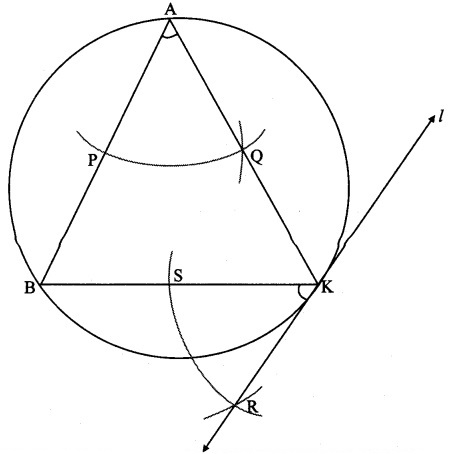
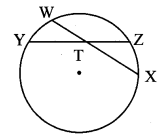
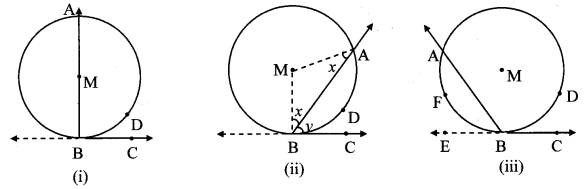
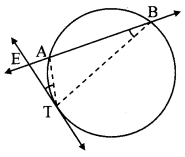
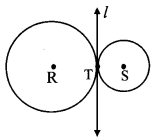
Draw any circle. Take any point A on it and construct tangent at A without using the centre of the circle.
Solution:
Analysis:
As shown in the figure, line l is a tangent to the circle at point A.
seg BA is a chord of the circle and ∠BCA is an inscribed angle.
By tangent secant angle theorem,
∠BCA = ∠BAR
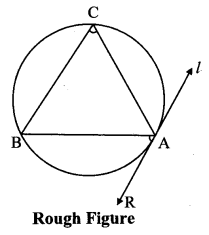
By converse of tangent secant angle theorem,
If we draw ∠BAR such that ∠BAR = ∠BCA, then ray AR (i.e. line l) is a tangent at point A.
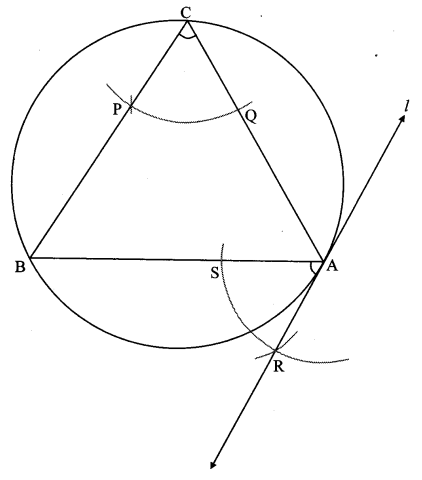
Question 4.
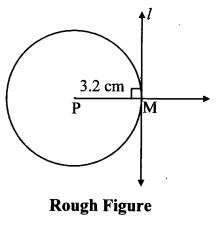
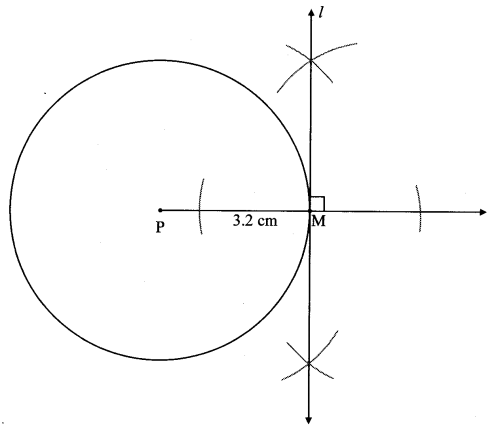
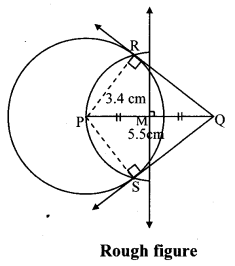
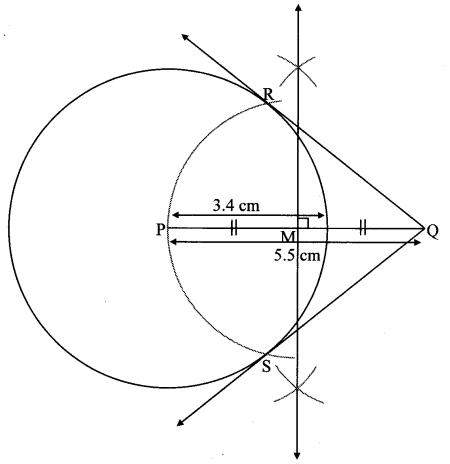
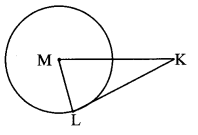
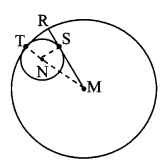
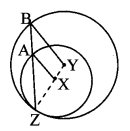
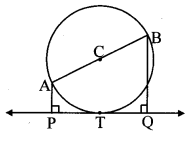
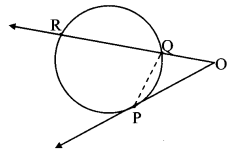
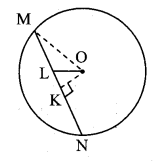
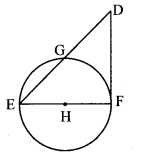
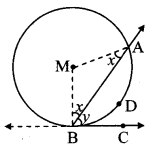
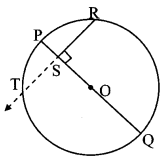
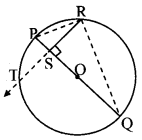
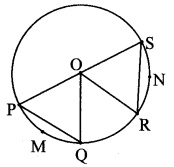
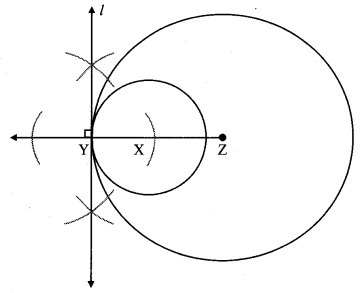
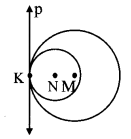
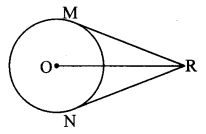
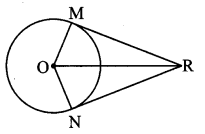
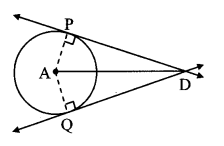
Draw a circle of diameter 6.4 cm. Take a point R at a distance equal to its diameter from the centre. Draw tangents from point R.
Solution:
Diameter of circle = 6.4 cm 6.4
Radius of circle = \(\frac { 6.4 }{ 2 } \) = 3.2 cm
Analysis:
As shown in the figure, let R be a point in the exterior of circle at a distance of 6.4 cm.
Let RQ and RS be the tangents to the circle at points Q and S respectively.
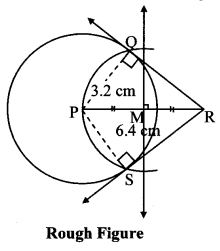
∴ seg PQ ⊥tangent RQ …[Tangent is perpendicular to radius]
∴ ∠PQR = 90°
∴ point Q is on the circle having PR as diameter. …[Angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle]
Similarly,
Point S also lies on the circle having PR as diameter.
∴ Points Q and S lie on the circle with PR as diameter.
On drawing a circle with PR as diameter, the points where it intersects the circle with centre P, will be the positions of points Q and S respectively.
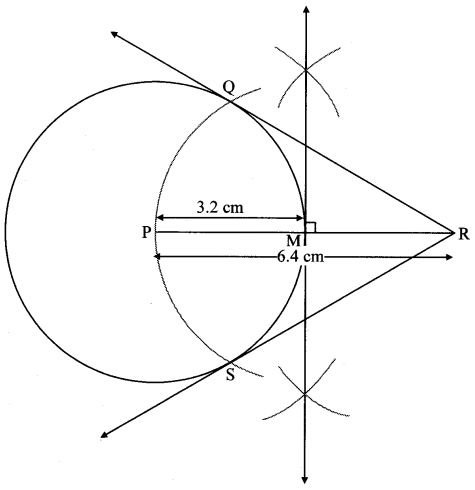
Question 5.
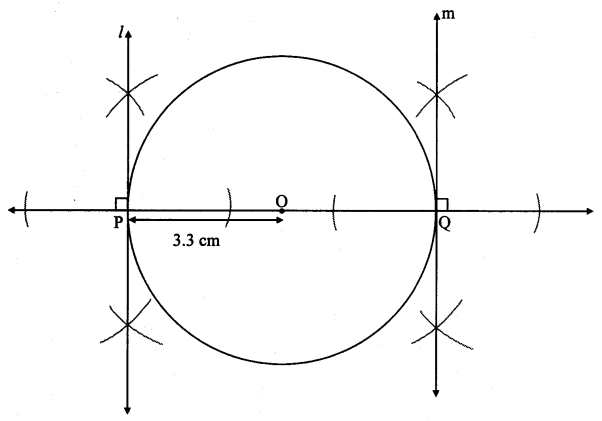
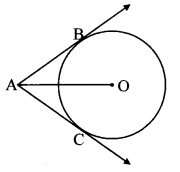
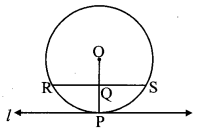
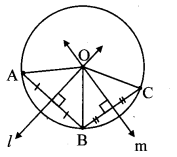
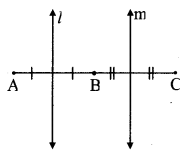
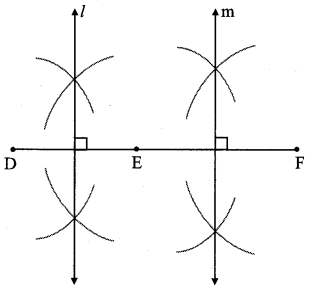
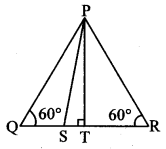
Draw a circle with centre P. Draw an arc AB of 100° measure. Draw tangents to the circle at point A and point B.
Solution:
m(arc AB) = ∠APB = 100°
Analysis:
seg PA ⊥ line l
seg PB ⊥line m … [Tangent is perpendicular to radius]
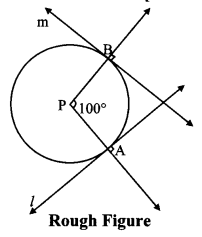
The perpendicular to seg PA and seg PB at points A and B respectively will give the required tangents at A and B.
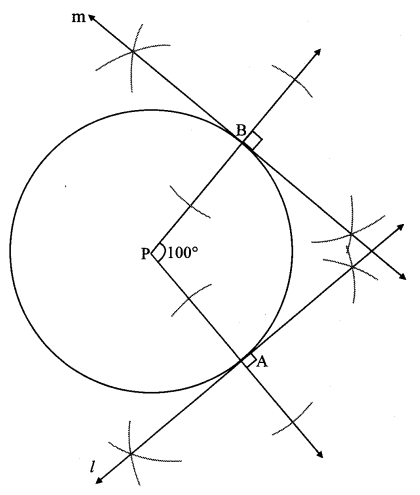
Steps of construction:
i. With centre P, draw a circle of any radius and take any point A on it.
ii. Draw ray PA.
iii. Draw ray PB such that ∠APB = 100°.
iv. Draw line l ⊥ray PA at point A.
v. Draw line m ⊥ ray PB at point B.
Lines l and m are tangents at points A and B to the circle.
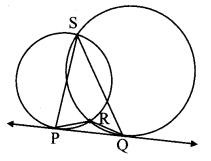
Question 6.
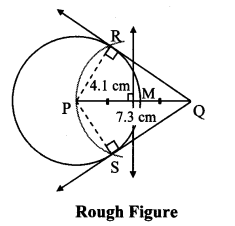
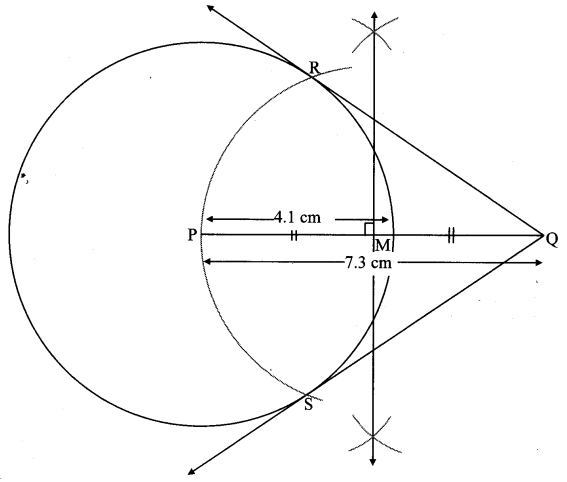
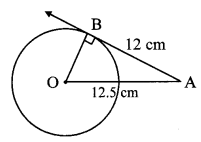
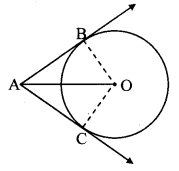
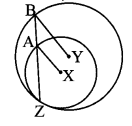
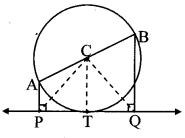
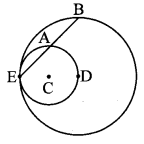
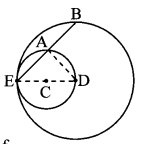
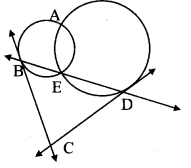
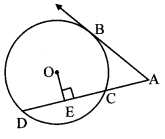
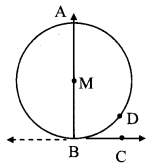
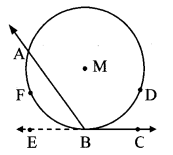
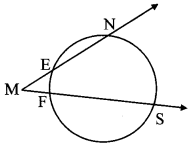
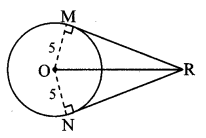
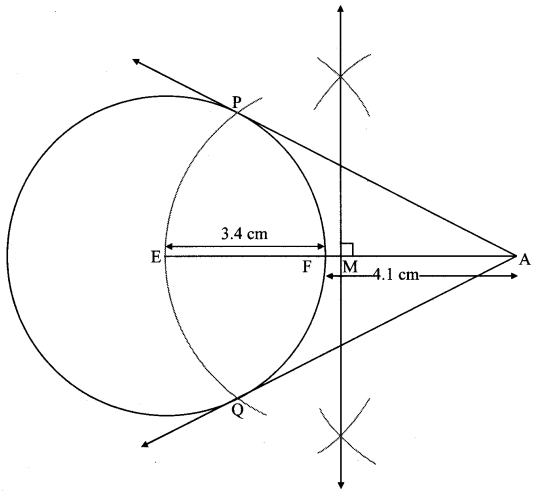
Draw a circle of radius 3.4 cm and centre E. Take a point F on the circle. Take another point A such that E – F – A and FA = 4.1 cm. Draw tangents to the circle from point A.
Solution:
Analysis:
Draw a circle of radius 3.4 cm
As shown in the figure, let A be a point in the exterior of circle at a distance of (3.4 + 4.1) = 7.5 cm.
Let AP and AQ be the tangents to the circle at points P and Q respectively.
∴ seg EP ⊥ tangent PA … [Tangent is perpendicular to radius]
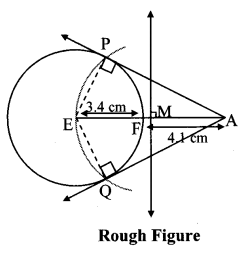
∴ ∠EPA = 90°
∴ point P is on the circle having EA as diameter. …[Angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle]
Similarly, point Q also lies on the circle having EA as diameter.
∴ Points P and Q lie on the circle with EA as diameter.
On drawing a circle with EA as diameter, the points where it intersects the circle with centre E, will be the positions of points P and Q respectively.
Question 7.
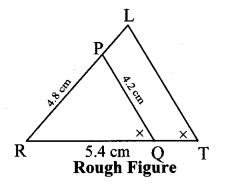
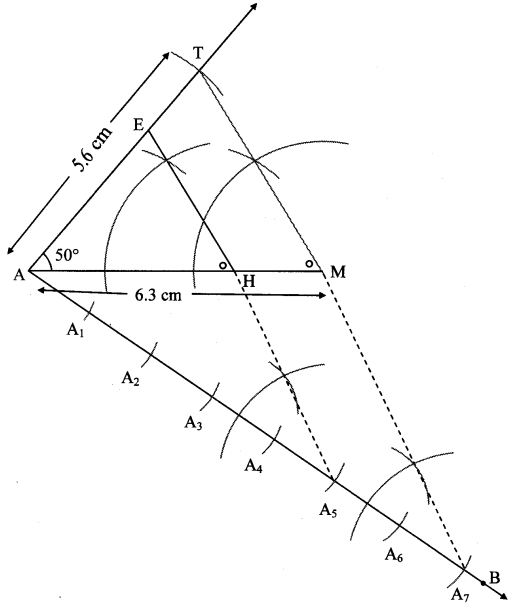
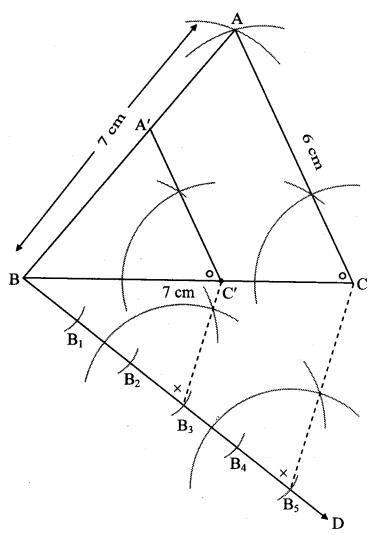
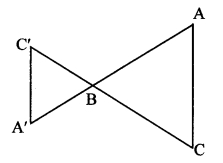
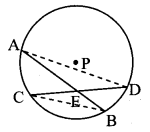
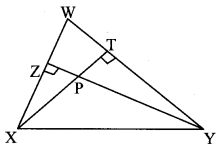
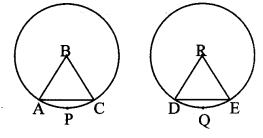
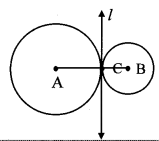
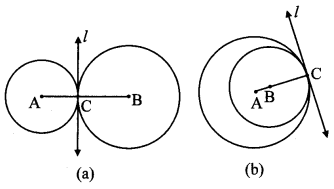
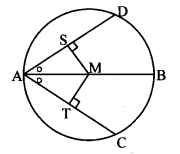
∆ABC ~ ∆LBN. In ∆ABC, AB = 5.1 cm, ∠B = 40°, BC = 4.8 cm, \(\frac { AC }{ LN } \) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 7 } \). Construct ∆ABC and ∆LBN.
Solution:
Analysis:
As shown in the figure,
Let B – C – N and B – A – L.
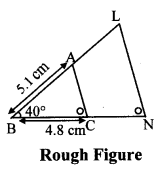
∆ABC ~ ∆LBN …[Given]
∴ ∠ABC ≅ ∠LBN …[Corresponding angles of similar triangles]
\(\frac { AB }{ LB } \) = \(\frac { BC }{ BN } \) = \(\frac { AC }{ LN } \) …(i)[Corresponding sides of similar triangles]
But. \(\frac { AC }{ LN } \) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 7 } \) …(ii)[Given]
∴ \(\frac { AB }{ LB } \) = \(\frac { BC }{ BN } \) = \(\frac { AC }{ LN } \) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 7 } \) …[From(i)and(ii)]
∴ sides of ∆LBN are longer than corresponding sides of ∆ABC.
∴ If seg BC is divided into 4 equal parts, then seg BN will be 7 times each part of seg BC.
So, if we construct ∆ABC, point N will be on side BC, at a distance equal to 7 parts from B.
Now, point L is the point of intersection of ray BA and a line through N, parallel to AC.
∆LBN is the required triangle similar to ∆ABC.
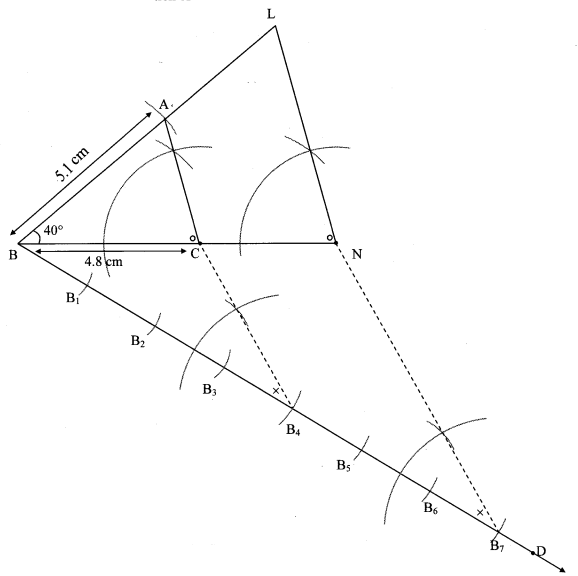
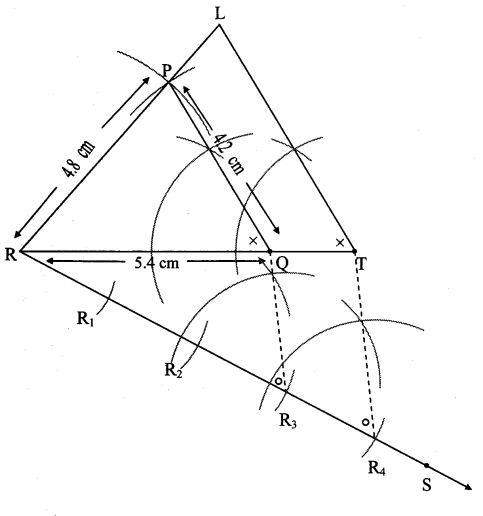
Steps of construction:
i. Draw ∆ABC of given measure. Draw ray BD making an acute angle with side BC.
ii. Taking convenient distance on compass, mark 7 points B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6 and B7 such that
BB1 = B1B2 = B2B3 B3= B44 = B4B5 = B5B6 = B6B7.
iii. Join B4C. Draw line parallel to B4C through B7 to intersects ray BC at N.
iv. Draw a line parallel to side AC through N. Name the point of intersection of this line and ray BA as L.
∆LBN is the required triangle similar to ∆ABC.
Question 8.
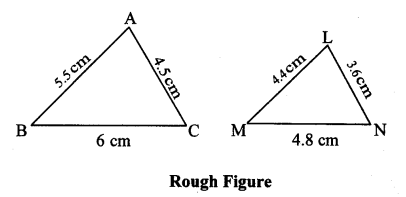
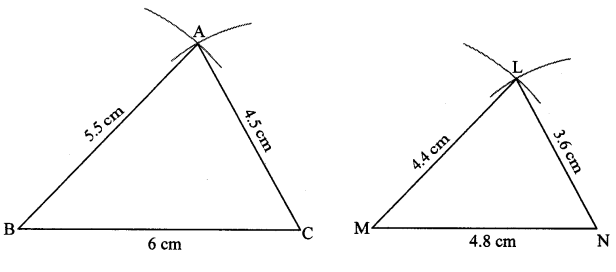
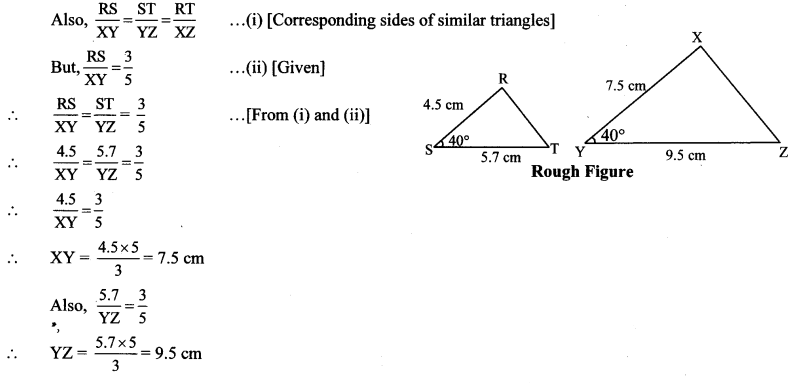
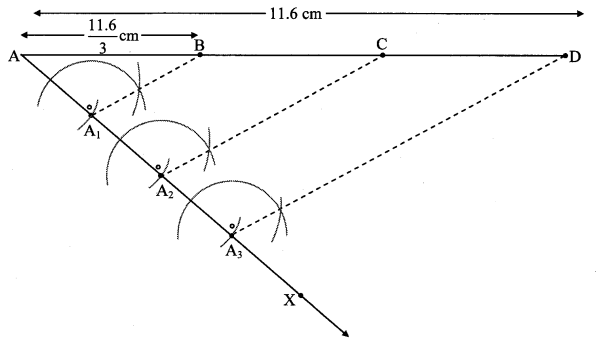
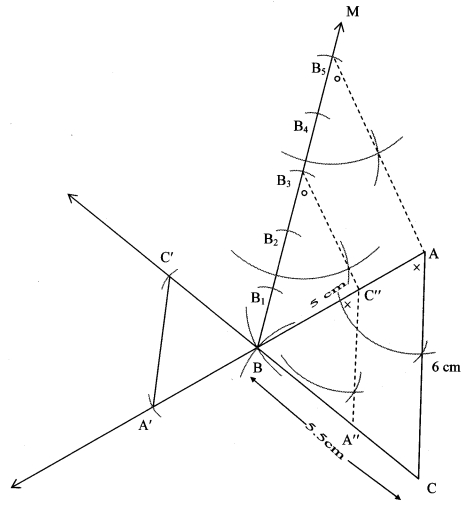
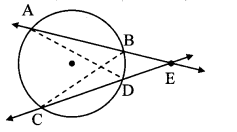
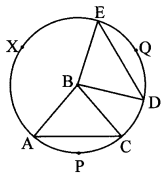
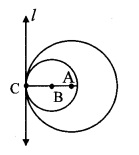
Construct ∆PYQ such that, PY = 6.3 cm, YQ = 7.2 cm, PQ = 5.8 cm. If = \(\frac { YZ }{ YQ } \) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 5 } \) then construct ∆XYZ similar to ∆PYQ.
Solution:
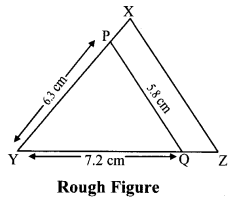
Analysis:
As shown in the figure,
Let Y – Q – Z and Y – P – X.
∆XYZ ~ ∆PYQ …[Given]
∴ ∠XYZ ≅ ∠PYQ …[Corresponding angles of similar triangles]
\(\frac { XY }{ PY } \) = \(\frac { YZ }{ YQ } \) = \(\frac { XZ }{ PQ } \) …(i)[Corresponding sides of similar triangles]
But, \(\frac { YZ }{ YQ } \) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 5 } \) ,..(ii)[Given]
∴ \(\frac { XY }{ PY } \) = \(\frac { YZ }{ YQ } \) = \(\frac { XZ }{ PQ } \) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 5 } \) …[From (i) and (ii)]
∴ sides of ∆XYZ are longer than corresponding sides of ∆PYQ.
∴ If seg YQ is divided into 5 equal parts, then seg YZ will be 6 times each part of seg YQ.
So, if we construct ∆PYQ, point Z will be on side YQ, at a distance equal to 6 parts from Y.
Now, point X is the point of intersection of ray YP and a line through Z, parallel to PQ.
∆XYZ is the required triangle similar to ∆PYQ.
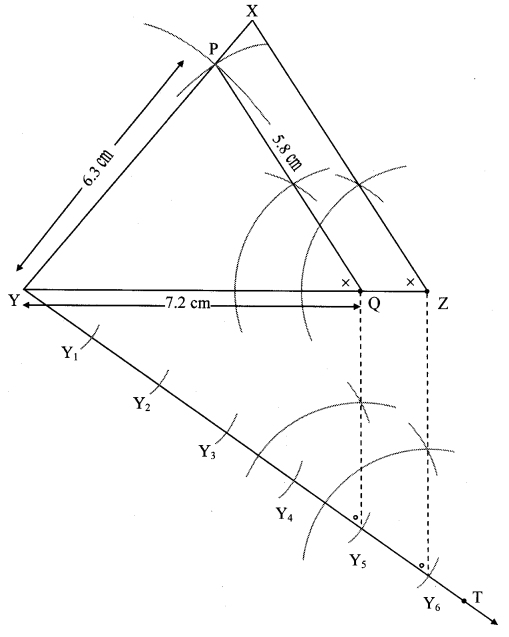
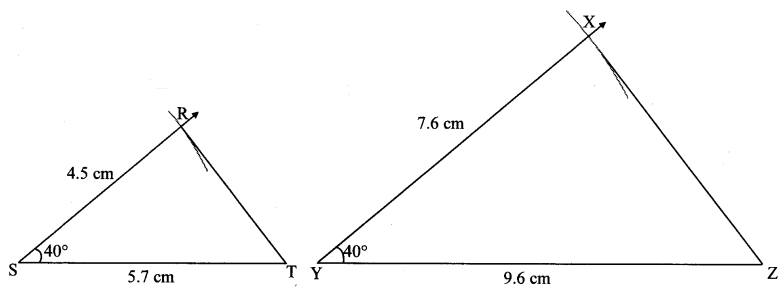
Steps of construction:
i. Draw ∆ PYQ of given measure. Draw ray YT making an acute angle with side YQ.
ii. Taking convenient distance on compass, mark 6 points Y1, Y2, Y3, Y4, Y5 and Y6 such that
YY1 = Y1Y2 = Y2Y3 = Y3Y4 = Y4Y5 = Y5Y6.
iii. Join Y5Q. Draw line parallel to Y5Q through Y6 to intersects ray YQ at Z.
iv. Draw a line parallel to side PQ through Z. Name the point of intersection of this line and ray YP as X.
∆XYZ is the required triangle similar to ∆PYQ.
Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Maths Solutions Part 2
- Circle Practice Set 3.1 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Circle Practice Set 3.2 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Circle Practice Set 3.3 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Circle Practice Set 3.4 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Circle Practice Set 3.5 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Circle Problem Set 3 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Geometric Constructions Practice Set 4.1 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Geometric Constructions Practice Set 4.2 Class 10 Maths Solutions
- Geometric Constructions Problem Set 4 Class 10 Maths Solutions