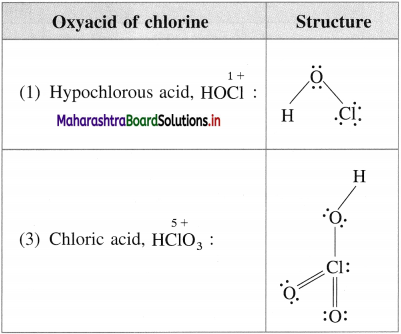
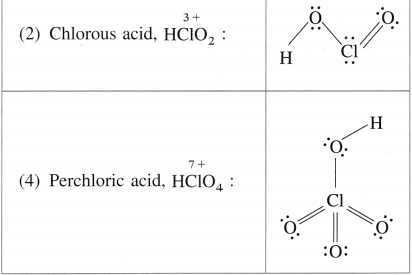
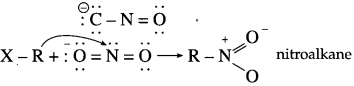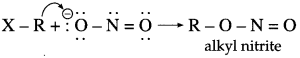Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Exercise Question Answers Solutions Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Textbook Solutions Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Exercise Solutions Maharashtra Board
Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 11 Exercise Solutions
1. Choose the correct option.
Question i.
Which of the following represents the increasing order of boiling points of (1), (2), and (3)?
(1) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – OH
(2) (CH3)2 CH – O – CH3
(3) (CH3)3COH
A. (1) < (2) < (3)
B. (2) < (1) < (3)
C. (3) < (2) < (1)
D. (2) < (3) < (1)
Answer:
(a) (1) < (2) < (3)
![]()
Question ii.
Which is the best reagent for carrying out following conversion ?
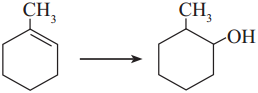
A. LiAlH4
B. Conc. H2SO4, H2O
C. H2/Pd
D. B2H6, H2O2 – NaOH
Answer:
B. Conc. H2SO4, H2O
Question iii.
Which of the following reaction will give ionic organic product on reaction ?
A. CH3 – CH2 – OH + Na
B. CH3 – CH2 – OH + SOCl2
C. CH3 – CH2 – OH + PCl5
D. CH3 – CH2 – OH + H2SO4
Answer:
C. CH3 – CH2 – OH + PCl5
Question iv.
Which is the most resistant alcohol towards oxidation reaction among the follwoing ?

Answer:
(c)
Question v.
Resorcinol on distillation with zinc dust gives
A. Cyclohexane
B. Benzene
C. Toluene
D. Benzene-1, 3-diol
Answer:
(b) Benzene
Question vi.
Anisole on heating with concerntrated HI gives
A. Iodobenzene
B. Phenol + Methanol
C. Phenol + Iodomethane
D. Iodobenzene + methanol
Answer:
B. Phenol + Methanol
Question vii.
Which of the following is the least acidic compound ?
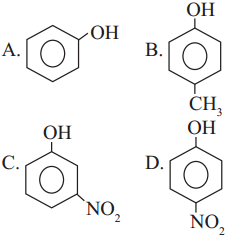
Answer:
(b)
Question viii.
The compound incapable of hydrogen bonding with water is ……
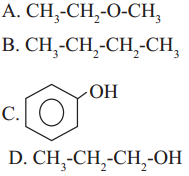
Answer:
(b)
![]()
Question ix.
Ethers are kept in air tight brown bottles because
A. Ethers absorb moisture
B. Ethers evaporate readily
C. Ethers oxidise to explosive peroxide
D. Ethers are inert
Answer:
C. Ethers oxidise to explosive peroxide
Question x.
Ethers reacts with cold and concentrated H2SO4 to form
A. oxonium salt
B. alkene
C. alkoxides
D. alcohols
Answer:
A. oxonium salt
2. Answer in one sentence/ word.
Question i.
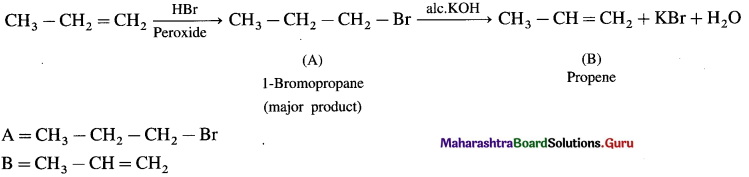
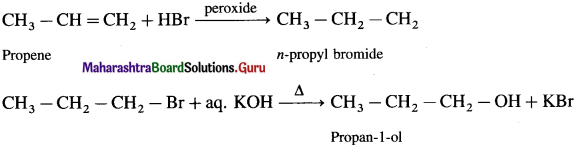
Hydroboration-oxidation of propene gives…..
Answer:
n-propyl alcohol (CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – OH)
Question ii.
Write the IUPAC name of alcohol having molecular formula C4H10O which is resistant towards oxidation.
Answer:

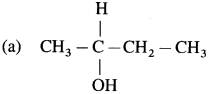
Question iii.
Write the structure of optically active alcohol having molecular formula C4H10O
Answer:
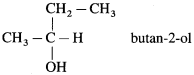
Question iv.
Write name of the electrophile used in Kolbe’s Reaction.
Answer:
Electrophile : Carbon dioxide (O = C = O)
3. Answer in brief.
Question i.
Why phenol is more acidic than ethyl alcohol ?
Answer:
(1) In ethyl alcohol, the -OH group is attached to sp3 – hybridised carbon while in phenols, it is attached to sp2 – hybridised carbon.
(2) Due to higher electronegativity of sp2 – hybridised carbon, electron density on oxygen decreases. This increases the polarity of O-H bond and results in more ionization of phenol than that of alcohols.
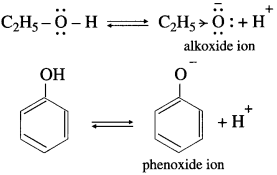
(3) Electron donating inductive effect (+1 effect) of the alkyl group destabilizes alkoxide ion. As a result alcohol does not ionize much in water, therefore alcohol is neutral compound in aqueous medium.
(4) In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localized on oxygen, while in phenoxide ion the negative charge is delocalized. The delocalization of the negative charge (structure I to V) makes phenoxide ion more stable than that of phenol.
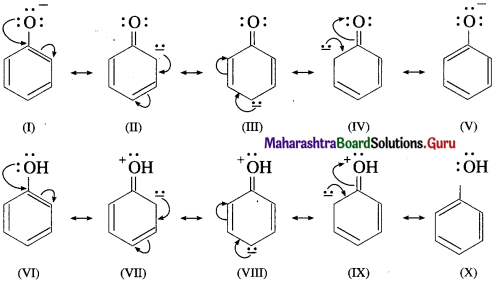
The delocalization of charge in phenol (structures VI to X), the resonating structures have charge separation (where oxygen atom of OH group to be positive and delocalization of negative charge over the ortho and para positions of aromatic ring) due to which phenol molecule is less stable than phenoxide ion. This favours ionization of phenol. Thus phenols are more acidic than ethyl alcohol.
![]()
Question ii.
Why p-nitrophenol is a stronger acid than phenol ?
Answer:
(1) In p-nitrophenol, nitro group (NO2) is an electron withdrawing group present at para position which enhances the acidic strength (-1 effect). The O-H bond is under strain and release of proton (H+) becomes easy. Further p-nitrophenoxide ion is more stabilised due to resonance.
(2) Since the absence of electron withdrawing group (like – NO2) in phenol at ortho and para position, the acidic strength of phenol is less than that of p-nitrophenol.
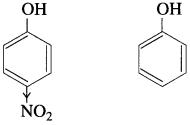
Question iii.
Write two points of difference between properties of phenol and ethyl alcohol.
Answer:
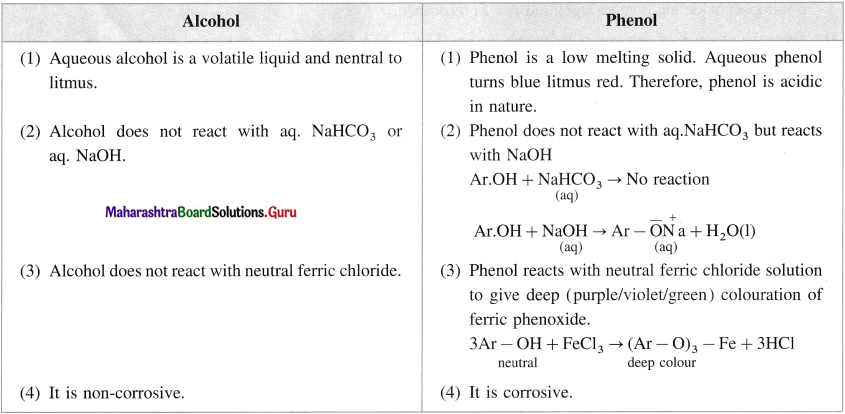
Question iv.
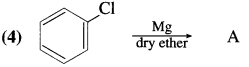
Give the reagents and conditions necessary to prepare phenol from
a. Chlorobenzene
b. Benzene sulfonic acid.
Answer:
(1) From chlorobenzene : Reagents required : NaOH and dil. HC1 Temperature : 623 K, Pressure : 150 atm
(2) From Benzene sulphonic acid : Reagents required : aq NaOH, caustic soda, dil. HC1 Temperature : 573 K
Question v.
Give the equations of the reactions for the preparation of phenol from isopropyl benzene.
Answer:
Preparation of phenol from cumene (isopropylbenzene) : This is the commercial method of preparation of phenol. When a stream of air is passed through cumene (isopropylbenzene) suspended in aqueous Na2CO3 solution in the presence of cobalt naphthenate catalyst, isopropyl benzene hydroperoxide or cumene hydroperoxide is formed. Isopropylbenzene hydroperoxide on warming with dil. H2SO4 gives phenol and acetone. Acetone is an important by-product of the reaction and is separated by distillation. The reaction is called auto oxidation.

![]()
Question vi.
Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between ethanol and ethyl bromide.
Answer:
When ethyl bromide is heated with aq NaOH; ethyl alcohol is formed whereas ethanol does not react with aq NaOH
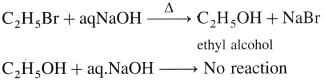
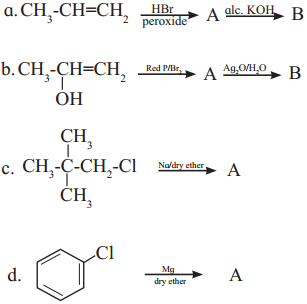
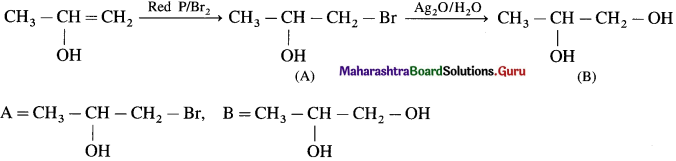
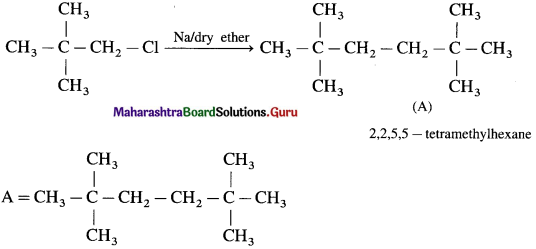
4. An ether (A), C5H12O, when heated with excess of hot HI produce two alkyl halides which on hydrolysis form compound (B)and (C), oxidation of (B) gave and acid (D), whereas oxidation of (C) gave a ketone (E). Deduce the structural formula of (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E).
Answer:
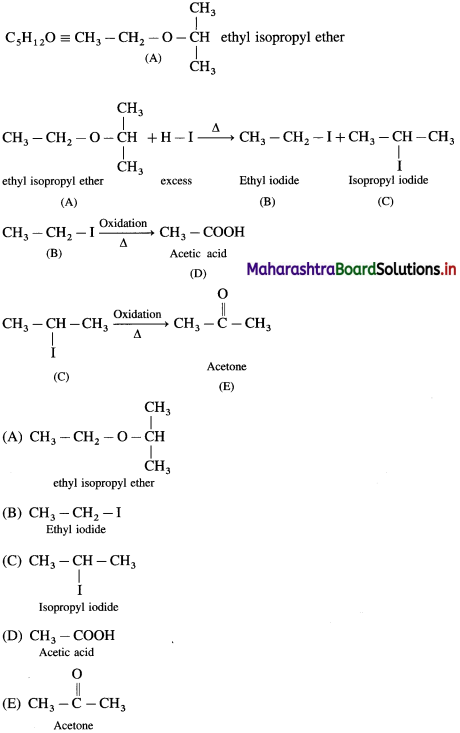
5. Write structural formulae for
a. 3-Methoxyhexane
b. Methyl vinyl ether
c. 1-Ethylcyclohexanol
d. Pentane-1,4-diol
e. Cyclohex-2-en-1-ol
Answer:
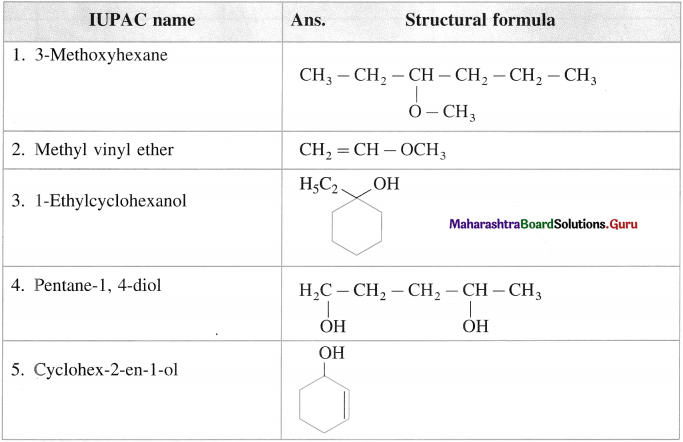
![]()
6. Write IUPAC names of the following
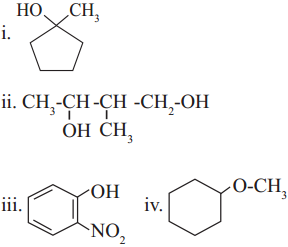
Answer:
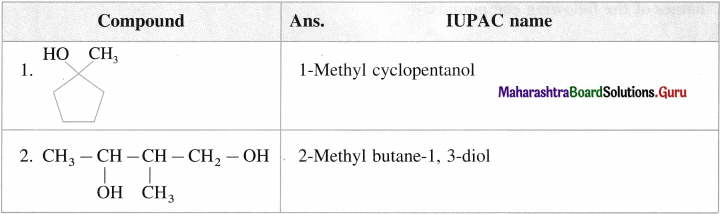

Activity :
• Collect information about production of ethanol as byproduct in sugar industry and its importance in fuel economy.
• Collect information about phenols used as antiseptics and polyphenols having antioxidant activity.
12th Chemistry Digest Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Intext Questions and Answers
Use your brain power! (Textbook Page No 235)
Question 1.
Classify the following alcohols as l0/2°/3° and allylic/benzylic
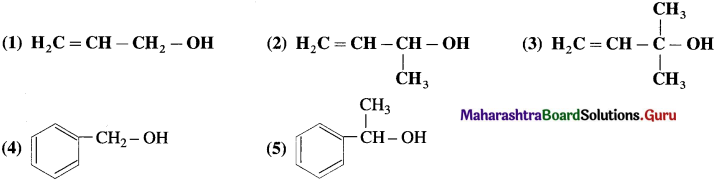
Answer:
(1) Ally lie alcohol (primary)
(2) Allylic alcohol (secondary)
(3) Allylic alcohol (tertiary)
(4) Benzylic alcohol (primary)
(5) Benzylic alcohol (secondary)
![]()
Use your brain power ….. (Textbook Page No 236)
Question 1.
Name t-butyl alcohol using carbinol system of nomenclature.
Answer:
Trimethyl carbinol.
Problem 11.1 (Textbook Page No 238)
Question 1.
Draw structures of following compounds:
(i) 2,5-DiethIphenoI
(ii) Prop-2-en-I-oI
(iii) 2-methoxypropane
(iv) Phenylmethanol
Solution :

Try this ….. (Textbook Page No 238)
Write IUPAC names ol (he following compounds.
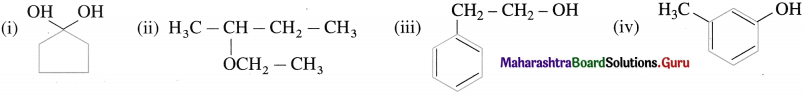
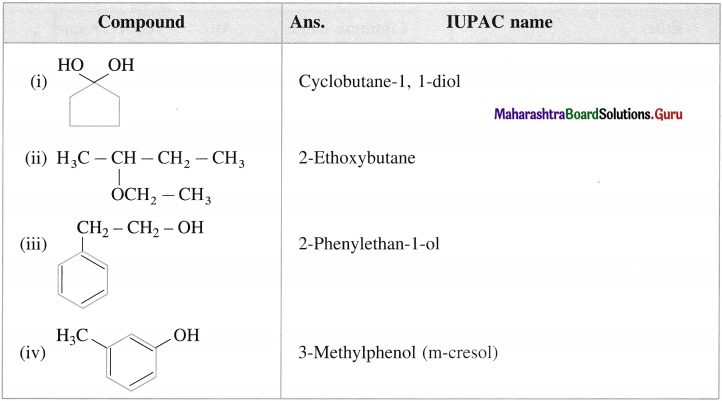
Do you know (Textbook Page No 238)
Question 1.
The mechanism of hydration of ethylcnc to ethyl alcohol.
Answer:
The mechanism of hydration of ethylene involves three steps:
Step 1: Ethylene gets protonated to form carbocation by electrophilic attack of H3O (Formation of carbocation intermediate).
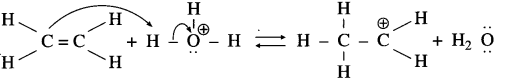
Step 2 : Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation
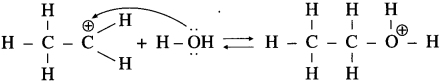
Step 3 : Deprotonation to form an alcohol
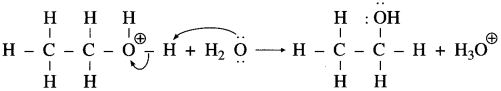
![]()
Problem 11.2 : (Textbook Page No 239)
Question 1.
Predict the products for the following reaction.

Solution:
The substrate (A) contains an isolated ![]() and an aldehyde group. H2/Ni can reduce both these functional groups while LiAlH4 can reduce only – CHO of the two, Hence
and an aldehyde group. H2/Ni can reduce both these functional groups while LiAlH4 can reduce only – CHO of the two, Hence
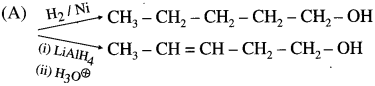
Try this ….. (Textbook page 240)
Question 1.
Arrange O – H, C – H and N – H bonds in increasing order of their bond polarity.
Answer:
Increasing order of polarity :C – H, N – H, O – H
Problem 11.3 : (Textbook Page No 241)
Question 1.
The boiling point of n-butyl alcohol, isobutyl alcohol, sec-butyl alcohol and tert-butyl alcohol are 118 °C, 108 °C. 99 °C and 82 °C respectively. Explain.
Solution:
As branching increases, intermolecular van der Waal’s force become weaker and the boiling point decreases. Therefore, n-butyl alcohol has highest boiling point 118 °C and tert-butyl alcohol has lowest boiling point 83 °C. Isobutyl alcohol is a primary alcohol and hence its boiling point is higher than that of sec-butyl alcohol.
Problem 11.4 : (Textbook Page No 242)
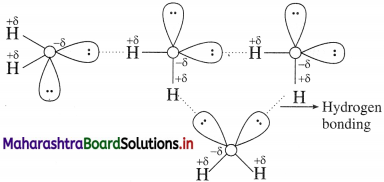
The solubility of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol is 0.2 g and 1.7 g/100 g of H2O respectively. Explain the difference.
Solution :
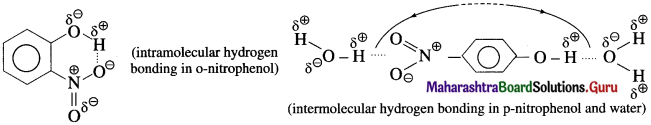
p-Nitrophenol has strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding with solvent water. On the other hand, o-nitrophenol has strong intramolecular hydrogen bonding and therefore the intermolecular attraction towards solvent water is weak. The stronger the intermolecular attraction between solute and solvent higher is the solubility. Hence p-nitrophenol has higher solubility in water than that of o-nitrophenol.
Problem 11.5 : (Textbook Page No 243 & 244)
Question 1.
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of acid strength and justify.
(1) CH3 – CH2 – OH
(2) (CH3)3 C – OH
(3) C6H5 – OH
(4) p-NO2 – C6H4 – OH
Solution :
Compounds (3) and (4) are phenols and therefore are more acidic than the alcohols (1) and (2). The acidic strengths of compounds depend upon stabilization of the corresponding conjugate bases. Hence let us compare electronic effects in the conjugate bases of these compounds :

The conjugate base of the alcohol (1) is destabilized by + 1 effect of one alkyl group, whereas conjugate base of the alcohol (2) is destabilized by +1 effect of three alkyl groups. Hence (2) is weaker acid than (1)

Phenols : The conjugate base of p-nitrophenol (4) is better resonance stabilized due to six resonance structures compared to the five resonance structure of conjugate base of phenol (3). The resonance structure VI has – ve charge on only electronegative oxygens. Hence the phenol (4) is stronger acid than (3). Thus the decreasing order of acid strength is (4), (3), (1), (2).
![]()
Use your brain power (Textbook Page No 244)
Question 1.
What are the electronic effects exerted by – OCH3 and – Cl? Predict the acid strength of
![]()
Answer:
The electronic effects exerted by – Cl and – O CH3 are as follows :
(1) Cl being more electronegative atom it pulls the bonding electrons towards itself. This is known as negative inductive effect (- I).
(2) – OCH3 is less electronegative group which repels the bonding electrons away from it. This is known as positive inductive effect ( + I).
(3) The relative to parent phenol, ![]() is more acidic than
is more acidic than ![]() .
.
Problem 11.6 : (Textbook Page No 245)
Question 1.
Mechanism of acid catalyzed dehydration of ethanol to give ethene.
Answer:
The mechanism of dehydration of ethanol involves the following order :
Step 1 : Formation of protonated alcohols : Initially ethyl alcohol gets protonated to form ethyl oxonium ion.
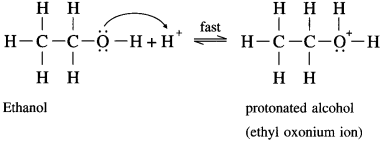
Step 2 : Formation of carbocation : It is the slowest step and hence, the rate determining step of the reaction.
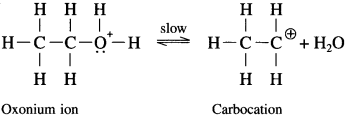
Steps 3: Formation of ethene: Removal of a proton (H+) from carbocation.
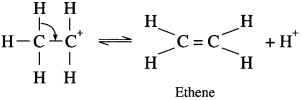
The acidused in step I is released in step 3, the equilibrium is shifted to the right, ethene is removed as it is formed.
Problem 11.6 : (Textbook Page No 245)
Question 1.
Write the reaction showing major and minor products formed on heating butan-2-ol with concentrrated sulphuric acid.
Solution :
In the reaction described butan-2-ol undergoes dehydration to give but-2-ene (major) and but-l-ene (minor) in accordance with Saytzeff rule.
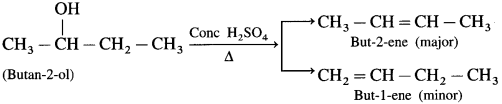
Problem 11.7 : (Textbook Page No 246)
Question 1.
Write and explain reactions to convert propan-l-ol into propan-2-ol.
Solution :
The dehydration of propane-l-ol to propene is the first step. Markownikoff hydration of propene is the second step to get the product propan-2-ol. This is brought about by reaction with concemtrated H2SO4 followed by hydrolysis.
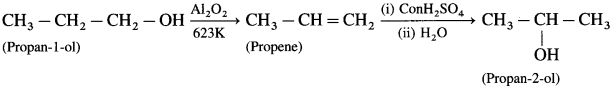
![]()
Problem 11.8 : (Textbook Page No 246)
Question 1.
An organic compound gives hydrogen on reaction with sodium metal. It forms an aldehyde having molecular formula C2H4O on oxidation with pyridinium chlorochromate. Name the compounds and give equations of these reactions.
Solution :
The given molecular formula C2H4O of aldehyde is written as CH3 – CHO. Hence the formula of alcohol from which this is obtained by oxidation must be CH3 – CH2 – OH. The two reactions can, therefore, be represented as follows :
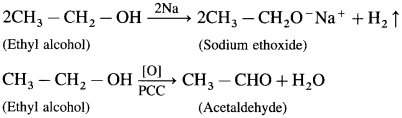
(Do you know? Textbook Page No 248)
Question 90.
Write the mechanism of dehydration of alcohol to give ether.
Answer:
Dehydration of alcohols to form ether is SN2 reaction. The mechanism of dehydration of ethanol involves the following steps.
Step 1 (Protonation) : Initially ethyl alcohol gets protonated in the presence of acid to form ethyl oxonium ion.
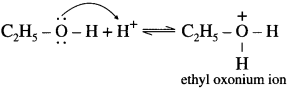
Step 2 (SN2 mechanism) : Protonated alcohol species undergoes a backside attack by second molecule of alcohol is a slow step.
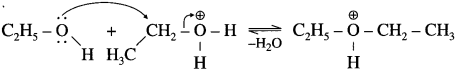
Step 3 (Deprotonation) : Formation of diethyl ether by elimination of proton

Problem 11.9 : (Textbook Page No 249)
Question 1.
Ethyl isopropyl ether does not form on reaction of sodium ethoxide and isopropyl chloride.

(i) What would be the main product of this reaction?
(ii) Write another reaction suitable for the preparation of ethyl isopropyl ether.
Solution :
(i) Isopropyl chloride is a secondary chloride. On treating with sodium ethoxide it gives elimination reaction to form propene as the main product.
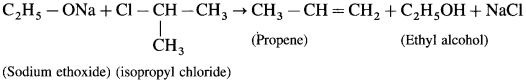
(ii) Ethyl isopropyl ether can be prepared as follows using ethyl chloride (10 chloride) as substrate.
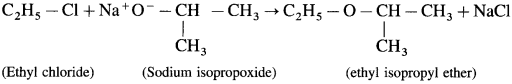
![]()
Do you know? (Textbook Page No 250)
Question 1.
The mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxy ethane.
Answer:
The reaction mechanism takes place as follows :
Step 1 : Protonation of ether Initially the ether molecule (methoxy ethane) protonated by cone. HI to form oxonium ion.
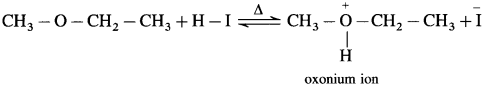
Step 2 : Iodide is a good nucleophile. It attacks the least substituted carbon of the oxonium ion formed in step 1 and displaces an alcohol molecule by SN2 mechanism.
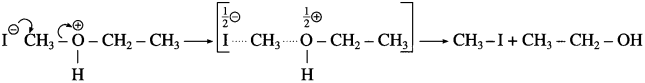
For example :
• Use of excess HI converts the alcohol into alkyl iodide.
• In the case of ether having one tertiary alkyl group the reaction with hot HI follows the SN1 mechanism, and tertiary iodide is formed rather than tertiary alcohol.
Step 1 :
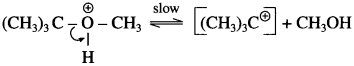
Step 2 :
![]()
Maharashtra State Board 12th Std Chemistry Textbook Solutions
- Coordination Compounds Class 12 Chemistry Textbook Solutions
- Halogen Derivatives Class 12 Chemistry Textbook Solutions
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Chemistry Textbook Solutions
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry Textbook Solutions
- Amines Class 12 Chemistry Textbook Solutions
- Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Textbook Solutions
- Introduction to Polymer Chemistry Class 12 Chemistry Textbook Solutions
- Green Chemistry and Nanochemistry Class 12 Chemistry Textbook Solutions
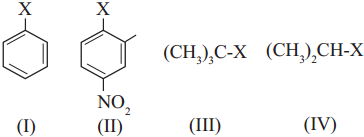









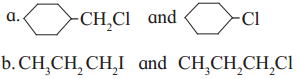
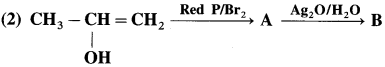
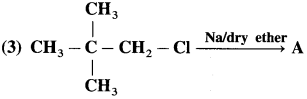






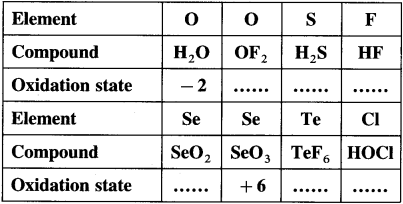
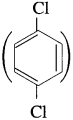 has mp. higher than those of o-and rn-isomers.
has mp. higher than those of o-and rn-isomers.
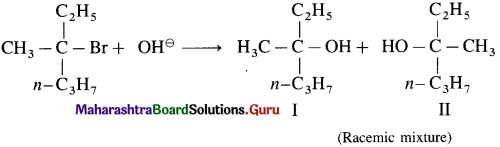
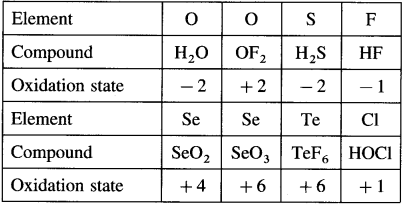
 carbon atom (the starred carbon atom) which is attached to four different groups, i.e., ethyl (-CH2 – CH3), methyl (CH3), chloro (Cl) and hydrogen (H) groups.
carbon atom (the starred carbon atom) which is attached to four different groups, i.e., ethyl (-CH2 – CH3), methyl (CH3), chloro (Cl) and hydrogen (H) groups.


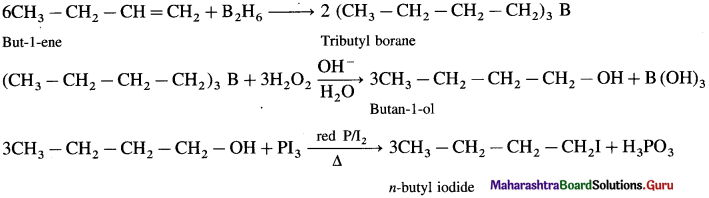
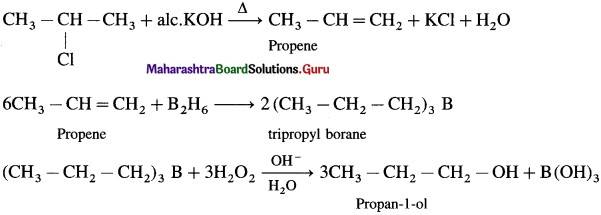










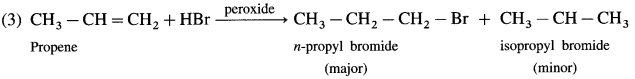
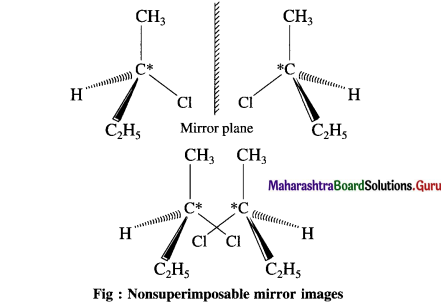
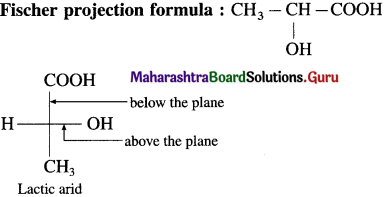
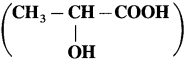 using Fischer projection formulae.
using Fischer projection formulae.