Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Marathi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 8 शब्दांचे घर Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Marathi Solutions Chapter 8 शब्दांचे घर (कविता)
Marathi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions Chapter 8 शब्दांचे घर Textbook Questions and Answers
कोण ते लिहा.
अ. शब्दांच्या घरात राहणारे
आ. घरात एकोप्याने खेळणारे
इ. अवतीभवती झिरपणारे
उत्तरः
अ. हळवे स्वर
आ. काना, मात्रा, वेलांटी
इ. गाणे
![]()
कवितेच्या खालील ओळी पूर्ण करा.
1. घरात होता, ………………..
…………………….. अक्षर – खेळ.
2. एखादयाची …………………
………………………………. भान.
3. कानोकानी …………………
………………… कवितेचाही लळा.
उत्तर:
1. घरात होता, काना – मात्रा – वेलांटीचा मेळ
एकोप्याने खेळायाचे सगळे अक्षर – खेळ.
2. एखादयाची धुसफुससुद्धा हवीहवीशी छान
प्रत्येकाला अर्थ वेगळा सुखदु:खाचे भान.
3. कानोकानी कुजबुजताना अंकुर मनकोवळा
चर्चा करा. सांगा.
प्रश्न 1.
शब्दांमुळे, भाषेमुळे दैनंदिन व्यवहारात कोणते फायदे होतात?
उत्तर:
जगामध्ये अनेक भाषा बोलल्या जातात. काळाच्या ओघात भाषेमध्ये, त्यातील शब्दांमध्ये बदल झाले असले तरी दैनंदिन व्यवहारासाठी, आपापसांतील संवादासाठी गरजेची असते ती भाषा. ‘संवाद’ हा शब्दांचा, भाषेचा सर्वांत मोठा फायदा आहे. आपली मते, आपले विचार शब्दबद्ध करून आपण स्वत:ला व्यक्त करू शकतो. लेखक, कवींसाठी जवळचा सखारे असतो तो म्हणजे शब्द. सांस्कृतिक, सामाजिक, आर्थिक, राजकीय, धार्मिक अशा सगळ्याच क्षेत्रांत भाषेचा वापर अपरिहार्य आहे. आत्मसंवादाचे व लोकसंवादाचे एक समर्थ माध्यम म्हणजे भाषा व त्यातील शब्द होय.
![]()
खेळूया शब्दांशी.
प्रश्न 1.
खालील शब्दांपासून अर्थपूर्ण शब्द बनवा.
उदा. लांटीवे – वेलांटी
- सफुधुस
- रकुअं
- कानीनोका
उत्तर:
- धुसफुस
- अंकुर
- कानोकानी
प्रश्न 2.
खालील शब्दांना कवितेत आलेली विशेषणे लिहा.
- ……………. घर
- …………… स्वर
- …………… अंकुर
- ……………… वाट
उत्तर:
- सुंदर घर
- हळवे स्वर
- मनकोवळा अंकुर
- मोकळी वाट
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
खालील शब्दसाखळी पूर्ण करा.
सुनीता → तारा → राघवेंद्र → द्रव → वजन → नमन →
उत्तर:
सुनीता → तारा → राघवेंद्र → द्रव → वजन → नमन → नकाशा → शारदा → दार → रवा → वारसा → साहस → समई → ईडलिंबू.
प्रकल्प:
‘शब्द’ या विषयावर आधारित सुविचार मिळवा. त्यांचा संग्रह करा. त्याची सुंदर चिकटवही बनवा.
खेळ खेळूया.
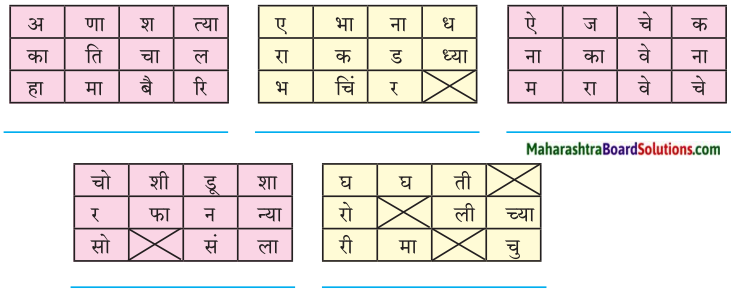
प्रश्न 1.
खालील चौकटी वाचा व त्या प्रमाणे उरलेल्या चौकटी पूर्ण करा.
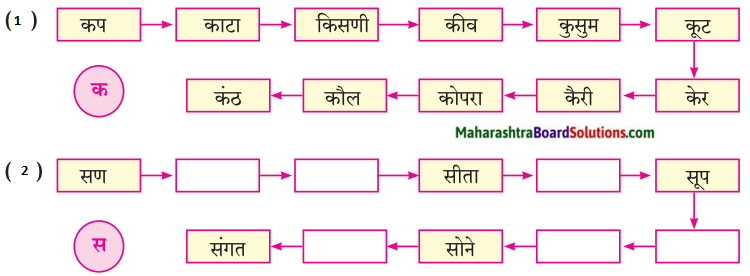
उत्तर:
शब्दकोडे सोडवूया.
प्रश्न 1.
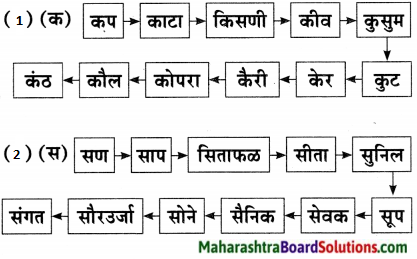
खालील चौकोनातील अक्षरांमध्ये शब्दयोगी अव्यये लपलेली आहेत. उभ्या, आडव्या, तिरप्या पद्धतीने अक्षरे घेऊन शब्दयोगी अव्यये बनवा व लिहा.
उत्तरः
- साठी
- सह
- खाली
- सकट
- प्रमाणे
- समोर
- पुढे
- मागे
- वर
- नजीक
- सारखा
- नंतर
![]()
वाचा.
प्रश्न 1.
विरामचिन्हांचा वापर करून परिच्छेद सुवाच्य अक्षरात पुन्हा लिहा.
मुलांनो शाळेत तुम्हांला अनेक मित्र असतात तुमची काळजी घेणारे तुमचे आरोग्य जपणारे असे अनेक मित्र तुमच्या सभोवती आहेत कोण बरे आहेत हे मित्र असा प्रश्न तुम्हांला निश्चितच पडेल आपल्याकडे फळे फुले सावली देणारे वृक्ष आपल्याला पिण्यासाठी पाणी देणाऱ्या नदया श्वसनासाठी ऑक्सिजन देणारी हवा आपण ज्यावर निवांतपणे राहतो अशी जमीन अर्थातच आपल्या सभोवतालचा निसर्ग हाच आपला खरा मित्र आहे
उत्तर:
“मुलांनो, शाळेत तुम्हांला अनेक मित्र असतात. तुमची काळजी घेणारे, तुमचे आरोग्य जपणारे असे अनेक मित्र तुमच्या सभोवती आहेत. कोण बरे आहेत हे मित्र? असा प्रश्न तुम्हांला निश्चितच पडेल. आपल्याला फळे, फुले, सावली देणारे वृक्ष; आपल्याला पिण्यासाठी पाणी देणाऱ्या नदया, श्वसनासाठी ऑक्सिजन देणारी हवा, आपण ज्यावर निवांतपणे राहतो अशी जमीन; अर्थातच आपल्या सभोवतालचा निसर्ग हाच आपला खरा मित्र आहे.”
शिक्षकांसाठी:
विद्यार्थ्यांना पाठ्यपुस्तकातील सर्व भाषिक खेळ खेळण्याची संधी दयावी. असे विविध भाषिक खेळ स्वत: तयार करून विद्यार्थ्यांकडून अधिकाधिक सराव करून घ्यावा.
Class 7 Marathi Chapter 8 शब्दांचे घर Additional Important Questions and Answers
कोण ते लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
खेळताना सोबत करणारी
उत्तरः
विरामचिन्हे
![]()
कवितेच्या खालील ओळी पूर्ण करा.
अवतीभवती ………………………
…………………………. सुंदर घर
उत्तर:
अवतीभवती झिरपत राही गाणे काळीजभर
सुंदर सुंदर शब्दांचे सुंदर सुंदर घर.
एका वाक्यात उत्तरे लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
सुंदर सुंदर शब्दांचे घर कसे होते?
उत्तरः
सुंदर सुंदर शब्दांचे सुंदर सुंदर घर होते.
प्रश्न 2.
घरात कोणाचा मेळ होता?
उत्तर:
घरात काना-मात्रा आणि वेलांटीचा मेळ होता.
प्रश्न 3.
मधले अंतर कुरवाळाया घरात काय होते?
उत्तर:
मधले अंतर कुरवाळाया घरात रेघांचे छप्पर होते.
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
प्रस्तुत कवितेतून कवीने कोणाचे वर्णन केले आहे?
उत्तरः
प्रस्तुत कवितेतून कवीने सुंदर शब्दांच्या सुंदर घराचे वर्णन केले आहे.
प्रश्न 5.
घरात सगळे एकोप्याने काय खेळायचे?
उत्तरः
घरात सगळे एकोप्याने अक्षर-खेळ खेळायचे.
खालील प्रश्नांची 2-3 वाक्यांत उत्तरे लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
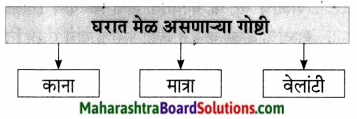
शब्दांच्या घरात कोण कोण असल्याचे कवी सांगतो?
उत्तरः
शब्दांच्या घरात हळवे स्वर राहत आहेत. यांबरोबरच काना, मात्रा, वेलांटी व विरामचिन्हेही राहतात.
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
सुंदर घरात सुंदर शब्दांमधून काय स्फुरते?
उत्तरः
सुंदर घरात शब्द कुजबुजताना एखादा अंकुर फुटतो तर कधी कवितेचाही लळा लागतो. याच शब्दांमधून गाणे उमटून अवतीभवती झिरपत राहते. सुंदर शब्दांतून या अशा अनेक गोष्टी स्फुरतात.
प्रश्न 3.
पुढील कवितेच्या आधारे सूचनेनुसार कृती करा.
आकलन कृती
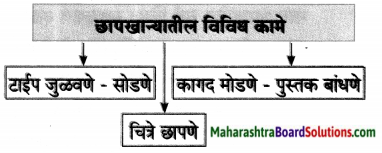
प्रश्न 1.
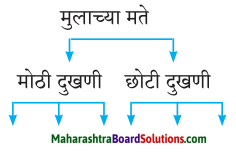
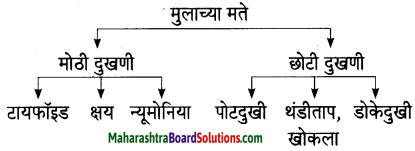
खालील आकृतिबंध पूर्ण करा.
उत्तरे:
एका वाक्यात उत्तरे लिहा.
प्रश्न 1.
सर्व अक्षरे खेळ कसे खेळायचे?
उत्तरः
सर्व अक्षरे एकोप्याने खेळ खेळायचे.
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
वाट मोकळी होऊन कसला लळा लागतो?
उत्तर:
वाट मोकळी होऊन कवितेचा लळा लागतो.
कविता – पाठ्यपुस्तक पृष्ठ क्रमांक
सुंदर सुंदर शब्दांचे ………………..
……………………… सुंदर सुंदर घर
आकलन कृती
प्रश्न 1.
कोण ते लिहा.
1. मधले अंतर कुरवाळणारे. [ ]
2. अवतीभवती झिरपत राहणारे. [ ]
उत्तर:
1. रेघांचे छप्पर
2. गाणे
प्रश्न 2.
जोड्या जुळवा.
| ‘अ’ गट | ‘ ब ‘ गट |
| 1. रेघांचे | अ. लळा |
| 2. झिरपणारे | ब. भान |
| 3. सुखदुःखाचे | क. छप्पर |
| 4. कवितेचा | ड.गाण |
उत्तरः
| ‘अ’ गट | ‘ ब ‘ गट |
| 1. रेघांचे | क. छप्पर |
| 2. झिरपणारे | ड. गाण |
| 3. सुखदुःखाचे | ब. भान |
| 4. कवितेचा | अ. लळा |
![]()
काव्यसौंदर्य
प्रश्न 1.
‘एखादयाची धुसफुससुद्धा हवीहवीशी छान
प्रत्येकाला अर्थ वेगळा सुखदुःखाचे भान’
वरील ओळींतील आशयसौंदर्य स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तरः
‘शब्दांचे घर’ या कवितेत कवी कल्याण इनामदार यांनी शब्दांचा वावर कुठे व कसा असतो याचे सहज चित्रण केले आहे. शब्दांच्या या घरात इतर अनेक गोष्टी राहात असताना या घरात काही शब्दांची चिडचिडदेखील हवीहवीशी वाटते. प्रत्येक शब्दाचा वेगवेगळा अर्थ असूनही त्या शब्दांना एकमेकांच्या सुखदु:खाची जाण आहे. शब्दांच्या या गुणांमुळेच शब्दांचे सुंदर घर बनले आहे.
व्याकरण व भाषाभ्यास
प्रश्न 1.
खालील शब्दांपासून अर्थपूर्ण शब्द बनवा.
उदा. लांटीवे – वेलांटी
- परझित
- रछप्प
- जरळीभका
उत्तर:
- झिरपत
- छप्पर
- काळीजभर
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
खालील शब्दांना कवितेत आलेली विशेषणे लिहा.
………….. धुसफुस
…………… भान
उत्तर:
हवीहवीशी धुसफुस
सुखदुःखाचे
प्रश्न 3.
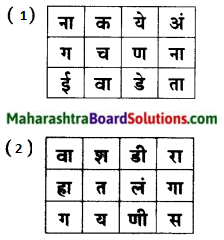
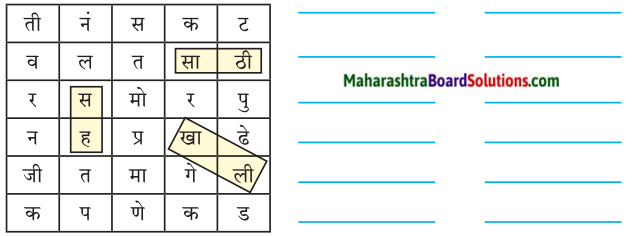
खालील चौकोनातील अक्षरांमध्ये शब्दयोगी अव्यये लपलेली आहेत. उभ्या, आडव्या, तिरप्या पद्धतीने अक्षरे घेऊन शब्दयोगी अव्यये बनवा व लिहा.
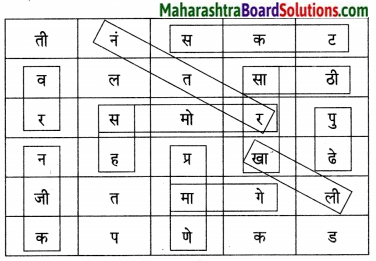
उत्तरः
- सकट
- प्रमाणे
- समोर
- पुढे
- मागे
- वर
- नजीक
- सारखा
- नंतर
प्रश्न 4.
खालील चौकटी वाचा व त्या प्रमाणे उरलेल्या चौकटी पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:

![]()
प्रश्न 4.
कवितेमध्ये आलेले यमक जुळणारे शब्द शोधा.
- घर
- मेळ
- छान
- लळा
उत्तर:
- स्वर
- खेळ
- भान
- मनकोवळा
प्रश्न 5.
खालील शब्दांना विरोधी अर्थाचे शब्द लिहा.
- सुंदर
- हवीशी
- सुख
उत्तर:
- कुरूप
- नकोशी
- दु:ख
प्रश्न 6.
खालील वाक्प्रचारांचा अर्थ सांगून वाक्यात उपयोग करा.
उत्तर:
1. मेळ असणे: एकत्र असणे
चाळीत सर्वभाषिक लोक रहात असले तरी त्यांच्यात मेळ असलेला दिसून येतो.
2. कानात कुजबुजणे : हळू आवाजात बोलणे
पल्लवीने आंतरजातीय विवाह केल्याचे कळताच सर्व नातेवाईक आपसात कुजबुजू लागले.
प्रश्न 7.
रिकाम्या जागी योग्य तो शब्द लिहून लिंग ओळखा.
- ………………. घर
- ………….. धुसफुस
- …………….. अंकुर
- …………….. कविता
- ……………… छप्पर
- …………….. काना
उत्तर:
- ते घर – नपुसकलिंग
- ती धुसफुस – स्त्रीलिंग
- तो अंकुर – पुल्लिंग
- ती कविता – स्त्रीलिंग
- ते छप्पर – नपुसकलिंग
- तो काना – पुल्लिंग
![]()
लेखन विभाग
प्रश्न 1.
‘शब्द’ या विषयार आधारित सुविचार संग्रहित करा.
उत्तर:
1. चंद्र – शुक्रापर्यंतचं अंतर तोडणारा माणूस शब्दांपर्यंतच अंतर तोडू शकत नाही.
2. घासावा शब्द। तासावा शब्द।
तोलावा शब्द। बोलण्यापूर्वी ।।
शब्द हेचि कातर । शब्द सुईदोरा।
बेतावेत शब्द। शास्त्राधारे।।
3. बोलणारा सहज बोलून जातो, पण त्याला कुठे माहीत
असते, ऐकणाऱ्याच्या मनावर शब्द कोरला जातो.
4. हृदयापासून निघालेले शब्द थेट हृदयाला भिडतात.
प्रश्न 2.
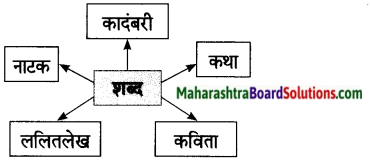
शब्दांमधून निर्माण होणारे साहित्यप्रकार सांगा.
उत्तर:
शब्दांचे घर Summary in Marathi
काव्य परिचय:
‘शब्दांचे घर’ ही कल्याण इनामदार लिखित कविता शब्दांचे वेगळेपण, त्यांची खासियत आपल्यासमोर घेऊन येते. प्रस्तुत कवितेतून कवीने आपल्या भोवतीचा शब्दांचा वावर, शब्दांच्या वेगवेगळ्या सुंदर तहा असल्याचे मार्मिकरित्या मांडले आहे.
Shabdanche Ghar is a very beautiful poem written by Kalyan Inamdar which shows disparity and speciality of words. Poet has perfectly showed different uses and varieties of words.
कवितेचा भावार्थः
सुंदर सुंदर शब्दांचे एक सुंदर सुंदर घर आहे. त्या घरात कोमल, हळवे स्वर राहतात. या घरात काना-मात्रा-वेलांटीचा मेळ साधून आलाय. अक्षरे देखील एकजुटीने सुंदर खेळ खेळतात. त्यांना सोबत करणारी विरामचिन्हे देखील खेळतात. एकजुटीने राहणारे हे सुंदर शब्दांचे सुंदर घर आहे.
या शब्दांच्या घरामध्ये काही शब्दांची चिडचिड सुद्धा छान हवीहवीशी वाटते. प्रत्येक शब्दाचा आपापला वेगळा अर्थ असला तरी एकमेकांच्या सुखदु:खाची जाणीव एकमेकांना आहे. त्यांच्यात दुरावा निर्माण झाला तरी त्यांना एकत्र ठेवण्यासाठी त्यांच्यावर रेषांचे छप्पर मांडले आहे. असे हे एकमेकांना सांभाळून घेणारे सुंदर शब्दांचे सुंदर घर आहे. शब्द उमललेले कोवळे भाव एकमेकांच्या कानी कुजबुजून सांगतात. मनातील भावनांना वाट मोकळी करताच कवितेचा लळा लागतो. भावना कवितेतून उमटू लागतात. सभोवताली मनात गाणे पाझरत राहते. असे हे लळा लावणारे सुंदर शब्दांचे सुंदर घर आहे.
![]()
शब्दार्थ:
- स्वर – सूर – tunes
- एकोपा – एकजूट – unity
- हळवे – कोमल – emotional
- भान – लक्ष, ध्यान – attention
- सुंदर – देखणे, मनोहर – beautiful
- छप्पर – छत, घरावरील आच्छादन – a roof
- रेघ – रेषा, ओळ – a line
- झिरपणे – पाझरणे – to trickle
- लळा – जिव्हाळा – attachment
- काळीज – हृदय – the heart
- अंकुर – जमिनीतून उगवलेले ताजे, कोवळे दल – a plant shoot
- विरामचिन्हे – (Punctuations)
- धुसफूस – मनातल्या मनात होणारी ‘चडफड’ (grumbling)
- स्फुरणे – अकस्मात सुचणे (to occur to the mind)
- श्वसन – श्वास (respiration)
- सखा – मित्र (friend)
- समर्थ – सक्षम (capable)
- कातर – कात्री (scissors)