Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 History Solutions Chapter 10 The Expansion of the Maratha Power Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 History Solutions Chapter 10 The Expansion of the Maratha Power
Class 7 History Chapter 10 The Expansion of the Maratha Power Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Write the meaning:
The Expansion Of The Maratha Power Question Answer Question 1.
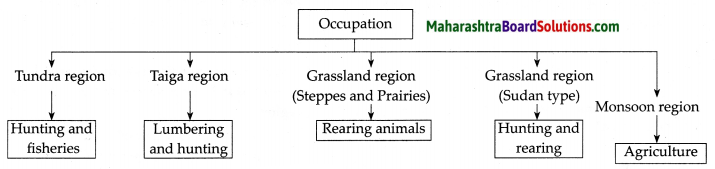
Chauthai.
Answer:
One fourth part of the revenue
The Expansion Of The Maratha Power Question 2.
Sardeshmukhi.
Answer:
One tenth part of the revenue
![]()
2. Write the answer in one word:
Class 7 History Chapter 10 The Expansion Of The Maratha Power Question 1.
Balaji was from this town in Konkan.
Answer:
Shrivardhan
The Expansion Of The Maratha Power Class 7 Question 2.
He ruled Bundelkhand.
Answer:
King Chhatrasal
10 The Expansion Of The Maratha Power Question 3.
Bajirao died at this place.
Answer:
Raverkhedi
The Expansion Of The Maratha Power Answer Question 4.
He defeated the Portuguese.
Answer:
Chimajiappa
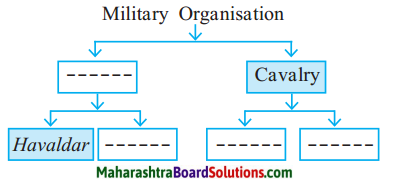
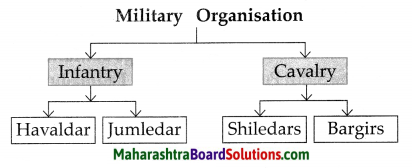
3. Write about them in your own words:
10. The Expansion Of The Maratha Power Question 1.
KanhojiAngre
Answer:
- Kanhoji Angre was the chief of the Maratha Navy.
- He choose Maharani Tarabai’s side.
- He attacked areas which belong to Shahu Maharaj.
- Shahu Maharaj appointed Balaji as Peshwa.
- Balaji was sent against Kanhoji.
- Balaji diplomatically turned Kanhoji towards Shahu Maharaj’s side.
![]()
Question 2.
The Battle of Palkhed
Answer:
- Mughal Emperor Farukhsear appointed Nijam-ul-Mulk as the Subhedar of Deccan.
- The Emperor gave Marathas the right to collect chauthai, Sardeshmukhi from the Mughals.
- The Nizam was against it.
- Bajirao decided to attack the Nizam and he defeated Nizam at Palkhed near Aurangabad.
Question 3.
Balaji Vishwanath:
Answer:
- Balaji Vishwanath was a prominent Maratha Sardar.
- He hailed from Shrivardhan, a town in Konkan.
- He was industrious and experienced.
- He convinced many Sardars to join hands with Shahu Maharaj.
- Kanhoji Angre, the chief of the Maratha Navy was against Shahu Maharaj and sided with Maharani Tarabai.
- He was sent against Kanhoji.
- Balaji avoided the war and diplomatically turned Kanhoji towards Shahu Maharaj’s side.
Question 4.
Bajirao I
Answer:
(i) After the death of Balaji Vishwanath, Shahu Maharaj made Bajirao I Peshwa in CE1720.
(ii) He expanded the Maratha Empire during his tenure of 20 years.
(iii) Nizam, the Subhedar of Deccan did not allow the Marathas the right to collect chauthai and sardeshmukhi.
(iv) Bajirao attacked Nizam and defeated him at Palkhed near Aurangabad.
(v) Under the leadership of his brother Chimajiappa. Bajirao sent Malharrao Holkar,: Ranoji Shinde and Udaji Pawar to strengthen the position of the Marathas in Malwa.
(vi) Mughal Subhedar Mohammad Khan Bangush attacked on Bundelkhand. The king of Bundelkhand, Chhatrasal requested Bajirao to help him.
(vii) Bajirao defeated Bangush. The King Chhatrasal honoured Bajirao on large scale.
![]()
4. Give reasons:
Question 1.
Two separate Maratha States were formed.
Answer:
(i) There was a battle between Shahu Maharaj and Maharani Tarabai for the throne/gadi.
(ii) Shahu Maharaj won the battle and captured Satara.
(iii) He got himself crowned and Satara became the capital of the Maratha kingdom.
(iv) In 1710, Maharani Tarabai declared her minor son Shivaji II as Chhatrapati at Panhalgad. Since then, a separate state of Kolhapur apart from Satara state came into existence in the Maratha Empire.
Question 2.
Azamshah released Chattrapati Shahu Maharaj from his custody.
Answer:
(i) Azamshah thought that if he released Shahu Maharaj from his custody, then there will be a fight between Maharani Tarabai and Shahu Maharaj for the throne of Chhatrapati.
(ii) The Maratha power will become weak and therefore Azamshah released Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj from his custody.
Question 3.
Delhi Darbar needed the help of the Marathas.
Answer:
(i) The Mughal Empire was threatened by the north-west Irani and Afgani attacks.
(ii) Local kings like Pathans, Rajputs, Jats and Rohilas also posed a threat for them.
(iii) The internal competition and tussle in die court also weakened the Mughal powers. Hence, Delhi Darbar needed the help Marathas.
Activity:
Get a biography of Maharani Tarabai and present an inspiring event in her life.
![]()
Class 7 History Chapter 10 The Expansion of the Maratha Power Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the sentence by choosing the appropriate word from the options given below:
Question 1.
Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj had got himself crowned at _______.(Pune, Satara, Malwa)
Answer:
Satara
Question 2.
At the time of Aurangzeb’s death, Shahajada _______ was in the south. (Azamshah, Aurangzeb, Farukhsear)
Answer:
Azamshah
Question 3.
Maharani Tarabai declared her minor son as Chhatrapati _______ at Panhala. (Shivaji II, Savai, Madhavrao)
Answer:
Shivaji II
Question 4.
_______ became the Subhedar of the Deccan. (Nijam-ul-Mulk, Farukhsear, Madhavrao)
Answer:
Nijam-ul-Mulk
Question 5.
Bajirao sent his brother ________ to subdue the Portuguese. (Chimajiappa, Malharrao Holkar, Ranoji Shinde)
Answer:
Chimajiappa
Question 6.
Bajirao defeated _________ of Bundelkhand. (Bangush, Nadir Shah, Farukhsear)
Answer:
Bangush
Question 7.
When Kanhoji Angre attacked Shahu Maharaj, he sent ______ against Kanhoji Angre. (Balaji Vishwanath, Bajirao, Shahu Maharaj)
Answer:
Balaji Vishwanath
![]()
Question 8.
After the death of Balaji Vishwanath, Shahu Maharaj made ________ as the Peshwa. (Chimajiappa, Bajirao I, Udaji Pawar)
Answer:
Bajirao I
Question 9.
Iran’s Emperor ___________ attack on India. (Nadirshah, Abdulla (Hassan), Hussein Ali)
Answer:
Nadirshah
Question 10.
After the death of Aurangzeb ________ and ______ dominated the Mughal Court.(Abdulla (Hasan), Hussein Ali, Nijam-Ul-Mulk)
Answer:
Abdulla (Hasan) and Hussein Ali
Question 11.
After the death of Emperor Aurangzeb the fight for __________ started between his sons. (Delhi’s throne, Chauthai-Sardeshmukhi, Subhedar of Deccan)
Answer:
Delhi’s throne
Question 12.
Prince Shahu was in the custody of _________ (Maharani Tarabai, Azamshah, Bahadur Shah)
Answer:
Azamshah
Question 13.
_______ became the capital of Maratha kingdom. (Satara, Kolhapur, Pune)
Answer:
Satara
Question 14.
__________was the chief of the Maratha Navy. (Balaji, Vishwanath, Kanhoji Angre, Bajirao I)
Answer:
Kanhoji Angre
Question 15.
Bajirao took his last breath at _______ (Raverkhedi, Bhopal, Palkhed)
Answer:
Raverkhedi
Question 16.
________ established the Maratha domination in North India by his bravery.
(Chimajiappa, Bajirao, King Chhatrasal)
Answer:
Bajirao
Match the following:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Shahu Maharaj
(2)Shivaji II (3) Nijam-ul-Mulk (4) Nadir Shah |
(a) Iran’s Emperor
(b) Satara (c) Panhalgad (d) Subhedar of Deccan |
Answer:
1 – b
2 – c
3 – a
4 – d
![]()
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) King Chhatrasal
(2)The Battle of Bhopal (3) Chauthai (4) Sardeshmukhi |
(a) One fourth part of the income
(b) Bundelkhand (c) Bajirao (d) One tenth part of the income. |
Answer:
1 – b
2 – d
3 – a
4 – c
Explain the meanings of:
Question 1.
Subhedar.
Answer:
Historical rank in the army
Question 2.
Sanad.
Answer:
Authority
Write the answer in one word:
Question 1.
These places were under Portuguese rule.
Answer:
Vasai and Thane
Question 2.
The Emperor of Iran who invaded India.
Answer:
Nadir Shah
Question 3.
He was the chief of the Maratha Navy.
Answer:
KanhojiAngre
Question 4.
He was a great warrior.
Answer:
Bajirao
![]()
Question 5.
He was the first Peshwa.
Answer:
Balaji Vishwanath
Question 6.
The second Peshwa.
Answer:
Bajirao
Question 7.
Aurangzeb’s son.
Answer:
Shahajada Azamshah
Question 8.
Tarabai proclaimed her younger son as.
Answer:
Chhatrapati Shivaji II
Answer the following in one sentences:
Question 1.
Who was in the custody of Azamshah?
Answer:
Prince Shahu was in the custody of Azamshah.
Question 2.
What was the new political policy of Marathas?
Answer:
The new political policy of the Marathas was to protect and expand their own Empire instead of fighting with Mughal powers.
Question 3.
What had weakened the Mughal powers?
Answer:
The threat from local kings, internal competition and tussle in the court weakened the Mughal powers.
Question 4.
Who was Kanhoji Angre?
Answer:
Kanhoji Angre was the Chief of the Maratha Navy.
Question 5.
With whose help did Balaji receive the authority to recover Chauthai and Sardeshmukhi?
Answer:
With the help of Sayyid brothers, Abdulla (Hassan) and Hussein Ali, Balaji received the authority to recover Chauthai and Sardeshmukhi.
Question 6.
Whom did Bajirao send to Malwa to strengthen the position of the Marathas?
Answer:
Bajirao sent Malharrao Holkar, Ranoji Shinde and Udaji Pawar under the leadership of his x brother Chimajiappa to Malwa to strengthen the position of Marathas.
![]()
Question 7.
Whose help did King Chhatrasal seek to protect his kingdom Bundelkhand.
Answer:
The King Chhatrasal requested Bajirao to protect his kingdom Bundelkhand.
Question 8.
Which parts from Konkan coastal area were under Portuguese rule?
Answer:
Vasai and Thane from Konkan coastal area were under Portuguese rule.
Question 9.
Whom did Bajirao send to defeat Portuguese? ‘
Answer:
Bajirao sent his brother Chimajiappa to defeat the Portuguese.
Question 10.
What rights did Balaji get from the Mughal Emperor?
Answer:
Balaji got from the Mughal Emperor the sanads to collect Chauthai and Sardeshmukhi
Question 11.
Why did Chhatrasal ask Balaji for help?
Answer:
Mohammad Khan Bangush, the Mughal Subhedar of Allahabad attacked Bundelkhand and defeated Chhatrasal. So, Chhatrasal asked Balaji for help.
Question 12.
Where did Bajirao defeat the Nizam?
Answer:
Bajirao defeated the Nizam at Palkhed near Aurangabad.
Question 13.
What were the great qualities of Bajirao?
Answer:
Bajirao was a great warrior, a powerful ruler who established the Maratha dominance in North.
![]()
Write notes on the following:
Question 1.
The Battle of Bhopal
Answer:
- The emperor became restless due to Bajirao’s attack.
- He called the Nizam to protect Delhi.
- The Nizam attacked Bajirao with his large army.
- Bajirao defeated him at Bhopal.
- The Nizam agreed to secure the sanad of Malwa subhedari to Marathas from the Badshah.
Give explanations for the following:
Question 1.
Portuguese.
Answer:
- Vasai and Thane from Konkan coastal area were under Portuguese rule.
- Portuguese rulers used to exploit people.
Question 2.
King Chhatrasal requested Bajirao for help.
Answer:
- King Chhatrasal established his own kingdom in Bundelkhand.
- Mughal Subhedar Mohammad Khari Bangush attacked Bundelkhand and defeated king Chhatrasal.
- Hence, King Chhatrasal requested Bajirao for help.
Question 3.
Shahu Maharaj knew the integrities of the Mughals.
Answer:
- The early part of Shahu Maharaj’s life was spent in Mughal camps.
- He has seen Mughal politics from close quarters.
- He was aware of the strong and weak points of the Mughal empire very well.
- He also knew some influential people in Mughal Darbar.
- All these factors helped him in the changing circumstances to decide the new direction for Maratha politics.
Answer the following in short:
Question 1.
How did Balaji Vishwanath turned Kanhoji towards the side of Shahu Maharaj?
Answer:
- Kanhoji Angre was the chief of the Maratha Navy.
- He chose Maharani Tarabai’s side.
- He attacked areas which belonged to Shahu Maharaj.
- Shahu Maharaj sent Balaji Vishwanath against Kanhoji.
- Balaji avoided the war and won Kanhoji towards the side of Shahu Maharaj.
![]()
Question 2.
Why did Bajirao decide to attack Delhi?
Answer:
- The Marathas established their supremacy in Malwa and Bundelkhand.
- Bajirao demanded Malwa Subhedari from the Badshah (Emperor).
- The Emperor rejected his demand Hence Bajirao decided to attack Delhi.