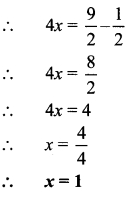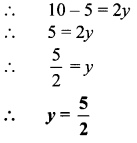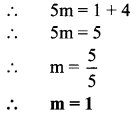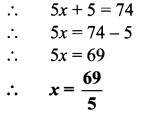Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions covers the 7th Std Maths Practice Set 39 Answers Solutions Chapter 9 Direct Proportion and Inverse Proportion.
Direct Proportion and Inverse Proportion Class 7 Practice Set 39 Answers Solutions Chapter 9
Question 1.
Suresh and Ramesh together invested Rs 144000 in the ratio 4 : 5 and bought a plot of land. After some years they sold it at a profit of 20%. What is the profit each of them got?
Solution:
Total investment = Rs 144000
Profit earned = 20%
∴ Total profit = 20% of 144000 = \(\frac{20}{100} \times 144000\) = Rs 28800
Proportion of investment of Suresh and Ramesh = 4:5
Let the profit of Suresh be Rs 4x and that of Ramesh be Rs 5x.
4x + 5x = 28800
∴ 9x = 28800
∴ \(x=\frac { 28800 }{ 9 }\)
= 3200
∴ Suresh’s profit = 4x = 4 × 3200 = Rs 12800
Ramesh’s profit = 5x = 5 × 3200 = Rs 16000
∴ The profit earned by Suresh and Ramesh are Rs 12800 and Rs 16000 respectively.
Question 2.
Virat and Samrat together invested Rs 50000 and Rs 120000 to start a business. They suffered a loss of 20%. How much loss did each of them incur?
Solution:
Total investment = Rs 50000 + Rs 120000 = Rs 170000
Loss incurred = 20%
∴ Total loss = 20% of 170000 = \(\frac{20}{100} \times 170000\) = Rs 34000
Proportion of investment = 50000 : 120000
= 5 : 12 …. (Dividingby 10000)
Let the loss incurred by Virat be Rs 5x and that by Samrat be Rs 12x.
5x + 12x = 34000
∴ 17x = 34000
∴ \(x=\frac { 34000 }{ 17 }=2000\)
∴ Virat’s loss = 5x = 5 × 2000 = Rs 10000
Samrat’s loss = 12x = 12 × 2000 = Rs 24000
∴ The loss incurred by Virat and Samrat are Rs 10000 and Rs 24000 respectively.
Question 3.
Shweta, Piyush and Nachiket together invested Rs 80000 and started a business of selling sheets and towels from Solapur. Shweta’s share of the capital was Rs 30000 and Piyush’s Rs 12000. At the end of the year they had made a profit of 24%. What was Nachiket’s investment and what was his share of the profit?
Solution:
Total investment = Rs 80000
Nachiket’s investment = Total investment – (Shweta’s investment + Piyush’s investment)
= 80000 – (30000+ 12000)
= 80000 – 42000 = Rs 38000
Profit earned = 24%
∴ Total profit = 24% of 80000 = \(\frac { 24 }{ 100 }\) x 80000 = Rs 19200
Proportion of investment = 30000 : 12000 : 38000
= 15 : 6 : 19 …. (Dividing by 2000)
Let the profit of Shweta, Piyush and Nachiket be Rs 15x, Rs 6x and Rs 19x respectively.
15x + 6x + 19x = 19200
∴ 40x = 19200
∴ \(x=\frac { 19200 }{ 40 }=480\)
∴ Nachiket’s profit = 19x = 19 × 480 = Rs 9120
∴ Nachiket’s investment is Rs 38000 and his profit is Rs 9120.
Question 4.
A and B shared a profit of Rs 24500 in the proportion 3 : 7. Each of them gave 2% of his share of the profit to the Soldiers’ Welfare Fund. What was the actual amount given to the Fund by each of them?
Solution:
Proportion of share = 3:7
Let the profits of A and B be Rs 3x and Rs 7x respectively.
3x + 7x = 24500
∴ 10x = 24500
∴ \(x=\frac { 24500 }{ 10 }=2450\)
Profit earned by A = 3x = 3 × 2450 = Rs 7350
Amount given by A = 2% of his profit
= \(\frac { 2 }{ 100 }\) × 7350 = Rs 147
Profit earned by B = 7x = 7 × 2450 = Rs 17150
Amount given by B = 2% of his profit
= \(\frac { 2 }{ 100 }\) × 17150 = Rs 343
∴ The amount given by A and B to the Soldiers’ Welfare Fund are Rs 147 and Rs 343 respectively.
Question 5.
Jaya, Seema, Nikhil and Neelesh put in altogether Rs 360000 to form a partnership, with their investments being in the proportion 3 : 4 : 7 : 6. What was Jaya’s actual share in the capital? They made a profit of 12%. How much profit did Nikhil make?
Solution:
Total investment = Rs 360000
Profit earned = 12%
∴ Total profit = 12% of 360000
= \(\frac{12}{100} \times 360000\) = Rs 43200
Proportion of investment = 3 : 4 : 7 : 6
Let the investment of Jaya, Seema, Nikhil and Neelesh be Rs 3x, Rs 4x, Rs 7x and Rs 6x respectively.
3x + 4x + 7x + 6x = 360000
∴ 20x = 360000
∴ \(x=\frac { 360000 }{ 20 }\)
= 18000
∴ Jaya’s investment = 3x = 3 x 18000 = Rs 54000
Also, profit made by them is Rs 43200
∴ 3x + 4x + 7x + 6x = 43200
∴ 20x = 43200
∴ \(x=\frac { 43200 }{ 20 }\)
= 2160
∴ Nikhil’s profit = 7x = 7 x 2160 = Rs 15120
∴ Jaya’s share in the capital was Rs 54000 and the profit made by Nikhil was Rs 15120.
Maharashtra Board Class 7 Maths Chapter 9 Direct Proportion and Inverse Proportion Practice Set 39 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
Saritaben, Ayesha and Meenakshi started a business by investing Rs 2400, Rs 5200 and Rs 3400. They made a profit of 50%. If they reinvested all their profit by adding it to the capital, find out the proportions of their shares in the capital during the following year. (Textbook pg. no. 67)
Solution:
Total investment = Rs 2400 + Rs 5200 + Rs 3400 = Rs 11000
Total profit = 50% of 11000 = \(\frac{50}{100} \times 11000\) = Rs 5500
Proportion of shares = 2400 : 5200 : 3400
= 12 : 26 : 17 …. (Dividingby 200)
Let the profit of Saritaben, Ayesha and Meenakshi be Rs 12x, Rs 26x and Rs 17x respectively.
12x + 26x + 17x = 5500
∴ 55x = 5500
∴ x = 100
∴ Saritaben’s profit = 12x = 12 × 100 = Rs 1200
Ayesha’s profit = 26x = 26 × 100 = Rs 2600
Meenakshi’s profit = 17x = 17 × 100 = Rs 1700
∴ Saritaben’s new investment = 2400 + 1200 = Rs 3600
Ayesha’s new investment = 5200 + 2600 = Rs 7800
Meenakshi’s new investment = 3400 + 1700 = Rs 5100
∴ New proportion of shares = 3600 : 7800 : 5100
= 12 : 26 : 17 …. (Dividing by 300)
∴ The proportion of the shares in the capital during the following year is 12 : 26 :17
Question 2.
Are the amount of petrol filled in a motorcycle and the distance traveled by it, in direct proportion? (Textbook pg. no. 63)
Solution:
Yes.
If amount of petrol filled in the motorcycle is less, it will travel less distance and if the amount of petrol filled is more, it will travel more distance.
Hence, the amount of petrol filled in the motorcycle and the distance traveled by it are in direct proportion.
Question 3.
Can you give examples from science or everyday life of quantities that vary in direct proportion? (Textbook pg. no. 63)
Solution:
- Number of chairs and the number of spectators.
- Quantity (litres) of water and number of vessels required to store the water.