By going through these Maharashtra State Board 12th Science Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 Transition and Inner Transition Elements students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 Transition and Inner Transition Elements
d – Series :
- 3d-Series : 21Sc to 30Zn
- 4d-Series: 39Y to 48Cd
- 5d-Series : 57La to 80Hg
- 5d-Series : 89Ac to 112Cn
Electronic Configuration :
- 3d-Series: [Ar] 3d1-10 4s1-2
- 4d-Series:[Kr] 4d1-10 5s1-2
- 5d-Series: [Xe] 4f14 5d1-10 6s1-2
- 6d- Series: [Rn] 5f14 6d1-10 7s1-2
| Electronic configuration | Expected | Observed |
| (i) 24Cr (ii) 29Cu | [Ar] 3d44y2 [Ar] 3d9 As2 | [Ar] 3d5 As1 [Ar] 3d10 As1 |
![]()
For 3d-Series :
- Atomic radii decrease from Sc to Cu
- Ionic radii decrease from Sc to Ni
- First ionisation enthalpy increases from Sc to Zn.
Transition elements show variable oxidation states common being + 2.
1 Bohr Magneton (B.M) = \(\frac{e h}{4 \pi m_{\mathrm{e}} c}\)
Spin only formula : \(\mu=\sqrt{n(n+2)}\)
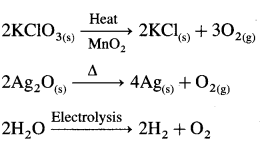
KMnO4
Preparation from MnO2

Strong oxidising agent
- in acidic medium
- in neutral or weakly alkaline medium
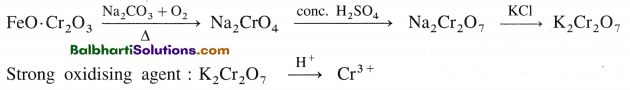
K2Cr2O7 :
Preparation from chromite ore :
Metallurgy :
1. Metal extraction processes –
- Pyrometallurgy
- Hydrometallurgy
- Electrometallurgy
2. Steps involved in the extraction of pure metal-
- Concentration
- Conversion of an ore into oxides
- Reduction of an ore
- Refining of metals
3. Extraction of iron from haematite ore by Blast furnace
![]()
f-Block elements :
Lanthanoids : 5 8Ce to 7 1Lu
Actinoids : 9 0Th to 1 0 3Lr
Electronic configuration :
Lanthanoids : [Xe] 4f1-14 5d0-1 6s2
Actinoids : [Rn] 5f1-14 6d0-1 7s2
Position in periodic table :
| f-Block elements | Group | Period |
| Lanthanoids | 3 | 6 |
| Actinoids | 3 | 7 |
Lanthanoid contraction, Actinoid contraction