Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 5 Environmental Studies Solutions Chapter 24 Substances, Objects and Energy Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 5 EVS Solutions Part 1 Chapter 24 Substances, Objects and Energy
5th Std EVS 1 Digest Chapter 24 Substances, Objects and Energy Textbook Questions and Answers
1. What’s the solution?
Question a.
We need to make a sherbet quickly for some guests. But we only have sugar candy in the house.
Answer:
We can pound sugar candy into a fine powder. When the powder is fine, it will quickly dissolve in water. Therefore we can make sherbet quickly.
![]()
Question b.
We need to rub salt on a corncob but only salt crystals are available.
Answer:
We can pound salt crystals. Either we can use mortar pestle or we can also crush the crystals of salt in a grinder. Such powdered salt can be easily applied on the corncob.
2. Use your brain power!
Question a.
Why do tablets of camphor decrease in size day by day ?
Answer:
Tablets of Camphor are in solid state. Camphor has a property to turn into gaseous state directly from a solid state. Therefore, camphor decreases in size gradually. One can also notice the fragrance of camphor as it turns into vapour.
![]()
Question b.
How do we save fuel by using public transport ?
Answer:
Each automobile vehicle needs fuel either in the form of petrol, diesel, or CNG. If all the people use a separate vehicle, the amount of fuel consumed would be much more. If many people start using public transport, fuel consumption would be reduced. A single bus or a train can carry many people and thus it can save lots of fuel.
3. Answer the following questions.
Question a.
When and why do clothes smell of naphthalene?
Answer:
The naphthalene balls are continuously converted into small particles in the gaseous state. These particles settle down on the clothes in which they are kept. Therefore if naphthalene balls are kept for a long time in the clothes, they smell of naphthalene due to these particles.
Question b.
In which states is water found in nature?
Answer:
Water is found in all three states in nature, solid, liquid and gaseous state. Ice is the solid state of water. Water in lakes, sea etc. are in liquid state and steam or vapour is the gaseous state of water.
![]()
Question c.
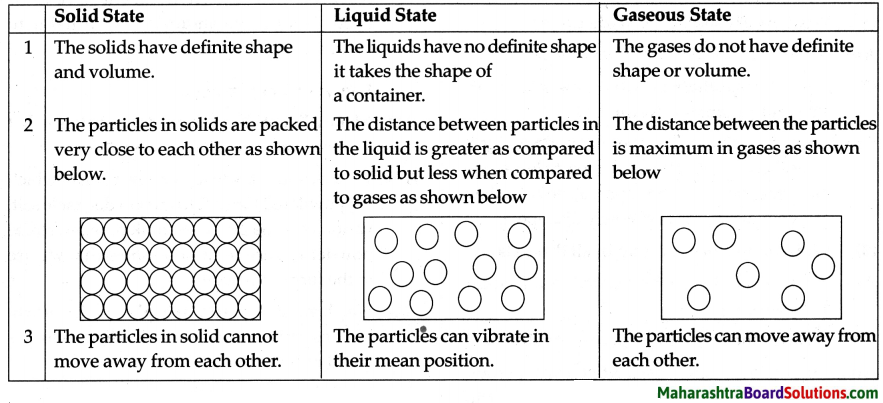
What is the difference between the solid, liquid and gaseous states of a substance?
Answer:
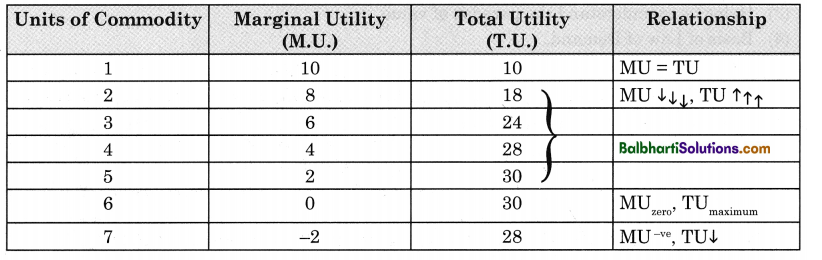
The differences in the solid, liquid and gaseous state of substances is given in the table below:
Question d.
What is meant by energy?
Answer:
The capacity to do the work is called energy.
Activities :
Question 1.
Make different kinds of articles from clay.
![]()
Question 2.
Visit a wood workshop and observe the work being done there.
Question 3.
Obtain some information about the power generation plants in Maharashtra and present it in the classroom.
Environmental Studies Part 1 Standard 5th Solutions Chapter 24 Substances, Objects and Energy Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blank with the correct answers from the options given below:
Question 1.
All substances we see around us are made up of very tiny ………
(a) dust
(b) particles
(c) mud
Answer:
(b) particles
Question 2.
…………….. of particles of any substance must come together to form a particle that can be visible to our eyes.
(a) Lakhs
(b) Thousands
(c) Hundreds
Answer:
(a) Lakhs
![]()
Question 3.
Naphthalene balls which are kept open are continuously converted to small particles in the …… state.
(a) liquid
(b) solid
(c) gaseous
Answer:
(c) gaseous
Question 4.
Different substances have different …………..
(a) material
(b) properties
(c) code
Answer:
(b) properties
Question 5.
…………… is required to do work.
(a) Energy
(b) Strength
(c) Health
Answer:
(a) Energy
Question 6.
When something burns energy is released in the form of …………..
(a) heat
(b) rain
(c) cold
Answer:
(a) heat
Question 7.
Energy in the form of motion is called ……… energy.
(a) Kinesthetic
(b) Kinetic
(c) Solar
Answer:
(b) Kinetic
Question 8.
Stores of …………….. and ……. which are used as fuels, on earth are limited.
(a) mineral oil
(b) uranium
(c) coal
Answer:
(a) mineral oil, (c) coal
![]()
Question 9.
Energy obtained from sun is called …………… energy
(a) lunar
(b) solar
(c) tidal
Answer:
(b) solar
Question 10.
Energy obtained by breaking the tiniest particle of a substance is called …
(a) solar
(b) atomic
(c) kinetic
Answer:
(b) atomic
Question 11.
Sunlight, wind and water are ……………. sources of energy
(a) exhaustible?
(b) depleting
(c) non-exhaustible
Answer:
(c) non-exhaustible
Question 12.
When iron or copper is made smooth with a file, we get …………….. of iron or copper.
(a) particles
(b) soil
(c) saudust
Answer:
(a) particles
Question 13.
Liquids are also made of small…….
(a) droplets
(b) particles
(c) dust
Answer:
(b) particles
![]()
Question 14.
…………… is found in three states – solid, liquid and gaseous.
(a) Mineral oil
(b) Carbon
(c) Water
Answer:
(c) Water
Question 15.
In nature, every substance occurs in a………… state.
(a) special
(b) specific
(c) partial
Answer:
(b) specific
Question 16.
Aluminium and coal are is. ………. state.
(a) solid
(b) liquid
(c) gaseous
Answer:
(a) solid
Question 17.
Kerosene and petrol are in ……
(a) solid
(b) liquid
(c) gaseous
Answer:
(b) liquid
![]()
Question 18.
Nitrogen and Oxygen are in … ………….state.
(a) solid
(b) liquid
(c) gaseous
Answer:
(c) gaseous
Question 19.
The capacity of a body to do work is called
(a) work out
(b) energy
(c) exercise
Answer:
(b) energy
Question 20.
When petrol or diesel burns in a motor vehicle, …………… gets released.
(a) fire
(b) fuel
(c) energy
Answer:
(c) energy
Question 21.
Machines can be run using ……………….
(a) energy
(b) fuels
(c) water
Answer:
(b) fuels
![]()
Question 22.
Coal, diesel, CNG, LPG, petrol are all substances from which energy is obtained in form of
(a) heat
(b) rain
(c) cold
Answer:
(a) heat
Question 23.
When a person or vehicle moves, heat energy gets converted into …….
(a) electricity
(b) rain
(c) motion
Answer:
(c) motion
Question 24.
Electricity is also a form of ………….
(a) machine
(b) energy
(c) heat
Answer:
(b) energy
Question 25.
We use ……………. to run the T.V.
(a) wires
(b) plugs
(c) electricity
Answer:
(c) electricity
![]()
Question 26.
In a solar cooker …………………. energy is used.
(a) solar
(b) electricity
(c) L.P.G.
Answer:
(a) solar
Question 27.
Plants use……. to prepare their food.
(a) LPG
(b) induction
(c) sunlight
Answer:
(c) sunlight
Question 28.
When we burn substances like coal or mineral oil, the …………………. energy, they contain is converted into heat energy.
(a) solar
(b) stored
(c) lunar
Answer:
(b) stored
Question 29.
Stores of coal and mineral oil on earth are
(a) unlimited
(b) limited
(c) plenty
Answer:
(b) limited
![]()
Question 30.
………… batteries produce electricity using sunlight
(a) Water
(b) Solar
(c) Tidal
Answer:
(b) Solar
Name the following:
Question 1.
Any three substances found in solid state.
Answer:
Iron, copper, aluminium, wood
Question 2.
Three substances found in liquid state.
Answer:
Water, milk, cough syrup.
Question 3.
Three substances found in gaseous state.
Answer:
Naphthalene balls, iodine crystals
![]()
Question 4.
Substances which goes into gaseous state directly from solid state.
Answer:
Naphthalene balls
Question 5.
Properties of substances.
Answer:
Transparency, hardness, colour, smell, solubility in water.
Question 6.
Fuels used for running machines.
Answer:
LPG, CNG, coal, diesel, petrol.
Question 7.
Examples of kinetic energy.
Answer:
Moving wind mill, sailing boats, running water, moving car etc.
Question 8.
Forms of energy.
Answer:
Sound, heat, light, electricity.
Question 9.
Main source of energy used by us.
Answer:
Electricity
![]()
Question 10.
Energy sources which do not cause pollution
Answer:
Wind energy, solar energy.
Answer in one sentence :
Question 1.
What are all subtances made up of?
Answer:
All substances are made up of fine particles.
Question 2.
Why do naphthalene balls grow smaller in size and gradually disappear?
Answer:
Naphthalene when left open continuously gets converted into small gaseous particles, so, as these particles leave the naphthalene balls, they grow smaller is size and slowly disappear.
Question 3.
Which substance is found in all three states?
Answer:
Water is found in all three states – solid, liquid and gaseous.
Question 4.
What are the different properties of substance?
Answer:
Different substances have different properties, like hardness, transparency, colour, smell, solubility in water etc.
![]()
Question 5.
What is ‘energy?
Answer:
The capacity of a body to do work is called energy
Question 6.
How is energy released?
Answer:
When petrol or diesel burns in a motor vehicle, energy gets released.
Question 7.
Name some substance from which energy is obtained.
Answer:
Coal, diesel, CNG, LPG, petrol are all substances from which energy is obtained.
Question 8.
What is Kinetic energy?
Answer:
Energy in the form of motion is called Kinetic energy.
Question 9.
Why should we find alternate sources of energy?
Answer:
Stores of coal and mineral oil on earth are very limited and fast depleting therefore we must find alternate sources of energy.
![]()
Question 10.
What are solar batteries?
Answer:
Batteries which produce electricity using sunlight are called solar batteries.
Question 11.
Why should we make a habit of using minimum amount of electricity?
Answer:
In any method of electricity generation, resources from the environment have to be used. Hence, we should make a habit to conserve electricity
Use your brain power!
Question 1.
What uses of heat energy do we see in our daily life?
Answer:
We use heat energy to cook food, to heat water, to press our clothes, to keep us warm during cold winters in areas where temperature is very low, etc.
Question 2.
Why do tablets of camphor decrease in size day by day?
Answer:
Camphor particles present in the tablets escape by getting converted directly to gaseous state. Therefore the tablets of camphor decrease in size day by day.
![]()
Question 3.
How do we save fuel by using public transport?
Answer:
If people drive car instead of using public transport while going to work, more fuel will be burnt, as each car will burn the fuel to release energy and work. However if public transport is used. We need to use fuel, only for one transport vehicle. Hence it will save a lot of fuel if people use the public transport.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What is meant by energy? Name the sources of energy
Answer:
The capacity of a body to do work is called energy. Energy is obtained by burning fuel is in the form of heat. This heat is used to do work. The sources of energy are the sun, coal, diesel, CNG, LPG, petrol, wind, moving water and electricity
Question 2.
What is the original source of energy for the electricity produced at a thermal power station? How is electricity generated?
Answer:
In a thermal power station coal is the original source of energy. Here coal is burnt to release heat. The heat generated is utilised to convert water to steam. Then steam is used to rotate the turbines. As the turbine rotates electricity is produced.
![]()
Can you tell?
1. Write a few lines on the black board with a chalk. Now observe the chalk.
Question a.
What change do you see in the chalk?
Answer:
The chalk becomes smaller in size, after writing.
Question b.
Why did the chalk become smaller in size after writing on the board?
Answer:
When we wrote on the board the pieces of chalk stick to board, therefore the chalk became smaller in size.
2. Wipe the board with a duster and then tap the duster against the table.
Question a.
What do you see?
Answer:
A fine white particles of chalk fell of the duster when we tapped it against the table.
Question b.
From where did these white particles come?
Answer:
When we rubbed the board, the chalk particles from the board stuck to the duster and when we tapped the duster these chalk particles fell.
Question c.
If there is a sudden shower, we take shelter under a roof on the road side. Even though the rain does not fall on us directly we get wet to some extent why?
Answer:
The raindrops slow down the roof and fall on the ground. They break into fine droplets when they fall and bounce off the ground. These droplets make us wet. Hence though the rain does not fall on us directly we get wet to some extent.
![]()
Question d.
Asmita went to buy an earthen pot. There she saw many things kept for sale. How did she identify what she needed? From what substance had the potter made all the things?
Answer:
Asmita identified the things kept from their shape and colour. The potter had made all the things using clay.
Question e.
What is the difference between a substance and an object?
Answer:
Difference between substance and object is given below:
| Substance | Object |
| 1. Substances are made up of tiny particles. | 1. Objects are made using substances. |
| 2. Substances may or may not have definite shape. They occur in a specific state. | 2. Objects have definite shape. Their parts are put together in a particular way. |
| 3. Wood, aluminium, coal, iron etc are examples of substances. | 3. Table, chair, flower pots, lamp etc. are examples of objects. |
Question f.
There is a car. Its tank is full of fuel, but it does not move. Why is that?
Answer:
The energy has to be released from the fuel to make the car move. The energy is released when the petrol burns. The petrol starts burning only after we turn on the car engine. Since the engine is not on, the car does not move even when its tank is full of fuel.
Question g.
When we have run a long distance, we feel tired. We have to stop. Why is that?
Answer:
We need energy to run. Hence when we run a long distance, the food present in the body is continuously burn to release energy. This energy is used to do the work of running. After running a long distance the food gets exhausted and the energy released decreases and therefore we feel tired and we stop.
![]()
Glossary :
- fossil fuel – fuel formed in the earth o from plant or animal remains
- exhaustible – the resources which can not be renewed or recycled
- depleting – reduction in quantity
- corncob – core of Indian com.