Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 7 कागज की थैली Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Hindi Solutions Chapter 7 कागज की थैली
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 6 Solutions Chapter 7 कागज की थैली Textbook Questions and Answers
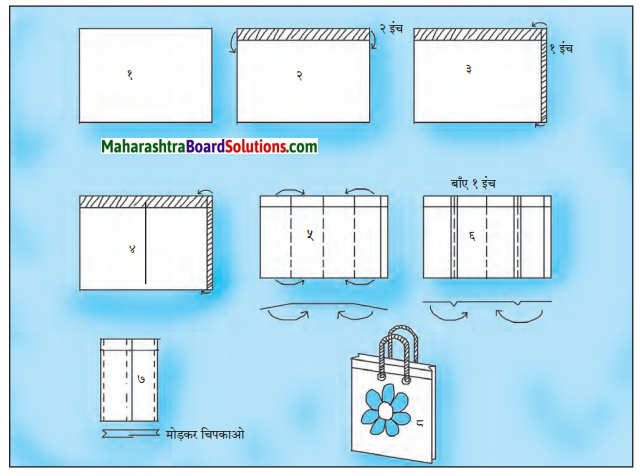
Answer:
पाठ का मुख्य भावः
प्रस्तुत पाठ के माध्यम से छात्रों को कार्यानुभव के माध्यम से सिखाने का प्रयास किया गया है। छात्रों को स्वयं को कागज की थैली | बनाने के लिए कहकर उन्हें प्लास्टिक थैली का उपयोग छोड़कर कागज की थैली का उपयोग करने के लिए प्रेरित किया गया है।
![]()
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 6 Solutions Chapter 7 कागज की थैली Additional Important Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखिए:
Question 1.
कागज का उपयोग करके हम क्या-क्या बना सकते
Answer:
कागज का उपयोग करके हम पतंग, जहाज़, नाव, तोरण व कागज की सुंदर पत्रिकाएँ बना सकते हैं। उसे उपहार के रूप में दे सकते हैं।।
Question 2.
कागज की कौन-कौन सी वस्तुएँ बनाकर हम समारोह की रौनक को बढ़ा सकते हैं?
Answer:
कागज की झलियाँ वरंगबिरंगी पताकाएँ बनाकर हम समारोह की रौनक को बढ़ा सकते हैं।
Question 3.
कागज की थैली कों हम किस प्रकार सजा सकते हैं ?
Answer:
कागज की थैली पर लेंस, मोती, रंगीन काँच चिपकाकर उसे सजा सकते हैं।
Question 4.
कागज की थैली का उपयोग हम किस प्रकार कर सकते हैं?
Answer:
कागज की थैली का उपयोग हम जन्मदिन के अवसर पर थैली में उपहार डालकर देने के लिए कर सकते हैं।
![]()
Question 5.
कागज की सामग्री का उपयोग करके स्वंय के आधार पर पवन चक्की तैयार कीजिए।
Answer: