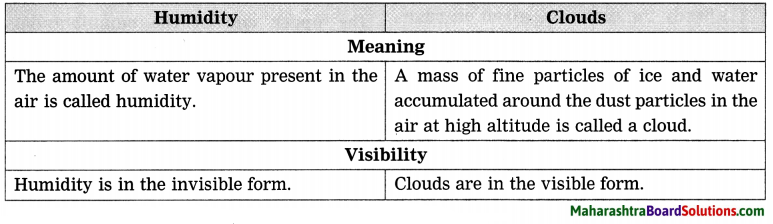
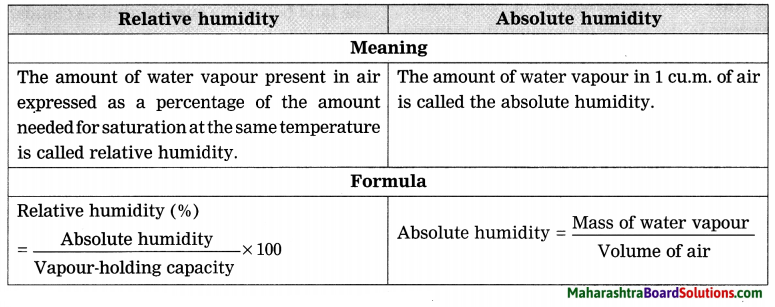
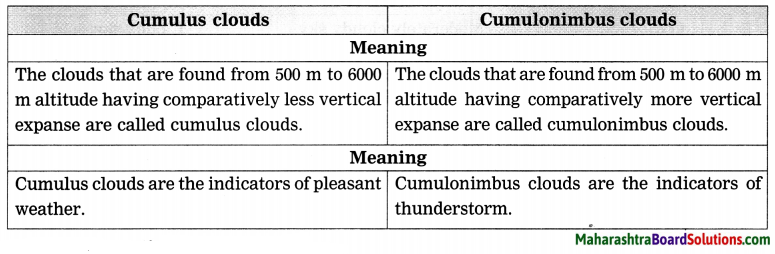
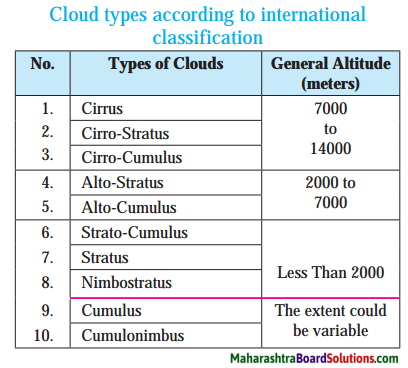
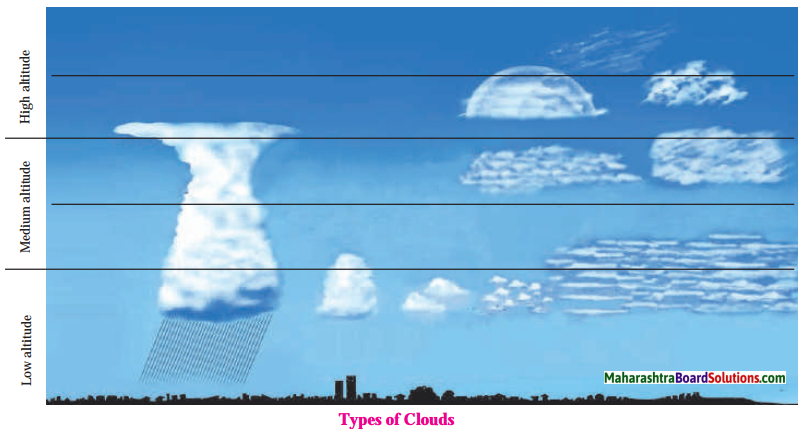
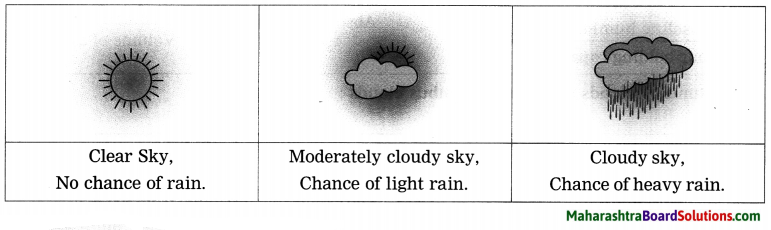
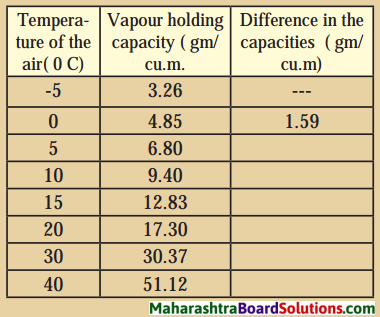
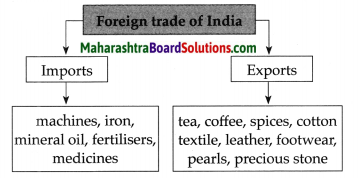
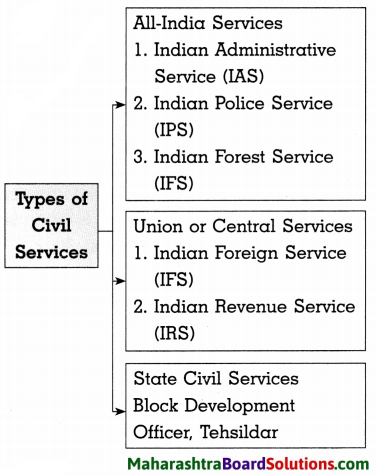
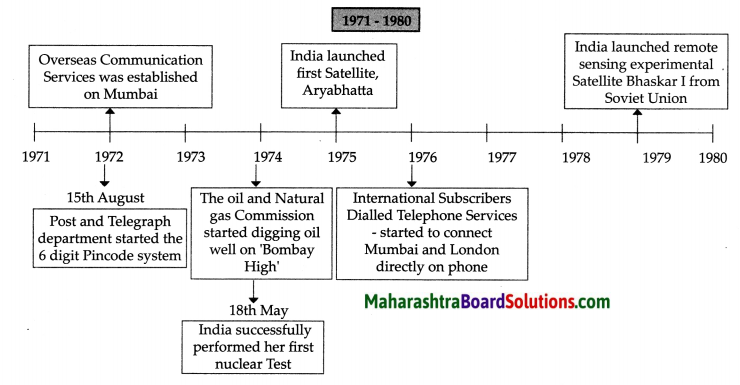
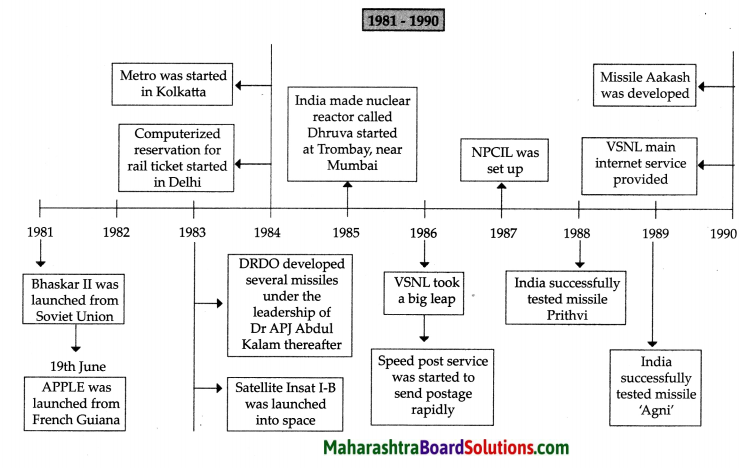
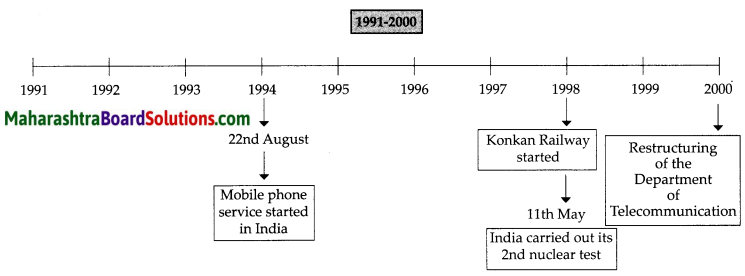
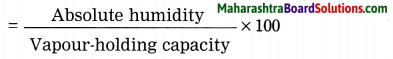Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Geography Solutions Chapter 4 Structure of Ocean Floor Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Geography Solutions Chapter 4 Structure of Ocean Floor
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Structure of Ocean Floor Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Choose the correct option:
Question a.
Like there are landforms on land, ocean floor also has submerged landforms because ………….
(i) there is land under water
(ii) there are volcanoes under water
(iii) land is continuous and there is water in deeper parts
(iv) though land is continuous, its level is not the same everywhere like that of water
Answer:
(iv) though land is continuous, its level is not the same everywhere like that of water
![]()
Question b.
Which part of the ocean floor is most useful to the man?
(i) Continental shelf
(ii) Continental slope
(iii) Abyssal plains
(iv) Marine deeps
Answer:
(i) Continental shelf
Question c.
Which one of the following option is related to marine deposits?
(i) Rivers, glaciers, continental shelf, remains of plants and animals
(ii) Volcanic ash, continental shelf, remains of plants and animals
(iii) Volcanic ash, lava, fine particles of soil
(iv) Volcanic ash, remains of plants and animals, abyssal plants
Answer:
(iii) Volcanic ash, lava, fine particles of soil
2. Question a.
Name the landforms shown in the following figure.
(Note: The answer is given directly.)
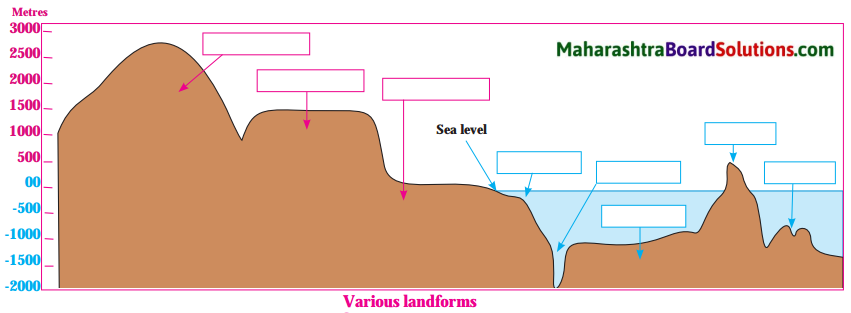
Answer:
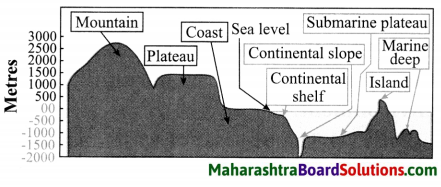
Question b.
Which of these landforms are useful for deep sea research?
Answer:
Submarine plateau and marine trench are the landforms useful for deep sea research.
Question c.
Which of these are appropriate to be used for the protection of marine borders and naval base building?
Answer:
Continental shelf is appropriate to be used for the protection of marine borders and naval base building.
![]()
3. Give geographical reasons:
Question a.
The study of ocean floor is useful to man.
Answer:
- Various minerals, rocks, fine I soil particles are found on the sea floor.
- Remains of marine plants and animals are also found on the ocean floor.
- To study the marine life, mineral wealth as well as the process of volcanic eruption, the study of ocean floor is useful to man. ‘
Question b.
The continental shelf is a paradise for fishing activity.
Answer:
- Being a shallowest part of the ocean bed, sunlight reaches up to continental shelf easily.
- As its effect, algae, plankton, etc. grows on a large scale on continental shelf.
- Algae, plankton, etc. is food for fish. Therefore, fish are found on a large scale on continental shelf. Therefore, the continental shelf is paradise for fishing activity.
![]()
Question c.
Some marine islands are actually the peaks of sea mountains.
Answer:
- The hundreds of kilometres wide and thousands of kilometres long hills found on the ocean bed are called submerged hills.
- Peaks of some of the submerged hills come above the sea level.
- These peaks are the visible land areas surrounded from all sides by water. These peaks are called islands. Thus, some marine islands are actually the peaks of sea mountains.
Question d.
The continental slope is considered to be the boundary of continents.
Answer:
- Continental slope lies beyond the continental shelf.
- The deep abyssal plain begins beyond the continental slope. Therefore, the continental slope is considered to be the boundary of continents.
Question e.
The disposal of waste materials in the oceans by man is harmful to the 1 environment.
Answer:
- The disposal of waste materials in the oceans by man increases the pollution of sea water.
- This disposed waste materials harm the life of marine animal life and marine plant. Thus, the disposal of waste materials in the oceans by man is harmful to the environment.
4. Observe the map on Pg 27 in ‘Give it a try’ and answer the following questions:
Question a.
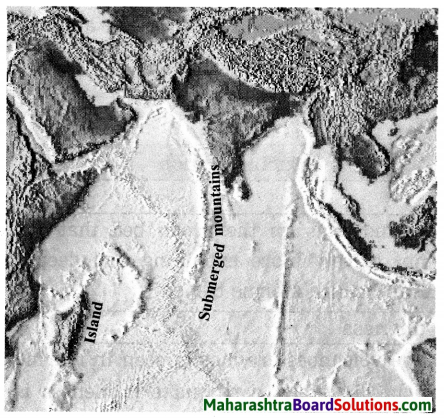
Madagascar and Sri Lanka are related to which landform of the ocean floor?
Answer:
Madagascar and Sri Lanka are related to island of the ocean floor.
Question b.
Near which continent are these landforms located?
Answer:
Madagascar is located near the continent of Africa and Sri Lanka is located near the continent of Asia.
![]()
Question c.
Which islands in our country are examples of peaks of submerged mountains?
Answer:
Andaman and Nicobar islands in our country are examples of peaks of submerged mountains.
Activity:
Question a.
prepare a model of the ocean floor.
Answer:
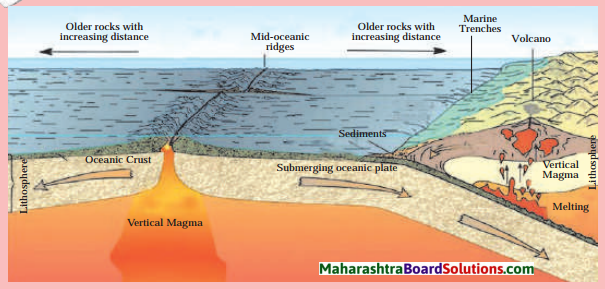
1. While studying the ocean floor, we must keep in mind the age of the ocean bed. By studying the deposits on the ocean bed, it occurred to the scientists that the deposits at the ocean floor are not older than 200 million years.
2. The maximum age of the rocks on the continents is supposed to be 3200 million years. Then where have the deposits on the sea bed which are older than 200 million years gone? This made the scientists restless. Then they started the study of the rocks along with the deposits.
3. This made them realize that the rocks are also not older than 200 million years. It was inferred that the ocean floor is very young as compared to the earth’s surface. Now this is unanimously accepted. This research was then used in the study of the concept of plate tectonics.
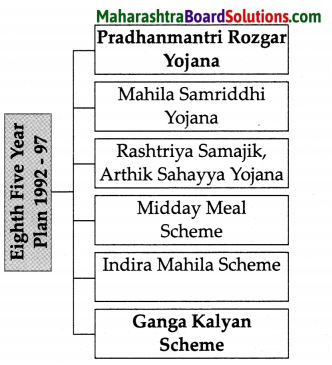
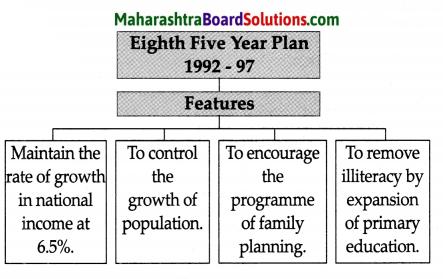
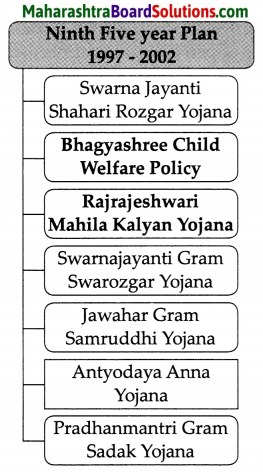
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Structure of Ocean Floor Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct answer and complete the sentences:
Question a.
Continental slope has slope.
(a) flatter
(b) broader
(c) steeper
(d) lower
Answer:
(c) steeper
![]()
Question b.
The average depth of the oceans is around metres.
(a) 7300
(b) 3700
(c) 3900
(d) 3300
Answer:
(b) 3700
Examine the following statements and correct the incorrect ones:
Question a.
Abyssal plain lies beyond the continental shelf.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct statement: Abyssal plain lies beyond the continental slope.
Question b.
Around 51 per cent of the surface of the earth is covered by water.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct statement: Around 71 per cent of the surface of the earth is covered by water.
Question c.
Natural gas and mineral oil can be obtained from the continental shelf.
Answer:
Correct.
![]()
Question d.
For survey purpose in India, the height of sea level at Kanyakumari is considered to be zero.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct statement: For survey purpose in India, the height of sea level at Chennai is considered to be zero.
Question e.
Active volcanoes are mostly seen in marine trenches.
Answer:
Correct.
Answer the following questions in one sentence each:
Question a.
What is called continental shelf?
Answer:
The land near the coast and submerged under the sea is called continental shelf.
Question b.
What is called continental slope?
Answer:
The steeper slope of the sea bed beyond the extent of continental shelf is called continental slope.
![]()
Question c.
What is called abyssal plain?
Answer:
The flat part of the sea bed that lies
beyond the continental slope is called abyssal plain.
Question d.
What is called submerged hills?
Answer:
The hundreds of kilometres wide and thousands of kilometres long hills found on the ocean bed are called submerged hills.
Question e.
What is called marine islands?
Answer:
Peaks of some of the submerged hills that come above the sea level are called marine islands.
Question f.
What is called submarine plateau?
Answer:
The flat and extensive summit of marine island is called submarine plateau.
Question g.
What is called marine deep?
Answer:
The landforms on the ocean bed that are comparatively less extending and shallower ones are called marine deep.
![]()
Question h.
What is called marine trench?
Answer:
The landforms on the ocean bed that are comparatively more extending and deeper ones are called marine trench.
Match the columns and complete the chain:
Question a.
| ‘A’ Column | ‘B’ Column | ‘C’ Column |
| 1. Andaman – Nicobar | (i) Submarine plateau | (a) Pacific Ocean |
| 2. Chagos | (ii) Located on continental shelf | (b) Bay of Bengal |
| 3. Mariana | (iii) Islands | (c) Arabian Sea |
| 4. Mumbai High | (iv) Marine deep | (d) Indian Ocean |
Answer:
| ‘A’ Column | ‘B’ Column | ‘C’ Column |
| 1. Andaman – Nicobar | (iii) Islands | (b) Bay of Bengal |
| 2. Chagos | (i) Submarine plateau | (d) Indian Ocean |
| 3. Mariana | (iv) Marine deep | (a) Pacific Ocean |
| 4. Mumbai High | (ii) Located on continental shelf | (c) Arabian Sea |
Answer the following questions in brief:
Question a.
What is marine deposits?
Answer:
- Marine deposit is a type of marine deposition.
- The rivers and glaciers flowing from the continent bring pebbles, clay, soil, etc. with them when they meet sea or ocean.
- These materials get deposited on the continental shelf. The deposits are known as marine deposits.
- Due to pressure of sea water and deposition of layers over layers of sediments, sedimentary rocks are formed.
- Marine life and the availability of minerals in the sea bed can be studied with the help of marine deposits.
![]()
Question b.
What is marine oozes?
Answer:
- Marine oozes is a type of marine deposit.
- Lava and ash erupting out of volcano, fine soil particles, remains of plants and animals, etc. get deposited on marine abyssal plains. Deposits of these materials on the abyssal plains are known as marine oozes.
- Marine oozes are in the form of fine clay. The percentage of remains of plants and animals in marine oozes is up to 30 per cent.
- Marine oozes are also useful to study marine life and the availability of minerals in the sea bed.
Question c.
Write in brief about the continental shelf.
Answer:
1. The land near the seacoast and submerged under the sea is called continental shelf. The depth of continental shelf is about 200 metres below the sea level.
2. Continental shelf is found to be narrow along the coasts of some continents and broad along the coasts of some other continents.
3. Being a shallowest part of the ocean bed, sunlight reaches up to continental shelf easily. As its effect, the food for fish like algae, plankton, etc. grows on a large scale on continental shelf. Therefore, continental shelf is useful for fishing occupation.
4. Various minerals, natural gas and mineral oil, etc. can also be obtained from mining the continental shelf. For example, Mumbai High located on the continental shelf of the Arabian Sea is a source from where the mineral oil and natural gas is obtained.
![]()
Question d.
Write in brief about the continental slope.
Answer:
- The steep slope of the sea bed beyond the extent of continental shelf is called continental slope.
- The depth of the continental slope is from 200 metres to 3600 metres below the sea level.
- The continental slope is found to be comparatively narrower.
- The lower boundary of the continental slope is considered as the boundary of I continent.
Question f.
Write in brief about the abyssal plains.
Answer:
- The flat part of the sea bed that lies beyond the continental slope is called abyssal plains.
- Various submerged landforms like
submerged hills, submerged mountains, etc. are seen on abyssal plains. - Submarine plateaus are also found on the abyssal plains.
Question g.
Write in brief about mean sea level.
Answer:
- The average of the highest high tide and the lowest low tide is considered to calculate the mean sea level.
- This average is considered to be zero sea level.
- The altitude of any place above the sea level is measured and expressed in positive value. (For example, Mount Everest is 8848 metres high.)
- The depth of any place below the sea level is measured and expressed in negative value. (For example, Mariana Trench is 11034 metres below sea level.)
Study the following map/figure/graph and answer the following questions:
Can you tell?

Question a.
What parameters were used for classifying the landforms on the earth?
Answer:
Altitude and the shape of the land were the parameters used for classifying the landforms on the earth.
![]()
Question b.
What parameters were used for naming the landforms below water?
Answer:
Depth from the seafloor and the shape of the land were the parameters used for naming the landforms below water.
Give it a try.
Question a.
Name the submerged landforms shown in the diagram.
(Note: The answer is given directly.)
Answer:
Question b.
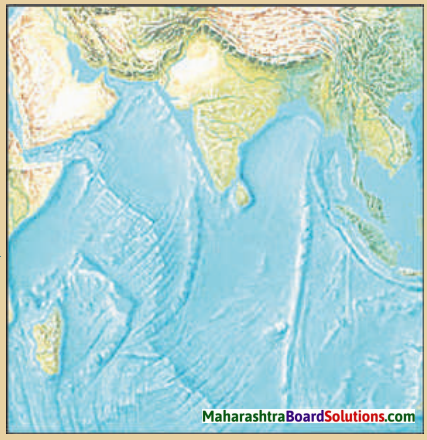
Identify the ocean shown in the map of the ocean floor.
Answer:
The ocean shown in the map of the ocean floor is Indian Ocean.
![]()
Question c.
Which region would be ideal for fishing and why?
Answer:
The region near Madagascar island would be ideal for fishing. Madagascar island has a shallow continental shelf. The warm stream and cold stream also meet near Madagascar island. Therefore, the region near Madagascar island would be ideal for fishing.
2. Name the landforms shown in the following figure and answer the following questions:
(Note: The answer is given directly.)
Question a.
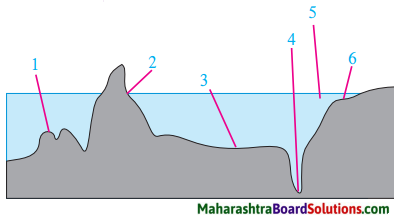
Answer:
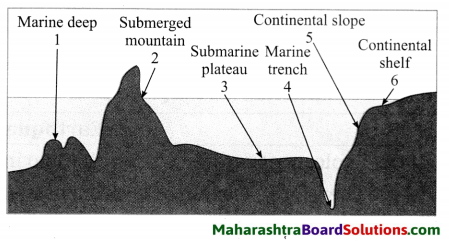
Thought-Provoking Questions
Think about it.
Question a.
If the classification of landforms on land can be done on the basis of altitude and size, then how can the landforms submerged underwater are classified?
Answer:
If the classification of landforms on land can be done on the basis of altitude and size, then the landforms submerged underwater are classified on the basis of the depth from the seafloor and the shape of the land there.
![]()
Use your brainpower!
Do this activity when you go to the seashore with your parents or teachers. Observe the materials which have come with the waves. Classify them as per the flowchart given below:
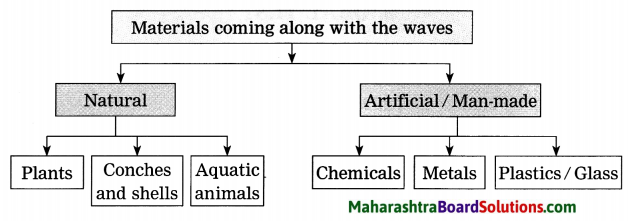
Question a.
Which of these are perishable items?
Answer:
Plants, conches and shells, aquatic animals of these are perishable items.
Question b.
Which are non-perishable?
Answer:
Chemicals, metals and plastic/glass are non-perishable.
Question c.
What will happen because of perishable items?
Answer:
Perishable items will not create pollution of seacoast and seawater on a large scale. The remains of perishable items will get deposited in the form of marine oozes on the ocean bed.
Question d.
What will happen because of non-perishable items?
Answer:
Non-perishable items will create pollution of seacoast and seawater on a large scale.
Question f.
Suggest measures to control deposition of non-perishable items on the coast.
Answer:
The following measures can be taken to control deposition of non-perishable items on the coast:
- Plastic bags, plastic or glass containers must be prohibited on the seacoasts.
- Strict action must be taken against offenders carrying the banned products on the seacoasts.
- Hoardings explaining the importance of clean seacoasts must be displayed on all the seacoast.
![]()
Question g.
How will you run a campaign of environmental conservation to keep the coasts clean?
Answer:
We will run a campaign of environmental conservation to keep the coasts clean as follows:
- We will display hoardings explaining the importance of clean seacoasts on the seacoasts.
- We will arrange street plays, dramas, etc. highlighting the importance of clean seacoasts.
- We will arrange special programmes during the festivals like Ganeshotsav, Diwali, Christmas, etc. to keep the seacoasts clean.
Open-Ended Questions:
Question a.
Suggest measures to control deposition of non-perishable items on the coast.
Answer:
The following measures can be taken to control deposition of non-perishable items on the coast:
- Plastic bags, plastic or glass containers must be prohibited on the seacoasts.
- Strict action must be taken against offenders carrying the banned products on the seacoasts.
- Hoardings explaining the importance of clean seacoasts must be displayed on all the seacoasts.
![]()
Question b.
How will you run a campaign of environmental conservation to keep the coasts clean?
Answer:
We will run a campaign of environmental conservation to keep the coasts clean as follows:
- We will display hoardings explaining the importance of clean seacoasts on the seacoasts.
- We will arrange street plays, dramas, etc. highlighting the importance of clean seacoasts.
- We will arrange special programmes during the festivals like Ganeshotsav, Diwali, Christmas, etc. to keep the seacoasts clean.