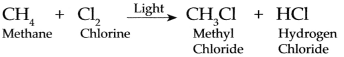
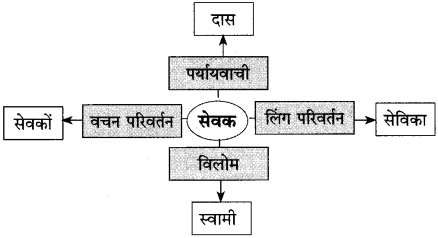
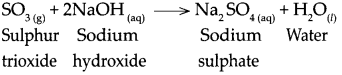
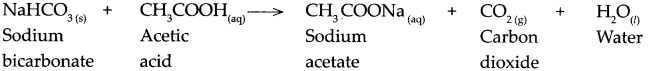
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Hindi Solutions Lokbharti Chapter 8 गजल Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Hindi Lokbharti Chapter 8 गजल
Hindi Lokbharti 10th Std Digest Chapter 8 गजल Textbook Questions and Answers
सूचना के अनयुार कृहत्ँ कीहजए:
(1) गजल की पंक्तियों का तातप्:
a. नीं के अंदर हदिाे ————
b. आईना बनकर हदिो ————
उत्तर:
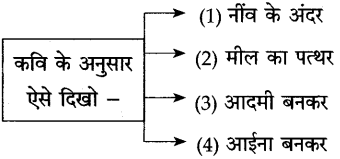
(i) हमें प्रशंसा और वाहवाही का लोभ त्यागकर नींव की ईंटों के समान कुछ अच्छा और सुदृढ़ काम करना चाहिए।
(ii) हमें ऐसी शख्सियत बनना चाहिए कि कैसी भी प्रतिकूल परिस्थिति क्यों न हो, हम विचलित न हों। बिना टूटे, बिना बिखरे हर परिस्थिति का डटकर सामना करें। अपने लक्ष्य को प्राप्त करें।
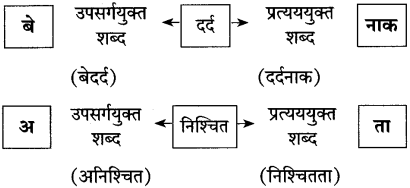
(2) कृति पूण् कीहजए:
उत्तर:
(3) हजनके उततर हनम् शब् हों ऐसे प्र तै्र कीहजए:
1. भीड़
2. जुगनू
3. हततली
4. आसमान
उत्तर:
1. कवि अक्सर किसी शक्ल को कहाँ देखना चाहता है?
2. वक्त की धुंध में साथ रहने को किसने कहा?
3. कवि खिलते फूल के स्थान पर कहाँ दिखने को कहता है?
4. गर्द बनकर कहाँ लिखना चाहिए?
(4) हनम्हलखखत पंक्तियों से प्र तीिनमूल् हलखखए:
१. आपको मिसूस ……………………………………….. भीतर हदिो।
२. कोई ऐसी श् ……………………………………….. मुझे अ्र हदिो।.
उत्तर:
(ii) हे ईश्वर, मैं चाहता हूँ कि मैं जिसे भी देखू, मुझे उसी में तुम नजर आओ। अर्थात मानव मात्र ईश्वर का अंश है।
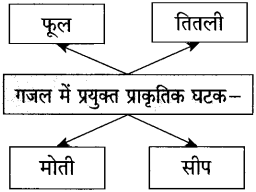
(5) कृहत पूण् कीहजए:
गजल मे प्रयुक्त प्कृहतक घट
उत्तर:
(6) कहि के अनयुार ऐसे हदखो:
यदि मेरा घर अंतररक में होता,’ हिष् पर अससी से सौ शब्दों मे हनबंध लेखन कीहजए।
उत्तर:
पिछले कई वर्षों में अंतरिक्ष विज्ञान में जो प्रगति हुई है, वह सराहनीय है। पहले अंतरिक्ष यात्रा कल्पना से अधिक कुछ नहीं थी लेकिन आज अंतरिक्ष यात्रा के सपने सच हो गए हैं। रूस ने अंतरिक्ष यान के द्वारा अपने अंतरिक्ष यात्री यूरी गागरिन को पहली बार अंतरिक्ष में भेजा था। फिर तो अमेरिकी अंतरिक्ष यात्री नील आर्मस्ट्रांग और एडविन एल्ड्रिन सबसे पहले चंद्रमा पर पहुचनेवाले अंतरिक्ष यात्री हो गए।
![]()
अब तो ऐसा लगता है कि कभी-न-कभी हम को भी अंतरिक्ष में जाने का मौका मिल सकता है। लेकिन यह कब संभव होगा, कहा नहीं जा सकता। काश, मेरा घर अंतरिक्ष में होता…. यदि सच में मेरा घर अंतरिक्ष में होता तो कितना अच्छा होता। जिस आसमान को दूर से देखा करते हैं, हम उसकी खूब सैर करते। चाँद, सितारों को नजदीक से देखते। बादलों के बीच लुका-छिपी खेलते। परियों के देश में जाते।
वे किस तरह रहती हैं, जानने-देखने का अवसर पाते। हम अंतरिक्ष से अपनी सुंदर धरती को देखते। अपने प्यारे भारत को देखते। आकाशगंगा के विभिन्न ग्रहों-उपग्रहों को देखते। सौरमंडल के सबसे सुंदर ग्रह शनि और उसके वलयों को देखते। उनके जितना निकट जा सकते, अवश्य जाते। स्पेस वॉक करते। वहाँ फैली शांति का अनुभव करते। वहाँ के प्रदूषणरहित वातावरण में रहने का मौका मिलता, जिससे हमारा स्वास्थ्य बहुत बढ़िया हो जाता। काश ऐसा हो पाता…
प्रयु गजल की अपनी पसंदीदा हकनिी चार पंक्तियों का केंद्रीय भाव सपष् कीहजए।
Hindi Lokbharti 10th Textbook Solutions Chapter 8 गजल Additional Important Questions and Answers
पद्यांश क्र.1
प्रश्न.
निम्नलिखित पठित पद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
कृति 1: (आकलन)
(1) आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
उत्तर:
(2) विधानों के सामने सत्य / असत्य लिखिए:
(i) स्वर्णिम शिखर बनकर जीना ही जीना है।
(ii) मील का पत्थर बनकर जीना अच्छा नहीं है।
(iii) मोमबत्ती के धागे जैसा जीवन जियो।
(iv) जिंदगी टूटकर नहीं बिखरनी चाहिए।
उत्तर:
(i) असत्य
(ii) असत्य
(iii) सत्य
(iv) सत्य।
![]()
(3) उचित जोड़ियाँ मिलाइए:
| अ | आ |
| (i) शिखर | गर्द |
| (ii) आस्मान | जिंदगी |
| (iii) पत्थर | स्वर्णिम |
| (iv) शक्ल | मील |
| नींव |
उत्तर:
| अ | आ |
| (i) शिखर | स्वर्णिम |
| (ii) आस्मान | गर्द |
| (iii) पत्थर | मील |
| (iv) शक्ल | जिंदगी |
(4) दो ऐसे प्रश्न तैयार कीजिए, जिनके उत्तर निम्नलिखित शब्द हों:
(i) आईना
उत्तर:
(i) पत्थरों के शहर में क्या बनकर दिखना चाहिए?
(5) एक शब्द में उत्तर लिखिए:
(i) पत्थर के शहर में यह बनकर दिखना है –
(ii) दिखने का शौक है तो यह बनो –
उत्तर:
(i) आईना।
(ii) नींव।
कृति 2: (शब्द संपदा)
(1) निम्नलिखित शब्दों के समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए:
(i) शक्ल = ……………………
(ii) शिखर = ……………………
(iii) गर्द = ……………………
(iv) पत्थर = ……………………
उत्तर:
(i) शक्ल = चेहरा
(ii) शिखर = शीर्ष
(ii) गर्द = धूल
(iv) पत्थर = पाषाण।
(2) निम्नलिखित शब्दों के विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिखिए:
(i) आदमी x
(ii) शहर x
(ii) आसमान x
(iv) टूटना x
उत्तर:
(i) आदमी x जानवर
(ii) शहर x गाँव
(iii) आसमान x जमीन
(iv) टूटना x जुड़ना।
![]()
कृति 3: (सरल अर्थ)
प्रश्न.
उपयुक्त पदयांश की आरंभ की चार पंक्तियों का सरल अर्थ 25 से 30 शब्दों में लिखिए।
उत्तर:
किसी भी अट्टालिका के चमचमाते शिखरों को सभी देखते हैं। उनकी शान की प्रशंसा भी करते हैं। लोग समाज में इन शिखरों के समान ही सम्मान पाना चाहते हैं। परंतु वास्तव में देखा जाए तो इन शिखरों से अधिक महत्व है उन ईंटों और पत्थरों का, जिनके कारण ये शिखर बन सके। यदि नींव की ईंटों ने गुमनामी के अंधेरे में रहना स्वीकार न किया होता, तो इन शिखरों का अस्तित्व ही न होता। यदि हम समाज के लिए कुछ करना चाहते हैं, तो हमें प्रशंसा और जैं सुदृढ़ काम करना चाहिए।
पद्यांश क्र. 2
प्रश्न.
निम्नलिखित पठित पद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
कृति 1: (आकलन):
(1) सही विकल्प चुनकर वाक्य फिर से लिखिए:
(i) वक्त की इस धुंध में तुम …………………………….. बनकर दिखो। (सितारा/चिराग/रोशनी)
(ii) हम सभी के लिए एक …………………………….. है। (दुनिया/मर्यादा/मंच)
(iii) कोई …………………………….. कली फूल बनने से डर जाए। (छोटी/सुंदर/नाजुक)
(iv) कोई ऐसी शक्ल तो मुझको दिखे इस …………………………….. में। (भीड़/संसार/घर)
उत्तर:
(i) वक्त की इस धुंध में तुम रोशनी बनकर दिखो।
(ii) हम सभी के लिए एक मर्यादा है।
(iii) कोई नाजुक कली फूल बनने से डर जाए।
(iv) कोई ऐसी शक्ल तो मुझको दिखे इस भीड़ में।
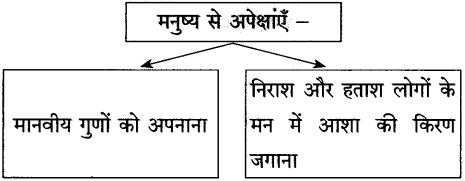
(2) निम्नलिखित पंक्तियों से प्राप्त जीवनमूल्य लिखिए:
(i) एक जुगनू ने …………………………….. रोशनी बनकर दिखो।
उत्तर:
(i) जब वक्त साथ न दे रहा हो। हर तरफ असफलता और निराशा का साम्राज्य हो। ऐसे समय में एक छोटी-सी आशा की किरण भी बहुत बड़ा सहारा बन सकती है। हमें निराश, हताश लोगों के मन में आशा की किरण जगाना चाहिए।
(3) ऐसे प्रश्न तैयार कीजिए, जिनके उत्तर निम्नलिखित शब्द हों:
(iv) मोती।
उत्तर:
(iv) मोती को किसके अंदर दिखना चाहिए?
(4) जोड़ियाँ मिलाइए:
| ‘अ’ | ‘आ’ |
| (i) धुंध | सीप |
| (ii) मर्यादा | तितली |
| (iii) मोती | रोशनी |
| (iv) फूल | मनुष्य |
उत्तर:
| ‘अ’ | ‘आ’ |
| (i) धुंध | रोशनी |
| (ii) मर्यादा | मनुष्य |
| (iii) मोती | सीप |
| (iv) फूल | तितली |
कृति 2: (शब्द संपदा)
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के लिंग पहचानकर लिखिए:
(i) जुगनू – ……………………….
(ii) रोशनी – ……………………….
(iii) मोती – ……………………….
(iv) सीप – ……………………….
उत्तर
(i) जुगनू – पुल्लिंग
(ii) रोशनी – स्त्रीलिंग
(iii) मोती – पुल्लिंग
(iv) सीप – स्त्रीलिंग
![]()
कृति 3: (सरल अर्थ):
प्रश्न.
उपर्युक्त पद्यांश की प्रथम चार पंक्तियों का सरल अर्थ 25 से 30 शब्दों में लिखिए।
उत्तर:
जब वक्त हमारा साथ न दे रहा हो। हर तरफ असफलताएँ धुंध के समान छाई हों। निराशा रूपी अंधकार का साम्राज्य हो। ऐसे: समय में एक छोटी-सी आशा की किरण भी बहुत बड़ा सहारा बन सकती है। ठीक उसी प्रकार, जैसे घने अंधकार में चमकता हुआ जुगनू । तुम्हें भी निराश, हताश लोगों के मन में आशा की किरण जगाना चाहिए।
सभी मनुष्यों के लिए समाज में रहने के लिए कुछ सीमाएँ हैं, जिनका हमें पालन करना होता है। तभी समाज हमें और हमारे व्यवहार को स्वीकार करता है। अगर तुम चाहते हो कि लोगों में तुम्हारी कोई पहचान बने तो जिस प्रकार सीप के अंदर मूल्यवान मोती छिपा होता है, उसी प्रकार तुम्हें समाज के कल्याण के लिए श्रेष्ठ कर्म करने चाहिए।
भाषा अध्ययन (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न.
सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
1. शब्द भेद:
अधोरेखांकित शब्दों के शब्दभेद पहचानिए:
(i) मैं दिल्ली में अच्छा घर ढूँढ़ रहा हूँ।
(ii) वे तेजी के साथ बगीचे की ओर चल पड़े।
(iii) तुम अब पढ़ने बैठ जाओ।
उत्तर:
(i) अच्छा – गुणवाचक विशेषण।
(ii) बगीचे – जातिवाचक संज्ञा।
(iii) तुम – पुरुषवाचक सर्वनाम।
2. अव्यय:
निम्नलिखित अव्ययों का अपने वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए:
(i) के मारे.
(ii) या
(iii) पर।
उत्तर:
(i) के मारे – लड़का डर के मारे काँप रहा था।
(ii) या – वे खेलने या घूमने गए होंगे।
(iii) पर – गाड़ी थी, पर पर्याप्त पेट्रोल नहीं था।
3. संधि:
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
| संधि शब्द | संधि विच्छेद | संधि भेद |
| नरेश | ………………… | ………………… |
| अथवा | ||
| ………………… | दिक् + अंबर | ………………… |
उत्तर:
| संधि शब्द | संधि विच्छेद | संधि भेद |
| नरेश | नर + ईश | स्वर संधि |
| अथवा |
||
| दिगंबर | दिक् + अंबर | व्यंजन संधि |
4. सहायक क्रिया:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में से सहायक क्रियाएँ पहचानकर उनका मूल रूप लिखिए:
(i) वे गरीबों को फल बाँटते रहे।
(ii) देरी करने को मेरा मन गवारा नहीं कर पाया।
(iii) उनके शब्द मेरे कानों में गूंजने लगे।
उत्तर:
सहायक क्रिया – मूल रूप
(i) रहे – रहना
(ii) पाया – पाना
(iii) लगे – लगना
5. प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया:
निम्नलिखित क्रियाओं के प्रथम प्रेरणार्थक और द्वितीय प्रेरणार्थक रूप लिखिए:
(i) छोड़ना –
(ii) डूबना –
(iii) सूखना। –
उत्तर:
| क्रिया | प्रथम प्रेरणार्थक रूप | द्वितीय प्रेरणार्थक रूप |
| (i) छोड़ना | छुड़ाना | छुड़वाना |
| (ii) डूबना | डुबाना | डुबवाना |
| (iii) सूखना | सुखाना | सुखवाना |
6. मुहावरे:
(1) निम्नलिखित मुहावरों का अर्थ लिखकर वाक्य में प्रयोग किजिए:
(i) नाम-निशान न रहना
(ii) रटता जाना।
उत्तर:
(i) नाम-निशान न रहना।
अर्थ: अस्तित्व मिट जाना।
वाक्य: भूकंप के कारण पुराने कार्यालय का नाम-निशान नहीं रहा।
(ii) रटते जाना।
अर्थ: बार-बार कहते जाना।
वाक्य: विजय गाँव जाने की बात रटता जा रहा है।
![]()
(2) अधोरेखांकित वाक्यांशों के लिए कोष्ठक में दिए गए उचित मुहावरे का चयन करके वाक्य फिर से लिखिए: (तोलकर बोलना, तीर की तरह निकल जाना, कानों में गूंजना, ठहाका लगाना)
(i) पाकिटमार महिला का बटुआ छीनकर बहुत तेजी से निकल गया।
(ii) माता-पिता द्वारा दी गई सीख जीवनभर ध्वनित होती रहती है।
(iii) सज्जन हमेशा सोच-समझकर बोलता है।
उत्तर:
(i) पाकिटमार महिला का बटुआ छीनकर तीर की तरह निकल गया।
(ii) माता-पिता द्वारा दी गई सीख जीवनभर कानों में गूंजती रहती है।
(iii) सज्जन हमेशा तौलकर बोलते हैं।
7. कारक:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में प्रयुक्त कारक पहचानकर उनका भेद लिखिए:
(i) ईश्वर की प्राप्ति आसानी से नहीं होती।
(ii) एक बच्चा कुर्सी पर चढ़ा तो दूसरा नाचने लगा।
(iii) मैंने तय किया कि आज किसी से नहीं मिलूँगा।
उत्तर:
(i) की – संबंध कारक।
(ii) पर – अधिकरण कारक।
(iii) से – करण कारक।
8. विरामचिह्न:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में यथास्थान उचित विरामचिह्नों का प्रयोग करके वाक्य फिर से लिखिए:
(i) “गरम गरम भूनकर मसाला लगाकर दूंगा’
(ii) आदमी ने आकर पूछा-अभी भोजन तैयार होने में कितना विलंब है
(iii) हाँ, सूर ने एक जगह लिखा है-मैं दसों दिशाओं में देख लेता हूँ
उत्तर:
(i) “गरम-गरम भूनकर मसाला लगाकर दूंगा।”
(ii) आदमी ने आकर पूछा – “अभी भोजन तैयार होने में कितना विलंब है?”
(iii) हाँ, सूर ने एक जगह लिखा है- ‘मैं दसों दिशाओं में देख लेता हूँ।’
9. काल परिवर्तन:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों का सूचना के अनुसार काल परिवर्तन कीजिए:
(i) ठीक ग्यारह बजे प्रधानमंत्री बाहर आते हैं। (सामान्य भूतकाल)
(ii) मुझे भाई का जला हुआ चेहरा याद आता है। (सामान्य भविष्यकाल)
(iii) गुरुदेव अपने समय पर स्नान करते हैं। (पूर्ण भूतकाल)
उत्तर:
(i) ठीक ग्यारह बजे प्रधानमंत्री बाहर आए।
(ii) मुझे भाई का जला हुआ चेहरा याद आएगा।
(iii) गुरुदेव ने अपने समय पर स्नान किया था।
10. वाक्य भेद:
(1) निम्नलिखित वाक्यों का रचना के आधार पर भेद पहचानकर लिखिए:
(i) ईश्वर ने हमें मनुष्य जीवन दिया है।
(ii) हमारा उद्देश्य, सजना, सँवरना ही नहीं है, बल्कि हमारे द्वारा किए गए कार्य सुंदर होने चाहिए।
उत्तर:
(i) सरल वाक्य
(ii) संयुक्त वाक्य।
![]()
(2) निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को अर्थ के आधार दी गई सूचना के अनुसार वाक्य परिवर्तन कीजिए:
(i) चाची जली-भुनी रहती थी। (संदेहवाचक वाक्य)
(ii) मन अब सुकून अनुभव कर रहा था। (निषेधवाचक वाक्य)
उत्तर:
(i) शायद चाची जली-भुनी रहती थी।
(ii) मन अब सुकून अनुभव नहीं कर रहा था।
11. वाक्य शुद्धिकरण:
निम्नलिखित वाक्य शुद्ध करके लिखिए:
(i) इस मंदिर में अनेकों बूध की मूर्तियाँ हैं।
(ii) माँ को यहाँ से गए बस एक मिनेट हुई है।
(iii) मेरा घर तुमसे अच्छा है।
उत्तर:
(i) इस मंदिर में बुद्ध की अनेक मूर्तियाँ हैं।
(ii) माँ को यहाँ से गए बस एक मिनट हुआ है।
(iii) मेरा घर तुम्हारे घर से अच्छा है।
गजल Summary in Hindi
गजल विषय-प्रवेश :
प्रस्तुत गजल में माणिक वर्मा ने हमें निरंतर आगे बढ़ते रहने की प्रेरणा दी है। कवि का मानना है कि बाहरी रंग-रूप तो। अस्थायी होता है। सुंदरता हमारे विचारों में, हमारे कामों में होनी चाहिए।
गजल कविता का सरल अर्थ
1. आपसे किसने ………………………… भीतर देखो।
किसी भी अट्टालिका के चमचमाते शिखरों को सभी देखते हैं। उनकी शान की प्रशंसा भी करते हैं। लोग समाज में इन शिखरों के समान ही सम्मान पाना चाहते हैं। परंतु वास्तव में देखा जाए तो इन शिखरों से अधिक महत्व है उन ईंटों और पत्थरों का, जिनके कारण ये शिखर बन सके। यदि नींव की ईंटों ने गुमनामी के अंधेरे में रहना स्वीकार न किया होता, तो इन शिखरों का अस्तित्व ही न होता। यदि हम समाज के लिए कुछ करना चाहते हैं, तो हमें प्रशंसा और वाहवाही का लोभ त्यागकर नींव की ईंटों के समान कुछ अच्छा और सुदृढ़ काम करना चाहिए।
यदि आप मंजिल की ओर अग्रसर हैं तो अपने अच्छे कर्मों के कारण उसी प्रकार आसमानों तक छा जाइए, जैसे आँधी आने पर पृथ्वी से आकाश तक धूल-ही-धूल दृष्टिगोचर होती है। अर्थात आपके द्वारा किए गए अच्छे कामों का प्रभाव और चर्चा हर तरफ हो। और यदि आप मंजिल की ओर बढ़ते हुए मार्ग में कहीं बैठ जाते हो तो मील के पत्थर के समान बनो। मील का पत्थर जिस प्रकार एक पथिक को अपनी मंजिल की ओर बढ़ते समय सहायता करता है, उसी प्रकार क्रियाशील न होते हुए भी आप दूसरों की मदद करें।
ईश्वर ने हमें मनुष्य जीवन दिया है। हमारा उद्देश्य केवल सजना, सँवरना और सुंदर दिखना ही नहीं होना चाहिए। हमारे द्वारा किए गए काम सुंदर होने चाहिए। ईश्वर द्वारा प्रदत्त इस श्रेष्ठ मानव जीवन में हमें मानवीय गुणों को अपनाना चाहिए। हमारा कोई भी काम ऐसा न हो, जो मानवता के दायरे से बाहर हो। समाज में सभी के प्रति हमारा व्यवहार ऐसा हो कि सारा संसार हमें एक अच्छे मनुष्य के रूप में जाने। हमें ऐसी शख्सियत बनना चाहिए कि कैसी भी प्रतिकूल परिस्थिति क्यों न हों, हम विचलित न हों। बिना टूटे, बिना बिखरे हर परिस्थिति का डटकर सामना करें। अपने लक्ष्य को प्राप्त करें।
हमें प्रत्येक मानव से सहानुभूति रखनी चाहिए। यह तभी संभव हो सकेगा, जब हम उनके हर दुख-तकलीफ को समझें। जैसे मोमबत्ती का धागा सदा उसके साथ रहता है। उसके साथ जलता है। उसी प्रकार जब हम दीन-दुखियों की पीड़ा को समझेंगे, तो उसे दूर करने का यथासंभव प्रयास करेंगे। इस प्रकार हम अपना मानव-धर्म निभा पाएँगे।
2. एक जुगनू ………………………… अक्सर देखो।
जब वक्त हमारा साथ न दे रहा हो; हर तरफ असफलताएँ धुंध के समान छाई हों; निराशा रूपी अंधकार का साम्राज्य हो; ऐसे समय में एक छोटी-सी आशा की किरण भी बहुत बड़ा सहारा बन सकती है। ठीक उसी प्रकार, जैसे घने अंधकार में चमकता हुआ जुगनू। तुम्हें भी निराश, हताश लोगों के मन में आशा की किरण जगाना चाहिए।
सभी मनुष्यों के लिए समाज में रहने के लिए कुछ सीमाएँ हैं, जिनका हमें पालन करना होता है। तभी समाज हमें और हमारे व्यवहार को स्वीकार करता है। अगर तुम चाहते हो कि लोगों में तुम्हारी कोई पहचान बने तो जिस प्रकार सीप के अंदर मूल्यवान मोती छिपा होता है, उसी प्रकार तुम्हें समाज के कल्याण के लिए श्रेष्ठ कर्म करने चाहिए। तुम्हारी यह कल्याण-भावना तुम्हें एक पहचान देगी, सम्मान देगी।
यदि कोई कोमल कली फूल बनने से डर रही हो। कली जानती है कि उसके खिलते ही तितली उसका रस चूसने के लिए आएगी और फूल बनी कली को परेशान करेगी। तुम फूल को तितली से बचाने का प्रयास करो। अर्थात उसके डर को दूर करने में उसकी मदद करो।
यह संसार मनुष्यों का एक सागर है। भीड़ में जाने-अनजाने अनगिनत चेहरे हर तरफ दिखाई देते हैं। हे ईश्वर, मैं चाहता हूँ कि मैं जिसे भी देखू, मुझे उसी में तुम नजर आओ। तुम तो सर्वव्यापक हो।