Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 English Solutions Chapter 2.4 How Doth the Little Busy Bee Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 English Lesson 2.4 How Doth the Little Busy Bee Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 7 English Chapter 2.4 How Doth the Little Busy Bee Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Write the meaning of:
doth, opening (in the context of the poem), cell.
Question 1.
Write the meaning of:
doth, opening (in the context of the poem), cell.
Answer:
- Doth: In this poem the meaning of ‘doth’ is the word of old origin,
- Meaning of doth: Archaic, third person singular present of do. Doth is a form of the word ‘do’ which is defined as to perform an action. They get back to their nest and relax.
- Opening: Meaning of opening is blooming when a plant or tree blooms. It produces flowers. When a flower blooms, it opens.
- Cell: Meaning of cell is functional and structural unit of life.
![]()
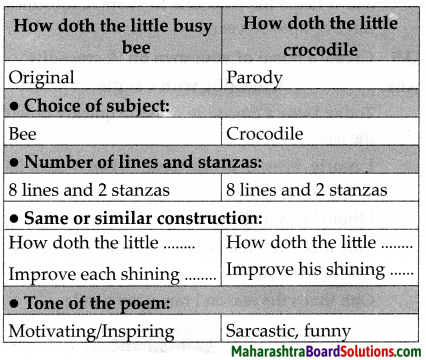
2. A parody is playful, comic imitation of a writer’s style. A parody is like a verbal cartoon. Compare the original poem and its parody given on page 35 using the following points:
Question 1.
Compare the original poem and its parody given on page 35 using the following points:
Answer:
3. Answer the following questions and write in short, why the parody sounds funny.
Question a.
What does the bee stand for?
Answer:
The bee stands for hard-work and positivity
Question b.
What does the crocodile stand for?
Answer:
The crocodile stands for laziness, mischief and negativity.
![]()
Question c.
Why does the bee work hour after hour?
Answer:
The bee works hour after hour to store the nectar that it collects from the flowers.
Question d.
Why does the crocodile work?
Answer:
The crocodile works only to fill its stomach.
Question e.
Is the bee a gentle creature? Is the crocodile gentle?
Answer:
The bee is a gentle creature. The crocodile is not gentle.
4. Desciibe a crocodile in your own words. Which of the words and phrases in the poem will you use In a realistic description?
Put a tick mark against the ones you will use.
- little [ ]
- shining tail [ ]
- golden scale [ ]
- cheerful [ ]
- grIn [ ]
- claws [ ]
- gently smiling [ ]
- jaws [ ]
Question 1.
Describe the crocodile in your own words.
Answer:
The crocodile is a large reptile. The crocodile to me looks very frightening, ferocious and ugly. The scaly skin of the crocodile makes me feel very creepy. They have different colours which ranges from brown to grey. Some are greenish-brown in colour. They have sharp teeth and claws. They have big strong jaws. They appear to be grinning because of the way their jaw is placed. The tail of the crocodile is very powerful and it helps the crocodile to swim. Crocodiles can live upto 80 years!
![]()
5. Note that most of the times well-known works are parodied, because people can enjoy the parody better when they know the original. Try to find more examples of parodies in English or other languages.
Question 1.
Note that most of the times well-known works are parodied, because people can enjoy the parody better when they know the original. Try to find more examples of parodies in English or other languages.
6. What do you like better – the original poem or the parody? Why?
Question 1.
What do you like better – the original poem or the parody? Why?
Answer:
I like the parody. I like the parody because it is funny, interesting and the best part is that it is very easy to memorize.
Class 7 English Chapter 2.4 How Doth the Little Busy Bee Additional Important Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Why does the parody sound funny?
Answer:
The parody sounds funny because it is just in complete contrast with ‘How doth the little busy bee’. The bee is hard working and positive. She is using every minute fruitfully while in contrast the crocodile is wasting its time doing nothing still manages to keep its stomach full.
![]()
Question 2.
Match the nouns with the adjectives used to describe them:
| Column ’A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. bee | a. shining |
| 2. food | b. smiling |
| 3. tail | c. busy |
| 4. jaws | d. sweet |
| 5. scale | e. little |
| 6. crocodile | f. golden |
Answer:
| Column ’A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. bee | c. busy |
| 2. food | d. sweet |
| 3. tail | a. shining |
| 4. jaws | b. smiling |
| 5. scale | f. golden |
| 6. crocodile | f. golden |
![]()
Read the following extract and do the activities.
Answer the questions in one word.
Question i.
What does the bee gather all the day?
Answer:
honey
Question ii.
How does the bee spread her wax?
Answer:
neatly
Complex Factual Questions:
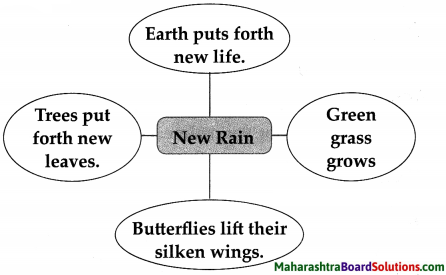
Question 1.
How does the bee build her cell?
Answer:
The bee builds her cell skilfully.
![]()
Question 2.
What food does the bee make?
Answer:
The bee makes sweet food.
Poetic Device:
Question 1.
Make a list of the rhyming words
Answer:
hour – flower; cell – well
Question 2.
What is the rhyme scheme of the first stanza?
Answer:
The rhyme scheme of the first stanza is abcb
Question 3.
What is the rhyme scheme of the second stanza?
Answer:
The rhyme scheme of the second stanza is abac
Read the following extract and do the activities.
Simple Factual Questions:
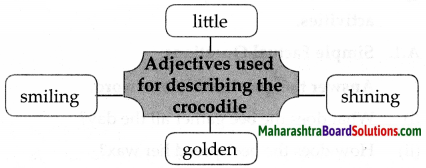
Question 1.
Complete the web.
Answer:
Complex Factual Questions:
Question 1.
Which river is mentioned in the above poem?
Answer:
River Nile is mentioned in the above poem.
![]()
Question 2.
Whom does the crocodile welcome?
Answer:
The crocodile welcomes little fishes.
Question 3.
How does the extract portray the crocodile?
Answer:
The extract portrays the crocodile as a deceiving, idle reptile.
Question 4.
Write the rhyme scheme for the 2nd stanza.
Answer:
The rhyme scheme is abab.
Question 5.
And welcomes little fishes in, With gently smiling jaws!
Identify the figure of speech of the above lines and explain.
Answer:
- Personification: The human quality of welcoming and smiling is given to a reptile for better poetic effect.
- Exclamation: The line ends with an exclamatory mark.
![]()
Poetic Device:
Question 1.
Pick out the rhyming words from the 1st stanza.
Answer:
Crocodile – Nile, tail – scale
Writing Skills:
Question 1.
Create a poem of your own on ‘A crocodile’.
Answer:
Crocodile with a smile
Today I saw a crocodile walking quickly down the isle
I nearly missed a heartbeat, when I saw its clawy feet.
I thought I saw it cry a tear,
This made me really lose my fear. Looking at me it gave a smile
Ohh that’s the reason I ran away a mile.
How Doth the Little Busy Bee Summary in English
In this poem, the poet Isaac Watts tells us about the busy bee who does not waste time but works day in and day out to collect nectar from the flowers and stores it in the hives built by the bees. The poet appreciates the skills of the bees, used in making the cells and sealing them for future use. The poet is trying to tell us that we should take the example of these small creatures and use our time fruitfully. Isaac Watts
The parody “How doth the – a small little crocodile” written be Lewis Caroll tries to poke fun at the poem “How doth the little busy bee”. The parody in a humorous way speaks about the idleness and cunningness of a crocodile in contrast to the hardworking bee. The busy bee works all day for its honey but in contrast the crocodile remains idle yet gets his fill.
Introduction:
‘How doth the little busy bee’ written by Isaac Watts is a poem in which the hard work of the bee is appreciated. A parody is playful comic imitation of a writer’s style. A parody deliberately copies someone or something in an amusing way. It may be simply a humorous imitation of a well-known or popular work.
![]()
Glossary:
- doth (v) – does (old English)
- opening (adj) – blooming
- cell (n) – a small hexagonal compartment in a honeycomb
- labours (v) – works hard
- grin (v) – to smile with lips parted to reveal the teeth
- claws (n) – curved pointed nail on each of the foot of a mammal, reptile or bird
- scale (n) – small flat hard and bony covering the skin, particularly of a fish or reptile
- jaw (n) – the part of the face below the mouth
- skilfully (adv) – cleverly.
- cheerfully (adv) – happily.
- gather (v) – to collect.
- parody (n) – a humorous way of writing in which the original work of another writer is copied in an exaggerated way.
7th Std English Balbharati Textbook Solutions
- From a Railway Carriage Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- The Souvenir Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- Abdul Becomes a Courtier Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- How Doth the Little Busy Bee Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- Learn Yoga from Animals Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- Chasing the Sea Monster Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- Great Scientists Class 7 English Textbook Solutions