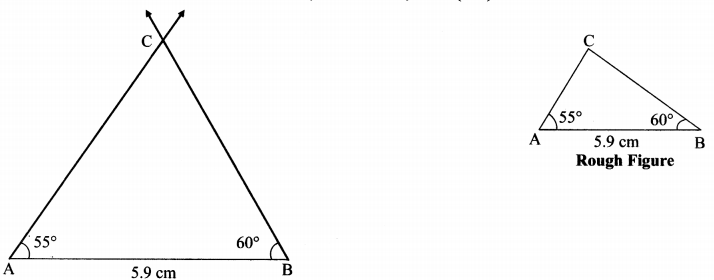
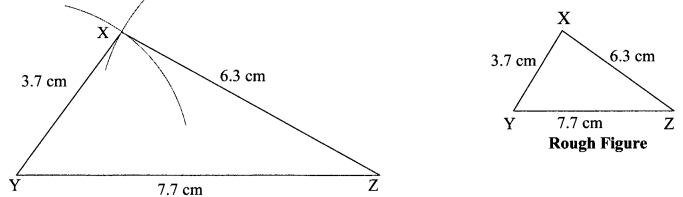
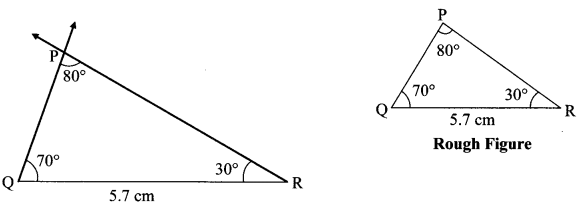
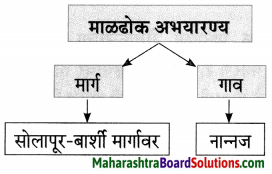
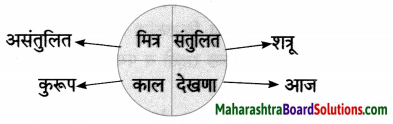
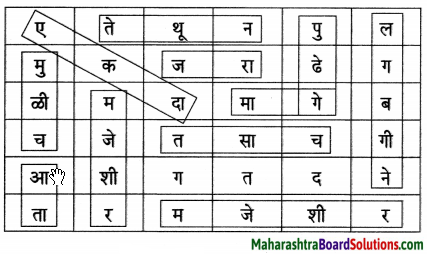
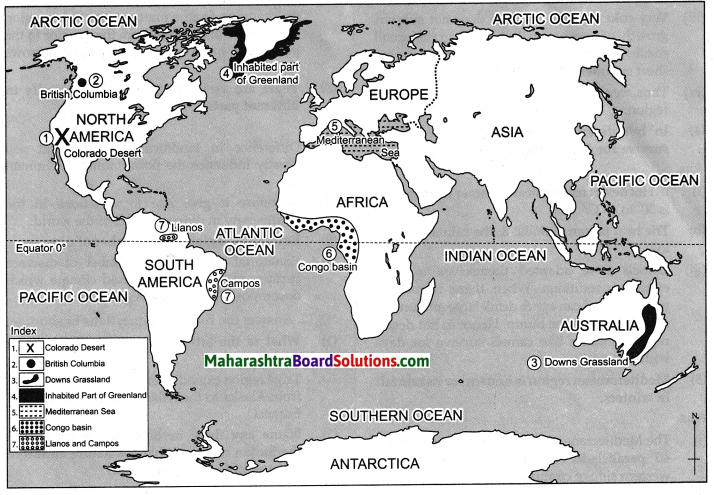
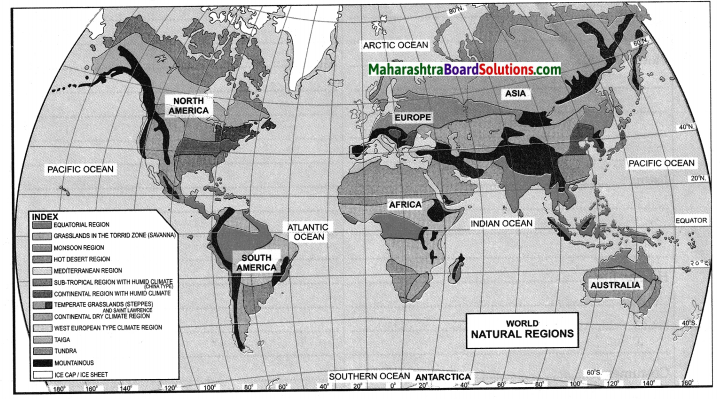
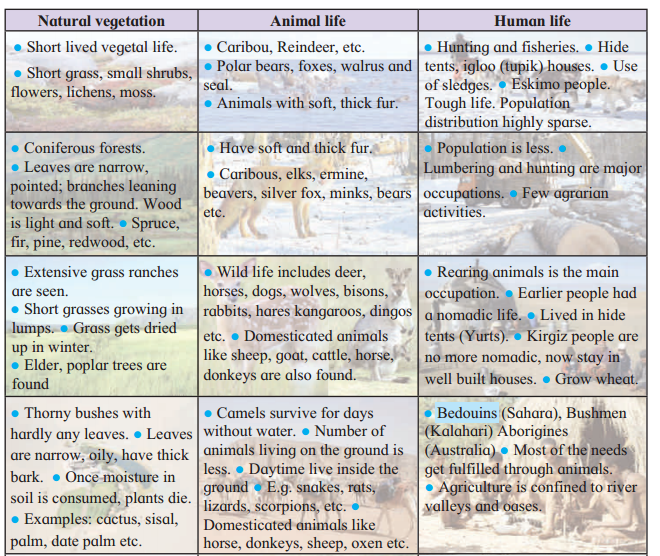
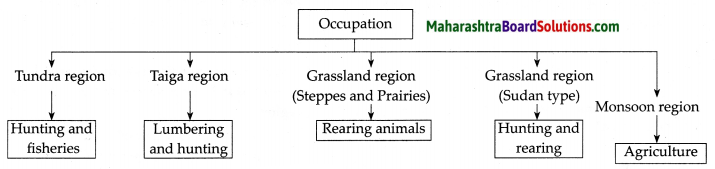
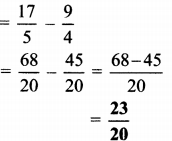Hindi Digest Std 7 Maharashtra Board | 7th Std Hindi Digest Pdf
7th Standard Hindi Digest Pdf | Std 7 Hindi Digest Pdf
Hindi Digest Std 7 Maharashtra Board पहली इकाई
- Chapter 1 वाचन मेला
- Chapter 2 फूल और काँटे
- Chapter 3 दादी माँ का परिवार
- Chapter 4 देहात और शहर
- Chapter 5 बंदर का धंधा
- Chapter 6 ‘पृथ्वी’ से ‘अग्नि’ तक
- Chapter 7 जहॉं चाह, वहाँ राह
- Chapter 8 जीवन नहीं मरा करता है
- अभ्यास – १
- पुनरावर्तन – १
7th Std Hindi Digest Pdf दूसरी इकाई
- Chapter 1 अस्पताल
- Chapter 2 बेटी युग
- Chapter 3 दाे लघुकथाएँ
- Chapter 4 शब्द संपदा
- Chapter 5 बसंत गीत
- Chapter 6 चंदा मामा की जय
- Chapter 7 रहस्य
- Chapter 8 हम चलते सीना तान के
- अभ्यास – २
- अभ्यास – ३
- पुनरावर्तन – २
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Textbook Solutions