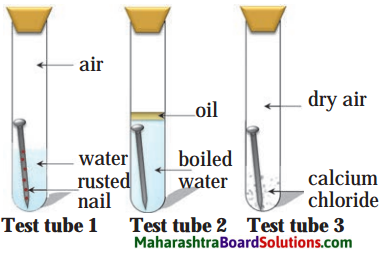
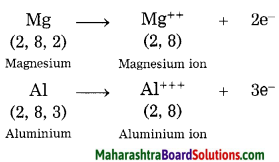
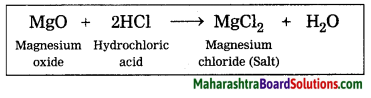
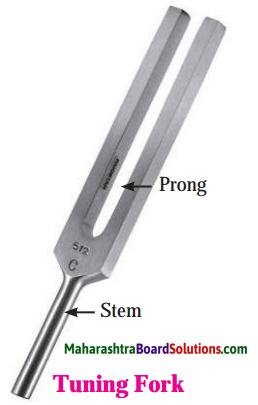
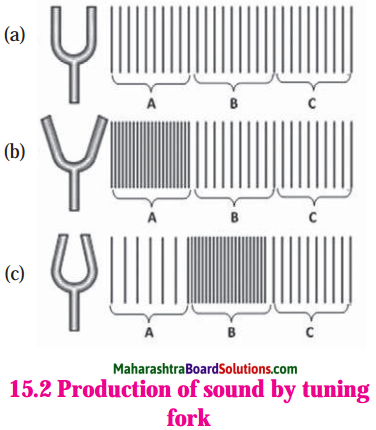
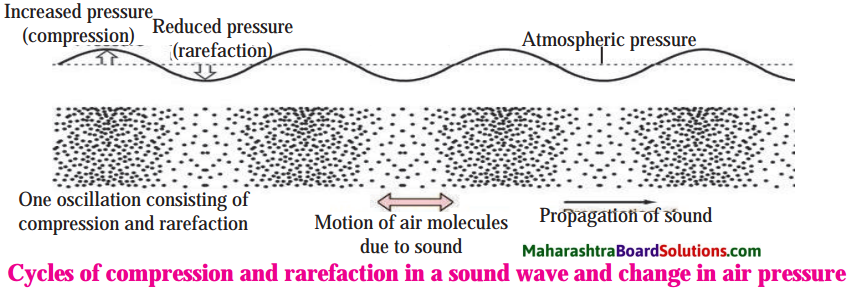
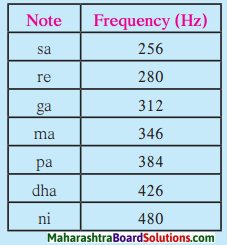
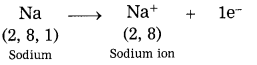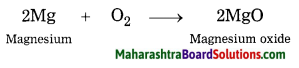Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 History Solutions Chapter 14 Formation of State of Maharashtra Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 8 History Solutions Chapter 14 Formation of State of Maharashtra
Class 8 History Chapter 14 Formation of State of Maharashtra Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options:
Question 1.
The State of …………….. was formed on 1 May, 1960.
(a) Goa
(b) Karnataka
(c) Andhra Pradesh
(d) Maharashtra
Answer:
(d) Maharashtra
Question 2.
…………….. put forth the proposal of Samyukta Maharashtra with Mumbai in the Mumbai Municipal Corporation.
(a) G. T. Madkholkar
(b) Acharya Atre
(c) D. V. Potdar
(d) Shankarrao Dev
Answer:
(b) Acharya Atre
Question 3.
…………….. accepted the responsibility as first Chief Minister of Maharashtra.
(a) Yashwantrao Chavan
(b) Pruthviraj Chavan
(c) Shankarrao Chavan
(d) Vilasrao Deshmukh
Answer:
(a) Yashwantrao Chavan
2. Explain the following statements with reasons:
Question 1.
Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti came to be established.
Answer:
- The demand for a state of Marathi speaking people of all regions was put forth in the Nagpur Pact in 1953.
- There was no positive response from the Central Government for formation of Samyukta Maharashtra with Mumbai.
- The agitation was made severe through strikes, demonstrations, rallies, etc. which were organised from time to time.
- As the issue of the demand of Marathi speaking people started becoming complicated, discontent spread throughout the state.
- A meeting was held under the leadership of Keshavrao Jedhe on 6 February, 1956 at Tilak Smarak Mandir in Pune and the Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti was formed.
Question 2.
The role of newspapers was important in Samyukta Maharashtra Movement.
Answer:
- The role of newspapers was equally important in Samyukta Maharashtra Movement. They worked to awaken the people.
- Navyug, Prabhat, Navakal, Sakai, Prabodhan, Kesari are newspapers which played important role.
- The ‘Maratha’ newspaper by Acharya Atre had a significant role in Samyukta Maharashtra movement.
- Balasaheb Thackeray took pen name ‘Mavla’ and drew caricatures in ‘Navyug’.
- Lokshahir Annabhau Sathe, Shahir Amar Sheikh and Shahir D. N. Gavankar aroused public awakening on a large scale through their writings.
![]()
3. Write short notes:
Question 1.
Samyukta Maharashtra Parishad:
Answer:
- On 12 May 1946, a resolution was passed regarding Samyukta Maharashtra in the Sahitya Sammelan at Belgaon.
- On this background, Maharashtra Ekikaran Parishad was convened under the leadership of Shankarrao Dev at Mumbai on 28 July.
- A resolution was passed that all Marathi speaking regions should be united in one state.
- It should include the regions of Mumbai, Central provinces Marathwada and Gomantak.
Question 2.
Contribution of Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti:
Answer:
Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti f contributed in the following way to form Samyukta Maharashtra.
1. Samyukta Maharashtra movement spread throughout the state and reached in rural areas.
2. Common people also joined the movement spontaneously.
3. When it was clear that Mumbai will not be included in Maharashtra, Samiti held demonstrations to protest and arouse public agitation.
4. The grand success of Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti in Lok Sabha, Vidhan Sabha and Mumbai Municipal Corporation in 1957 made it clear that the voters were in favour of Samyukta Maharashtra.
5. The agitations led by Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti during the visit of Prime Minister Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru made the approach of Central Government favourable in the formation of Maharashtra state.
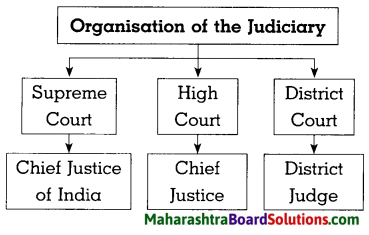
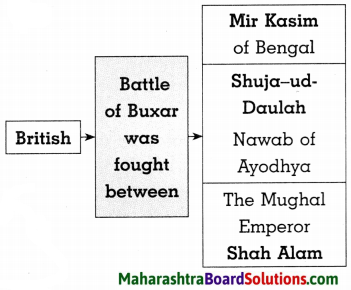
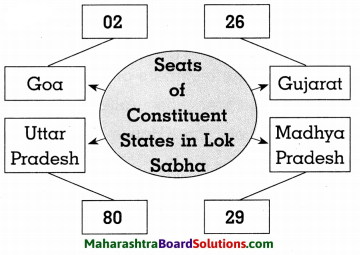
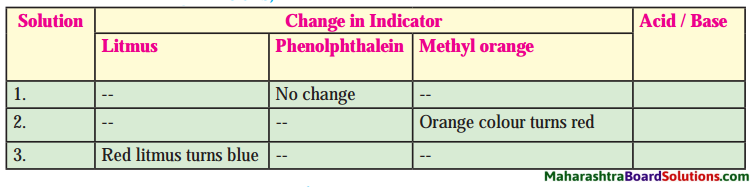
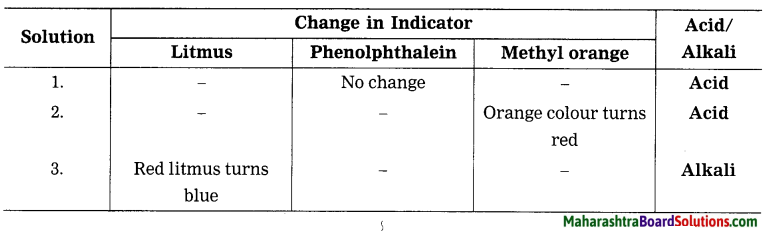
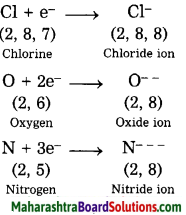
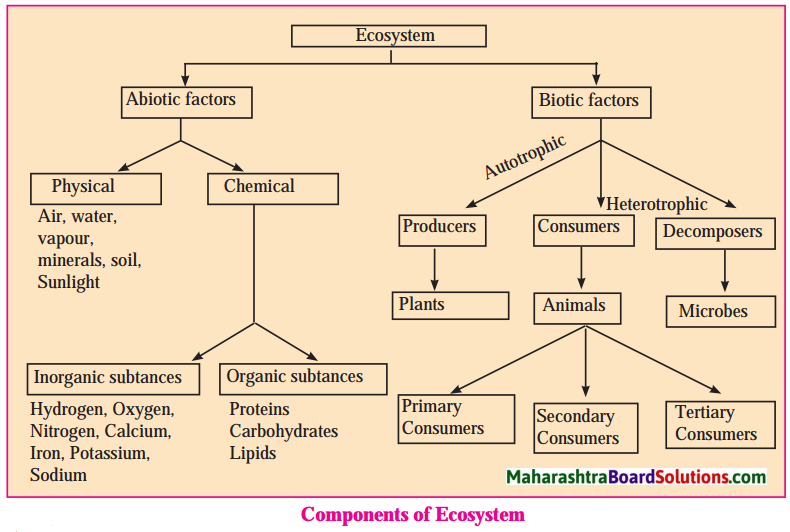
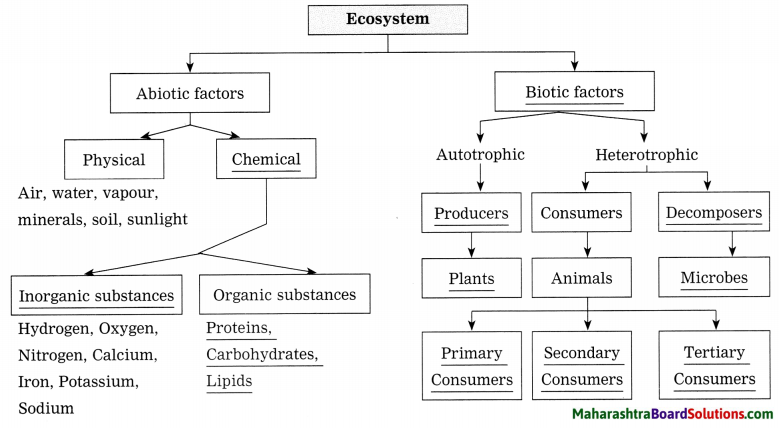
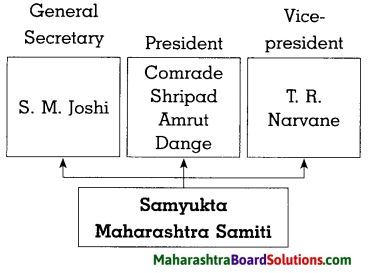
4. Complete the following diagram.
Question 1.
Answer:
Do you Know?

Contribution of Marathi newspapers and Shahirs: In this movement the role of newspapers was important. Prabodhan, Kesari, Sakal, Navakal, Navyug, Prabhat many such newspapers worked for awakening of the people. Acharya Atre started the ‘Maratha’ newspaper which played an important role in Samyukta Maharashtra Movement.
Balasaheb Thackeray took up the pen name ‘Mavia’ and drew caricatures to make the movement comprehensive. Lokshahir Annabhau Sathe, Shahir Amar Sheikh and Shahir D.N.Gavankar through their writings aroused public awakening on a large scale.
![]()
Project:
Collect information about the personalities who greatly contributed to the formation of Maharashtra and prepare a project based on it with the help of your teachers.
Class 8 History Chapter 14 Formation of State of Maharashtra Additional Important Questions and Answers
Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options:
Question 1.
………………… organised rallies to protest against the report of JVP Committee.
(a) Sane Guruji
(b) P. K. Atre
(c) Senapati Bapat
(d) Prabodhankar Thackeray
Answer:
(c) Senapati Bapat
Question 2.
…………….. established Dar Commission for forming linguistic province.
(a) Morarji Desai
(b) Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
(d) Yashwantrao Chavan
Answer:
(c) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
Question 3.
According to 1953 Pact, Assembly session would be held once in a year at …………….
(a) Pune
(b) Mumbai
(c) Nagpur
(d) Aurangabad
Answer:
(c) Nagpur
![]()
Question 4.
Police used lathi charge and tear …………….. gas on the March led by
(a) Bhai Madhavrao Bagal
(b) Comrade Shripad Amrut Dange
(c) S.M. Joshi
(d) Senapati Bapat
Answer:
(d) Senapati Bapat
Question 5.
Acharya Atre started the newspaper …………….. which played an important role in Samyukta Maharashtra Movement.
(a) Navyug
(b) Prabodhan
(c) Maratha
(d) Navakal
Answer:
(c) Maratha
Name the following:
Question 1.
Demanded reconstruction of a state based on language in 1915.
Answer:
Lokmanya Tilak
Question 2.
Commission which advocated bilingual Mumbai.
Answer:
‘Commission for Reconstruction of States’
Question 3.
Samiti established at Tilak Smarak Mandir, Pune.
Answer:
Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti
![]()
Question 4.
The Act passed by the Parliament in April 1960.
Answer:
Mumbai Reorganisation Act.
Answer the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
What was the appeal made by Shankarrao Dev in the meeting held on Kamgar Maidan?
Answer:
Shankarrao Dev appealed to the people in the following words, “We will oppose the separation of Mumbai from Maharashtra up to our last breath.”
Question 2.
What was the suggestion given by the Commission for Reconstruction of States?
Answer:
The Commission for Reconstruction of States suggested creation of bilingual Mumbai State.
Question 3.
What was the resolution proposed by S. M. Joshi on 7 November, 1955 at the meeting of labourers?
Answer:
At the meeting of the labourers on 7 November, 1955 S. M. Joshi proposed a resolution that Samyukta Maharashtra should be created with Mumbai and Vidarbha.
![]()
Question 4.
Where was the memorial of 106 martyrs erected? What is it called?
Answer:
The memorial of 106 martyrs was erected in Mumbai near Flora Fountain. It is called ‘Flutatma Smarak.’
Question 5.
Who played an important role in establishing Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti?
Answer:
Acharya P K. Atre, Madhu Dandavate, Prabodhankar Keshav Thackeray, Y. K. Souni played important role in establishing Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti.
Question 6.
Name the lokshahirs who aroused awakening among people during Samyukta Maharashtra Movement.
Answer:
Lokshahirs Annabhau Sathe, Shahir Amar Sheikh and Shahir D. N. Gavankar aroused public awakening among the people during Samyukta Maharashtra Movement.
Do as Directed:
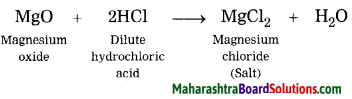
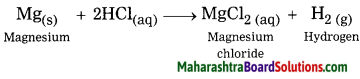
Complete the following diagram:
Question 1.
Answer:
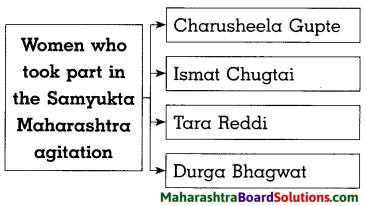
Question 2.
Answer:
Complete the table:
Question 1.
| Foundation year | Name of the Commission/Samiti | Name of the President |
| 1. 28 July | ………………………………………. | Shankarrao Dev |
| 2. ………………………… | Dar Commission | Justice S. R. Dar |
| 3. 29 December, 1943 | ……………………………………….. | Justice Fazal Ali |
| 4. 6 February, 1956 | Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti | ……………………………. |
Answer:
| Foundation year | Name of the Commission/Samiti | Name of the President |
| 1. 28 July | Maharashtra Ekikaran Parishad | Shankarrao Dev |
| 2. 17 June, 1947 | Dar Commission | Justice S. R. Dar |
| 3. 29 December, 1943 | Commission for Reconstruction of States | Justice Fazal Ali |
| 4. 6 February, 1956 | Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti | Comrade Shripad Amrut Dange |
Write short notes:
Question 1.
Dar Commission:
Answer:
- The President of Constituent Assembly, Dr. Rajendra Prasad established the Dar Commission on 17 June, 1947.
- The Commission started the work under the leadership of Justice S. K. Dar to form states on linguistic basis.
- On 10 December, 1948, the report of Dar Commission was published but the issue remained unsolved.
![]()
Question 2.
Commission for Reconstruction of States:
Answer:
- Indian Government appointed a ‘Commission for Reconstruction of States’ on 29 December, 1953.
- It was formed under the Chairmanship of Justice Fazal Ali.
- In the proposal presented by the commission on 10 October, 1955, a creation of bilingual Mumbai State was advocated.
Answer the following questions in brief:
Question 1.
What started the demand for an independent state of Marathi speaking people?
Answer:
- The demand for an independent Marathi speaking state started before independence.
- N. C. Kelkar presented the idea that the entire Marathi speaking population should be under one dominion.
- In 1915, Lokmanya Tilak demanded the reconstruction of a state based on language.
- An important resolution regarding Samyukta Maharashtra was passed in the Sahitya Sammelan at Belgaon. It began the movement to form Independent state of Marathi speaking people.
Question 2.
Write information on the workers meeting held on 7 November, 1955.
Answer:
- The struggle of Marathi speaking people for formation of Maharashtra with Mumbai had started.
- On 7 November, 1955 a meeting of labourers was held.
- Labour Organisation or Communists, Praja Socialists, Socialists, Peasants and Workers Party, Janasangh, etc. participated in the meeting.
- Comrade Shripad Amrut Dange was the President of this meeting.
- S. M. Joshi proposed a resolution to create a Samyukta Maharashtra with Mumbai and Vidarbha.
![]()
Question 3.
What were the provisions in the Nagpur Pact?
Answer:
The following provisions were made in the Nagpur Pact:
- Samyukta Maharashtra should be formed including Western Maharashtra 8 and Vidarbha along with Marathwada.
- Assurance was given regarding equitable financial provisions for development.
- Ample finance will be provided for technical and vocational education.
- Government services will be provided in accordance with the population in the region.
- Once in a year an Assembly session will be held at Nagpur.
Question 4.
What happened on the day a grand march was taken to Vidhan Sabha?
Answer:
- For the formation of Samyukta Maharashtra, a grand march was taken to the Vidhan Sabha led by Senapati Bapat.
- The government declared a ban.
- The police started lathi charge and used tear gas on the protestors who broke the ban.
- On the same evening, Comrade Shripad Dange guided a mob of fifty thousand on Kamgar Maidan.
- To give impetus to the Samyukta Maharashtra Movement, it was further decided to hold one day strike on 21 November, 1955.
Question 5.
Which events took place in the final stages of establishment of Maharashtra state?
Answer:
The following events took place in the final stages of establishment of Maharashtra state:
- Due to agitation of Samyukta Maharashtra Movement, central government gave consent to the formation of two linguistic states.
- The Congress President, Indira Gandhi also supported the Samyukta Maharashtra Movement.
- In April 1960, the Parliament passed the Mumbai Reorganisation Act.
- According to this act, Maharashtra State was formed on 1st May, 1960.
- Pandit Nehru on the occasion of Labour Day made a formal announcement of the formation of Maharashtra State at a special ceremony at Raj Bhavan.
- Yashwantrao Chavan accepted the responsibility of first Chief Minister of Maharashtra.
Explain the following statements with reasons:
Question 1.
Severe response was seen 9, throughout Maharashtra against JVP Committee report.
Answer:
- The Congress appointed a three ministers committee on 29 December, 1948 to study the conditions of creating linguistic provinces.
- The report suggested that Congress accepted the concept of linguistic state in principle but the time was not proper for it.
- Due to this, severe response of the people was seen throughout Maharashtra against JVP Committee report.
Answer the following questions in detail:
Question 1.
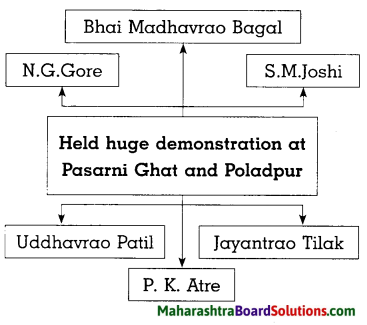
How did the Central Government favour Maharashtra’s movement under the leadership of Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti?
Answer:
- Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru was going to unveil statue of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj mounted on a horse on Pratapgad on 30 November, 1957.
- Under the leadership of Bhai Madhavrao Bagal, Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti held huge demonstrations.
- Leaders like S. M. Joshi, N. G. Gore, Jayantrao Tilak, R K. Atre participated in the protest at Pasarni Ghat and Poladpur.
- Pandit Nehru became aware of sentiments of the Marathi speaking people.
- The Congress President Indira Gandhi supported the Samyukta Maharashtra Movement.
- Finally, the Central government gave consent for formation of two states-Gujarat and Maharashtra from former Mumbai (Bombay) state
![]()
Question 2.
Observe the given picture and identify. Write about his contribution in Samyukta Maharashtra.

Answer:
- This picture is of Acharya R K. Atre. He made important contribution to Samyukta Maharashtra Movement.
- He played important role in formation of Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti.
- He presented and supported the pro- united Maharashtra Movement through his newspaper ‘Maratha’.
- He was in the forefront of the demonstrations at Pasarni Ghat and Poladpur during the visit of Prime Minister Pandit Nehru at Pratapgad.
Question 3.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of linguistic reorganisation of states?
Answer:
Advantages:
- The feeling of unity is very strong among the people speaking common language.
- It guarantees social security.
- It facilitates communication between people.
- It helps in achieving linguistic and cultural unity.
Disadvantages:
- Linguistic reorganisation may narrow perspective of the people.
- Excessive pride in one’s language creates hatred towards other language.
- Learning other languages and enjoying the literature never takes places.
- It creates hurdles in social and cultural development.