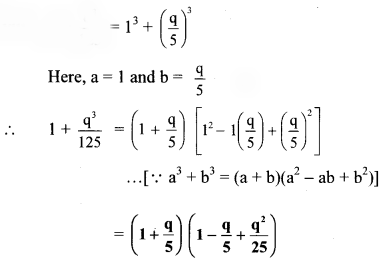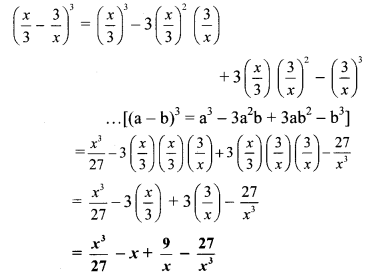Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 6.2 8th Std Maths Answers Solutions Chapter 6 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions.
Practice Set 6.2 8th Std Maths Answers Chapter 6 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions
Question 1.
Factorise:
i. x³ + 64y³
ii. 125p³ + q³
iii. 125k³ + 27m³
iv. 2l³ + 432m³
v. 24a³ + 81b³
vi. \(y^{3}+\frac{1}{8 y^{3}}\)
vii. \(\mathrm{a}^{3}+\frac{8}{\mathrm{a}^{3}}\)
viii. \(1+\frac{\mathrm{q}^{3}}{125}\)
Solution:
i. x³ + 64y³
= x³ + (4y)³
Here, a = x and b = 4y
∴ x³ + 64y³ = (x + 4y) [x² – x(4y) + (4y)²]
….[∵ a³ + b³ = (a + b)(a² – ab + b²)]
= (x + 4y)(x² – 4xy + 16y²)
ii. 125p³ + q³
= (5p)³ + q³
Here, a = 5p and b = q
∴ 125p³ + q³ = (5p + q)[(5p)² – (5p)(q) + q²]
…[∵ a³ + b³ = (a + b)(a² – ab + b²)]
= (5p + q)(25p² – 5pq + q²)
iii. 125k³ + 27m³
= (5k)³ + (3m)³
Here, a = 5k and b = 3m
∴ 125k³ + 27m³
= (5k + 3m) [(5k)² – (5k)(3m) + (3m)²]
…[∵ a³ + b³ = (a + b)(a² – ab + b²)]
= (5k + 3m)(25k² – 15km + 9m²)
iv. 2l³ + 432m³
= 2 (l³ + 216m³)
… [Taking out the common factor 2]
= 2[l³ + (6m)³]
Here, a = l and b = 6m
2l³ + 432m³ = 2 {(l + 6m)[l² – l(6m) + (6m)²]}
…[∵ a³ + b³ = (a + b)(a² – ab + b²)]
= 2(l + 6m)(l² – 6lm + 36m²)
v. 24a³ + 81b³
…[Taking out the common factor 3]
= 3 [(2a)³ + (3b)³]
Here, A = 2a and B = 3b
∴ 24a³ + 81b³
= 3 {(2a + 3b) [(2a)² – (2a)(3b) + (3b)²]}
…[∵ A³ + B³ = (A + B) (A² – AB + B²)]
= 3(2a + 3b)(4a² – 6ab + 9b²)
vi. \(y^{3}+\frac{1}{8 y^{3}}\)
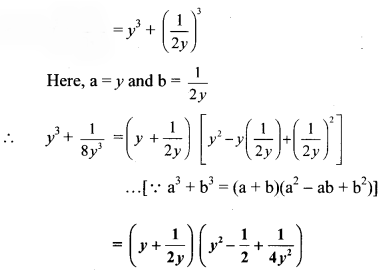
vii. \(\mathrm{a}^{3}+\frac{8}{\mathrm{a}^{3}}\)
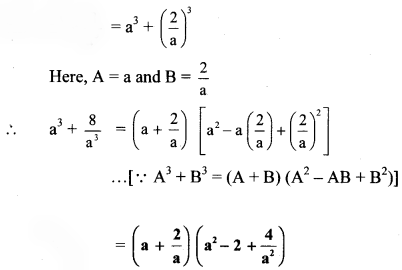
viii. \(1+\frac{\mathrm{q}^{3}}{125}\)