Class 9 English Chapter 2.2 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 English Solutions My English Coursebook Chapter 2.2 Helen Keller and Anne Sullivan Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Helen Keller and Anne Sullivan Poem 9th Std Question Answer
My English Coursebook Std 9 Digest Chapter 2.2 Helen Keller and Anne Sullivan Textbook Questions and Answers
Warming up!
Chit-chat:
- What is your favourite school subject?
- Which subject do you find the most difficult?
- What do you do to try to understand it better?
- Can I help you to ……….. ?
- Can you help me to ………………. ?
![]()
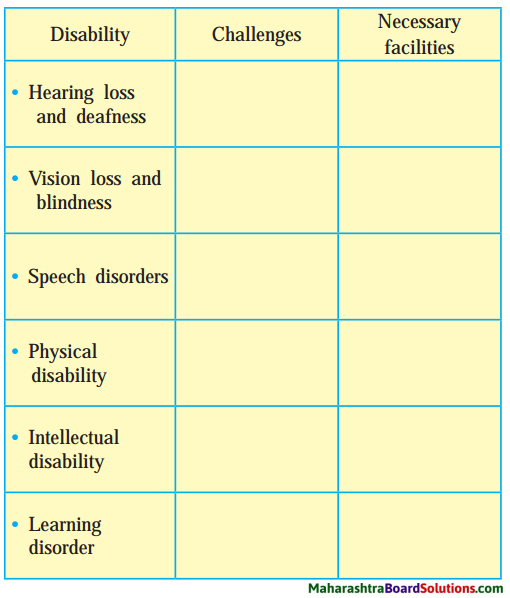
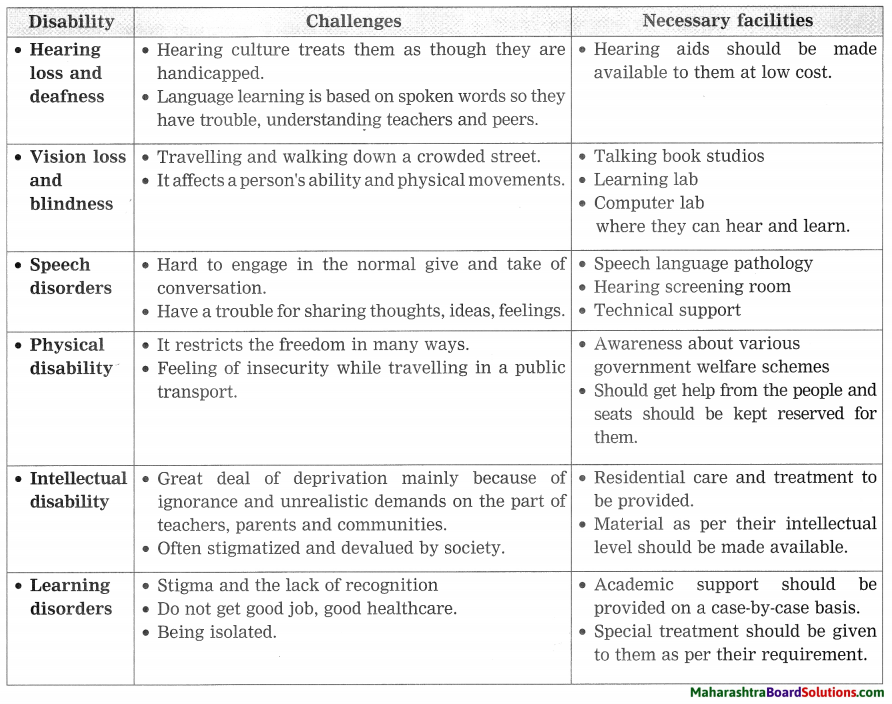
1. Discuss the challenges that people have to face due to disabilities.
What provisions should be made in public places so that everyone gets the same access to public facilities?
Observe your surroundings and write whether such facilities are available. How can you help to improve the situation?
Question 1.
Discuss the challenges that people have to face due to disabilities :
Answer:
- Unfriendly public places –
- abused – exploited – excluded
- inferiority complex
Question 2.
What provisions should be made in public places so that everyone gets the same access to public facilities?
Answer:
- Suitably altering buses, airplanes, train compartments to make them accessible to persons with disabilities.
- Making necessary curbs, cuts and slopes in pavement for wheelchair users.
- Providing ramps at all public places.
- Engraving edges of railway platforms for the benefits of the visually impaired.
![]()
Question 3.
Observe your surroundings and write whether such facilities are available. How can you help to improve the situation?
Answer:
English Workshop:
1. Say whether the following sentences are true or false:
Question 1.
Say whether the following sentences are true or false:
(a) The most important day in Helen Keller’s life was when her teacher came to her.
(b) When young Helen stretched out her hand, her mother took it.
(c) Young Helen learnt to spell many words without understanding them.
(d) One day, young Helen understood that everything has a name.
(e) Young Helen did not try to put the pieces of the doll together.
(f) Young Helen felt sorry that she had broken the doll.
Answer:
(a) The most important day in Helen Keller’s life was when her teacher came to her. – True
(b) When young Helen stretched out her hand, her mother took it. – False
(c) Young Helen learnt to spell many words without understanding them. – True
(d) One day young Helen understood that everything has a name. – True
(e) Young Helen did not try to put the pieces of doll together. – True
(f) Young Helen felt sorry that she had broken the doll. – False
![]()
2. Listen carefully and classify the following into ‘one’ and ‘many’.
day, contrasts, teacher, lives, months, years, afternoon, porch, signs, face, fingers, leaves, blossoms, anger, bitterness, weeks, struggle, ship, darkness
Question 1.
Listen carefully and classify the following into ‘one’ and ‘many’.
day, contrasts, teacher, lives, months, years, afternoon, porch, signs, face, fingers, leaves, blossoms, anger, bitterness, weeks, struggle, ship, darkness

Answer:
| one | many |
| day, teacher, afternoon, porch, face, anger, bitterness, struggle, ship, darkness | contrast, lives, months, years, signs, fingers, leaves, blossoms, weeks. |
3. This narrative is written in the first person – using ‘I’. Rewrite the following sentences using ‘Helen Keller/Young Helen’ appropriately in place of ‘I’ and making other neccessary changes in the sentences
Question a.
I did not know what the future held of marvel or surprise for me.
Answer:
Young Helen did not know what the future held of marvel or surprise for her.
Question b.
The morning after my teacher came she led me into her room and gave me a doll.
Answer:
The morning after Helen Keller’s teacher came, she led her into her room and gave her a doll.
![]()
Question c.
On entering the door I remembered the doll I had broken.
Answer:
On entering the door, young Helen remembered the doll she had broken.
Question d.
Then my eyes filled with tears for I realised l what I had done, and for the first time I felt repentance and sorrow.
Answer:
Then young Helen’s eyes filled with tears: for she realised what she had done, and for the first time she felt repentance and sorrow.
![]()
4. Read the following sentences and frame at least two relevant questions on each.
(a) I was like that ship before my education began.
Questions with ‘who’, ‘what’, ‘when’.
Example: Who was like that ship before her education began?)
(b) One day I was playing with the new doll.
(c) I learnt a great many new words that day.
(d) She brought my hat.
(e) We walked down the path to the well-house.
(f) That living word awakened my soul.
Question b.
One day I was playing with the new doll.
Answer:
(i) When was I playing with the new doll?
(ii) What was I doing one day?
![]()
Question c.
I learnt a great many words that day.
Answer:
(i) What did I learn that day?
(ii) Who learnt many words that day?
Question d.
She brought my hat.
Answer:
(i) What did she bring?
(ii) Who brought my hat?
Question e.
We walked down the path to the well-house.
Answer:
(i) Where did we walk down?
(ii) Who walked down the path to the well- house?
Question f.
That living word awakened my soul.
Answer:
(i) What awakened my soul?
(ii) What did that living word awaken?
![]()
5. Write about your own experience. Do you remember an occasion when you did something successfully for the first time? Write about it in short (10-12 lines). Prepare an outline of your composition before you write it.
Question 1.
Write about your own experience. Do you remember an occasion when you did something successfully for the first time? Write about it in short (10-12 lines). Prepare an outline of your composition before you write it.
Answer:
The occasion when I was successful
When our teacher gave us an assignment to write a poem on nature, it was quite a difficult job for me. I tried my level best to arrange some words but I could not do it successfully. Then I took the help of my brother. He guided me how to do it. As per his guidance I collected some words related to nature. Then I tried to weave the words in lines. I tried to match the rhymes also.
Somewhere it was quite easy, whereas somewhere it was a difficult job for me. At last, after a lot of efforts and trials, I was successful to write a poem based on ‘Nature’. It gave me immense pleasure and joy. When I read it in the class, I got good praise and applause from the teacher as well as from my classmates. It was really a memorable occasion for me.
6. Gather more information about the following:
Question a.
Different types of impairment that limit a person’s activity or make it difficult for him/her to mix with others in society.
Answer:
Different types of impairment that limit a person’s activity.
- Visual impairment
- Hearing impairment
- impairment of speech production
- impairment of language comprehension
- Intellectual impairment
- Reading impairment
![]()
Question b.
How modern technology can be used to overcome these problems.
Answer:
Modern technology has been playing an important role in our day-to-day life. But it is more useful for the disabled people than the common man in the society. It facilitates as per the requirement of the person. It will be a boon for them. Devices like Captioned Television, Live Speech Captioning, Telecommunication Devices for the Deaf are useful for Hearing impairments. In the same way, other devices based on modern technology are also available for other impairments.
7. Complete the following sentences using your own ideas:
(a) The most important day I remember in all my life is the one on which ………… .
(b) I did not know what ………… .
(c) One day. while I was playing ………… .
(d) I realised what ………… .
(e) I do not remember what ………… .
Question a.
The most important day I remember in all my life is the one on which ………… .
Answer:
The most important day I remember in all my life is the one on which I was saved in a horrible accident when I was learning to ride bike. I lost my control and dashed the car in front of me. I fell down with bike on my legs. The people around came and lifted the bike and I was rescused.
Question b.
I did not know what ………… .
Answer:
I did not know what to do at that situation.
![]()
Question c.
One day. while I was playing, ………… .
Answer:
One day, while I was playing, I got fracture in my leg.
Question d.
I realised what ………… .
Answer:
I realised what I was doing was wrong.
Question e.
I do not remember what ………… .
Answer:
I do not remember what exactly I did at that moment.
![]()
Language study:
7. Find three examples of the following from the passage.
(a) articles
(b) compound words
(c) present participles
(d) past participles
Question 1.
Find three examples of the following from the passage.
(a) articles
(b) compound words
(c) present participles
(d) past participles.
My English Coursebook 9th Class Solutions Chapter 2.2 Helen Keller and Anne Sullivan Additional Important Questions and Answers
Read the following passage and do the activities:
Simple Factual Activity:
Question 1.
Say whether the following statements are True or False:
(Answers are given directly.)
Answer:
- Anne Mansfield Sullivan was Helen Keller’s mother. – False
- The author compares herself to the great ship that groped her way towards the shore. – False
- The writer was standing on the porch dumb and expectant on that eventful day. – True
- Helen’s eyes filled with tears when she realised what she had done. – True
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks and complete the following sentences: (Answers are directly given.)
- The writer was interested in finger play so she tried to imitate.
- When young Helen succeeded in making the letters correctly, she was flushed with childish pleasure and pride.
- Earlier in the day Helen and Miss Sullivan had a tussle over the words mug and water.
- When Miss Sullivan brought Helen’s hat, she realised that she was going out into the warm sunshine.
Question 3.
Complete the following sentences:
(Answers are directly given.)
1. The writer and her teacher were attracted by the fragrance of the honeysuckle with which the well house was covered.
2. As the cool stream gushed over Helen’s hand, she realised that water meant the wonderful cool something that was flowing over her hand.
Complex Factual Activities:
Question 1.
The author refers to two contrasting emotions, what are they?
Answer:
- The first is when her teacher Anne Sullivan came in her life and she was filled with wonder.
- On the afternoon of that eventful day she guessed vaguely from her mother’s signs and guessed something unusual was about to happen.
![]()
Question 2.
Match the following:
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. The afternoon sun penetrated the mass of honeysuckle … | (a) when she considered the immeasurable contrasts between the two lives. |
| 2. The writer was filled with wonder … | (b) how near the harbour she was. |
| 3. The familiar leaves and blossoms came forth … | (c) and fell on the writer’s upturned face. |
| 4. The writer was like compass or sounding-line and no way of knowing… | (d) to greet the sweet southern spring. |
Answer:
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. The afternoon sun penetrated the mass of honeysuckle … | (c) and fell on the writer’s upturned face. |
| 2. The writer was filled with wonder … | (a) when she considered the immeasurable contrasts between the two lives. |
| 3. The familiar leaves and blossoms came forth … | (d) to greet the sweet southern spring. |
| 4. The writer was like compass or sounding-line and no way of knowing… | (b) how near the harbour she was. |
Question 3.
What did young Helen’s teacher do when they first met?
Answer:
When Helen met her teacher for the first time, she caught Helen’s hand and held her close in her arms.
![]()
Question 4.
What were Helen’s reactions when she succeeded in making letters correctly?
Answer:
When Helen succeeded in making the letters correctly, she was flushed with childish pleasure and pride. She ran downstairs and held up her mother’s hand and made the letters for doll. She was simply making her fingers go in monkey-like imitation.
Question 5.
Arrange the following sentences in chronological order:
1. Helen learnt many words without understanding them.
2. Helen learnt the word ‘doll’ by imitation from her teacher for the very first time.
3. She realized that everything has a name.
4. When she was successful in making the letters of ‘doll’, she showed it to her mother.
Answer:
2. Helen learnt the word ‘doll’ by imitation from her teacher for the very first time.
4. When she was successful in making the letters of ‘doll’, she showed it to her mother.
1. Helen learnt many words without understanding them.
3. She realized that everything has a name.
Question 6.
What were the barriers? How could they be swept away?
Answer:
When the writer realised that every object had a name, each name gave birth to a new thought. Every object that she touched seemed to quiver with life as everything was strange and new to her. As every living word could give her new experience but some of them couldn’t. By trying to touch every living object she could name it. But she could not do it with objects that were invisible. ’
![]()
Question 7.
Why did young Helen feel repentance and sorrow?
Answer:
When young Helen broke her new doll into pieces, she had no idea that every part of it had a name. But when she realized that every object that existed has a name, she saw everything with a strange, new sight. When she remembered her broken doll she felt repentance and sorrow for what she had done.
Activities based on vocabulary:
Question 1.
Guess the meaning of:
Answer:
- immeasurable contrasts – a vast difference
- eventful day – the day full of events/activities
- upturned – directed upward
- unconsciously – without realizing
- white darkness – It is symbolic to her condition (she was quite close to her destiny without being able to know it.)
Question 2.
Find out antonyms for the following from the extract. (Answers are directly given.)
Answer:
- shrinked × stretched
- died/ceased × existed
- pain × pleasure
- dully × keenly.
![]()
Question 3.
Pick out 4 infinitives from the extract:
Answer:
- to reveal
- to imitate
- to impress
- to love.
Question 4.
Classify the following words in the given columns:
fragrance, attract, stream, learn, hearth, enter, sorrow, realise
Answer:
| Nouns | Verbs |
| fragrance, stream, hearth, sorrow | attract, learn, enter, realise |
Question 5.
Find out four compound words from the lesson:
Answer:
- honeysuckle
- sounding-line
- everything
- well-house.
![]()
Activities based on contextual grammar:
Question 1.
Add a tail tag to the following sentences:
(Answers are directly given.)
- She did not know what the future held of marvel or surprise for her, did she?
- Helen was like that ship before her education began, wasn’t she?
- Helen had no way of knowing how near the harbour was, had she?
- The afternoon sun penetrated the mass of honeysuckle, didn’t it?
Rewrite the sentences by using ‘As soon as’:
Question 1.
On entering the door, I remembered the doll I had broken.
Answer:
As soon as I entered the door, I remembered the doll I had broken.
Personal Response:
Question 1.
What is the difference between wordless sensation and thought?
Answer:
Sensation is a physical feeling or perception resulting from something that happens to or comes into contact with the body. It is the ability to feel something physically and express without using words.
Thought is an idea or opinion produced by thinking or occurring suddenly in the mind. Sensation is different from thought. Thoughts are generated centrally in the brain and sensations occur at different places.
![]()
Question 2.
How can modern technology be used to overcome impairments?
Answer:
Technology has created a revolution in the life of disabled learners.
a. Disabled students have an adequate educational opportunities but application of computer based technology has created a sea of changes in available options for disabled students.
b. Computer programs have been designed to make it easier for disabled students to access material, communicate their ideas and work and participate in educational experiences.
Question 3.
Why should we help disabled people?
Answer:
We should help disabled people because though no fault of their own, they are in a situation where they require more assistance. If we help them wherever they want our help, they can boost their confidence to get success in their life. We are human and we are supposed to have empathy. So it is our duty to assist them wherever they want.
![]()
Activities Based on Language study
Do as directed:
Question 1.
Complete the words by using correct letters:
- w _ i c h
- h o u _ e
- g _ e e t
- a _ g e r
Answer:
- w h i c h
- h o u s e
- g r e e t
- a n g e r.
![]()
Question 2.
Copy the following sentences in your notebook:
Answer:
1. “Light! give me light!” was the wordless cry of my soul.
2. Those words that were to make the world blossom for me ‘like Aaron’s rod, with flower.’
Question 3.
Put the following words in alphabetical order :
1. porch, dumb, expectant, blossom.
2. interested, imitate, impress, impatient.
Answer:
1. blossom, dumb, expectant, porch.
2. imitate, impatient, impress, interested.
Question 4.
Punctuate the following sentences :
1. why dont you try to understand my situation ruta said her father
2. the tourist exclaimed what a beautiful place kashmir is
Answer:
1. “Why don’t you try to understand my situation Ruta?” said her father.
2. The tourist exclaimed, “What a beautiful place Kashmir is!”
![]()
Question 5.
Write four small words (minimum 3 letters each) using the letters in the given f word:
“immeasurable”
Answer:
- sure
- measure
- ease
- able.
Question 6.
Spot the error and rewrite the correct sentences:
1. My father have been working in a bank from last 20 years.
2. Yesterday I will see him while going to office.
Answer:
1. My father has been working in a bank from last 20 years.
2. Yesterday I saw him while going to office.
![]()
Question 7.
Write related words as shown in the example
(Answers are directly given.)
Answer:

Question 8.
Complete the following word-chain of adjectives. Add four words, each beginning with the last letter of the previous word:
white → …………… → ……………… → ………………. → …………….. .
Answer:
white → enormous → sacred → decent → tired.
Do as directed:
Question 1.
Make your own meaningful sentence by using the phrase ‘to be able to’.
Answer:
I was not able to complete my paper in given time.
Question 2.
Add a prefix or suffix to make new words and use any one of the root words in your own sentence:
Answer:
1. unusual
2. conscious
Sentence: He was late as usual.
![]()
Oral Work:
Question 1.
What is the difference between finger play, spelling a word mechanically and writing a meaningful word?
Question 2.
Read aloud the paragraph ‘We walked down… be swept away’ using proper intonation.
My English Coursebook 9th Class Pdf Unit 2