Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 English Solutions Chapter 2.7 Yonamine and Bushi Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 6 English Lesson 2.7 Yonamine and Bushi Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 6 English Chapter 2.7 Yonamine and Bushi Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Read the story and write about the following in short.
Question a.
Yonamine Chiru of Okinawa
Answer:
Yonamine Chiru was the most admired girl in Okinawa. She was intelligent, tall, strong, beautiful and so well trained in Karate that no one could beat her. She had put a condition that she would marry the man who would defeat her in a fair fight.
Question b.
Kojo
Answer:
Kojo was one of the first men to ask for Yonamine Chiru’s hand. He was so tall and well-built that his hands were like shovels, and his legs resembled tree trunks. He played foul and broke the rules of the game and thus lost his chance to marry Yonamine Chiru.
![]()
Question c.
Bushi Kiyo
Answer:
Bushi Kiyo had decided to marry a girl who enjoyed wrestling. He was trained under the Karate master Sakugawa. He was such an expert that he was recruited by Shoko, the king of Okinawa, to be his personal guard. He did not want to marry a delicate, fragile girl, but someone who was big and strong. He defeated Yonamine Chiru in a wrestling match and thus won her hand in marriage.
2. Discuss and write 1 – 2 lines about the following.
Question a.
Yonamine’s idea about marriage.
Answer:
Yonamine had her own ideas about marriage. She had declared firmly that she would only marry a man who could beat her in a fair fight.
Question b.
How Bushi defeated Yonamine in the wrestling match?
Answer:
The wrestling match began with Yonamine and Bushi bowing to each other and then began the attack. Both used their best techniques and it looked as if the match was going to be a tie. But, at a crucial moment in the fight, Yonamine paused very briefly. Bushi took advantage of this and brought her down with a swift punch.
![]()
Question c.
Why Bushi told Yonamine not to travel at night?
Answer:
Yonamine decided to visit her parents. She told Bushi that she would leave in the evening and return the next day in time to cook dinner. Bushi told her not to travel during the night because there were bandits roaming about and it was not safe for a woman to go out alone after dark.
Question d.
Yonamine’s fight with Bushi (disguised as a bandit).
Answer:
Bushi’s wife decided to go to visit her parents one evening. Bushi warned her not to go out alone at night because it would be dangerous as there were bandits around. Yonamine, his wife told him not to worry as she could . take care of herself. To teach her a lesson, because he thought she was overconfident, he disguised as a bandit. He ran ahead of her and hid behind a tree. He confronted her as a bandit would. Yonamine with her swift, sharp attacks made the attacker unconscious. Yonamine then dragged the attacker and tied him to a tree and then set off to her parents’ home, as if nothing had happened.
Question e.
The lesson that Bushi learnt.
Answer:
Bushi learnt not to underestimate anybody, especially women.
![]()
3. Divide the story into different sections to show the different events and time periods in it. Give a suitable title to each section.
Examples:

Question 1.
Divide the story into different sections to show the different events and time periods in it. Give a suitable title to each section.
Examples:

Answer:
- Bushi Kiyo accepts the challenge.
- Bushi Kiyo wins Yonamine Chiru’s hand.
- Bushi Kiyo and Yonamine happily married.
- Bushi Kiyo decides to teach his wife a lesson.
- Bushi Kiyo learns a lesson himself.
4. Write a short monologue using one of the following ideas. Write down the monologue and present it in the class.
Question a.
Yonamine’s father worrying about getting her married.
Answer:
I am Yonamine Chiru’s father. My daughter is intelligent, strong, beautiful and well trained in Karate that no one can beat her. This is where the problem lies. She has become of a marriageable age and I would love to see her
married. After all she is my only child and I want her to be happy. She is the heir to all my fortunes and I want to see her married off happily when I am alive.
I know that there are men who wants to marry her but I am unsure if they want my daughter or her fortune. To add to this misery my daughter has put a condition regarding her marriage that she would marry only that man who would defeat her in a fair fight. She is so well trained in Karate that I barely see anyone defeating her. I am really worried for my daughter and I hope she finds her match.
![]()
Question b.
Bushi disguised as a bandit
Answer:
I am Bushi Kiyo, husband of Yonamine. My wife is overconfident and thinks herself to be strong and an expert in Karate. I forbade her to travel at night but she refused to listen. I felt that she must be taught a lesson for her own good. So as Yonamine left for her father’s place, I disguised myself as bandit wearing shabby clothes, smearing dark colour over my hands.
I covered my face with a scarf and hid behind a clump of trees. When I saw Yonamine passing by, I jumped from behind the trees and tried to attack her. But Yonamine was too swift and sharp and attacked me instead. Besides she also tied me up to a tree and left for her father’s house.
![]()
5. Form groups and hold debates on the following topics. Make bulleted lists of points in favour of the topic (pros) and those against it (cons). (3 – 6 points each)
Question a.
Debate on ‘Boys cannot cook or do any housework’.
Answer:
| Pros (for) | Cons (against) |
| 1. Today, boys can cook and do household chores. A vivid example is the programme ‘Master Chef’ in which we see more boys than girls participating and normally the boys end up winning the finals. | 1. That is outside the house. In the house they expect everything to be done either by their mothers or sisters. |
| 2. After the 1960’s men/boys do more work than they used to. | 2. Even today boys feel that cooking and household chores are women’s work. |
| 3. There is less housework to do because of machines that makes work easy and so is quickly done by the ladies in the house. | 3. Boys should remember that it is their house too and should get started and help in the chores and lighten the work. |
Let us conclude this debate by letting everyone present that there is no ‘her job’ or ‘his job’. Today men and women have to share equal responsibilities because in most of the families both parents are bread earners. Sharing responsibilities makes work lighter and quicker and a sense of equality prevails.
![]()
Question b.
Girls cannot do everything that boys do.
Answer:
| Pros | Cons |
| 1. Indian society still thrives on male ego wherein girls are secondary and are not allowed to do what they wants. | 1. Today time has changed. Girls can do whatever they sets their heart to. |
| 2. There is no taboo for boys. Indian society feels that boys are better than girls in every respect. | 2. Today a lot of changes in the laws have given girls the confidence to stand equal to their male counterpart. |
| 3. Girls are not allowed to take part in many games as well as jobs terming them as ‘boy’s games’ or ‘boy’s jobs’. | 3. Today society has become more open to the idea that girls too are capable of playing any game or doing any task. |
Question c.
You should never lose a match.
Answer:
| Pros | Cons |
| 1. Whenever we play, we should play to win. | 1. Winning and losing are two sides of the same coin. |
| 2. Participate only if you know for sure that you will win or don’t participate at all. | 2. One cannot predict the result of the game. You cannot tell how the ball will turn. You can be a hero or a zero. You cannot always win. |
| 3. Winning is a great feeling. You feel you have conquered the world. | 3. This feeling is only for some time. Losing is also a part of the game. We learn from our mistakes and can always do better. |
![]()
Question d.
You should admit your mistakes.
Answer:
| Pros | Cons |
| 1. It is always right and a good habit to admit your mistakes. You feel good. | 1. Many a times when mistakes are admitted it fires back. You are always blamed. |
| 2. Admitting a mistake makes you understand that you have done something wrong and you should not repeat the same. | 2. Admitting a mistake, many-a-times is not taken positively. You are taunted about it every time. |
| 3. Admitting your mistake keeps your conscience clear. | 3. Though one should admit one’s mistake, one does not admit because of the attitude of the people around him. |
6. Visit a library: Read more stories from Japan, China and Korea.
Question 1.
Visit a library: Read more stories from Japan, China and Korea.
Class 6 English Chapter 2.7 Yonamine and Bushi Important Questions and Answers
Answer in one or two sentences.
Question 1.
Why was Yonamine the most admired girl in Okinawa?
Answer:
Yonamine was intelligent, tall, strong, big and beautiful and a matchless Karate player. This made her the most admired girl in Okinawa.
Question 2.
What was Yonamine’s idea about her marriage?
Answer:
Yonamine stated firmly, “I will only marry a man who can beat me in a fair fight!”
![]()
Question 3.
Who was the first young man to ask Yonamine’s hand? Why was he rejected?
Answer:
Kojo, a tall and well-built man, was the first to ask Yonamine’s hand. He was rejected because he played foul with her in a contest of martial arts.
Question 4.
How did Yonamine defeat Kojo?
Answer:
Kojo broke the rules of the games by throwing a punch at Yonamine. She twisted his arm so powerfully that he fell down and he was defeated.
Question 5.
Who was Bushi Kiyo?
Answer:
Bushi Kiyo was an expert Karate player and the personal guard of Shoka, the King of Okinawa.
Question 6.
Describe Kiyo’s features.
Answer:
Kiyo was tall and slim, with dark piercing eyes and appeared fearless.
![]()
Question 7.
How do you know that Yonamine was a good housewife?
Answer:
Yonamine was kind and loving. She cooked and cleaned and kept the house spick and span.
Question 8.
What opinion did Bushi have of Yonamine?
Answer:
Bushi opined that Yonamine was overconfident of her strength and skill.
Question 9.
Why did Bushi disguise himself as a bandit?
Answer:
Bushi disguised himself as a bandit to scare Yonamine who dared to travel in the dark. Also he wanted to teach her a lesson for her own good.
![]()
Question 10.
What lesson did B ushi learn at the end of the day?
Answer:
Bushi learnt a lesson ‘Never to underestimate anybody, especially a woman.’
Reading Skills, Vocabulary and Grammar
Read the extract and do the activities.
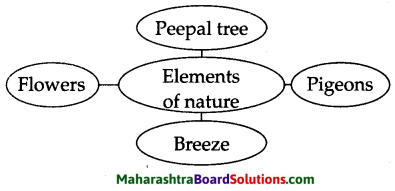
Question 1.
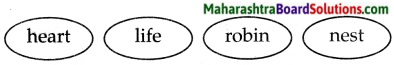
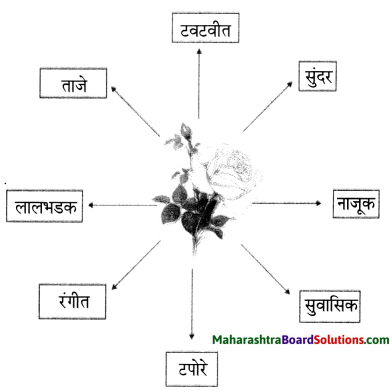
Complete the web diagram.
Answer:
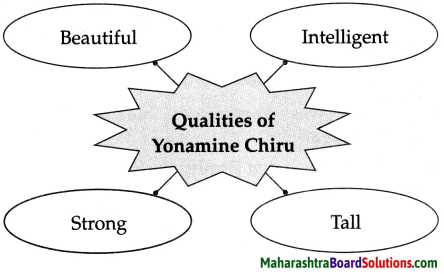
Question 2.
Complete the following sentences.
Question a.
Many wrestlers were eager ………….. .
Answer:
To win her in a contest of martial arts.
![]()
Question b.
Yonamine’s father began to worry …………… .
Answer:
When it was time to get her married.
Question 3.
What was Yonamine’s condition about marriage?
Answer:
Yonamine laid down a condition that she would only marry a man who could beat her in a fair fight.
Question 4.
She was intelligent, tall, strong and beautiful. (Pick out the adjectives in the sentence)
Answer:
Adjectives – intelligent, tall, strong, beautiful
Question 5.a.
Yonamine was the most admired girl. (Change into present tense)
Answer:
Yonamine is the most admired girl.
![]()
Question b.
She was a beautiful girl with a fortune! (Identify the kind of sentence)
Answer:
Exclamatory sentence
Question c.
She was a beautiful girl. (Change into negative)
Answer:
She was not an ugly girl.
Personal Response
Question 1.
Have you ever won a contest? How does it feel?
Answer:
Yes, I have won a couple of contests in singing and drawing. Winning a contest makes me feel very confident and a feeling of pride too. I put in my best and try not to be overconfident.
![]()
Language Study
Do as directed.
Question 1.
He loved his daughter. (Add a question tag)
Answer:
He loved his daughter, didn’t he?
Question 2.
She crossed the clump of trees. (Change into past perfect)
Answer:
She had crossed the clump of trees.
Question 3.
Add prefixes to the following so as to get their opposites:
- important
- wanted
- customary
- respect
- defeated
- cooked
Answer:
- unimportant
- unwanted
- uncustomary
- disrespect
- undefeated
- uncooked
![]()
Question 4.
Word building: Write the noun form of the following:
- intelligent
- strong
- beautiful
- important
- rich
- splendid
Answer:
- intelligence
- strength
- beauty
- importance
- richness
- splendour
Question 5.
He loved his daughter. (Change into Negative sentence)
Answer:
He did not hate his daughter.
Question 6.
She cooked and cleaned and kept the house spick and span. (Pick out a phrase from the sentence which means neat, clean and tidy)
Answer:
spick and span
Question 7.
Yonamine’s father was a very happy man. (Separate subject and predicate)
Answer:
Subject – Yonamine’s father
Predicate – was a very happy man.
![]()
Question 8.
She held her attacker by the hand. (Pick out the verb and state its kind)
Answer:
held – transitive verb
Question 9.
Bushi disguised himself as a bandit. (Frame a Wh-question so as to get the underlined word as the answer)
Answer:
What did Bushi disguise himself as?
Question 10.
But he played foul! (Kind of sentence)
Answer:
Exclamatory sentence
Do you know?
1. Mannerisms in Japan, China and Korea Bowing is one aspect of each culture all over the world.
2. In Japan and Korea and a slight bow when greeting each other and a deeper bow in more formal situations is still considered appropriate. However in China the handshake has actually become a common greeting with only a slight head nod rather than the traditional bow.
Yonamine and Bushi Summary in English
The story revolves around a girl named Yonamine, who is intelligent, tall, strong, beautiful and admired by everyone. She is very good at Karate too. She is the only heir to her rich father’s property. Her father wants to see her happily married, but she has got certain conditions/ ideas about her marriage. She marries Bushi Kiyo after he passes the contest. She performs her duties as a wife and both are happy.
Once she decides to visit her parents at night. Her husband warns her against going out at night saying that it is not safe to travel at night, especially for ladies. Yonamine tells her husband not to worry and sets out to meet her parents. Bushi feels that his wife was overconfident and that she should be taught a lesson. He disguises as a bandit and attacks Yonamine. Yonamine with her swift and sharp actions hits her attacker, rendering him unconscious. She ties him to a tree and sets off to her parents’ home.
The next day she leaves her parents’ home to reach her home in time to cook her husband’s evening meal. Bushi who had been untied by his wife, reaches home dull and tired. Bushi returns the white sash his wife had used to tie him. When Yonamine realises that it was her husband she had tied up, she has a hearty laugh. Bushi learns a lesson not to underestimate anybody, especially a woman.
Introduction:
It is a true story that took place in Japan wherein Yonamine Chiru, a beautiful intelligent girl marries Bushi Kiyo after he defeats her in a wrestling match which was the condition of her marriage. They live a happy married life and an incident which took place makes Bushi Kiyo realise that he should not underestimate anybody, especially a woman.
Glossary:
- karate (n) – an Okinawa martial art
- inherit (v) – to receive money, property or title as heir at the death of the previous holder
- fortune (n) – a large amount of money or assets
- martial (adj) – relating to fighting or war
- foul (adj) – wicked or immoral
- customary (adj) – according to custom
- opponent (n) – a player of the opposite team
- recruited (v) – a person selected for service
- challenge (n) – dare
- fragile (adj) – thin
- earnest (adj) – reality, seriousness
- crucial (adj) – of great importance
- bandit (n) – one who robs others
- depart (v) – to leave
- fork (n) – an interjection in a road where one road is spilt into two
- captivity (n) – being imprisoned or confined
6th Std English Balbharati Textbook Solutions
- The Clothesline Class 6 Question Answers
- The Worth of a Fabric Class 6 Question Answers
- A Wall Magazine for your Class! Class 6 Question Answers
- Anak Krakatoa Class 6 Question Answers
- The Silver House Class 6 Question Answers
- Ad‘wise’ Customers Class 6 Question Answers
- Yonamine and Bushi Class 6 Question Answers