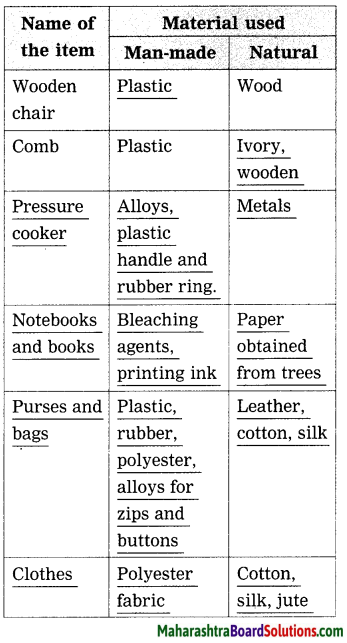
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 Reflection of Light Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 Reflection of Light
Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Reflection of Light Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the blanks:
Question i.
The perpendicular to the mirror at the point of incidence is called …………. .
Answer:
The perpendicular to the mirror at the point of incidence is called the normal.
Question ii.
The reflection of light from a wooden surface is ……….. reflection.
Answer:
The reflection of light from a wooden surface is irregular reflection.
![]()
Question iii.
The working of a kaleidoscope is based on the properties of …………… .
Answer:
The working of a kaleidoscope is based on the properties of reflection of light.
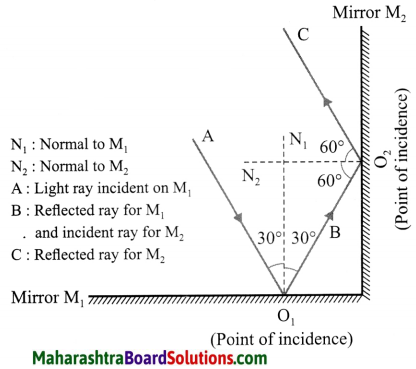
2. Draw a figure describing the following: The reflecting surfaces of two mirrors make an angle of 90° with each other. If a ray incident on one mirror has an angle of incidence of 30°, i draw the ray reflected from the second mirror. What will be its angle of reflection?
Question a.
Draw a figure describing the following: The reflecting surfaces of two mirrors make an angle of 90° with each other. If a ray incident on one mirror has an angle of incidence of 30°, draw the ray reflected from the second mirror. What will be its angle of reflection?
Answer:
For the ray C, the angle of reflection = 60°.
3. How will you explain the statement ‘We cannot see the objects in a dark room’?
Question a.
How will you explain the statement ‘We cannot see the objects in a dark room’?
Answer:
In a room that is completely dark, no light falls on objects. Hence, no light enters our eyes. Hence, there is no sensation of vision, i.e., we cannot see the objects.
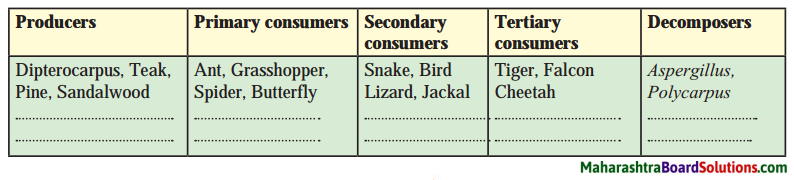
4. Explain the difference between regular and irregular reflection of light.
Question a.
Explain the difference between regular and irregular reflection of light.
Answer:
For regular reflection of light, the angles of incidence as well as the angles of reflection are the same for all parallel rays of light incident on the plane and smooth surface. Hence, the reflected rays are also parallel to one another.
For irregular reflection of light, the angles of incidence for parallel rays of light incident on the rough surface are not equal, and hence the angles of reflection are also not equal. Here, the reflected rays are not parallel to one another and spread over a large surface.
![]()
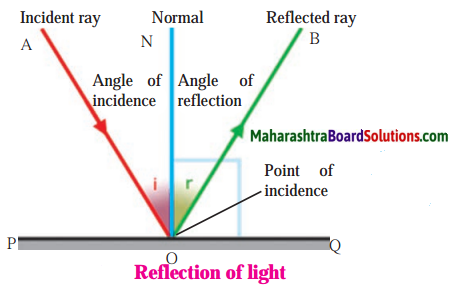
5. Draw a figure showing the following:
(a) Incident ray, (b) Normal, (c) Angle of incidence, (d) Angle of reflection, (e) Point of incidence, (f) Reflected ray.
Question a.
Draw a figure showing the following:
(a) Incident ray
(b) Normal
(c) Angle of incidence
(d) Angle of reflection
(e) Point of incidence
(f) Reflected ray.
Answer:
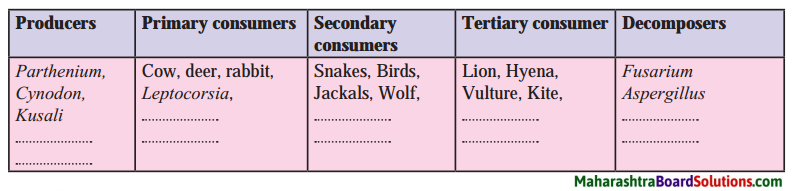
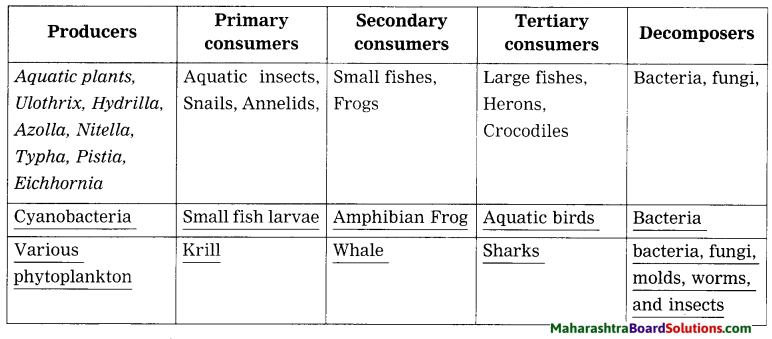
6. Study the following incident.
Swara and Yash were looking in a water-filled vessel. They could see their images clearly in the still water. At that instant, Yash threw a stone in the water. Now their images were blurred. Swara could not understand the reason for the blurring of the images.
Explain the reason for blurring of the images to Swara by answering the following questions:
Question i.
Is there a relation between the reflection of light and the blurring of the images?
Answer:
Yes.
![]()
Question ii.
Which types of reflection of light can you notice from this?
Answer:
Regular reflection of light when light is incident on the still water and irregular reflection of light when light is incident on the water as ripples are produced on its surface when a stone is thrown in the water.
Still water behaves as a plane and smooth surface while oscillating water behaves as a rough surface.
Question iii.
Are the laws of reflection followed in these types of reflection?
Answer:
Yes.
7. Solve the following examples.
Question a.
If the angle between the plane mirror and the incident ray is 40°, what are the angles of incidence and reflection?
Solution:
The angle between the plane mirror and the incident ray is 40°. Therefore, the angle of incidence (i) = the angle made by the incident ray with the normal to the plane mirror = 90° – 40° = 50°. The angle of reflection, r – i – 50°.
![]()
Question b.
If the angle between the mirror and reflected ray is 23°, what is the angle of incidence of the incident ray?
Solution:
The angle between the mirror and the reflected ray is 23°. Therefore, the angle of reflection (r) = the angle made by the reflected ray with the normal to the plane mirror = 90° – 23° = 67°.
∴ The angle of incidence, i = r = 67°.
Project:
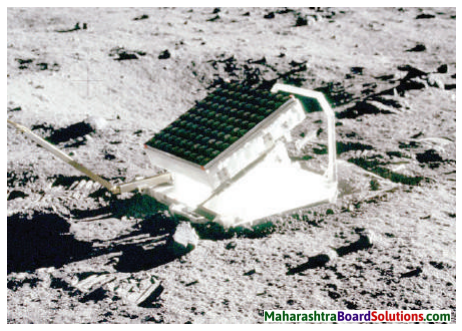
Question a.
Apollo astronauts who stepped on the moon have kept some large mirrors there. Collect information about how the distance to the moon is measured using these.
Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Reflection of Light Important Questions and Answers
Rewrite the following statements by selecting the correct option:
Question 1.
If the angle made by the incident ray with the surface of a plane mirror is 30°, the angle of reflection must be …….. .
(a) 30°
(b) 90°
(c) 60°
(d) 15°
Answer:
If the angle made by the incident ray with the surface of a plane mirror is 30°, the angle of reflection must be 60°.
Question 2.
If the angle of incidence is 40°, the angle made by the reflected ray with the surface of the plane mirror must be ……. .
(a) 40°
(b) 50°
(c) 20°
(d) 80°
Answer:
If the angle of incidence is 40°, the angle made by the reflected ray with the surface of the plane mirror must be 50°.
![]()
Question 3.
If the angle of incidence is 20°, the angle made by the reflected ray with the normal to the surface must be ……… .
(a) 20°
(b) 70°
(c) 10°
(d) 40°
Answer:
If the angle of incidence is 20°, the angle made by the reflected ray with the normal to the surface must be 20°.
Question 4.
In a kaleidoscope, the mirrors are inclined to each other at ……. .
(a) 60°
(b) 30°
(c) 45°
(d) 90°
Answer:
In a kaleidoscope, the mirrors are inclined to each other at 60°.
Question 5.
In a periscope, the mirrors are ………….. .
(a) parallel to each other
(b) at right angles to each other
(c) inclined at 45° to each other
(d) inclined at 60° to each other
Answer:
In a periscope, the mirrors are parallel to each other.
![]()
Find the odd one out and give the reason:
Question 1.
Plane mirror, Plywood, Wood, Rough tile.
Answer:
Plane mirror. In this case, regular reflection of light takes place. In other cases, reflection of light is irregular.
State whether the following statements are True or False. (If a statement is false, correct it and rewrite it.)
Question 1.
The sense of vision is the most important among our five senses.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
In a periscope, the angle between the incident ray and the normal to the mirror is 30°.
Answer:
False. (In a periscope, the angle between the incident ray and the normal to the mirror is 45°.)
Answer the following questions in one sentence each:
Question 1.
What is an incident ray?
OR
Define incident ray.
Answer:
A ray of light falling on a surface is called an incident ray.
Question 2.
What is the point of incidence?
OR
Define point of incidence.
Answer:
The point at which the incident ray strikes the surface is called the point of incidence.
[Note: It is also the point of reflection.]
![]()
Question 3.
What is the normal?
OR
Define normal.
Answer:
The perpendicular to a surface at the point of incidence is called the normal.
Question 4.
What is the reflected ray?
OR
Define reflected ray.
Answer:
The ray of light that leaves the surface at the point of reflection (the same as the point of incidence) is called the reflected ray.
Question 5.
What is the angle of incidence?
OR
Define angle of incidence.
Answer:
The angle between the incident ray and the normal is called the angle of incidence.
Question 6.
What is the angle of reflection?
OR
Define angle of reflection.
Answer:
The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is called the angle of reflection.
![]()
Try this:
Switch off the light in your room at night for some time and then turn it on again.
Question 1.
Could you see the objects in the room clearly when the light was switched off?
Ans.
No.
Question 2.
What did you feel when it was turned on again?
Answer:
We could see the objects clearly. From the above activity you can notice that there is some connection between the sense of vision and light. When we switch off the light at night, the objects in the room cannot be seen and they can be seen as before when the light is switched on again. Thus, we can see objects when the light coming from these objects enters our eyes.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What is reflection of light?
Answer:
When light rays fall on an object, their direction changes and they turn back. This is called the reflection of light.
Try this:
Material:
Torch light, mirror, a stand for hanging the mirror, black paper, comb, white paper, drawing board.
Activity :
1. Fit a white paper tightly over a table or drawing board.
2. Leaving out some portion in the middle of the comb, cover the rest with black paper so that light can only pass through the open central portion.
3. Hold the comb perpendicular to the white paper and throw torch light on its central portion.
4. Adjust the comb and torch so as to get light rays on the white paper. Now keep a mirror in the path of this ray of light as shown in the figure.
5. What do you observe?

Answer:
Light rays which fall on the mirror get reflected and travel in a different direction.
![]()
Question 2.
State the laws of reflection of light.
Answer:
- The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal lie in the same plane.
- The incident ray and the reflected ray are on the opposite sides of the normal.
Try this:
Verification of the laws of reflection of light.
Equipment: Mirror, drawing board, pins, white paper, protractor, scale, pencil.
Activity:
- Fit a white paper on the drawing board tightly as possible.
- On the paper draw a line PQ indicating the position of the mirror.
- Draw a perpendicular ON to PQ at point O.
- Draw a ray AO making an angle of 30° with ON.
- Fix two pins S and R along AO.
- Fix the mirror to a stand and place it along PQ perpendicular to the drawing board.
- Fix pins at T and U along the line joining the bottom of the reflected images of the pins at S and R.
- Remove the mirror and join the points T and U and extend it up to O.
- Measure ZTON.
- Repeat steps 4 to 9 for angle of incidence equal to 45° and 60° and write down the angles in the following table.
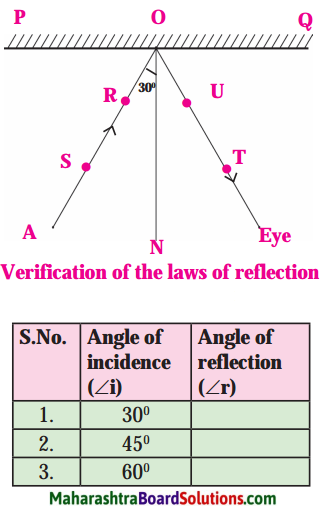
What relation do you find between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection? If you have done the experiment carefully, you will find that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection in all three cases. This verifies the laws of reflection.
Question a.
What will happen when a light ray is incident perpendicular to the mirror?
Answer:
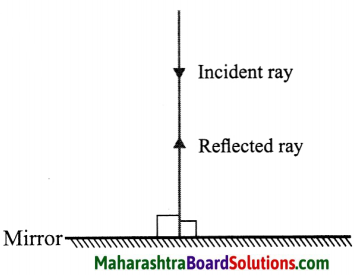
Here,
r = i = 90°.
Hence the light ray, on reflection, will retrace the path.
![]()
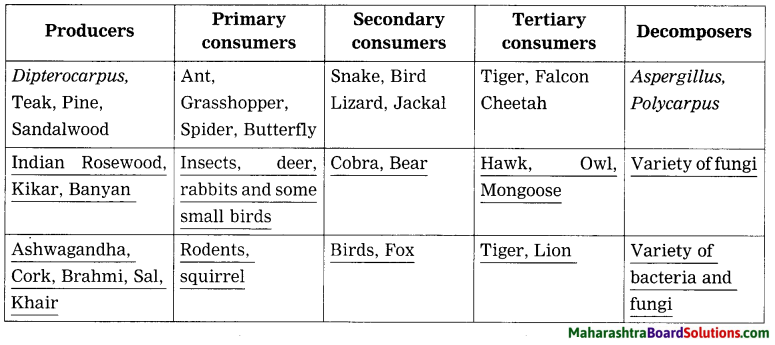
Question 3.
Figures (a) and (b) show three parallel rays, shown in grey, incident on smooth and rough surfaces. The reflected rays drawn using laws of reflection are shown in red.
1. Rays reflected from which surface are parallel to one another?
2. What conclusion can you draw from the figure?
Answer:
1. Rays reflected from the smooth surface are parallel to one another.
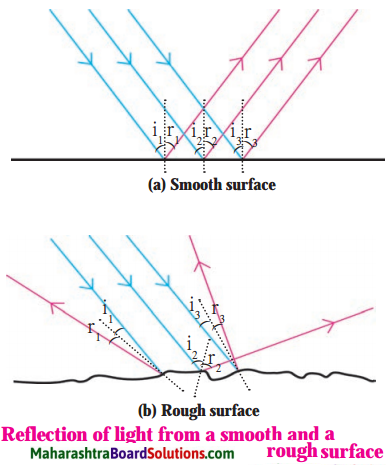
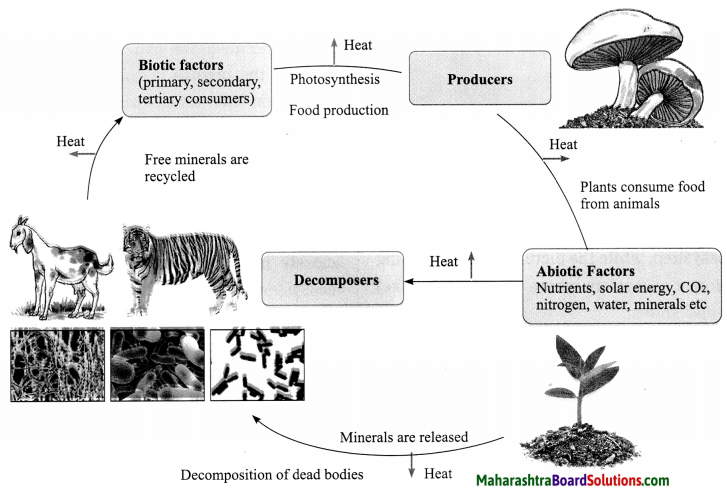
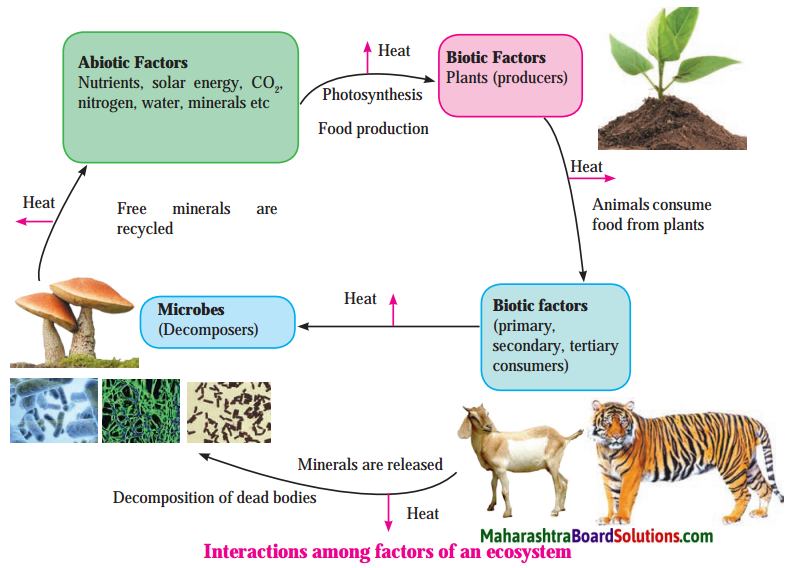
2.When the reflecting surface is plane and smooth, the angles of incidence (i) as well as of reflection (r) are the same for all parallel rays incident on the surface. If i1, i2, i3, … are the angles of incidence for incident parallel rays, and r1, r2, r3, …, are the corresponding angles of reflection, then, i1 = i2 = i3 = ……. = r1 = r2 = r3 = ….. This is called regular reflection. Here, the reflected rays are parallel to one another. If the reflecting surface is rough and parallel rays are incident on it, then the angles of incidence are not equal and hence the angles of reflection are also not equal. Here, i1 ≠ i2 ≠ i3 … and r1 ≠ r2 ≠ r3 …, but r1 = i1, r2 = i2, r3 = i3 … as laws of reflection are obeyed. This is called irregular reflection. [Fig.(b)]. Here, the reflected rays are not parallel to one another and spread over a large surface.
Question 4.
What is regular reflection of light?
Answer:
The reflection of light from a plane and smooth surface is called regular reflection of light.
Question 5.
What is irregular reflection of light?
Answer:
The reflection of light from a rough surface is called irregular reflection of light.
![]()
Always remember:
- Laws of reflection are followed in both and regular and irregular reflection.
- The reflection of light in irregular reflection has not been obtained because the laws of reflection are not followed. They are obtained because the surface is rough (irregular).
- In irregular reflection, the angles of incidence at different points are different. But at any one point, the angles of incidence and reflection are equal, i.e. i1 = r1, i2 = r2 …..
Can you recall?
Reflection of reflected light :
Question 1.
How do you see if the barber m a saloon has cut the hair on your neck properly or not?
Answer:
In a saloon, there are mirrors in your front and at back. The image of the back of your head is formed in the mirror at the back. The image of this image is formed in the mirror in front of you. Thus you can see how the hair at the backside of your head is cut.
Question 2.
What type of image do we see in a mirror? What happens to the left and right sides?
Answer:
The image in a plane mirror is upright (erect) and of the same size as the object, but the left and right sides are interchanged. Our right hand appears to be the left hand in the image and the left hand appears to be the right hand in the image. (This is called lateral inversion.)
Question 3.
How do we see the image of the moon in water?
Answer:
The moon is not self luminous. The sunlight falling on the surface of the moon is reflected. This reflected light is again reflected by water to give us the image of the moon.
![]()
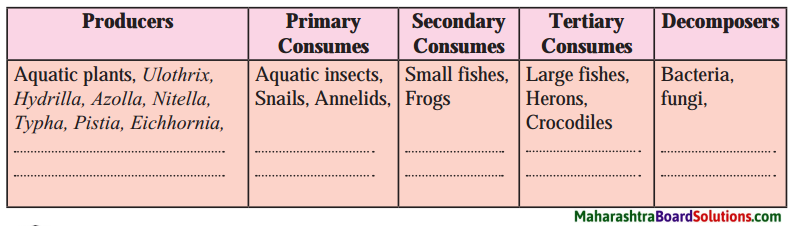
Try this:
Kaleidoscope:
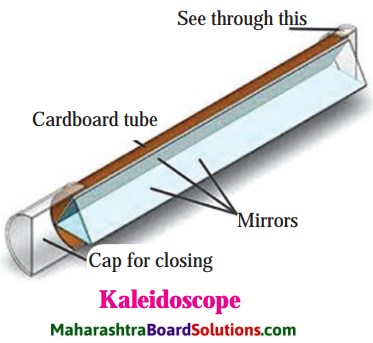
Activity:
- Take three rectangular mirrors of the same size.
- Using sticking tape, stick the mirrors together making a triangle with the reflecting surface facing inwards (see Fig.).
- Take a white paper of triangular shape and fix it with a tape at one end of the mirrors closing that end.
- Insert 4 – 5 coloured glass pieces in the hollow of the mirrors.
- Close the other end also with a paper and make a hole in it.
- Look through the hole towards light. You will see innumerable images of the glass pieces. These are formed due to reflections by the three mirrors.
You can see different designs in the kaleidoscope. The speciality of a kaleidoscope is that the designs do not easily repeat themselves. Every time the design is different. People making wall papers which are used to decorate walls and cloth designers use a kaleidoscope for making new designs.
Periscope:
Activity:
- Take a cardboard box. Make slits in the top and bottom sides of the box and place two mirrors so that they make an angle of 45° with the sides of the box and are parallel to each other. Fix them with a sticking tape.
- Make two windows of 1 inch each near the two mirrors. Now see through the bottom window.
- Make note of what you see.
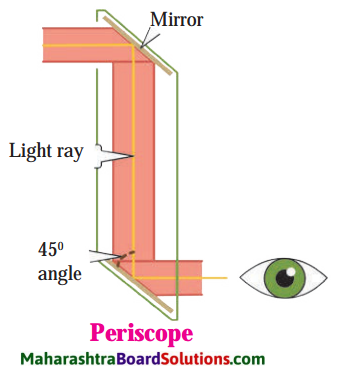
From the bottom window, one can see what is in front of the top window. This device is called a periscope. This is used in submarines to see objects above the surface of water. It is also used to observe and keep a watch on the objects or persons on the ground from an underground bunker. The kaleidoscope and periscope both use the properties of reflection of light.
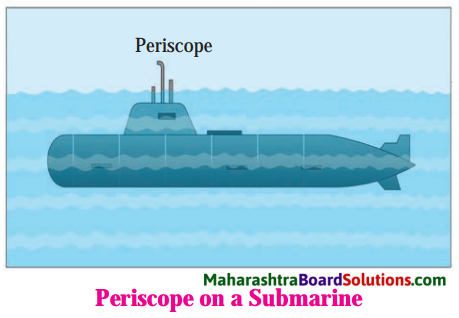
[Note: In a periscope, the angle of incidence is 45° and the two plane mirrors are parallel to each other. Hence, the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray.]
![]()
Example questions for practice:
Question 1.
If the angle between the plane mirror and the incident ray is 20°, what is the angle between the reflected ray
and the plane mirror?
Answer:
20°.
Question 2.
See Fig. In terms of O, what are the angles (i) AON (ii) BON (iii) AOB (iv) BOQ?
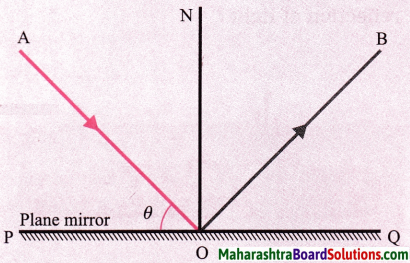
Answer:
(i) 90° – θ (ii) 90° – θ (iii) 180° – 2θ