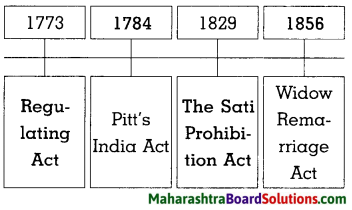
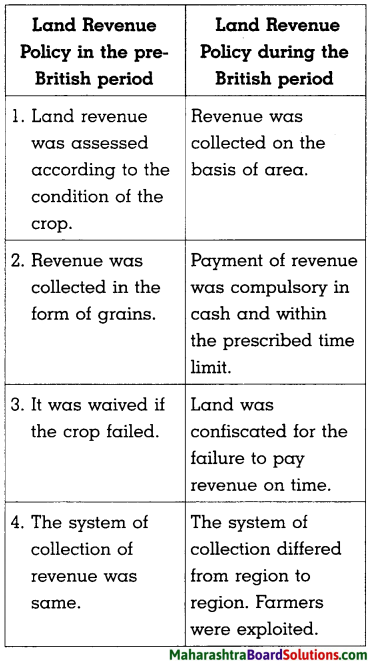
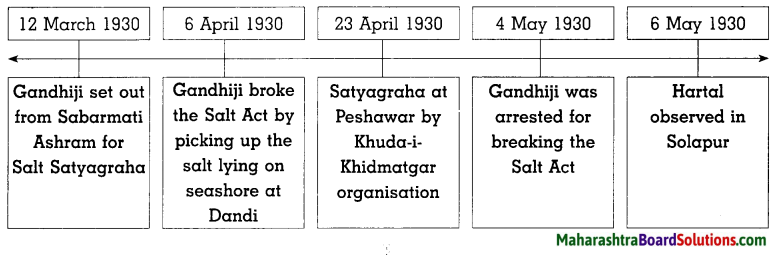
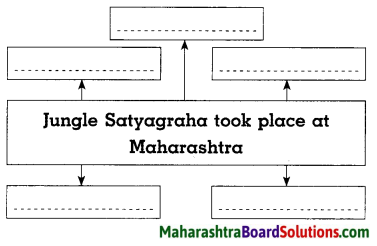
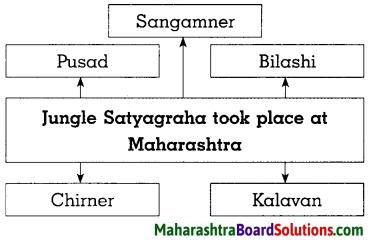
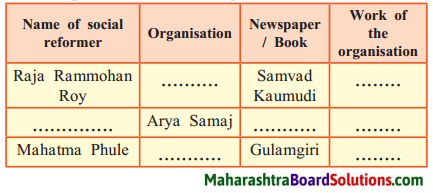
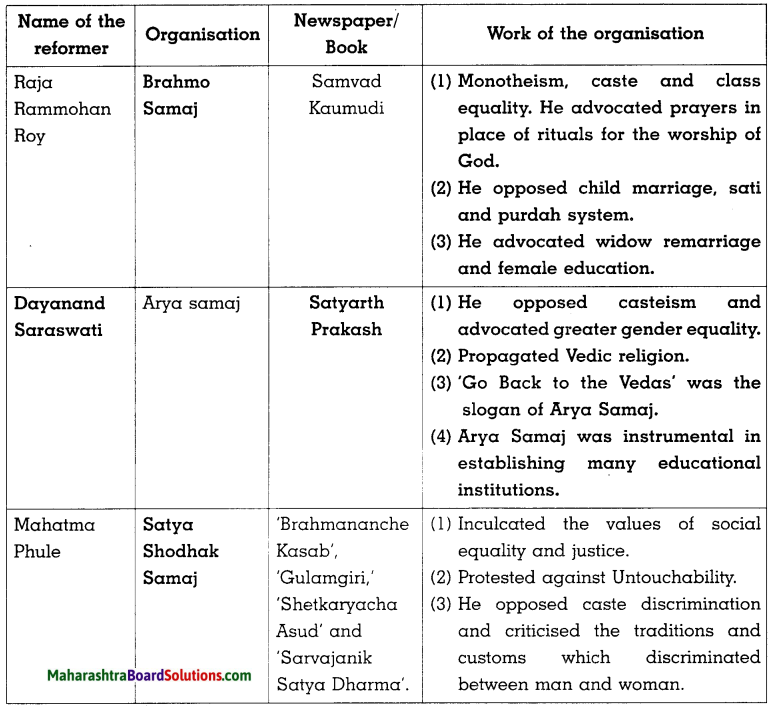
Sulabhbharati 8th Class Marathi Textbook Solutions Answers Digest
Maharashtra State Board 8th Std Marathi Sulabhbharati Textbook Solutions
Marathi Sulabhbharati Class 8 Solutions
- Chapter 1 आम्ही चालवू हा पुढे वारसा (गीत)
- Chapter 2 मी चित्रकार कसा झालो!
- Chapter 3 प्रभात (कविता)
- Chapter 4 आपण सारे एक
- Chapter 5 घाटात घाट वरंधाघाट
- Chapter 6 आभाळाची अम्ही लेकरे (कविता)
- Chapter 7 नातवंडांस पत्र
- Chapter 8 गीर्यारोहणाचा अनुभव
- Chapter 9 झुळूक (कविता)
- Chapter 10 आम्ही हवे आहोत का?
- Chapter 11 जीवन गाणे (कविता)
- Chapter 12 शब्दकोश (स्थूलवाचन)
- Chapter 13 संतवाणी