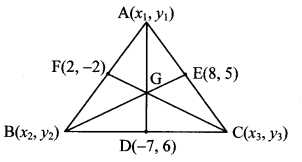
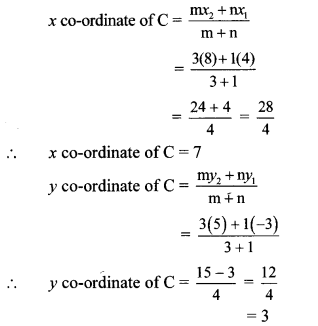
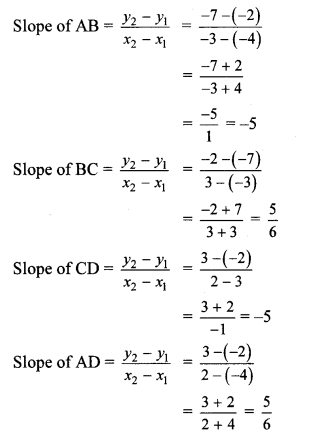
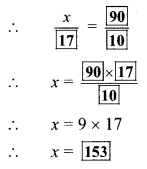
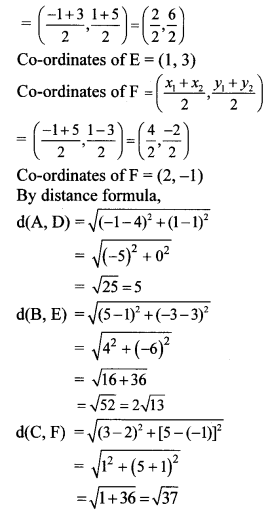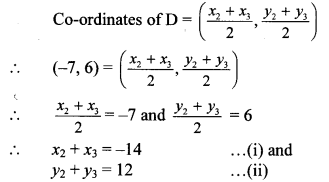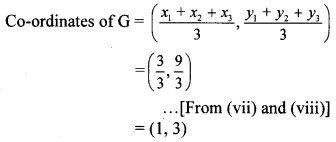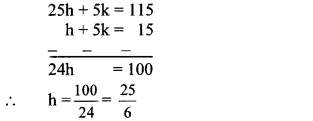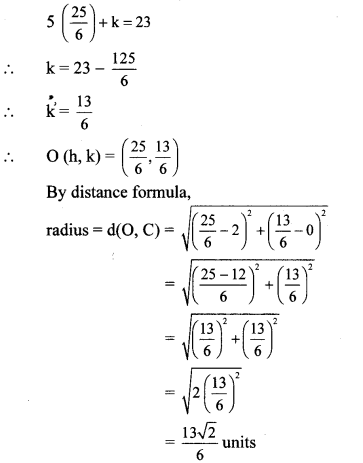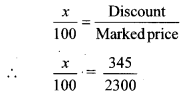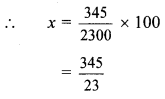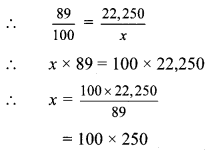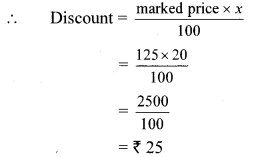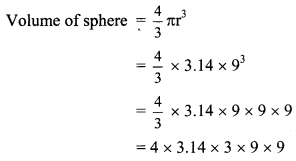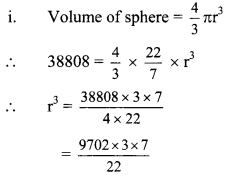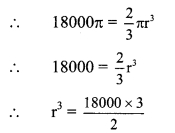Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Geography Solutions Chapter 3 Exogenetic Movements Part 1 Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Geography Solutions Chapter 3 Exogenetic Movements Part 1
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Exogenetic Movements Part 1 Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Answer in brief.
(a) What is mechanical weathering?
Answer:
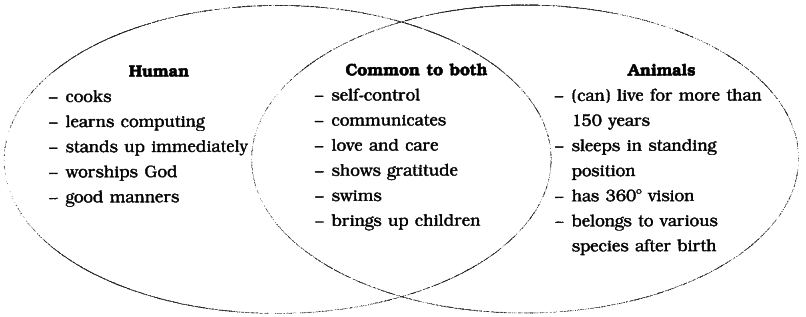
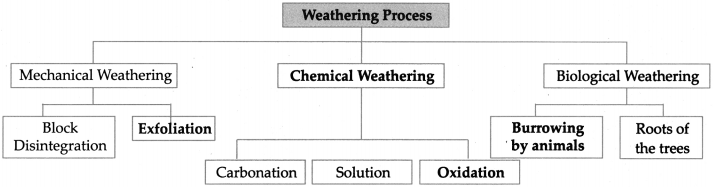
- The disintegration of rocks without any change in their chemical composition is called mechanical weathering.
- The minerals in the rocks expand because of heat and contract when the temperature decreases. Due to such continuous contracting and expansion, tension develops in the rock particles.
- Each mineral reacts differently to the temperature; some minerals expand more, while others do not expand as much. Consequently, the tension formed in the rocks also increases and decreases. As a result, cracks develop in the rocks and they break.

- In areas where the temperatures drop below 0°C for quite some time, the water accumulated in the cracks and crevices in the rocks freezes. Its volume increases which leads to tension in the rocks and they shatter.
- When the alkaline water of the sea fills in the cracks of the rocks, the soluble minerals in the rock get dissolved leading to the formation of small holes in the rocks.
- Because of the heat, this water turns into water vapour and only crystals of alkaline materials remain in the rocks. Crystals occupy more space which causes tension in the rock.
- Sometimes the outer layers of the rocks exert pressure on the inner or lower layers. When this pressure ceases to exist, the lower or inner layers get freed from the pressure. This also leads to weathering.
- In areas of heavy rainfall soaking of rock water also causes weathering of some rocks like sandstone and conglomerate. When water penetrates such rocks, the particles get loose and separate from the main rock.
(b) What are the main types of chemical weathering?
Answer:
The process of decomposition of rocks due to changes in their chemical composition is called chemical weathering.
Its main types are:
(i) Carbonation
- When the rain water mixes with the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere it leads to the formation of dilute carbonic acid.
- Many rocks like limestone get easily dissolved in such acids.
(ii) Solution
- Some minerals in the rock get dissolved in water.
- Because of this solution, alkalis in the rock dissolve and make them brittle.
(iii) Oxidation
- This process occurs in rocks which have iron present in them. The iron in the rock comes in contact with water and a chemical reaction takes place between iron and oxygen.
- Hence, a reddish coloured layer forms on the rocks. This is called rust.
- It occurs in rocks in areas with high rainfall.
(c) How does biological weathering occur?
Answer:
- It is the process by which rocks are broken into small fragments and fine particles due to the action of plants, animals and human beings.
- The roots of the plants enter the points and ! cracks of the rocks in search of moisture.
- As the roots grow bigger, they create tension in the rocks and start breaking them.
- Animals such as mice, rabbits and rats dig I holes, anthills etc. and weaken the rock, which makes them loose and break into pieces.
- Besides these, algae, moss1, lichen2, other flora grow in the rocks. They also help in weathering.
- Thus, the weathering caused by living organisms is called biological weathering,

(d) Distinguish between weathering and mass wasting.
Answer:
| Weathering | Mass Wasting |
| (i) Breaking or weakening of rocks is called as weathering. | (i) When weathered rock material moves down the slopes due to gravity and accumulate near the foothills or gentle slopes, it is mass wasting. |
| (ii) Weathering is of three types – Mechanical, Chemical and Biological. | (ii) Mass wasting is of two types – Rapid and Slow. |
2. Write whether the statements are true or false. Correct the incorrect ones.
(a) Climate affects earthquakes.
Answer:
False – Internal movements affect (leads to) earthquakes.
(b) Mechanical weathering is less effective in humid climates.
Answer:
True
(c) Mechanical weathering happens on a large scale in dry climates.
Answer:
True
(d) The breaking down of rocks into smaller particles is called weathering.
Answer:
True
(e) Lateritic rocks are formed through exfoliation.
Answer:
False – Lateritic rocks are formed due to oxidation.
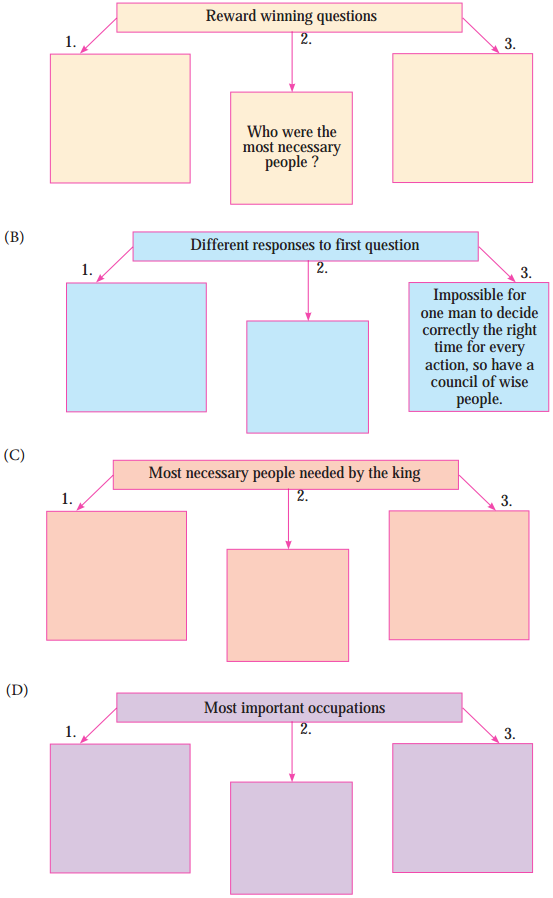
3. Complete the flowchart below.
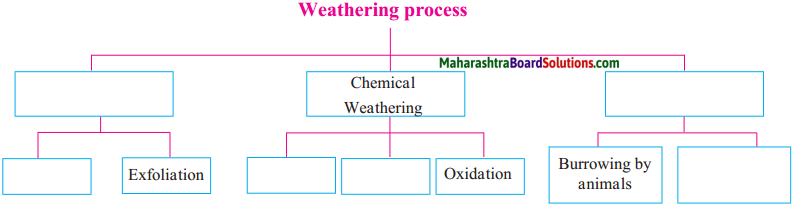
Answer:
4. Identify the type of weathering from the given description.
(a) Some animals live inside the grounds by making burrows.
(b) The rock rusts.
(c) Water which has accumulated in the crevices of the rocks freezes. Consequently, the rock breaks.
(d) The pipes supplying water in colder regions break.
(e) Sand formation occurs in deserts
Answer:
(a) Biological weathering
(b) Chemical weathering
(c) Mechanical weathering
(d) Mechanical weathering
(e) Mechanical weathering
![]()
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Exogenetic Movements Part 1 Intext Questions and Answers
Can You Tell?
(1) See the given pictures. Observe the physical appearance of the rocks in each picture. You can see that rocks are broken, fractured and have holes in them. In a picture you can also see that the statue has been deformed. Why are the rocks in such a condition? Think about them and briefly tell the reasons you can think of. Discuss the reasons. Check with the teachers if your reasons are relevant.
Answer:
- At some places the day temperatures are very high and the night temperatures are very low. In the given pictures the rocks may have broken due to temperature variation during day time and night time.
- In coastal areas when the sea waves hit the rocks, the rocks fracture and break down.
- Due to the roots of trees, and activities of burrowing animals like ant, rats etc. in the soft rocks, the rocks break down.
- The statues might be deformed due to heat and humidity.
Lets Recall
Question 1.
Have you seen the process of biological weathering3 around you?
Answer:
I have seen process of biological weathering3 around me. Many plants and trees have grown in an old dilapidated building which is located near my house. The roots of the trees have broken the walls and slabs of the building at many places.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Exogenetic Movements Part 1 Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the statements choosing the correct option from the bracket:
Question 1.
…………………… is formed due to chemical precipitation between water and alkalis.
(a) Limestone
(b) Sandstone
(c) Coal
(d) Iron
Answer:
(a) Limestone
Question 2.
…………………… process occurs in rocks which have iron present in them.
(a) Shattering
(b) Oxidation
(c) Carbonation
(d) Granular
Answer:
(b) Oxidation
![]()
Question 3.
Sometimes the weathered materials do not move downward but sink ‘in situ’. This is called ………………….. .
(a) carbonation
(b) exfoliation
(c) precipitation
(d) slumping
Answer:
(d) slumping
Question 4.
periglacial regions along the slopes, small layers of soil accumulate because of the movement of soil. This is called ………………….. .
(a) soil erosion
(b) solifluction
(c) shattering
(d) block disintegration
Answer:
(b) solifluction
Question 5.
Biological weathering occurs because of ………………….. .
(a) high temperatures
(b) frost
(c) crystal growth
(d) living organisms
Answer:
(d) living organisms
Question 6.
come minerals in the rock get dissolved in the water and undergo chemical weathering. This process is called ………………….. .
(a) solution
(b) carbonation
(c) exfoliation
(d) precipitation
Answer:
(a) solution
Question 7.
When dilute carbonic acids reacts with the minerals in the rocks the process is called as ………………….. .
(a) carbonation
(b) exfoliation
(c) precipitation
(d) slumping
Answer:
(a) carbonation
![]()
Question 8.
When the outer layers of the rock fall apart from the main rock due to difference in temperatures, the process is called ………………….. .
(a) shattering
(b) oxidation
(c) exfoliation
(d) carbonation
Answer:
(c) exfoliation
Question 9.
…………………… is a universal solvent1.
(a) Soil
(b) Water
(c) Carbon
(d) Oxygen
Answer:
(b) Water
Question 10.
Alkalis in the rock dissolve because of the solution and make them ………………….. .
(a) even
(b) sturdy
(c) brittle
(d) crusty
Answer:
(c) brittle
Match the Column:
I.
| (I) Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Mechanical weathering (2) Chemical weathering (3) Biological weathering |
(a) burrowing (b) frost (c) carbonation (d) erosion |
Answer:
(1-b),
(2- c),
(3 – a)
![]()
II.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Oxidation (2) Slumping (3) Solifluction |
(a) Mass movement occurring slowly (b) Carbon dioxide gets mixed with air (c) Chemical reaction between iron and oxygen (d) Weathered material which sink in situ |
Answer:
(1 – c),
(2 – d),
(3 – a)
Answer in one sentence each;
Question 1.
What are the Exogenetic processes?
Answer:
Exogenetic processes are external processes 1 that occur on or above the earth’s surface, E.g. weathering, erosion, transportation, deposition etc.
Question 2.
Explain the Process of weathering
Answer:
Breaking or weakening of rocks is called as weathering.
Question 3.
What is Mechanical Weathering?
Answer:
The disintegration of rocks without any change in their chemical composition is called mechanical weathering.
Question 4.
What is Chemical Weathering (Salt Weathering)?
Answer:
The process of decomposition of rocks due to changes in their chemical composition is called chemical weathering.
Question 5.
What do you mean by Biological Weathering?
Answer:
The weathering process caused by human beings, animals and plants is called biological weathering.
![]()
Question 6.
What is Slumping?
Answer:
Sometimes the weathered materials do not move downward but sink ‘in situ’ (where they ! are). This is called slumping. ;
Question 7.
What is Solifluction?
Answer:
In periglacial regions along the slopes, small layers of soil accumulate because of the movement of soil. This is called solifluction.
Question 8.
Explain Granular Weathering.
Answer:
When water penetrates in rocks like sandstones and conglomerates1, the particles get loose and separate from the main rock. This is called granular weathering.
Question 9.
What is Block Disintegration?
Answer:
When water accumulates in wide points and big blocks of rocks separate from each other, this is called block disintegration.
Question 10.
What is Exfoliation?
Answer:
When the outer layer of the racks fall apart from the main rock due to temperature, the process is called exfoliation.
Question 11.
What does the term ‘diurnal Range’ mean
Answer:
The difference between the daily maximum and minimum temperature is diurnal Range.
Question 12.
What is Solution?
Answer:
The minerals in rocks which dissolve in water leads to the formation of solutions.
Question 13.
Name the two types of mass movements.
Answer:
The two types of mass movements are:
(a) Rapid Mass Movement and
(b) Show Mass movement.
![]()
Question 14.
What are the types of Mechanical weathering?
Answer:
The types of Mechanical weathering are
(a) Temperatures
(b) Frost
(c) Crystal growth
(d) Release of pressure and
(c) water
Question 15.
Types of chemical weathering.
Answer:
The types of chemical weathering are:
(a) Carbonation
(b) Solution and
(c) Oxidation
Question 16.
Where does Mechanical weathering occur?
Answer:
Mechanical weathering occurs mainly in the arid climates.
Question 17.
Chemical weathering can be seen in which climates?
Answer:
In humid conditions, one can see chemical weathering.
Write whether the statements are TRUE or FALSE. Correct the incorrect statements.
Question 1.
Soil creep is uncommon in areas with dry climates and gentle slopes.
Answer:
False – It is a common phenomenon in such areas.
Question 2.
Shattering is a type of mechanical weathering
Answer:
True.
![]()
Question 3.
Granular weathering occurs in areas of heavy rainfall.
Answer:
True.
Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Mechanical Weathering and Chemical Weathering.
Answer:
| Mechanical Weathering | Chemical Weathering |
| (i) In this type of weathering, rocks get disintegrated but the chemical composition of the rocks does not change. | (i) It is a process where rocks get disintegrated and the chemical composition of the rocks change. |
| (ii) It is caused due to differences in the day and night temperature. | (ii) It is caused due to the reaction of oxygen, carbon dioxide and water with certain rock minerals. |
| (iii) It is more common in an extremely cold climates and hot dry desert climates. | (iii) It is more common in hot and humid climates. |
Fill the map with the given information and make a legend.
(1) Area affected by a landslide (mudslide) in Maharashtra.
(2) Wadgaon Darya
Give geographical reasons:
Question 1.
Oxidation process occurs in heavy rainfall areas.
Answer:
- The oxidation process occurs in rocks which have iron present in them.
- The iron in the rock comes in contact with water and a chemical reaction takes place between iron and oxygen.
- A reddish coloured layer forms on the rocks.
- Thus, the oxidation process occurs in heavy rainfall areas.
![]()
Question 2.
Chemical weathering occurs in areas of heavy rainfall.
Answer:
- The rain water travels through the atmosphere before reaching the ground. Carbon dioxide in the air gets mixed in the water in this process.
- Dilute carbonic acid gets formed. Materials like limestone get easily dissolved in such acids leading to weathering of rocks.
- Some minerals in the rock gets dissolved in water. Limestone is formed due to chemical precipitation between water and alkalis.
Similarly, because of the solution, alkalis in the rock dissolves and make them brittle. - Oxidation process occurs in rocks which have iron present in them. The iron in the rock comes in contact with water and a chemical reaction takes place between iron and oxygen.
- Hence, a reddish coloured layer forms on the rocks. This is called rust.
Question 3.
Mechanical weathering3 takes place in the cold regions.
Answer:
- In the cold regions, the temperature drops below 0°C for a period of time.
- The water that has percolated through the cracks in the rocks freezes and turns into ice.
- Ice requires greater space than water. Tension is developed when the ice tries to acquire greater space.
- The continuous process of freezing and melting finally leads to the breaking of the rock mass.
Question 4.
Rapid mass movements occurs along the steep slopes.
Answer:
- A thick layer of weathered material forms on the steep slopes.
- When it rains in such areas, the rainwater penetrates the weathered materials and their weight increases.
- Due to this the weathered materials move very rapidly and come down the steep slopes.
Question 5.
Mechanical weathering is seen in areas where the diurnal range of temperature is high.
OR
Change in temperature leads to Mechanical weathering.
Answer:
- The minerals in the rocks expand because of heat and contract when the temperature decreases.
- Due to such continuous contracting and expanding, tension develops in the rock particles.
- Each mineral reacts differently to the temperature. Some minerals expand more, while others do not expand as much.
- Consequently, the tension formed in the rocks also increases and decreases. As a result, cracks develop in the rocks and they break.
- Thus in areas, where the diurnal range of temperature is higher, mechanical weathering is seen.
Question 6.
Water plays an important role in chemical weathering.
Answer:
- Rock is a mixture of many minerals.
- Since many things get dissolved easily in water, it is considered a universal solvent.
- The solubility1 of the solution increases because the matter gets dissolved in water.
- Water speeds up the process of carbonation, solution and oxidation. These processes lead to the weathering of rocks.
- Thus water plays an important role in chemical weathering.
![]()
Question 7.
Frost leads to mechanical weathering.
Answer:
- In areas where the temperatures drop below 0°C for quite some time, the water accumulated in the cracks and crevices in the rocks freezes.
- The volume of water increases on freezing.
- This leads to tension in the rocks and they shatter.
- In this way frost leads to mechanical weathering.
Answer in brief:
Question 1.
What is a mass movement? What are the types of mass movements?
Answer:
The weathered rock materials move along the slopes due to gravity and accumulate near the foothills or the gentler slopes. When the weathered particles move down due to gravity alone, the process is called mass movements.
Types of Mass movements:
(i) Rapid mass movements:
- A thick layer of weathered material forms on the slope. When it rains in such areas, the rain water penetrates the weathered materials and their weight increases.
- The weathered materials move very rapidly and come down the slope.
- Sometimes the weathered materials sink in situ. (Where they are)
- Rockfalls, landslides, land subsidence are ; termed as rapid mass movements.
(ii) Slower mass movements:
- Soil creep is the most common phenomenon in areas with dry climate and gentler slopes.
- In periglacial regions along the soil. This is called as solifluction.
Question 2.
How does external processes occur?
Answer:
- External processes occur because of the forces working on the earth’s surface.
- They are mainly solar energy, gravitational force and kinetic energy associated with the moving objects on the earth’s surface.
![]()
Question 3.
What is exfoliation?
Answer:
- In regions of high temperatures, the exposed part of the rock heats more while the inner part is comparatively cooler.
- As a result, the outer layers of the rocks fall apart from the main rock.
- This is called the exfoliation of the rock.
Question 4.
Explain the process of oxidation.
Answer:
- The oxidation process occurs in rocks which have iron present in them.
- The iron in the rock comes in contact with water and a chemical reaction takes place between iron and oxygen.
- Hence, a reddish coloured layer forms on the rocks. This is called rust.
Explain:
Question 1.
Block Disintegration
Answer:
- Sometimes both temperature and water are responsible for weathering.
- The difference in temperature cause contraction and expansion of minerals in the rocks. This leads to widening theoints or cracks in the rocks.
- Water accumulates in such wideouts and big blocks of rocks separate from each other.
- This is called Block Disintegration.
Question 2.
Carbonation
Answer:
- Carbonation is a type of chemical weathering.
- The rainwater travels through the atmosphere before reaching the ground.
- Carbon dioxide in the air gets mixed in the water in this process and dilute carbonic acid gets formed.
- For e.g Water + Carbon Dioxide = Carbonic Acid (H2O +CO2 = H2CO3)
- Materials like limestone get easily dissolved in such acids.
![]()
Question 3.
Solution
Answer:
- Some minerals in the rock get dissolved in water.
- Limestone is formed due to chemical precipitation between water and alkalis.
- At Wadgaon Darya in Ahmadnagar district, limestone gets precipitated chemically i.e. undergoes chemical weathering again.
- Similarly, because of solution, alkalis in the rock dissolve and make them brittle.
Question 4.
Make a record of few landslides that have occured in India and write about them briefly.
Answer:
Landslide is a rapid mass movement which is caused majorly due to heavy rains, floods, earthquakes etc. The following are some fatal landsides in India.
- Guwahati landslide, Assam:- The landslide took place in the year 1948 due to heavy rains & over 500 people died in this landslide.
- Darjeeling landslide, West Negal:- This landslide happened in the year of 1968. It was triggered by floods and thousands of people died due to this landslide.
- Malpa landslide, Uttarkhand:- Consecutive landslides occured in August 1998 in village of Mapla due to which 380 people died as an entire village was destroyed in the landslide.

- Kedarnath landslide, Uttarakhand:- This landslide took place onune 16, 2013 & was the result of Uttar Khand floods. Over 5700 people were reported dead and over 4200 villages were affected by floods and post-flood landslide.
- Malin landslide, Maharashtra:- This landslide occured onuly 30, 2014, in a village in Malin. The landslide occured due to heavy rainfall and around 151 people died and 100 people went missing after the disaster.