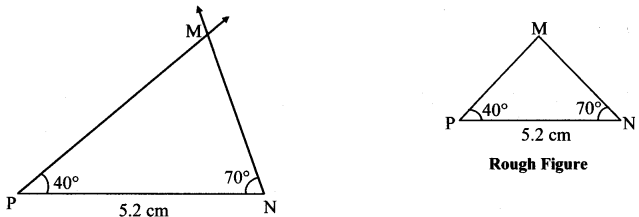
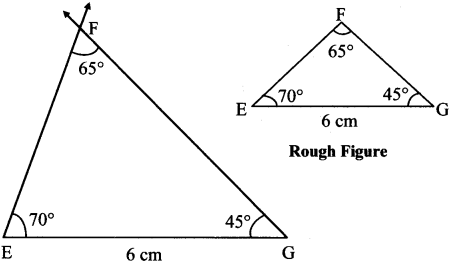
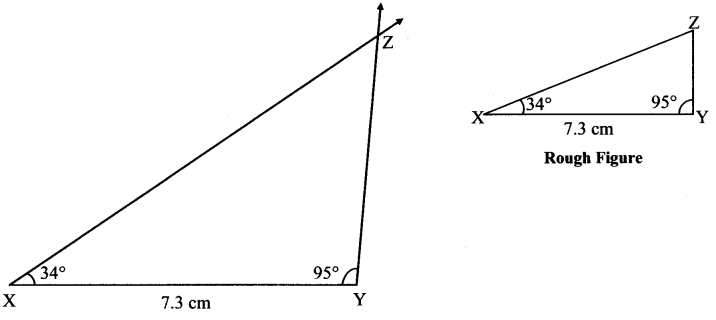
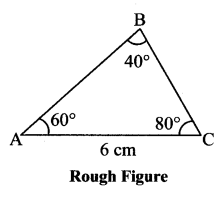
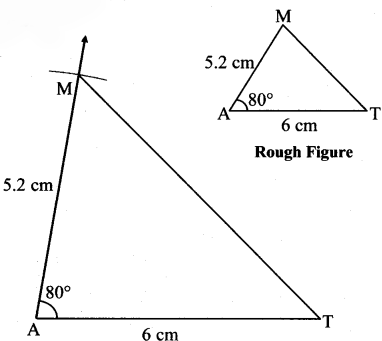
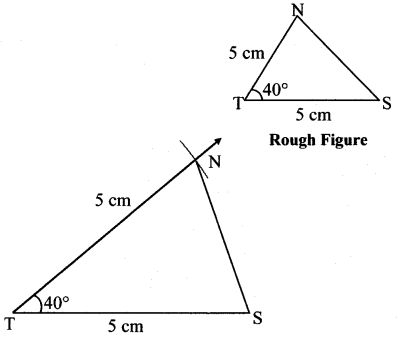
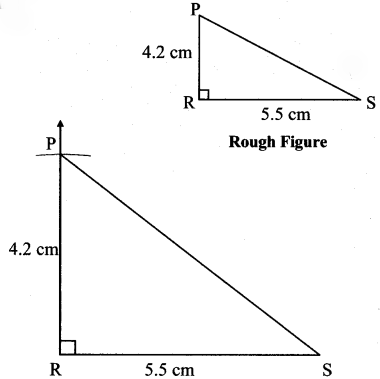
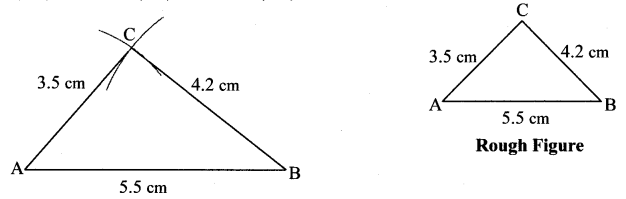
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions covers the 7th Std Maths Practice Set 5 Answers Solutions Chapter 1 Geometrical Constructions.
Geometrical Constructions Class 7 Practice Set 5 Answers Solutions Chapter 1
Construct triangles of the measures given below:
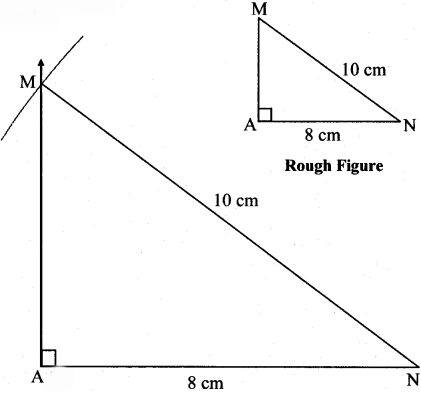
Question 1.
In ∆MAN, m∠MAN = 90°, l(AN) = 8 cm, l(MN) = 10 cm.
Solution:
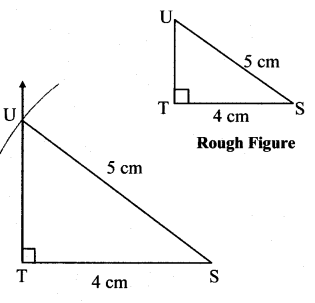
Question 2.
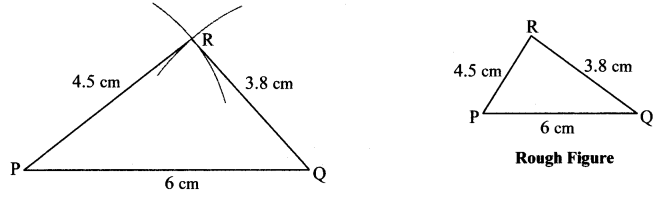
In the right-angled ∆STU, hypotenuse SU = 5cm and l(ST) = 4cm.
Solution:
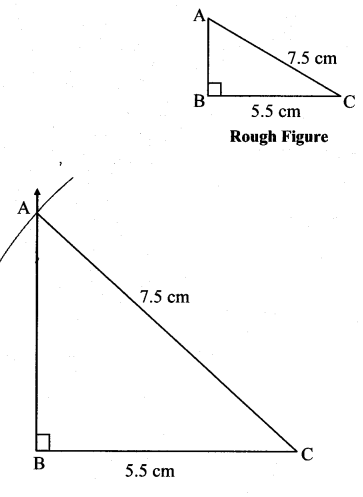
Question 3.
In ∆ABC, l(AC) = 7.5 cm, m∠ABC = 90°, l(BC) = 5.5cm.
Solution:
Question 4.
In ∆PQR, l(PQ) = 4.5 cm, l(PR) = 11.7cm, m∠PQR = 90°.
Solution:
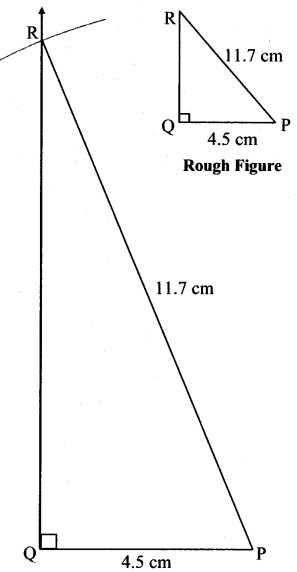
Question 5.
Students should take examples of their own and practice construction of triangles.
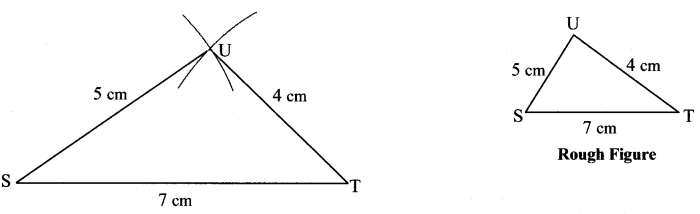
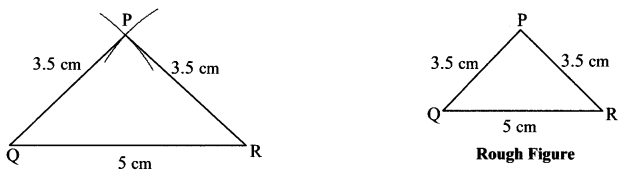
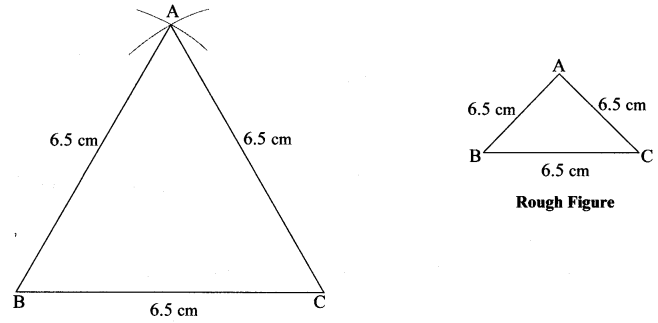
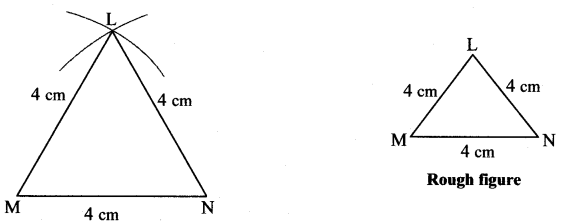
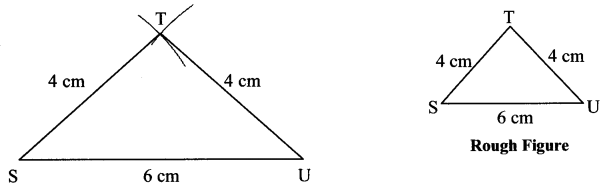
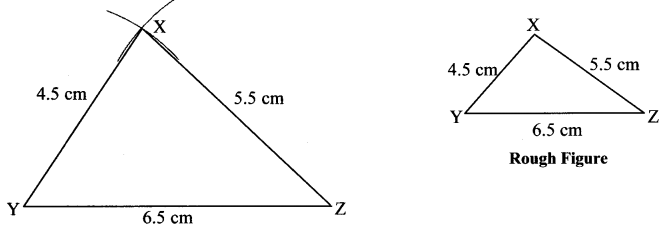
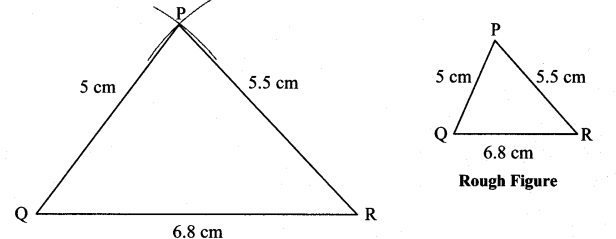
i. In ∆PQR, l(PQ) = 5 cm, l(QR) = 6.8 cm, l(PR) = 5.5 cm.
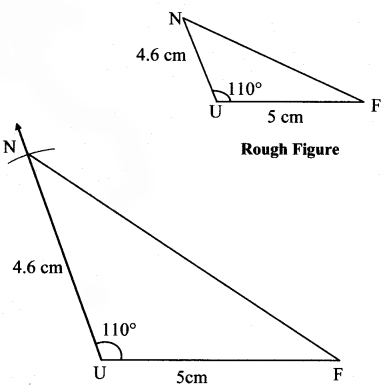
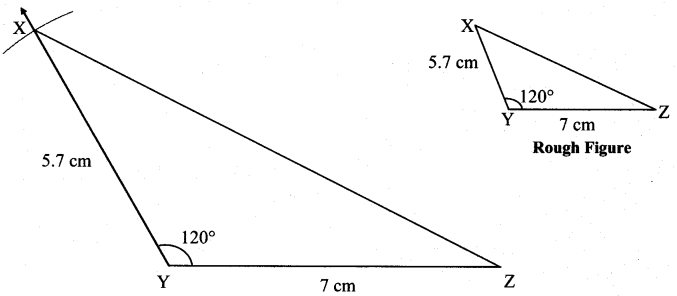
ii. In ∆XYZ, l(XY) = 5.7 cm, m∠Y = 120°, l(YZ) = 7 cm.
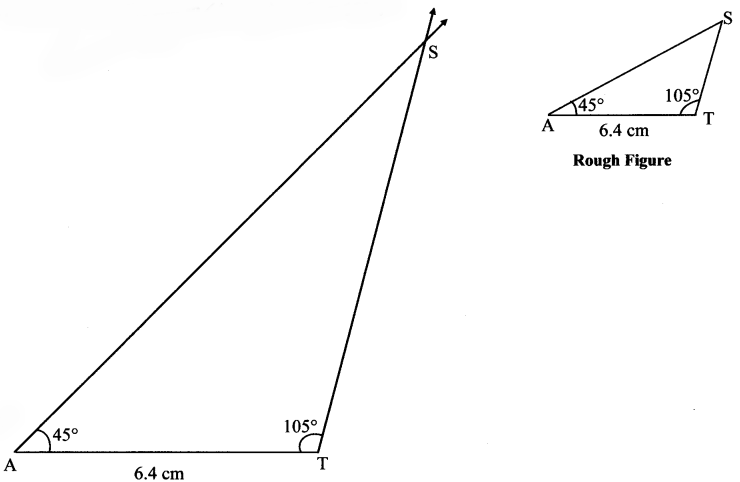
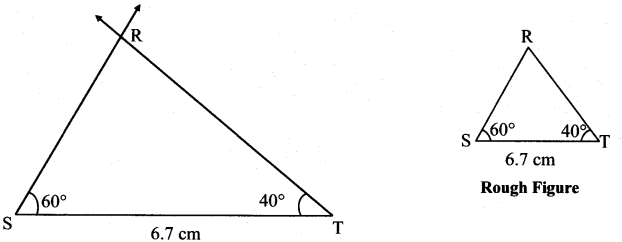
iii. In ∆RST, l(ST) = 6.7 cm, m∠S = 60°, m∠T = 40°.
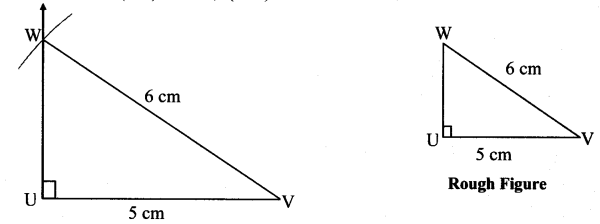
iv. In ∆UVW, m∠U = 90°, l(UV) = 5 cm, l(VW) = 6 cm.
Solution:
i. In ∆PQR, l(PQ) = 5 cm, l(QR) = 6.8 cm, l(PR) = 5.5 cm.
ii. In ∆XYZ, l(XY) = 5.7 cm, m∠Y = 120°, l(YZ) = 7 cm.
iii. In ∆RST, l(ST) = 6.7 cm, m∠S = 60°, m∠T = 40°.
iv. In ∆UVW, m∠U = 90°, l(UV) = 5 cm, l(VW) = 6 cm.