Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 History Solutions Chapter 1 The Indian Subcontinent and History Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra Board Class 6 History Solutions Chapter 1 The Indian Subcontinent and History
Class 6 History Chapter 1 The Indian Subcontinent and History Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Answer the following in one sentence:
Question 1.
What is history?
Answer:
History is a coherent account of the significant past events in the progress of human culture.
Question 2.
Where do human settlements flourish?
Answer:
Human settlements have flourished wherever the means of living are plentiful.
![]()
Question 3.
What do the people in the hilly region j depend on for their food?
Answer:
In the hilly regions people depend more on hunting and gathering for their food.
Question 4.
Which was the earliest civilization in India?
Answer:
The Harappan civilization was the earliest civilization in India.
2. Answer the following questions in short:
Question 1.
What does human life depend on?
Answer:
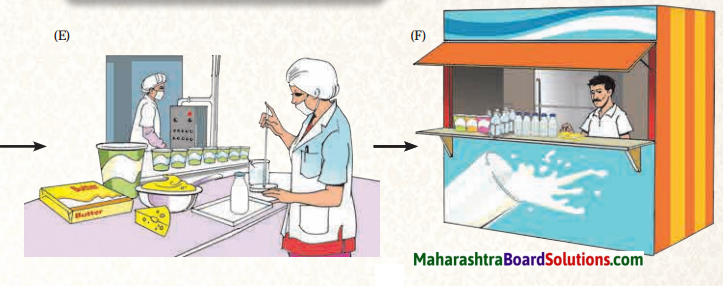
Human life in any region depends to a large extent on its geographical characteristics, diet, clothing, housing and occupation.
Question 2.
What features of our surroundings form the means of our livelihood?
Answer:
The climate, rainfall, agricultural produce, flora and fauna of the region where we live form the source or means of our livelihood.
Question 3.
Which region is known as the Indian subcontinent?
Answer:
Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and India together form the region known as south Asia. Considering the expanse and significance of India in this region, it is also known as the Indian subcontinent.
![]()
3. Give reasons:
Question 1.
There is a close relation between history and geography.
Answer:
- Time, place, society and individuals are four major pillars without which history cannot be written.
- Of these four components ‘place’ is related to geography or geographical conditions.
- This makes history and geography inseperable i.e. very closely related.
Question 2.
People are forced to leave their settlements.
Answer:
- Sometimes reasons like degradation of the environment, drought, invasion, etc. leads to scarcity of means.
- Therefore, people are forced to leave their settlements in their fight for survival.
4. Explain the difference in the human life in the hilly regions and that on the plains.
Answer:
| Human life in the Hilly region | Human life in the Plains |
| (1) Human life was very strenuous | (1) Life was more comfortable. |
| (2) Land was not fertile. therefore no So agriculture was wcarried on. | (2) Land was very Fertile So agriculture was carried on. |
| (3) Grains and vegetables Grains and are scarce. | (3) Grains and vegetables are found in plenty |
| (4) They depend on hunting and gathering for their food. | (4) They do not depend on hunting and gathering for their food. |
5. Observe the physical map of India and answer the questions based on it:
Question 1.
Which mountain ranges lie in the north of India?
Answer:
The Hindukush and the Himalayan mountain ranges.
Question 2.
Which are the routes to India from the north-east?
Answer:
The route to India from the north east is by sea.
Question 3.
Where do the Ganga and Brahmaputra meet?
Answer:
The Ganga and Brahmaputra meet in Bangladesh.
![]()
Question 4.
Name the islands to the east of the Indian peninsula.
Answer:
The Andaman and Nicobar islands are the Indian islands to the east of the Indian peninsula.
Question 5.
In which part of India do we see the Thar Desert?
Answer:
We see the Thar Desert in the north western part of India.
Activity:
- Obtain information about the lakes or reservoirs in your locality.
- Show the following on a world map :
1. The Himalaya Mountain
2. The Silk Road
3. Arabia
Class 6 History Chapter 1 The Indian Subcontinent and History Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the sentence by choosing the correct option:
Question 1.
________ is a coherent account of the significant past events in the progress of human culture.
(a) History
(b) Geography
(c) Civics
Answer:
History
Question 2.
Not much fertile land is available in the ______ region.
(a) plains
(b) hilly
(c) plateau
Answer:
hilly
Question 3.
Grains and vegetables are _______ in the hilly areas.
(a) scarce
(b) plenty
(c) moderate
Answer:
scarce
![]()
Question 4.
In the ______ regions, people depend more on hunting and gathering for their food.
(a) plateau
(b) plains
(c) hilly
Answer:
hilly
Question 5.
Human settlements have flourished wherever the means of living are _______.
(a) scarce
(b) plentiful
(c) moderate
Answer:
plentiful
Question 6.
_____ lies to the north of India.
(a) Andaman
(b) Western Ghats
(c) Himalayas
Answer:
Himalayas
Question 7.
_____ lies to the east of India.
(a) Bay of Bengal
(b) Eastern ghats
(c) Lakshadweep
Answer:
Bay of Bengal
Question 8.
_________ lies to west of India.
(a) Himalayas
(b) Arabian sea
(c) Brahmaputra
Answer:
Arabian sea
Question 9.
______ lies to the south of India.
(a) Indian Ocean
(b) Arabian Sea
(c) Pacific Ocean
Answer:
Indian Ocean
Question 10.
The Hindukush and Himalayan ranges have created an impenetrable wall on the nothern side of the ________ subcontinent.
(a) Indian
(b) Foreign
(c) Asian
Answer:
Indian
Question 11.
There is a land route through the Khyber and Bolan passes in the ______ mountains.
(a) Himalayan
(b) Satpuda
(c) Hindukush
Answer:
Hindukush
![]()
Question 12.
The _____ desert spreads across Rajasthan, Haryana and some parts of Gujarat.
(a) Bhor
(b) Thar
(c) Arabian
Answer:
Thar
Question 13.
The _______ river that originates in Himachal Pradesh reaches the Thar desert.
(a) Ganga
(b) Sindhu
(c) Ghaggar
Answer:
Ghaggar
Question 14.
A region that is bound by sea on three sides is called a ______.
(a) peninsula
(b) plateau
(c) island
Answer:
peninsula
Question 15.
A major part of the Indian peninsula is occupied by the_______ plateau.
(a) Maharashtra
(b) Bengal
(c) Deccan
Answer:
Deccan
Question 16.
The mountain ranges of the Vindhya and Satpuda are located to the of the ________ Deccan Plateau.
(a) east
(b) north
(c) west
Answer:
north
Question 17.
Deccan plateau was a part of the ______ empire, the largest in ancient India.
(a) Maurya
(b) Gupta
(c) Chola
Answer:
Maurya
Question 18.
Lakshadweep is a group of Indian islands in the _____ Sea.
(a) Red
(b) Dead
(c) Arabian
Answer:
Arabian
Question 19.
The Harappan civilization had spread mainly in the ________ part of the Indian subcontinent.
(a) southeastern
(b) northwestern
(c) southwestern
Answer:
north western
![]()
Match the following:
Question 1.
| Column (A) | Column (B) |
| (1) Himalayas | (a) South |
| (2) Indian Ocean | (b) East |
| (3) Arabian Sea | (c) North |
| (4) Bay of Bengal | (d) West |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – a
3 – d
4 – b
Question 2.
| Column (A) | Column (B) |
| (1) China | (a) Deccan plateau |
| (2) Vindhya range | (b) Not a part of Indian subcontinent |
| (3) Bangladesh | (c) In Bay of Bengal |
| (4) Andaman and Nicobar islands | (d) In the Hindukush mountains |
| (5) Khyber and Bolan passes | (e) Part of Indian subcontinent |
Answer:
1 – b
2 – a
3 – e
4 – c
5 – d
Answer the following in one sentence:
Question 1.
Give the four major pillars without which history could not have been written.
Answer:
Time, place, society and individuals are the four major pillars of history, without which history could not have been written.
Question 2.
What has created an impenetrable wall on j the northern side of the Indian subcontinent? j
Answer:
Two mountain ranges, the Hindukush and Himalayan ranges have created an impenetrable wall on the northern side of the Indian subcontinent.
Question 3.
Which passes form a route in the Hindukush mountains?
Answer:
The Khyber and the Bolan passes form a land route in the Hindukush mountains.
Question 4.
What is known as ‘Hakra’ in Pakistan?
Answer:
The Ghaggar river that originates in Himachal Pradesh reaches the Thar desert. It is known as ‘Hakra’ in Pakistan.
Question 5.
Which plateau occupies a major part of the Indian peninsula?
Answer:
The Deccan plateau occupies a major part of the Indian peninsula.
Question 6.
Which mountain range is to the north of the Deccan plateau?
Answer:
The Vindhya and Satpuda mountain ranges are located to the north of the Deccan plateau.
![]()
Question 7.
Name the Indian islands in the Bay of Bengal.
Answer:
Andaman and Nicobar are the Indian islands in the Bay of Bengal.
Question 8.
Which manuscript mentions the Indian islands?
Answer:
The manuscript ‘Periplus of the Erythrean Sea’ or ‘Handbook of the Red Sea’ by an unknown Greek sailor, makes a mention of Indian islands.
Question 9.
Which two ancient cities are in today’s Pakistan?
Answer:
The cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro are in today’s Pakistan.
Answer the following questions in short:
Question 1.
State the extent of our country, India.
Answer:
Our country India, extends far and wide:
- To its north lies the Himalayas.
- To the east, the Bay of Bengal.
- To the west, the Arabian Sea.
- And to the south, the Indian ocean.
- Except for the islands of Andaman, Nicobar and Lakshadweep, the rest of the country is contiguous.
Question 2.
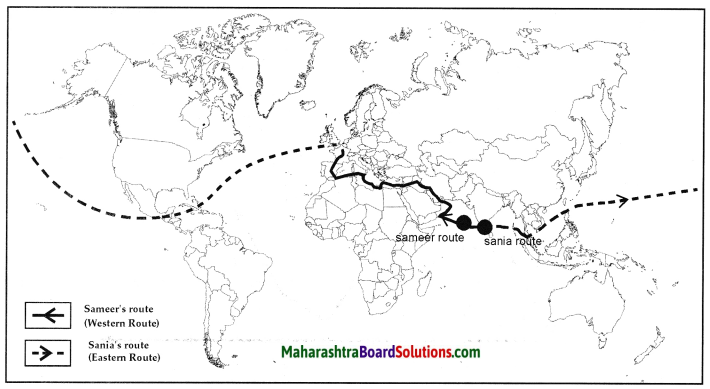
Describe the trade route from China to Arabia.
Answer:
- There is a land route through the Khyber and Bolan passes in the Hindukush mountains.
- This land route was connected to an ancient trade route.
- The trade route from China in the east passed through central Asia and reached Arabia in the west.
![]()
Give reasons:
Question 1.
The trade route from west to east was also called the silk route.
Answer:
- Silk was the main commodity exported to the western countries using this trade route.
- Therefore this trade route from west to east was called the ‘silk route’ or ‘silk road’.