Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Maths Solutions covers the Std 6 Maths Chapter 18 Three Dimensional Shapes Class 6 Practice Set 41 Answers Solutions.
6th Standard Maths Practice Set 41 Answers Chapter 18 Three Dimensional Shapes
Question 1.
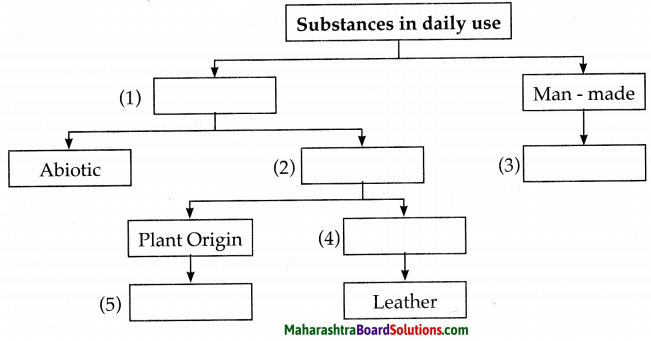
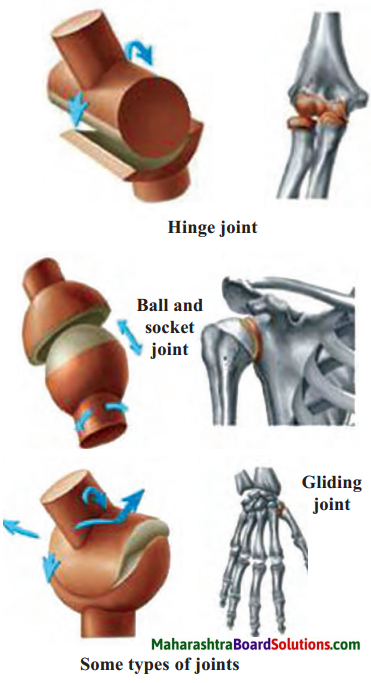
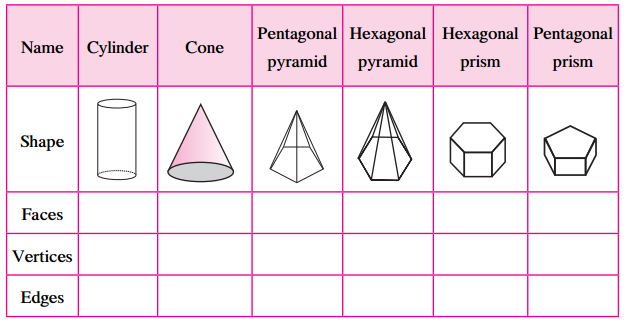
Write the number of faces, edges and vertices of each shape in the table.
Solution:
| Name | Cylinder | Cone | Pentagonal pyramid | Hexagonal pyramid | Hexagonal prism | Pentagonal prism |
| Faces | 3 (2 flat + 1 curved) | 2 (1 flat + 1 curved) | 6 (5 triangles + 1 pentagon) | 7 (6 triangles + 1 hexagon) | 8 (6 rectangles + 2 hexagons) | 7 (5 rectangles + 2 pentagons) |
| Vertices | 0 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 12 | 10 |
| Edges | 2 (circular) | 1 (circular) | 10 | 12 | 18 | 15 |
Maharashtra Board Class 6 Maths Chapter 18 Three Dimensional Shapes Practice Set 41 Questions and Activities
Question 1.
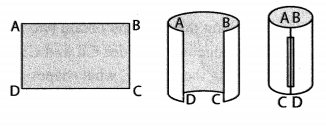
- Take a rectangular sheet.
- Bring together its opposite sides. What shape does it form? (Textbook pg. no. 94)
Solution:
It forms a hollow cylinder.
Question 2.
- Take a cylindrical tin.
- Take a rectangular sheet with one side equal to the height of the tin.
- Wrap it around the tin to cover it completely and cut away the extra paper.
- Then unfold it and spread it out on a table.
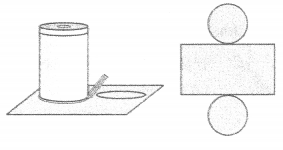
- Take another sheet. Place the tin on it and draw its circular outline.
- Cut away the paper around it. Cut out another circle like this one.
- Place these discs next to the rectangular paper as shown in the given figure. Which figure is obtained? (Textbook pg. no. 94)
Solution:
The figure obtained is the net of the closed cylinder.
Question 3.
Can you tell? (Textbook pg. no. 95)
When playing carom, you make a pile of the pieces as shown in the picture. What is the shape of this pile?
If you place a number of CD’s or round biscuits one on top of the other, what shape do you get?

Solution:
In all the cases, it will form a cylindrical shape (2 circular faces and 1 curved surface).
Question 4.
- Draw a net as shown in figure (a) on a card sheet and cut it out.
- Fold along the dotted lines of the square and bring the sides together so that the vertices A, B, C and D meet at a point.
What shape does it form? (Textbook pg. no. 95)
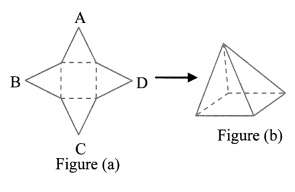
Solution:
The given net forms a quadrangular pyramid.
Question 5.
- Draw a net as shown in figure (a) on a card sheet and cut it out.
- Fold along the dotted lines of the triangle and bring the sides together so that the vertices A, B and C meet at a point.
What shape does it form? (Textbook pg. no. 95)
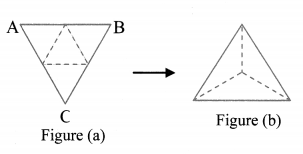
Solution:
The given net forms a triangular pyramid.
Question 6.
- Using a compass draw a circle with centre C on a paper.
- Draw two radii CR and CS.
- Cut out the circle.
- Cut along the radii and obtain two pieces of the circle.
- Bring together the sides CR and CS of each piece.
On completing the activity, what shapes did you get? (Textbook pg. no. 95)
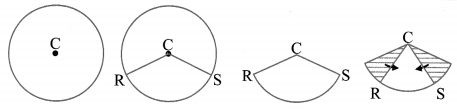
Solution:
On completing the activity, we get an open cone.
Read Also: