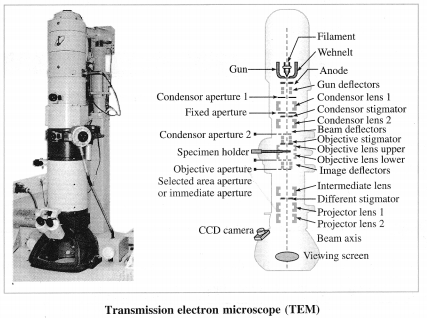
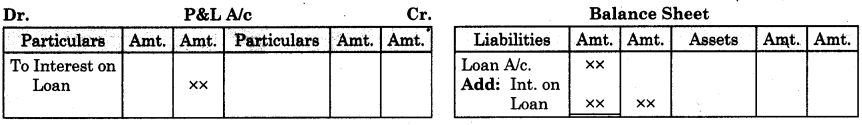
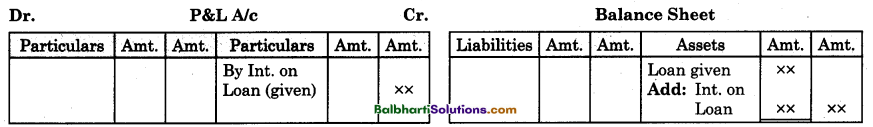
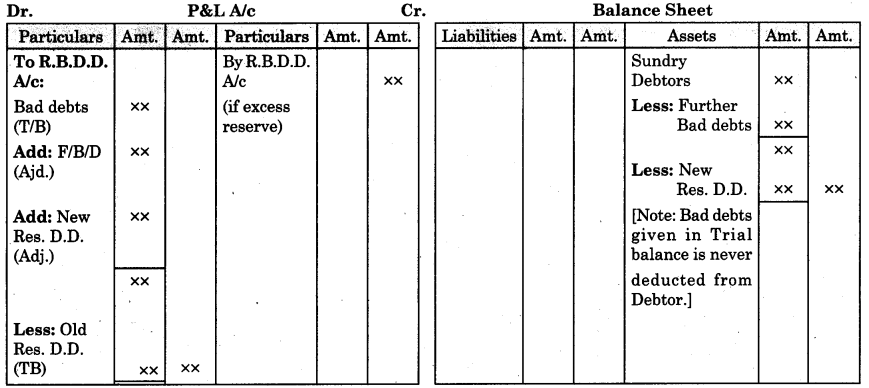
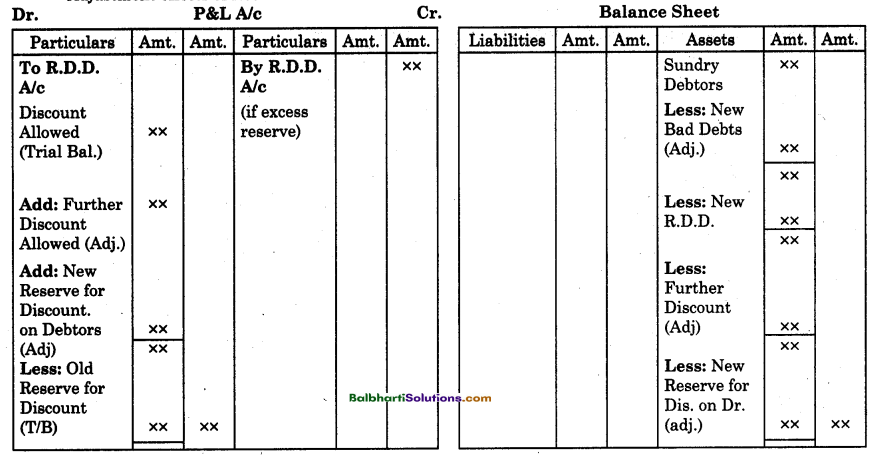
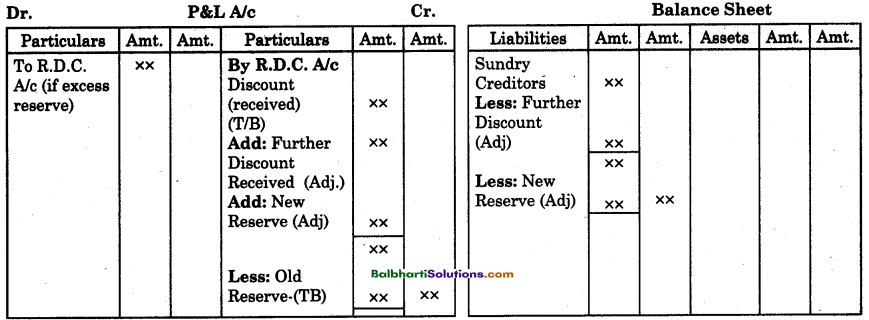
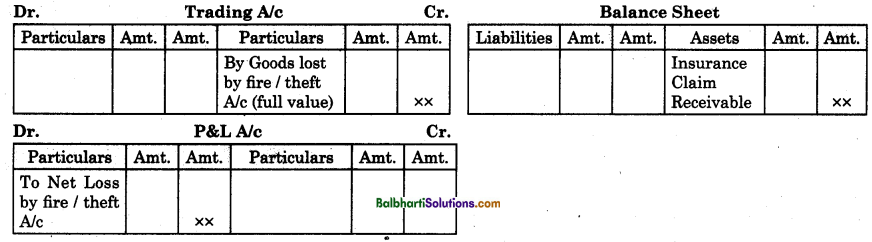
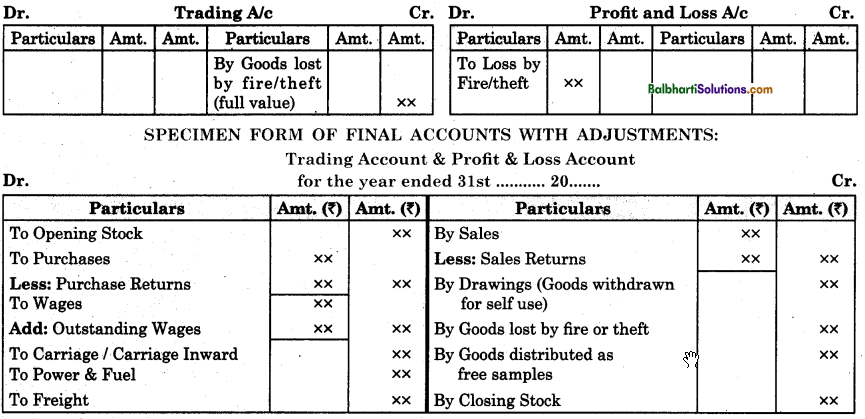
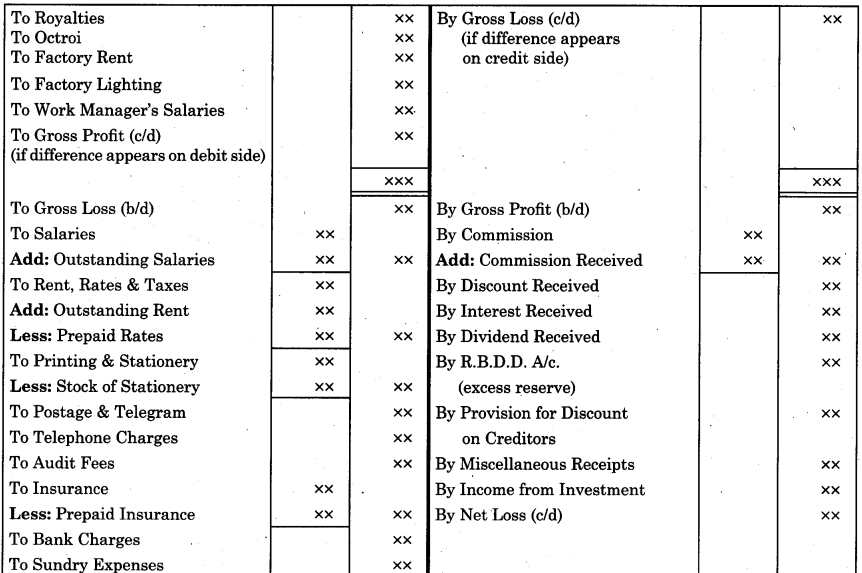
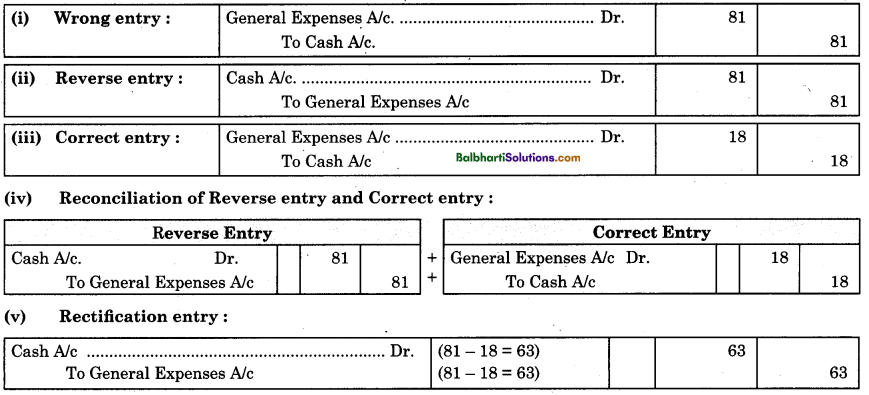
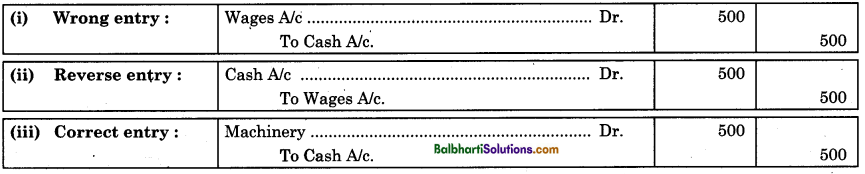
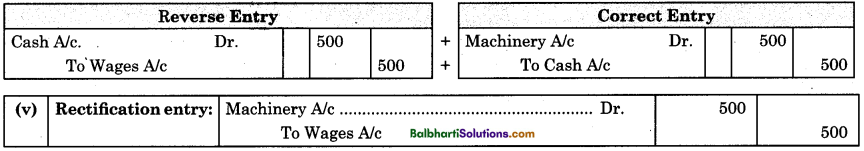
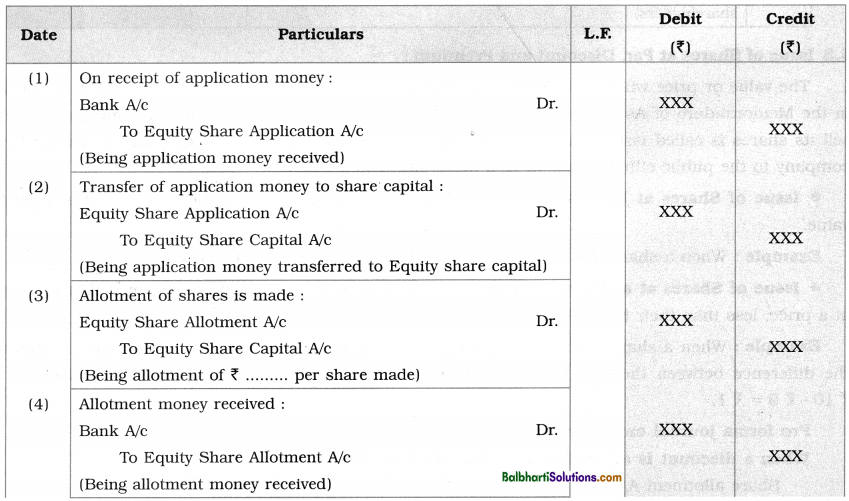
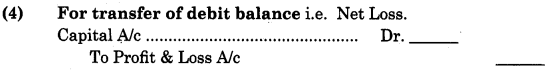By going through these Maharashtra State Board 12th Science Biology Notes Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Notes Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow
Introduction-
- Self-regulatory and self -sustaining structural and functional unit of biosphere.
- Consists of biotic and abiotic components.
- The term ecosystem was coined by Tansley.
- Ecosystems are of variable sizes from small pond to large ocean.
- Global ecosystem means entire biosphere.
- Two basic categories :
(1) Terrestrial (forest, grassland, desert)
(2) Aquatic (lakes, rivers, wetlands, estuaries) - Also classified as natural ecosystem which is not based on any human inputs and artificial ecosystem which is dependent on man for constant inputs of energy or material.
- Dynamics of ecosystem : Input of ecosystem means productivity, transfer of energy in ecosystem is by a food chain, food web and nutrient cycling and output of ecosystem means degradation and energy loss.
![]()
Ecosystem-
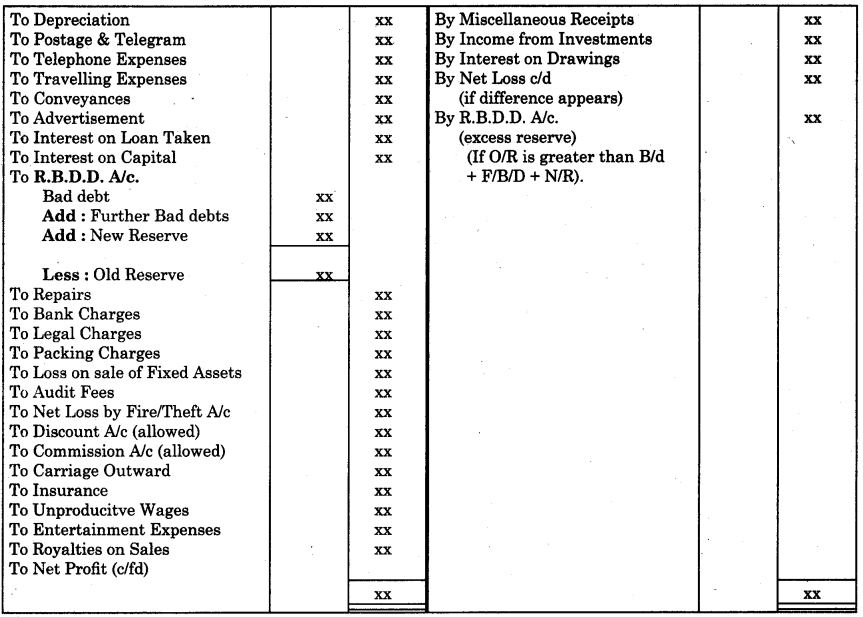
1. Structure and function :
(1) Physical structure of ecosystem means the interaction of biotic and abiotic components in that ecosystem.
(2) Species composition of an ecosystem is understood by identification and enumeration of resident plant and animal species.
(3) Spatial pattern is the variation in ecosystem due to space. This is of two types, viz. stratification and zonation.
- Stratification : Vertical distribution of species of plants and animals at different levels. E.g. Trees, herbs, shrubs among plant species. Epipelagic, meso pelagic, bathypelagic and benthic among aquatic communities.
- Zonation : Horizontal distribution of plants and animals either on land or in water. E.g. Zonation in aquatic system : intertidal, littoral, sublittoral zones.
Zonation in wetlands : Sub tidal channels, mudflats, Low marsh, high marsh
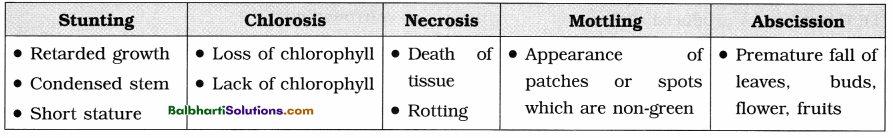
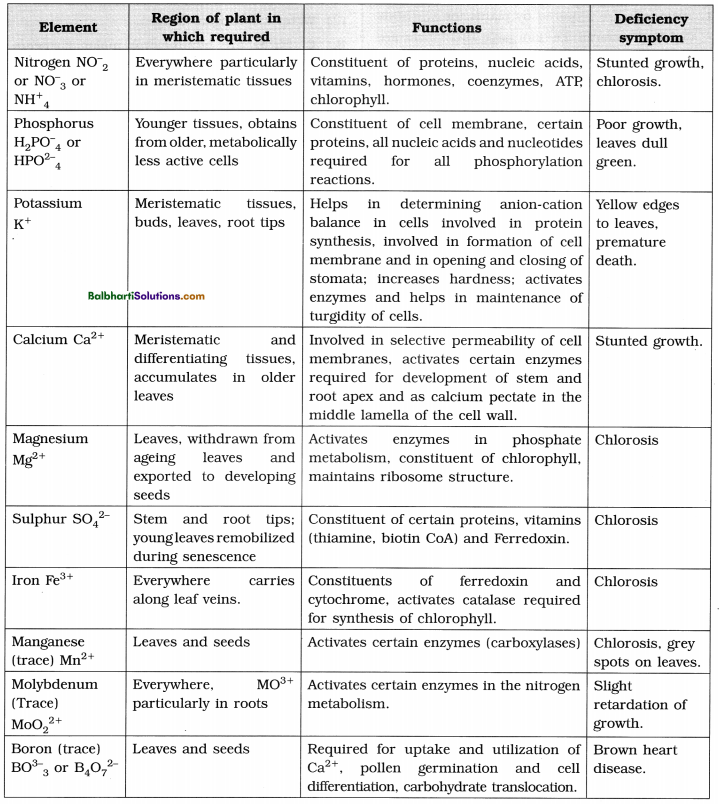
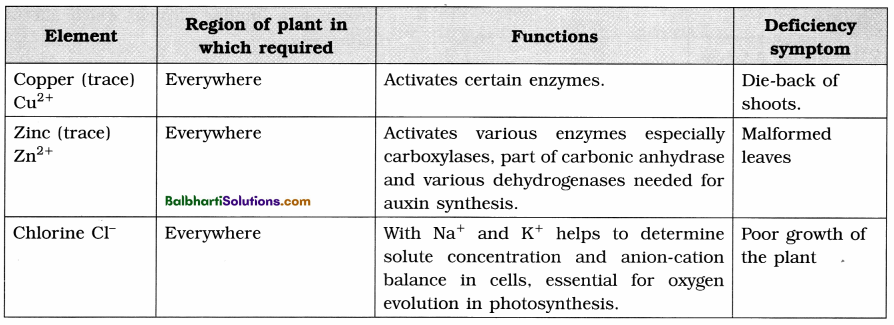
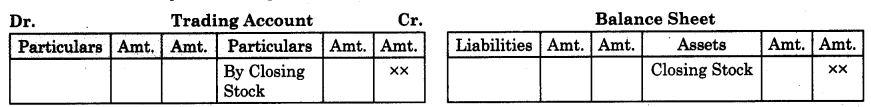
2. Functional aspects of ecosystem : Productivity, Decomposition, Nutrient cycling and Energy flow are the four functional aspects of any ecosystem.
(1) Productivity :
- Conversion of inorganic substances into organic material using solar energy by the autotrophs is called productivity. Consumption of autotrophs by heterotrophs.
- Solar energy is a must for any ecosystem for sustenance.
- Rate of generation of biomass in an ecosystem expressed as gram/sq. metre/ day.
- Gross primary productivity (GPP) : Rate of production of organic matter by photosynthesis.
- Net primary productivity (NPP) : Net
Primary Productivity = Gross primary productivity – respiratory losses. - NPP is available biomass which heterotrophs can use.
- Annual NPP of whole biosphere = 170 billion tons dry weight of organic matter. Ocean productivity = 55 billion tons.
Factors on which GPP depends :
- Resident plant species
- Availability of nutrients
- Photosynthetic capacity of plants
- Type of ecosystem
Secondary productivity : Rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers. This is available energy which is transferred to next trophic level.
(2) Decomposition :
- Breakdown of complex organic material and forming inorganic minerals from the dead matter is called decomposition.
- Detritus is raw material which is decomposed.
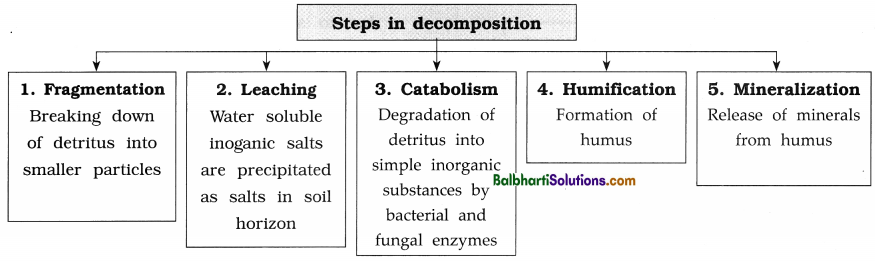
Factors regulating decomposition :
- Enough oxygen availability as it is an oxygen-requiring process.
- Chemical composition of detritus.
- Climatic factors.
- If detritus is rich in lignin and chitin the rate of decomposition rate is slower. If the detritus is rich in nitrogen and sugars the rate is faster.
- Most important factors for decomposition are temperature and soil moisture. These factors affect activities of soil microbes. In warm and moist environment decomposition is faster whereas in low temperature and in absence of oxygen, the decomposition is inhibited.
(3) Nutrient cycling : Storage and transport of nutrients.
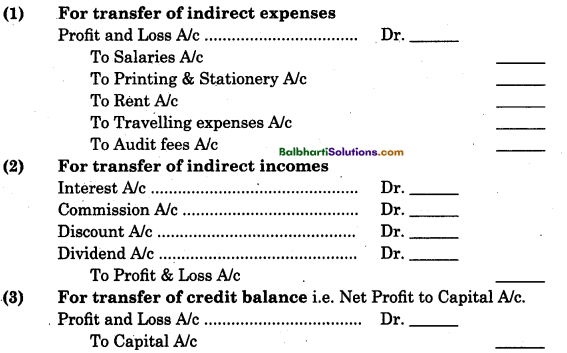
(4) Energy flow : Flow of energy from producer to consumer in unidirectional way. Dissipation and loss of heat during energy flow is inevitable.
![]()
Energy flow –
- The ultimate source of energy for all the globed ecosystems is sun. However, in deep sea hydrothermal ecosystem solar energy does not reach.
- Less than 50% of solar radiation that falls on the earth’s surface is photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). Only 2-10 % of PAR sustains the entire living world.
- Plants and autotrophic bacteria fix solar radiant energy into complex carbohydrates while using simple inorganic materials. Plants thus are the producers that supply the energy in the form of food to consumers.
- There is always unidirectional flow of energy ; from the sun to autotrophic producers and : then to heterotrophic consumers.
- Second Law of thermodynamics operates for the ecosystems too. The universal tendency towards increasing disorderliness is always counteracted by producers and consumers.
- Organisms in the ecosystem need a constant : supply of energy to survive and synthesise the : required molecules.
- Major primary producers are herbaceous and woody plants in a terrestrial ecosystem. In an aquatic ecosystem primary producers are phytoplankton and algae.
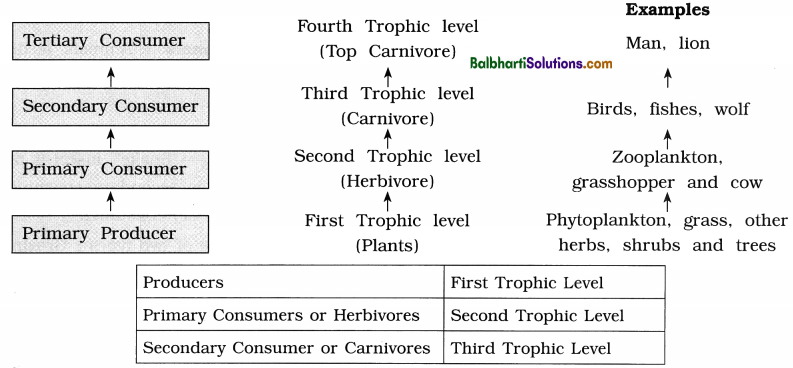
- Food chain/Food web : The chain or web formed due to interdependency among various organisms of the ecosystem is known as food chain.
- Energy that is trapped into an organism keeps on flowing. Producers trap the energy and pass it further to a consumer. If the producer dies, the death of organism starts the detritus food chain/web.
- All animals directly or indirectly depend on : plants to obtain their food. They cannot synthesise their own food so they are called ; heterotrophs or consumers.
- Primary consumers : Consumers feeding directly on the producers are called primary consumers. For example, Herbivorous animals. Insects, birds and some mammals are herbivores or primary consumers in the terrestrial ecosystem and molluscs are primary consumers in aquatic ecosystem.
- Secondary consumers : The animals consuming other animals are secondary consumers. For example, Carnivores. Primary carnivores are secondary consumers. Secondary consumers feed on primary consumers.
- Tertiary consumers : Animals feeding on secondary consumers are called tertiary consumers.
For example, in the food chain “Plant matter → Insect → Frog → Snake”, insect is primary consumer, frog is secondary consumer and snake is the tertiary consumer. - Food chains are of two types : Grazing food chain and detritus food chain.
(1) A simple grazing food chain (GFC) is shown as follows :

(2) The detritus food chain (DFC) is made up of decomposers. It starts with dead and decaying matter. Examples of decomposers are fungi and bacteria. Decomposers are also called heterotrophic saprotrophs. (sapro : to decompose). By degrading dead organic matter or detritus, decomposers meet their nutritional and energy requirements. Digestive enzymes of saprotrophs breakdown dead and waste materials into simple inorganic materials before their absorption which are subsequently absorbed by them.
(3) In an aquatic ecosystem energy flow occurs only through grazing food chains whereas in a terrestrial ecosystem, majority of energy flow occurs through the detritus food chain.
(4) There are interconnections between detritus i food chain and grazing food chain at some levels. Some organisms of DFC serve as prey & to the GFC animals. Some animals like cockroaches, crows, pig and mam, etc. are omnivores.
(5) The natural interconnection of food chains is called a food web.
15. Diagrammatic representations of trophic levels in an ecosystem
- At each successive trophic level, the amount of energy available goes on reducing. The trophic levels in any food chain transfer the energy when it is functioned.
- ‘10% Law’ of R. Lindermann, 1942 : The law states that ‘only 10% of the energy is transferred to each trophic level as net energy, from the previous trophic level’.
- Food chains are never in isolation, but are always interconnected to form food web for maintaining the stability of an ecosystem.
![]()
Ecological Pyramids-
1. Ecological pyramid is the expression drawn to indicate number, biomass or energy in an ecosystem.
2. The broad base and narrow apex of a pyramid rightly expresses the food or energy relationship within different trophic level. The producers or the first trophic level is shown as a base of each pyramid while the apex represents tertiary or top level consumer.
3. The three types of ecological pyramids are :
- Pyramid of number
- Pyramid of biomass and
- Pyramid of energy.
4. The calculations of energy content, biomass, or number include all organisms at that trophic level. Some organisms may occupy more than one trophic level simultaneously, e.g. A primary consumer sparrow can become secondary consumer when it feeds on insects. The trophic level thus represents a functional level and not a species as such.
5. All the pyramids, of number, of energy and biomass are upright in most of the ecosystems, i.e., producers always outnumber the consumers. Similarly biomass is more for producers than that of the herbivores. Herbivores or primary consumers outnumber carnivores. Energy at a higher trophic level is always less than energy at the lower trophic level.
6. Exceptions to pyramid structure :
- The pyramid of biomass in sea is also generally inverted as the biomass of fishes far exceeds that of phytoplankton.
- Many insects and birds thriving on a single huge tree will also show inverted pyramid of numbers.
7. When energy flows from a lower trophic level to the next trophic level, some energy is always lost as heat at each step. Therefore the pyramid of energy is always upright. It is never inverted. In the energy pyramid, the amount of energy in a given time and per unit area is shown by each bar.
8. Limitations of the ecological pyramids :
- Ecological pyramids do not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
- They are based on simple food chain. In nature simple food chains do not exist but all the trophic relationships are in the form of food web.
- Saprophytes play a major and vital role in the ecosystem but they are not shown in ecological pyramids.
9. C. Elton in 1927 developed the concept of ecological pyramids.
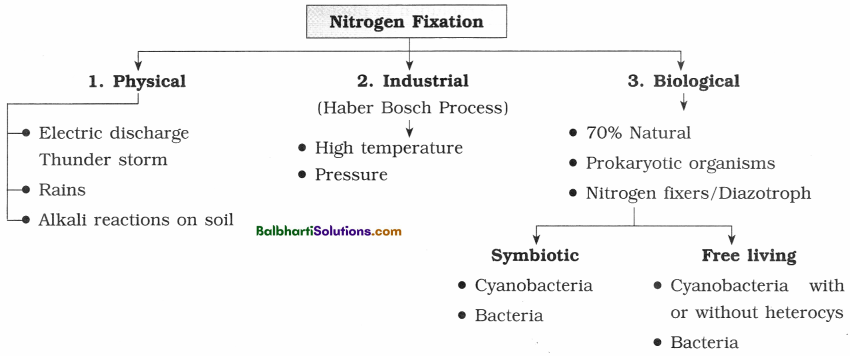
Nutrient cycles-
1. Nutrient cycling : Nutrient cycling or biogeochemical cycle is the movement of nutrient elements through various components of ecosystem.
2. Two types of nutrient cycles :
- Gaseous (nitrogen, oxygen and carbon) having reservoir in atmosphere.
- Sedimentary (Phosphorus, Sulphur) having Earth’s crust as reservoir.
3. Carbon Cycle : (Gaseous cycle)
- Five basic processes running the carbon cycle : Photos ynthesis, respiration, decomposition, sedimentation and combustion.
- Main component of all organic compounds in protoplasm is carbon.
- 49% of dry weight of organisms is carbon.
- Out of total global carbon, 71% carbon is present in oceans.
- Atmospheric Carbon dioxide regulation is done by oceanic reservoir.
- Long term storage places or sinks : Carbon which is a part of rocks and fossil fuels is called long tern storage of carbon.
- The fossil fuels from this sink when burnt, releases carbon dioxide into atmosphere.
- Elemental carbon found in seawater, atmosphere, – limestone, coal, soil and in living beings.
- Moment of carbon dioxide from atmosphere to plants is through photosynthesis.
- Carbon dioxide given out through plants and animals during respiration.
- Carbon also moves along the food chains.
- Carbon dioxide is released into atmosphere by decomposers during decomposition! process of organic matter on land and in oceans.
- Burning of fossil fuels in industries and for vehicular traffic releases carbon dioxide.
- 5.5 billion tonnes of carbon released in atmosphere, of these 3.3 billion tonnes stay in atmosphere and rest dissolves in seawater and gets deposited as calcium or magnesium carbonate compounds used for forming marine animals’ shells.
- Forest fires, volcanic activities are other natural sources releasing carbon dioxide.
- Anthropogenic activities such as deforestation and excessive burning of fossil fuel has tremendously increased amount of carbon dioxide in atmosphere.
4. Phosphorus cycle : (Sedimentary cycle)
- Phosphorus cyclically moves through hydrosphere, lithosphere and biosphere.
- It is a major constituent of biological
membranes, nucleic acids and cellular energy transfer systems. . - Animals require large quantities of phosphorus to make shells, bones, hooves and teeth.
- The natural reservoirs are rocks containing phosphates.
- Weathering of rocks release minute amounts of phosphates in soil solution which is needed by plants.
- Herbivores and other animals get phosphorus through plants.
- Decomposition of waste products and the dead organisms by phosphate-solubilizing bacteria release phosphorus.
- Phosphorus is always in short supply, thus acts as a limiting factor for the plant growth.
- Eutrophication : Eutrophication is the sudden influx of phosphorus in water bodies due to agricultural runoff or industrial effluents which are rich in phosphate content.
- Eutrophication causes overgrowth of algae which kills or harms the aquatic life
![]()
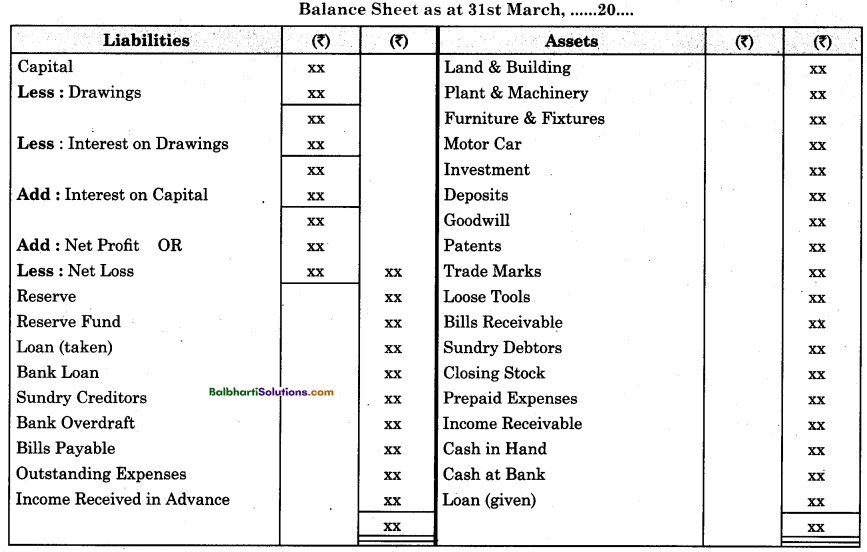
Ecological succession-
1. Ecological succession : The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession. It is a community response to the environment over time.
2. All communities constantly change their composition and structure in accordance with the changing environmental conditions. This change is orderly and sequential, parallel with the changes in the physical environment.
3. Climax community : Community that is in near equilibrium with the environment after the ecological succession.
The change is sequential and environmentally regulated in climax community.
4. Process of succession involves following sequential steps :
- Nudation
- Invasion
- Ecesis
- Aggregation
- Competition and co-action
- Reaction and stabilization.
Learn This As Well :
1916, Frederic Clements published a descriptive theory of succession which is called classical ecological theory. His theory of succession had a powerful influence on ecological thought. He has given following phases of succession :
- Nudation : Nudation is disturbance. Succession begins with the development of a bare site.
- Migration : The tiny seeds or propagules arrive during this phase.
- Ecesis : Ecesis is the establishment and initial growth of vegetation.
- Competition : When vegetation becomes well-formed and established, it grows and competes with other species for space, light and nutrients.
- Reaction : Autogenic changes such as the build-up of humus affect the habitat, and one plant community replaces another during this phase.
- Stabilization : The community which is better, becomes stable forming a Climax community.
5. Some populations become more numerous, whereas some populations decline and even disappear during the succession. Newer species also colonise the areas.
6. Sere : Sere is the entire sequence of communities that successively change in a given area. Serai stages or serai communities are the individual transitional communities in this sere.
7. Following changes take place in the successive serai stages :
- Change in the diversity of species of organisms,
- Increase in the number of species and organisms,
- Increase in the total biomass.
8. Similar succession is said to have taken place in past over millions of years forming the present day global communities. Succession and evolution were the parallel processes in the past and also at the present.
9. Succession is of two types, viz. Primary succession and secondary succession.
Primary succession : It is the process that starts where no living organisms are there, e.g. bare rock, newly cooled lava, newly created pond or reservoir. The primary succession is very slow process of establishment of a new biotic community. Factors such as soil, climatic conditions, etc. The natural processes that take place for thousands of years till the new community is established.
Secondary succession : It occurs in areas where all life forms were lost that existed before. It begins in places like abandoned farmlands, burned or cut forests, lands that have been flooded, etc. Secondary succession is faster as some abiotic factors such as soil or sediment are already present there.
10. Ecological succession usually focuses on changes in vegetation. But when the vegetation changes, it in turn affects various types of animals as animals are dependent on plants for their food and shelter.
11. Therefore, with process of succession the numbers and types of animals and decomposers also show change.
12. Natural or human induced disturbances (fire, deforestation, etc.), in a normal succession pattern can convert a particular serai stage of succession to an earlier stage or create new conditions that encourage some species and eliminate other species.
13. Succession of Plants :
- Succession of plants can be of hydrarch (in wet areas) or xerarch (in very dry areas) based on the nature of the habitat.
- In hydrarch succession, successional series progress from hydric to the mesic conditions.
- In xerarch succession, successional series progress from xeric to mesic conditions.
- Both hydrarch and xerarch successions lead to mesic (medium water) conditions but neither too xeric nor too hydric.
14. Pioneer species : The species that initially invade a barren area is called pioneer species.
![]()
Ecosystem Services-
1. Ecosystem services: Ecosystem services are the products of ecosystem and processes which comprise of economic, environmental, aesthetic goods and services.
2. Millennium ecosystem assessment report 2005 as given definition of ecosystem services as follows ecosystem services is dcfincd as benefits which are obtained by people from ecosystem.
3. There are four types of ecosystem services:
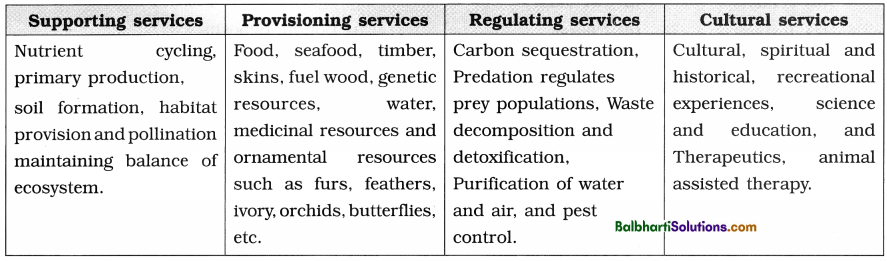
4. Main important ecological services on earth without which life would not have been possible:
- FIxation of atmospheric CO2 and release of O2, by photosynthesis and intake of oxygen and release
of CO2 in respiration. - Pollination of plants brought about by wind, water or other blotic agencies.
- MaintaIning biodiversity.