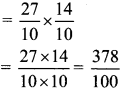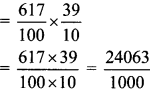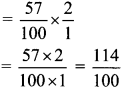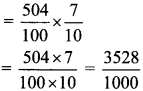Integers Class 6 Maths Chapter 3 Practice Set 6 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Maths Solutions covers the Std 6 Maths Chapter 3 Integers Class 6 Practice Set 6 Answers Solutions.
Std 6 Maths Practice Set 6 Solutions Answers
Question 1.
Write the opposite number of each of the numbers given below.
| Number | 47 | +52 | -33 | -84 | -21 | +16 | -26 | 80 |
| Opposite number |
Solution:
| Number | 47 | +52 | -33 | -84 | -21 | +16 | -26 | 80 |
| Opposite number | -47 | -52 | +33 | +84 | +21 | -16 | +26 | -80 |
6th Std Maths Digest Pdf Download
- Basic Concepts in Geometry Practice Set 1 Class 6 Maths Solution
- Angles Practice Set 2 Class 6 Maths Solution
- Angles Practice Set 3 Class 6 Maths Solution
- Integers Practice Set 4 Class 6 Maths Solution
- Integers Practice Set 5 Class 6 Maths Solution
- Integers Practice Set 6 Class 6 Maths Solution
- Integers Practice Set 7 Class 6 Maths Solution
- Integers Practice Set 8 Class 6 Maths Solution