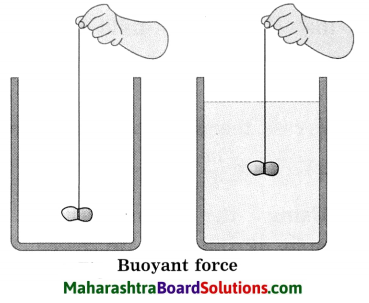
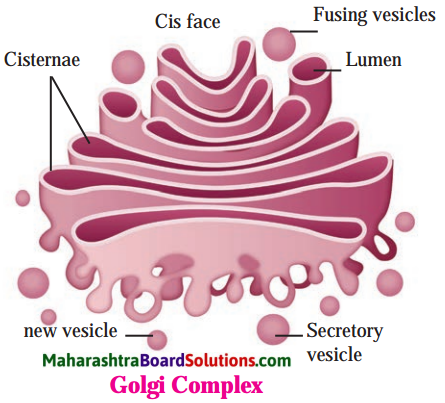
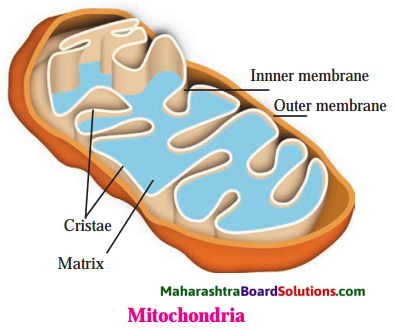
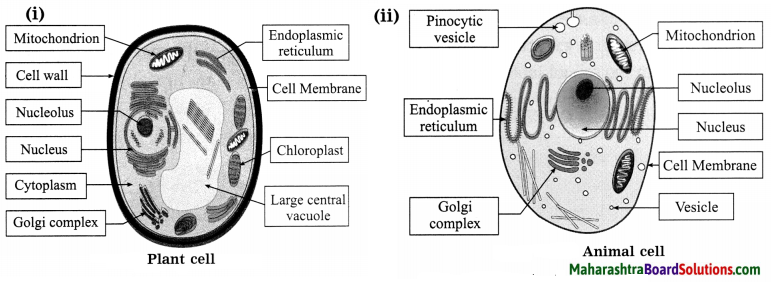
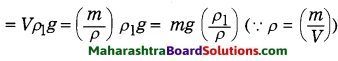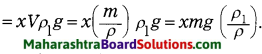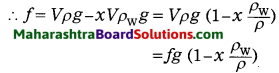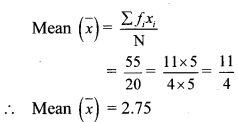Std 8 Science Chapter 2 Health and Diseases Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Health and Diseases Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Health and Diseases Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Health and Diseases Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Distinguish between- Infectious and non – infectious diseases.
| Infectious diseases | Non-infectious diseases |
| 1. The diseases which can be transmitted from one patient to other person are called infectious diseases. | 1. The diseases which cannot be transmitted from one patient to other person, are called non-infectious diseases. |
| 2. Contaminated air, water, food or carrier! vector animals or insects spread the infectious diseases. | 2. Non-infectious diseases are not transmitted through any medium. |
| 3. infectious diseases are acute diseases as they are suddenly caused due to infections from either bacteria, virus or protozoan. Thus, their symptoms are seen sooner. | 3. Some non-infectious diseases are due to hereditary causes, some are a clue to failure in metabolism, some due to deficiency of the nutrients. Their symptoms are not seen suddenly but are developed gradually. |
| 4. Antibiotics or antihelminth medicines are used to treat the infectious diseases. E.g. Tuberculosis, hepatitis, leprosy, cough and cold, etc. | 4. Antibiotics cannot be used for treating non-infectious diseases. These diseases have a proper treatment. E.g. Diabetes, cancer, heart diseases, etc.Tuberculosis, hepatitis, leprosy, cough and cold, etc. |
2. Identify the odd term.
Question a.
Malaria, hepatitis, elephantiasis, dengue.
Answer:
Hepatitis (All other diseases are caused by the carrier mosquito.)
Question b.
Plague, AIDS, Cholera, T.B.
Answer:
AIDS [All others are bacterial (caused by bacteria) diseases.]
3. Answer in one to two sentences.
Question a.
Which are various media of spreading the infectious diseases?
Answer:
Infectious diseases spread through contaminated air, water, food, vectors such as insects, animals and man.
Question b.
Give the names of five non-infectious diseases other than given in the lesson.
Answer:
Asthma, cataract, diseases of kidney such as kidney stones and renal failure, arthritis, Alzheimer which is a condition during old age, hypertension, migraine, etc.
Question c.
Which are the main reasons of diabetes and heart diseases?
Answer:
Improper lifestyle, wrong type of diet, lack of exercise, excessive mental stress and strain, imbalance in secretion of hormones, etc. are the main reasons for diabetes and heart diseases.
![]()
4. What can be achieved/can be prevented?
Question a.
Drinking boiled and filtered water.
Answer:
- When water is boiled, all the disease causing pathogens present in it are killed.
- Different diseases like cholera, enteritis, diarrhoea, dysentery, hepatitis, typhoid are caused by such water-borne pathogens.
- If we boil the water we are protected against all such diseases.
- If the i water is filtered we can avoid infections from nematode Dracunculus which causes Naru. By boiling and filtering water, even the epidemics by such infectious diseases can be controlled.
Question b.
Avoiding smoking and alcoholism.
Answer:
1. Smoking and alcoholism are two dangerous habits that cause addictions. Alcoholism causes disorders of liver.
2. The addict suffers from malnourishment.
3. His I mental and psychological conditions become abnormal. There is social and familial) impacts too due to alcoholistn.
4. Smoking is an invitation for cancer. In cigarettes/ bidis, there is hazardous nicotine. Nicotine is not only toxic but is also carcinogenic. Cancers of oral cavity, tongue, respiratory tract, lungs is very common among smokers. Therefore, addictions like smoking and alcoholism should always be avoided.
Question c.
Regular balanced diet and exercise.
Answer:
1. Regular and balanced diet results into perfect health. The disease fighting power or immunity of a person is increased due to healthy diet.
2. One can avoid of frequent infections and also mental well¬being is established.
3. Heart disease, diabetes, obesity, etc. can be avoided by not consuming high caloric junk food.
4. Exercise improves blood circulation. Many disorders which are caused by faulty lifestyle can be prevented by having regular balanced diet and exercise, thus one must always follow these for well-being.
Question d.
Proper checking of blood before blood donation.
Answer:
1. There are definite blood groups.
2. During blood transfusion, the donor’s and recipient’s blood should be well-matched with each other. Otherwise, blood gets clumped inside the body of recipient.
3. Through infected blood, the viruses such as those causing hepatitis B or AIDS are transmitted to other healthy persons. Thus, for prevention of transmission of such diseases, blood should be checked before blood donation.
5. Read the passage and answer the questions.
Master X’ is a 3-year-old child. He is living with his family in a slum. The public toilet is present near his house. His father is drunkard. His mother does not know the importance of balanced diet.
Question a.
Master ‘X’ can suffer from which different possible diseases in above conditions?
Answer:
Master ‘X’ stays in an area which is devoid of cleanliness. The public toilet is near his house. This indicates that he will have to fight against many infectious diseases. Because his father is a drunkard, there will always be a dearth of money in r the house. He may not be able to afford, enough and balanced food. Thus his diet must be deficient in vitamins and minerals.
Moreover, his mother is ignorant about the importance of health and a balanced diet. This must be causing Master ‘X’ malnourishment and loss of immunity. The financial conditions and the addition of the father must be causing stress in the house.
This will further add stress on Master ‘X’ resulting into susceptibility to infections. As it is due to the location the germs are around and thus they may be attacking Master ‘X’. He will on and off suffer from digestive disorders! such as typhoid, hepatitis, cholera, enteritis, etc.
![]()
Question b.
How will you help him and his family in this situation?
Answer:
Initially, we shall help Master ‘X’ to procure healthy and balanced diet having fruits, vegetables, milk, etc. His mother will be taught importance of the balanced diet. The surroundings should be clean and hygienic. Food should be covered, houseflies should not be allowed to contaminate the food. Germicidal floor cleaners and disinfectants should be used to keep off the houseflies and cockroaches. His father will be taken to de-addiction centres such as ‘Alcoholics Anonymous’. He will be persuaded to leave alcoholism.
Question c.
Which disease can occur to the i father of master ‘X’?
Answer:
Father of Master ‘X’ can develop diseases of liver and kidney.
6. Give the preventive measures of following diseases:
Question a.
Dengue:
Answer:
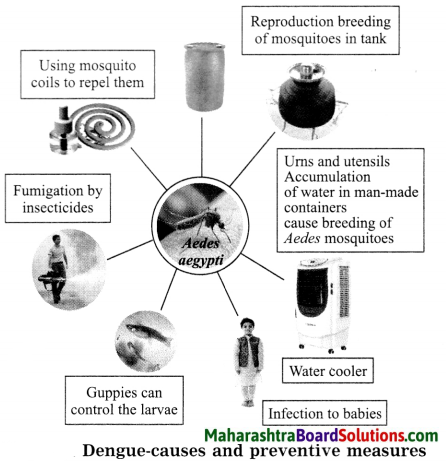
Dengue is transmitted through bite of mosquito of Aedes aegypti. DEN-1, 2 virus belonging to the type – flavivirus is the causative pathogen for Dengue. Wherever there is stagnant or accumulated water, there is possibility of mosquito breeding. Therefore, care is to be taken to drain of such water. Thus this is a very important preventive measure. Especially, in the man¬made containers and in clean water, the Aedes mosquito prefers to breed.
Therefore, such water storages should be either covered or should be decanted. Another way to keep off from dengue is to increase our immunity to fight against the virus. There is vaccine called CYD-TDV or Dengvaxia which is synthesised in 2017. But it is still not considered to be completely safe.
Question b.
Cancer:
Answer:
The most important preventive measure is to remain away from the carcinogenic substances. Tobacco, gutkha, cigarette, bidi, etc. are addictive things which are very bad for our health. The nicotine present in these cause cancers of oral cavity and of respiratory system. Radiations can also cause cancer.
We should not expose ourselves to hazardous radiations. Balanced and healthy diet, proper exercise and living stress free with mental balance are some of the preventive measures of the cancer. Only for few types of cancer like cervical cancer in women, vaccine has been developed.
![]()
Question c.
AIDS:
Answer:
When blood transfusion is done, the blood should be checked for the presence of HIV. The used syringes, needles, etc. should not be used without sterilization. Through blood and blood products and body fluids HIV finds its way into the body. Therefore, these precautions should be taken. Unsafe sexual contact is the most important mode of transmission of HIV. Thus one should never deal with such dangerous acts. Awareness about AIDS and HIV is the real preventive measure.
7. Explain the importance.
Question a.
Balanced diet.
Answer:
The diet that contains all the nutrients in the balanced proportion is called balanced diet. One can avoid malnutrition by taking balanced diet. The immunity increases due to balanced diet containing good proportion of vitamins and minerals. Some diseases can be avoided due to raised immunity. Wrong lifestyle and wrong diet can cause hypertension, diabetes or heart disease. To maintain our health and keep the body in equilibrium, we have to take balanced diet.
Question b.
Physical exercise/Yogasanas.
Answer:
By exercise and yoga, the blood circulation of body is improved. Body and joints remain flexible. Mental strain and stress is reduced. Insomnia (inability to fall asleep), arthritis, indigestion, and some other disorders can be avoided. The person who performs exercise, always remains away from the addictions. Yoga makes levels of hormones, enzymes, etc. in equilibrium. By keeping control over breathing through pranayama many respiratory and circulatory disorders can be prevented.
8. Make a list.
Question a.
Viral diseases.
Answer:
AIDS, Hepatitis, Influenza, Rabies, Polio.
Question b.
Bacterial diseases.
Answer:
Typhoid, Tuberculosis, Cholera, Leprosy.
![]()
Question c.
Diseases spread through insects.
Answer:
Malaria, Dengue, Elephantiasis.
Question d.
Hereditary diseases.
Answer:
Diabetes, Haemophilia, Muscular dystrophy, Colourblindness.
9. Write the information on modern diagnostics and treatments of cancer.
Question a.
Answer:
1. Following methods are used as diagnostic methods to detect the cancer. Techniques like CT scan, MRI scan, mammography, biopsy.
Treatment of the cancer is done by the following methods:
2. For treatment of cancer, some conventional methods are used. Along with these methods, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery are commonly used to treat cancerous growth and tumours. New and modern techniques of robotic and laparoscopic surgery are also used for the treatment.
10. Enlist the names and composition of the medicines present at your home.
Question 1.
Prepare posters giving information about various diseases, public awareness and arrange exhibition in school.
Question 2.
Visit the public health center/clinic nearby and collect the information about vaccination.
Question 3.
Compose a street-play to increase public awareness about dengue, malaria, swine flu and present ¡tin the area nearby your school.
![]()
Project:
Question 1.
Prepare posters giving information about various diseases, public awareness and arrange exhibition in school.
Question 2.
Visit the public health center/clinic nearby and collect the information about vaccination.
Question 3.
Compose a street-play to increase public awareness about dengue, malaria, swine flu and present it in the area nearby your school.
Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Health and Diseases Additional Important Questions and Answers
Rewrite the sentences after filling the blanks:
Question 1.
For eradication of tuberculosis everybody should be vaccinated by …………. vaccine.
Answer:
For eradication of tuberculosis everybody j should be vaccinated by B.C.G vaccine.
Question 2.
Hepatitis B can be transmitted by ………….
Answer:
Hepatitis B can be transmitted by blood transfusion.
Question 3.
For treating diarrhoea/dysentery…………. is given to the patient.
Answer:
For treating diarrhoea/dysentery O.R.S. is given to the patient.
![]()
Question 4.
…………. virus is responsible for the infection of swine flu.
Answer:
Influenza A (H1N1) virus is responsible for the infection of swine flu.
Question 5.
…………. mosquito spreads dengue.
Answer:
Aedes aegypti mosquito spreads dengue.
Question 6.
Malaria is caused by female mosquito of …………. genus.
Answer:
Malaria is caused by female mosquito of Anopheles genus.
Question 7.
…………. test is performed on blood to diagnose AIDS.
Answer:
ELISA test is performed on blood to diagnose AIDS.
One word in the following sentences is wrong. Change it to make the sentences correct:
Question 1.
Culex mosquito is seen in clean water.
Answer:
Culex mosquito is seen in dirty water.
Question 2.
Transmission of swine flu is done by dogs and human beings.
Answer:
Transmission of swine flu is done by pigs and human beings.
Question 3.
Hydrophobia is the main symptom of typhoid.
Answer:
Hydrophobia is the main symptom of rabies.
![]()
Question 4.
The maximum number of patients of diabetes are found in America.
Answer:
The maximum number of patients of diabetes are found in India.
Question 5.
Generic medicines are also called branded medicines.
Answer:
Generic medicines are also called general medicines.
Question 6.
If the secretion of insulin is increased, then the diabetes is caused.
Answer:
If the secretion of insulin is decreased, then the diabetes is caused.
Question 7.
Virus causing rabies enter the brain through food.
Answer:
Virus causing rabies enter the brain through neurons.
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Bacterial diseases | Bacteria |
| 1. Typhoid | (a) Mycobacterium tuberculi |
| 2. Cholera | (b) Bacillus |
| 3. Diarrhoea | (c) Vibrio choleri |
| 4. Tuberculosis | (d) Salmonella typhi |
Answer:
| Bacterial diseases | Bacteria |
| 1. Typhoid | (d) Salmonella typhi |
| 2. Cholera | (c) Vibrio choleri |
| 3. Diarrhoea | (b) Bacillus |
| 4. Tuberculosis | (a) Mycobacterium tuberculin |
![]()
Question 2.
| Importance of the day | Date |
| 1. World Diabetes Day | (a) 7th April |
| 2. World Heart Day | (b) 14th June |
| 3. World Blood Donation Day | (c) 29th September |
| 4. World Health Day | (d) 14th November |
Answer:
| Importance of the day | Date |
| 1. World Diabetes Day | (d) 14th November |
| 2. World Heart Day | (c) 29th September |
| 3. World Blood Donation Day | (b) 14th June |
| 4. World Health Day | (a) 7th April |
Identify the odd term:
Question 1.
Chemotherapy, Radiation therapy, Surgery, Pranayama
Answer:
Pranayama (All others are treatment for cancer.)
Question 2.
Chronic cough, Hoarse voice, Uncontrolled blood sugar level, Difficulty in swallowing.
Answer:
Uncontrolled blood sugar level (All others are symptoms of cancer of throat.)
![]()
Question 3.
Mantra, Vaccination, Black magic, Hatred.
Answer:
Vaccination (This is the only way for prevention of diseases. Rest of the others are blind faiths which are unscientific.)
Consider the relation between the items in the first pair and write the correlation for second pair:
1. Swine flu : Virus : :
Tuberculosis : : …………….
Answer:
Bacteria
2. Anopheles : Malaria :
Culex : …………………
Answer:
Elephantiasis
![]()
3. Housefly : Typhoid : : Dog : ………….
Answer:
Rabies
4. Decrease in blood platelets : :
Dengue : : Difficulty in breathing : ……………
Answer:
Swine flu
5. Cancer : Laparoscopic surgery : :
Heart disease :……………
Answer:
By-Pass surgery.
Distinguish between the following:
Question 1.
Typhoid and Tuberculosis :
Answer:
| Typhoid | Tuberculosis |
| 1. Typhoid is caused by bacteria (Salmonella) that is passed by contaminated food and water and is spread through house flies. | 1. Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium) which pass through the spittle of the patient. |
| 2. The infection of typhoid is through food or water via the mouth. | 2. The infection of tuberculosis is through air via the nose. |
| 3. Typhoid affects stomach and intestine. | 3. Tuberculosis affects lungs and chest. |
| 4. There is high fever for specific period in typhoid. | 4. There is continuous low grade fever in tuberculosis. |
| 5. There is stomachache and headache in typhoid. | 5. There is chest pain in tuberculosis. |
| 6. Vaccination for typhoid is given at the time of suspected epidemic. | 6. BCG vaccination is given to all at a young age only. |
What can be achieved/can be prevented?/Give reasons.
Question 1.
People suffering from communicable diseases should avoid going to public places.
Answer:
- Communicable diseases spread when people share space with a diseased person.
- If people suffering from l communicable diseases go to a public place, they would spread the disease causing germs in the air.
- These germs can be transmitted to other healthy persons.
- If the resistance power of the persons is less, they will fall sick by getting infected.
- This may break into an epidemic. Therefore, people suffering from communicable diseases should avoid going to public places.
![]()
Question 2.
Pet animals should be given anti-rabies vaccine.
Answer:
- We keep animals like cats and dogs at home as pets.
- They may get infected with the virus of rabies.
- If such an infected pet bites us, we may also get rabies.
- Rabies is a lethal disease.
- In order to protect the animals and to prevent rabies being transmitted, they should be given anti-rabies vaccine.
Question 3.
Tuberculosis is considered as the most communicable disease.
Answer:
- Tuberculosis is caused due to bacterial infection.
- It is an air-borne infection and spreads through the spittle of T.B. patient.
- When personal and public hygiene is not followed, this disease spreads very rapidly.
- It is estimated that every two minutes, one patient dies of T.B. in India. Tuberculosis, therefore, is considered as the most communicable disease.
Question 4.
ORS gives temporary relief to the patient of diarrhoea.
Answer:
- In diarrhoea, due to loose motions the patient becomes dehydrated.
- The eyes get sunken and the mouth becomes dry.
- If immediate help is not given, the condition can become critical. The absorption function of the intestine is disturbed.
- But by giving ORS, enough water, sugar and salt enter the body saving the life of the patient.
- The sugar and salt in the ORS gets absorbed in the intestine and reduce the dehydration.
- However, for eradication of infection, proper medical treatment is to be given, therefore, ORS gives only a temporary relief to the patient of diarrhoea.
Answer the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
Which virus causes dengue and how does it spread?
Answer:
Dengue is caused by DEN-1, 2 virus belonging to the type – flavivirus. Aedes aegypti type of mosquito spreads the disease by transferring this virus through its bite.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the reasons for spread of swine flu?
Answer:
Swine flu is caused by the virus influenza A (H1N1). Its carrier is pig. The contact with such pigs or infected persons can cause infection of swine flu. The infection spreads through sweat and through secretions of nose, throat and saliva of the diseased person.
Question 3.
What are the symptoms of swine flu?
Answer:
Symptoms of swine flu : Palpitations, difficulty in breathing, sore throat, body pain along with high fever.
Question 4.
In whom was HIV first reported?
Answer:
HIV was first reported in an African species of monkeys
Question 5.
What is a malignant tumour?
Answer:
Due to uncontrolled cell division
there is a formation of lump of cancerous cells. If this lump is without the covering, then it is called malignant tumour.
Question 6.
How is efficiency of the heart reduced?
Answer:
When the blood circulation for the heart muscles is obstructed, it does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. Due to this condition heart has to exert more and gets stressed resulting into loss of efficiency.
Question 7.
What are the different types of treatment for heart diseases?
Answer:
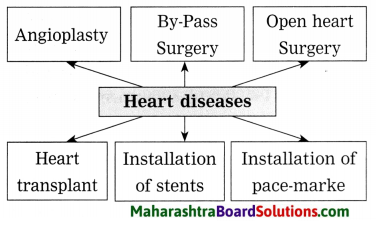
Angioplasty, By-Pass surgery, open heart surgery, installation of stents, installation of pacemaker, heart transplant are some of the treatment for heart diseases.
![]()
Question 8.
What is Pradhan Mantri Jan Aushadhi Yojana? When was it started?
Answer:
Government of India started the Pradhan Mantri Jan Aushadhi Yojana on 1st July 2015. Under this scheme people who are not able to afford best quality medicines are given generic medicines of the same quality at much reduced price.
Question 9.
When can eye donation be done? What is the advantage of eye donation?
Answer:
Anybody can donate eyes posthumously. Due to eye donation, some blind person can regain the sight.
Explain the importance:
Question 1.
Generic medicines.
Answer:
Generic medicines are also called general medicines. They are affordable for the common citizens of India. These medicines are manufactured and distributed without any patent. They are similar in quality and composition as the branded i medicines. The proportion of compounds in these medicines and its formula of preparation is readily available. Thus the money spent on the research is reduced. Therefore, generic medicines are much cheaper than the expensive branded medicines.
Question 2.
Blood donation.
Answer:
Blood donation is said to be the greatest donation that one can give. Blood donation can save someone’s life. By one unit blood of a single donor, three different patients can be saved. From such blood red blood cells, white blood cells and blood i platelets can be separated and given to different patients who are in need with corresponding component. Blood cannot be manufactured artificially and hence blood donation is the only way to collect blood. One healthy person can donate blood four r times in a year, thus saving 12 patients.
![]()
Question 3.
First Aid for Heart Disease.
Answer:
A person who is suffering from cardiac problems can get a heart attack suddenly. In such case, the patient should be given immediate and appropriate treatment to save his or her life. First and foremost one should call 108 for cardiac ambulance. Then the patient’s pulse or heartbeats should be checked to know his/her condition. Check the consciousness of the patient. Then make the patient to lie on a hard surface in horizontal position.
Perform C.O.L.S. or, ‘Compression Only Life Support’ on the patient. During this procedure, a pressure is given in the centre of the thorax of a patient for at least 30 times at the rate of 100 to 120 r strokes per minute. This is a first aid for the r heart attack. Before the arrival of doctor or proper medical aid, the life of a patient is saved.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Write a brief account about tuberculosis.
Answer:
Mycobacterium tuberculae is the bacteria which causes tuberculosis (TB) infection. This infectious and communicable disease passes through spittle of the patient. The sneezing and coughing of patient cause f droplet infections. With prolonged contact with the patient and using the objects of the patient there is greater chance of acquiring TB infection. Different body organs such as bones, uterus and lungs can be affected by tuberculosis.
The pulmonary TB i.e. TB of the lungs is more common. The symptoms of TB are prolonged cough, blood through spittle, decrease in the body weight and difficulty in breathing. B.C.G. vaccine can be given in young age for prevention of TB. The patient needs to be isolated if TB is detected. Regular antibiotics have to be taken. DOTS process of medication needs to be followed.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the symptoms of dengue.
Answer:
Symptoms of dengue are as follows:
- High and severe fever.
- Severe headache accompanied with vomiting.
- Pain in the eye sockets as if someone is pushing the eyes out.
- Rapid reduction in the number of blood platelets.
- Internal haemorrhages in the body.
Question 3.
How is rabies caused? What are the important symptoms of the rabies?
Answer:
Rabies is a viral disease. The bite of a rabid animal (the animal who is already infected with rabies virus) transfers the virus in the human blood through the bite wound. Dog, rabbit, monkey and cat can be infected with rabies if they are not vaccinated. The virus of rabies enters the brain through neurons. If not treated in time, rabies can be fatal.
Symptoms of rabies: There is a fever which lasts for 2 to 12 weeks. The victim becomes hyper-excited. He /She shows exaggerations in behaviour. Hydrophobia is very unique symptom in which person is scared and phobic of water. The symptoms can be seen within 90 to 175 days after the animal-bite.
When the dog or any animal bites, before the symptoms are seen, the victim should immediately take anti-rabies vaccine. This vaccination can save a person.
Question 4.
What are the causes of cancer?
Answer:
The carcinogenic substances can cause cancer. Thus such substances should never be used. Tobacco, gutkha and other nicotine containing products can cause cancer. Smoking and alcoholism can also induce cancer development. Cancer is also hereditary disease which is said to be caused by oncogenes. The lack of high fibre food in the diet and junk food in great quantities can induce the cancer development in some part of the alimentary canal.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the symptoms of cancer.
Answer:
- If part of the respiratory system is under the attack of cancer, it can cause, long term cough, hoarse voice, difficulty in swallowing or difficulty in breathing.
- The wounds do not become cured and the scar too is incurable. Inflammations does not subside.
- There is formation of tumour like lump in the breast of the females.
- In all the types of cancer there is unexplained weight loss.
Question 6.
What are the preventive measures to avoid the cancer?
Answer:
Complete control over diet should be followed. It should be’ healthy and nutritive. Such diet protects one from the cancer. The modern treatment processes should be immediately carried out, if the cancer is detected. With time-lapse, the growth of the cancer keeps on increasing. Physical exercises should be regularly done. Tobacco consumption, smoking are some addictions that can induce cancer. These should never be tried.
Question 7.
What are the causes and symptoms of diabetes?
Answer:
Causes of diabetes: The pancreas in normal persons secrete hormone insulin which maintains the sugar level in the blood. When there is deficiency of insulin, the symptoms of diabetes develop due to uncontrolled blood sugar level. Hereditary causes also can develop diabetes.
Obesity, lack of physical exercise, mental stress can also lead to diabetes. Overconsumption of fried food and over-indulgence in eating sweetmeats increase the chances of diabetes.
Symptoms of diabetes: The person who develops diabetes has frequent urination and continuous thirst. The body weight also reduces rapidly. Sometimes it may rise suddenly. There is continuous feeling of fatigue.
![]()
Question 8.
What are the causes of heart diseases?
Answer:
Addictions such as smoking, alcoholism and junk food lead to heart disease. Diabetes, hypertension, obesity are responsible for developing heart disease. Lack of physical exercise, no physical work, continuous sedentary mode are some causes which reduce the efficiency of the working of heart. Mental strain and stress, anger, frustration, anxiety are some psychological reasons that can lead to heart problems
Question 9.
What happens when medicines are missed?
Answer:
When medicines are taken without the consultation of doctor, there are certain problems. When the medicines and drugs are taken without any cause or symptom, then it is a misuse. Overdose of pain killers produce side effects. Some of these cause damage to nervous system, excretory system and liver. Overdose of antibiotics develops nausea, stomachache, loose motions and rash, white patches on tongue, etc.
Questions based on charts/tables:
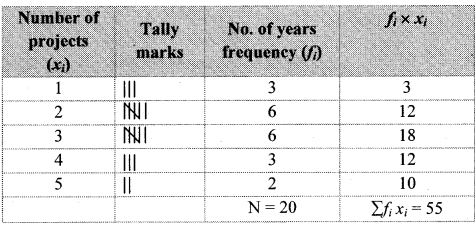
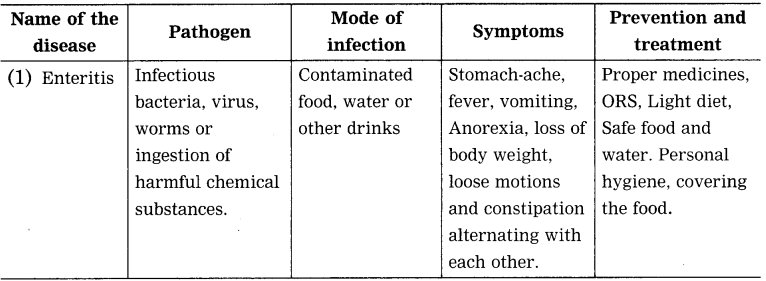
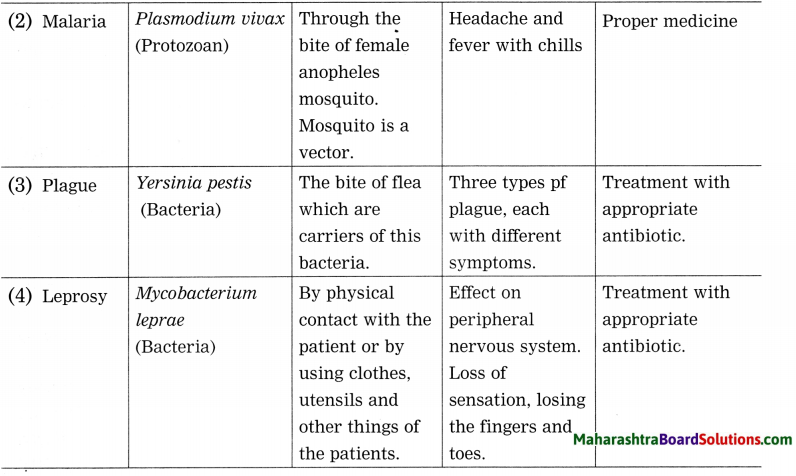
Question 1.
Complete the table: Prepare similar table of information as the table given on page 7 about various disease like enteritis, malaria, plague and leprosy.
Answer:
Question 2.
Draw a flow diagram to show treatment for heart diseases.
Answer:
Activity-based questions:
Question 1.
Enlist the names and composition of the medicines present at your home.
Answer:
Students are expected to write this answer based on the medicines in their own homes.
![]()
Question 2.
Observe and discuss :

Answer:
Observe the following pictures and write description in the boxes.
Open-Ended Questions:
Question 1.
Poor people do not afford the costly medicines. Is there any alternative for this? Which one?

Answer:
Some medicines are very costly. The poor people cannot afford such expensive medicines. In such cases, some social organizations may give some help to these patients. Some trusts like Tata trust can also offer help to the needy for the treatment.
Some hospitals have social workers who help the needy for raising the funds for poor patients. Another way is to use generic medicines.
These medicines are at par in quality with the branded medicines but they are quite less in the price. They are available in the generic medicine shops. One can also take benefit of Pradhan Mantri Jan Aushadhi Yojana.
Question 2.
What measures will you take to stop the breeding of mosquitoes?
Answer:
We have to take care that there is no water stagnated in and around the house. The garden plants and pots in the house should be checked for the mosquito larvae and eggs if any. If water is not receding and remaining accumulated, then the spraying of insecticides should be done with the help of elders. With the help of elders in the house, the complaint can be lodged in the Malaria eradication department in the nearby Municipality or Gram Panachyat office.
If the water is in ponds, we can release guppy fishes to eradicate the mosquito larvae. The fish feed on the larvae and automatically control the mosquito population.
![]()
Question 3.
Our behaviour with HIV infected person must be normal or should not be normal? What is your opinion? Write it with correct explanation.
Answer:
Our behaviour with HIV infected person must be normal. There are no chances of acquiring AIDS by having normal behaviour with the HIV positive person. HIV can pass only through body fluids and blood from HIV infected person to the other normal person. Similarly, the needles or syringes used by HIV infected person can cause the infection of HIV to the other person.
Such ways of contamination should always be avoided. The sexual contact or the blood transfusion with HIV positive person should always be avoided. But the normal behaviour such as hand-shake, eating together, studying in the same class will not matter at all in the transmission of AIDS.
Balbharati Maharashtra State Board 8th Std Science Textbook Solutions
- Living World and Classification of Microbes Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Health and Diseases Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Force and Pressure Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Current Electricity and Magnetism Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Inside the Atom Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Composition of Matter Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Metals and Nonmetals Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Pollution Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Disaster Management Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Cell and Cell Organelles Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions